Is There A Type 1 Diabetes Diet
The basics of a type 1 diabetes diet include making sure carbohydrate intake is matched with insulin and choosing healthy options to maximize nutrition in each calorie. People with type 1 diabetes will find it is easiest to match carbohydrates to insulin if they follow a low-glycemic load diet, so that the impact of carbohydrates on blood sugar is slow and gradual. This also makes it easier to predict and match to required insulin.
Because weight gain can be a side effect of injecting insulin, a type 1 diabetes diet should be healthy and low in calories to help the person maintain or lose weight. Food lists of low-glycemic load options can help people learn what to include in their diet.
How 2 Type 1
Do you live with type 1 diabetes? Do you care for someone who does? Whether you’ve been recently diagnosed or living with the disease for years, How 2 Type 1 is for you. This video, developed in partnership with the Diabetes Leadership Foundation, aims to provide support, knowledge, expert advice, and actionable steps to help you and others in the type 1 diabetes community thrive!
Type 1 Diabetes Causes
Insulin is a hormone that helps move sugar, or glucose, into your body’s tissues. Your cells use it as fuel.
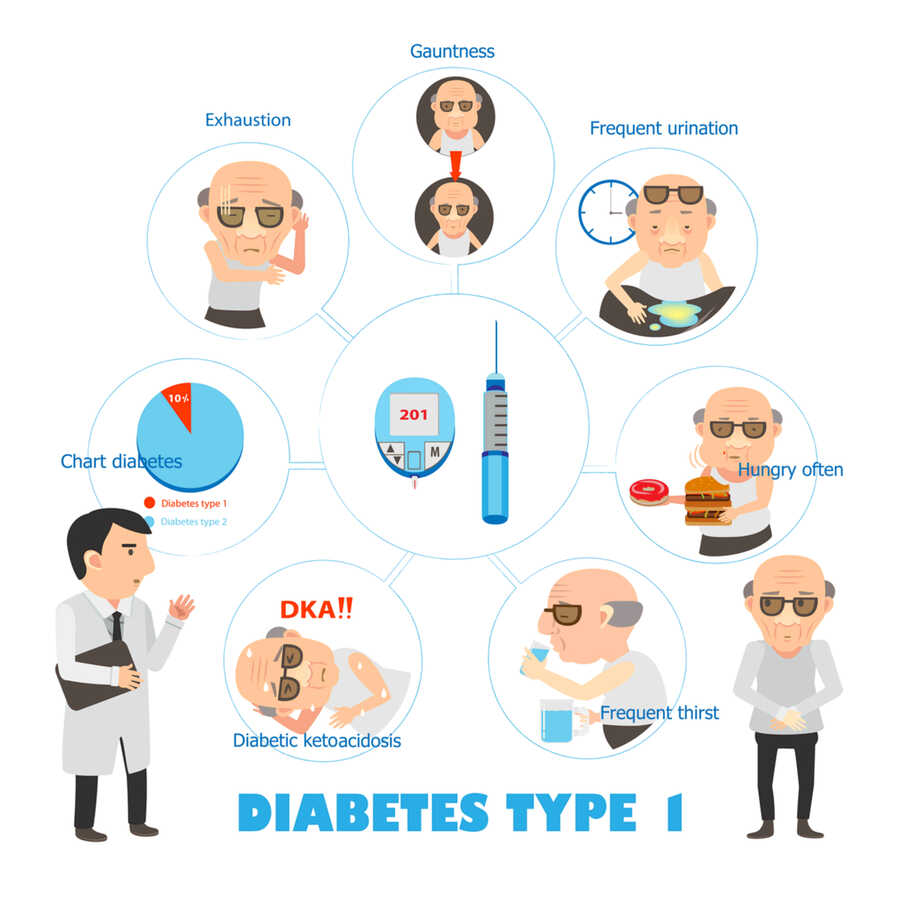
Damage to beta cells from type 1 diabetes throws the process off. Glucose doesnât move into your cells because insulin isnât there to do the job. Instead, it builds up in your blood, and your cells starve. This causes highblood sugar, which can lead to:
- Dehydration. When thereâs extra sugar in your blood, you pee more. Thatâs your bodyâs way of getting rid of it. A large amount of water goes out with that urine, causing your body to dry out.
- Weight loss. The glucose that goes out when you pee takes calories with it. Thatâs why many people with high blood sugar lose weight. Dehydration also plays a part.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis . If your body can’t get enough glucose for fuel, it breaks down fat cells instead. This creates chemicals called ketones. Your liver releases the sugar it stores to help out. But your body canât use it without insulin, so it builds up in your blood, along with the acidic ketones. This mix of extra glucose, dehydration, and acid buildup is known as ketoacidosis and can be life-threatening if not treated right away.
- Damage to your body. Over time, high glucose levels in your blood can harm the nerves and small blood vessels in your eyes, kidneys, and heart. They can also make you more likely to get hardened arteries, or atherosclerosis, which can lead to heart attacks and strokes.
Read Also: How To Lose Weight On Insulin
Can You Die From Diabetes Type 1 And Type 2 Life Expectancy
Diabetes is a disease which is caused either due to the lack of proper production of insulin by the pancreas or due to the improper use of insulin in the human body. This gives rise to the blood sugar level or the glucose level in the body as it is the hormone insulin which is responsible for the breakdown of the carbohydrates and the other essential nutrients in the food to release the much-needed energy by the cells. It is a disease which adversely affects the primary function of metabolism in the body thereby exposing our body to several other complications.
Diabetes affects different people in different manners and as such, it takes several forms. The most common type of diabetes is type 1 and type 2 diabetes. There are various factors and causes which contribute to each type and form of the disease.
Due to the several complications that are associated with this condition, diabetes is often considered a deadly disease that can kill you. It is not uncommon to hear of people who have died of diabetes in the past few years. In this article, we shall further deep dive into the various issues that diabetes accompanies and might lead to the death of the diabetic patient.
Treating Type 1 Diabetes
It’s important that diabetes is diagnosed as early as possible. If left untreated, type-1 diabetes is a life-threatening condition. It’s essential that treatment is started early.
Diabetes can’t be cured, but treatment aims to keep your blood glucose levels as normal as possible and control your symptoms, to prevent health problems developing later in life.
If you’re diagnosed with diabetes, you’ll be referred to a diabetes care team for specialist treatment and monitoring.
As your body can’t produce insulin, you’ll need regular insulin injections to keep your glucose levels normal. You’ll be taught how to do this and how to match the insulin you inject to the food you eat, taking into account your blood glucose level and how much exercise you do.
Insulin injections come in several different forms, with each working slightly differently. You’ll most likely need a combination of different insulin preparations.
Insulin is given to some patients by a continuous infusion of fast acting insulin . This is where a small device constantly pumps insulin into your bloodstream through a plastic tube that’s inserted under the skin with a needle.
There are alternatives to insulin injections and pumps, but they’re only suitable for a small number of patients. They are:
Read more about diagnosing diabetes and treating type 1 diabetes
Read Also: How To Avoid Diabetes In Early Stages
Eating A Healthy Balanced Diet
What you eat can make a difference to how you feel and how you manage your condition. Thats why weve got a huge range of tasty and nutritious recipes ready for you to try.
Whether youre cooking up a feast for dinner, or looking for something lighter for lunch, weve got you covered. Simply search by ingredient, meal type or dietary requirement and enjoy eating with diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes Treatment
People who have type 1 diabetes can live long, healthy lives. Youâll need to keep a close eye on your blood sugar levels. Your doctor will give you a range that the numbers should stay within. Adjust your insulin, food, and activities as necessary.
Everyone with type 1 diabetes needs to use insulin shots to control their blood sugar.
When your doctor talks about insulin, theyâll mention three main things:
- “Onset” is how long it takes to reach your bloodstream and begin lowering your blood sugar.
- “Peak time” is when insulin is doing the most work in terms of lowering your blood sugar.
- “Duration” is how long it keeps working after onset.
Several types of insulin are available.
- Rapid-acting starts to work in about 15 minutes. It peaks about 1 hour after you take it and continues to work for 2 to 4 hours.
- Regular or short-acting gets to work in about 30 minutes. It peaks between 2 and 3 hours and keeps working for 3 to 6 hours.
- Intermediate-acting wonât get into your bloodstream for 2 to 4 hours after your shot. It peaks from 4 to 12 hours and works for 12 to 18 hours.
- Long-acting takes several hours to get into your system and lasts about 24 hours.
Your doctor may start you out with two injections a day of two types of insulin. Later, you might need more shots.
Read Also: How Are Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Similar
Open Sores And Wounds
Having high blood sugar for a long time can lead to poor circulation and nerve damage. You may have developed these if youve had uncontrolled diabetes for a long time.
Poor circulation and nerve damage can make it hard for your body to heal wounds. This is especially true on the feet. These open wounds are called diabetic ulcers.
Diabetes and feet
- Get immediate medical care for an open sore or wound.
- Work with your doctor to better control your diabetes.
What Is The Treatment For Type 1 Diabetes Can It Be Cured
Currently, type 1 diabetes cannot be cured. People with type 1 diabetes require injectable insulin because their pancreas does not produce enough on its own. There are different types of insulin and different routes of administration. Most people with type 1 diabetes use both a long-acting insulin , and inject additional insulin before or after meals to match the carbohydrate content of the meal. An insulin pump may also be used to optimize insulin delivery to the body’s needs.
- Unfortunately, one of the major side effects of insulin is weight gain. People with type 1 diabetes can reduce weight gain by:
- Eating a healthy low-carbohydrate diet,
- Getting plenty of exercise, and
- Learning to use insulin correctly in order to use just the right amount
- Diet and level of activity.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Diabetes If You Re Skinny
Tests For Type 1 Diabetes
If you and your doctor are concerned about the possibility of diabetes, diagnosis may include several tests. The following diagnostic tests that can reveal the presence of type 1 diabetes:
Glycated hemoglobin test
This test measures the percentage of blood sugar attached to oxygen-carrying protein in the red blood cells . The higher the blood sugar levels, the more hemoglobin with sugar attached. A level of 6.5% or higher of A1C on two separate tests reveals the presence of diabetes.
Random blood sugar test
Blood samples are taken at random times, and the presence of type 1 diabetes may be confirmed after repeat testing. Blood sugar is measured in milligrams per deciliter or millimoles per liter . If a random blood sugar test reveals a level of 200 mg/dL or higher, the presence of diabetes is confirmed, especially when diabetic symptoms are already present.
Fasting blood sugar test
In this test, your doctor will take a blood sample after you had an overnight fast. A normal fasting blood sugar level of less than 100 mg/dL is considered normal. A fasting blood sugar level from 100 to 125 mg/dL is considered to be prediabetes. A level of 126 mg/dL or higher on two separate tests confirms diabetes.
If your doctor is uncertain of the diagnosis being type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes, theyll likely do more blood tests. The presence of autoantibodies or ketones in the urine will point to type 1 diabetes rather than type 2.
How Do You Manage Type 1 Diabetes
Living with T1D is a full-time balancing act requiring constant attention to avoid acute, life-threatening hypoglycemia or the long-term damage done by hyperglycemia . Blood sugar levels must be monitored either with finger pricks or a continuous glucose monitor. Insulin doses must then be carefully calculated based upon activity and stress levels, food intake, illness, and additional factors. These calculations are rarely perfect resulting in a tremendous emotional and mental burden for both patients and caregivers.
You May Like: What Kind Of Rice Can Diabetics Eat
Diabetes + Covid Vaccines: What You Need To Know
Editors Note: We have a simple goal: tap into the power of the global diabetes community to save lives. Visit coronavirusdiabetes.org to learn more about what you can do as a person with diabetes to keep yourself and others safe from COVID-19 until were all safe.
For information on how to get your vaccineFor more in depth information on COVID vaccines for kids with diabetes
COVID-19 vaccines are here. If you have diabetes and/or other underlying health concerns, you may have questions about timing, safety, and what to expect.
Its important to remember that having well-controlled diabetes alone does not seem to put anyone more at risk for contracting the novel coronavirus, but other factors like older age, high-exposure employment, consistently elevated blood glucose levels, or other non-diabetes related health factors like obesity and hypertension may increase your risk of infection.
We also know that diabetes care itself is made far more complicated after contracting COVID-19 and protecting anyone with diabetes from getting COVID-19 is our ultimate goal. Thats why we encourage everyone with diabetes to get vaccinated as soon as possible.
Treatment For Type 1 Diabetes
The impairment of the pancreas ability to produce insulin in type 1 diabetes means that insulin treatment is necessary.
Most people will take insulin by injection with insulin pens. Insulin can also be delivered by wearing an insulin pump. Use of an insulin pump will be considered in people that express an interest in having one and that meet certain eligibility criteria.
It is important that you are given education on how to balance insulin doses with dietary intake and physical activity and how to use blood glucose testing to help you control your diabetes.
Staying physically active and exercising regularly and eating a healthy diet are also important towards maintaining good blood glucose control and minimising the risk of long term diabetes complications. Although diet and exercise have a role to play in type 1 diabetes management, they cannot reverse the disease or eliminate the need for insulin.
- If you have recently been diagnosed, see our newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes guide.
Recommended Reading: Why Eat Sugar After Giving Blood
How Do You Get Type 1 Diabetes
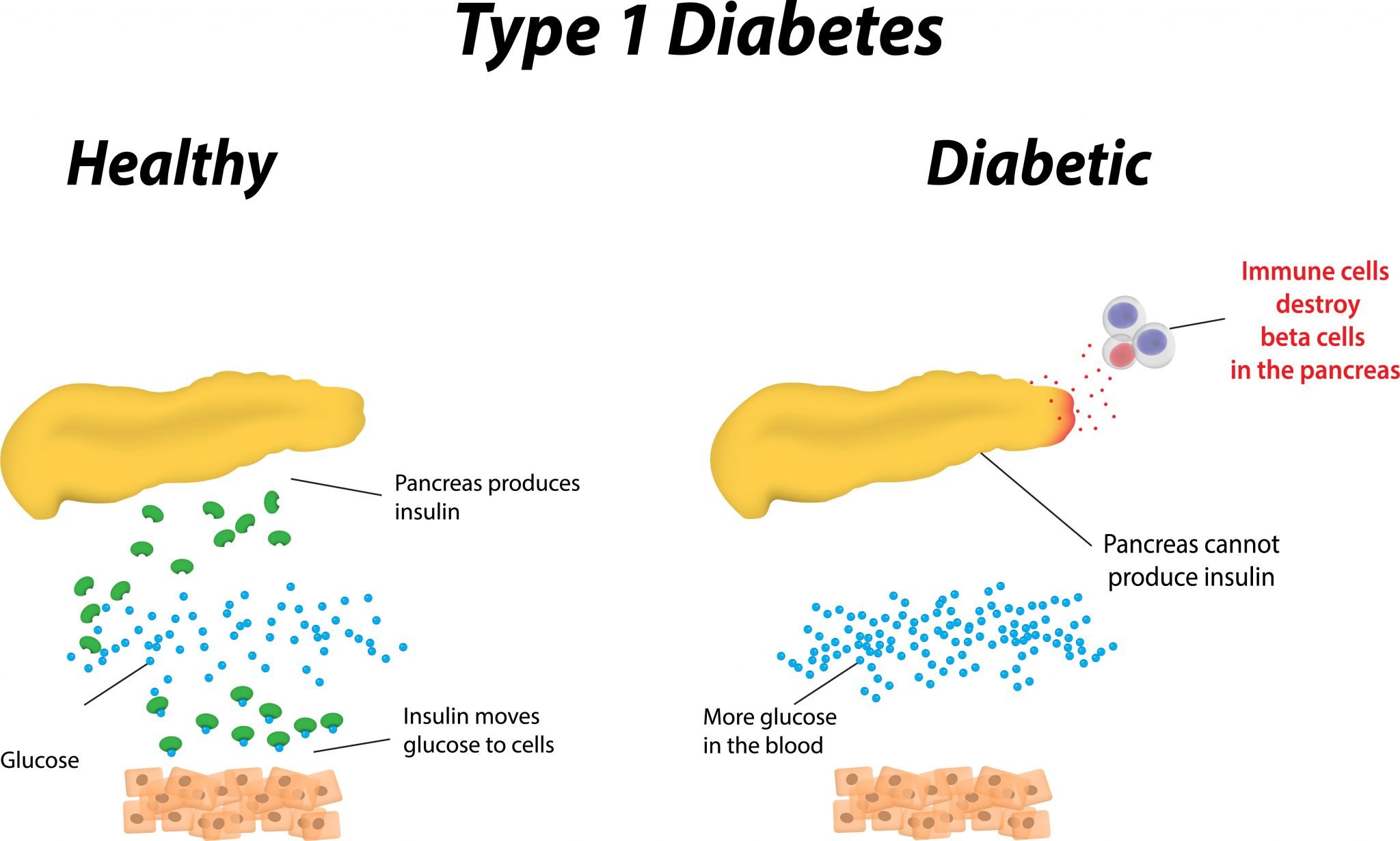
Type 1 diabetes is caused by the abnormal behavior of the human bodys immune system. In type 1 diabetes, the immune system perceives insulin-generating cells as intruders. In response, antibodies are created to destroy these cells. The targeted cells are called Beta cells and are generated by the pancreas. Diabetes Type 1 is considered a chronic metabolic condition that is generally linked to genetic complications. The disease is often diagnosed in children as their immune system is not well-developed yet.
Type 1 Diabetes: A Complex Trait
Researchers have claimed that the auto-immune response that occurs in patients with type 1 diabetes is primarily caused by gene mutations in the patients genetic makeup. In particular, genes in chromosome number six is susceptible. Chromosome number six also has the genes for antigens that are responsible for preventing the human immune system from attacking itself. Although the exact process of mutation is not yet fully understood, it is generally thought to be the cause of this disease.
Being a genetic condition means that it can be inherited from one generation to another. It is very common to find diabetes patients who have a history of the disease in their family.
Research in the United States has also found that type 1 diabetes is more commonly diagnosed in non-Hispanic white children as compared to other races.
Environmental Factors
Diet
References
How Does Diabetes Affect The Body
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2.
Both types of diabetes are chronic diseases that affect the way your body regulates blood sugar, or glucose. Glucose is the fuel that feeds your bodys cells, but to enter your cells it needs a key. Insulin is that key.
People with type 1 diabetes dont produce insulin. You can think of it as not having a key.
People with type 2 diabetes dont respond to insulin as well as they should and later in the disease often dont make enough insulin. You can think of it as having a broken key.
People with type 1 and type 2 diabetes may also experience irritability, mood changes, and unintentional weight loss.
People with type 1 and type 2 diabetes may also have numbness and tingling in their hands or feet. Good glucose management significantly reduces the risk of developing numbness and tingling in someone with type 1 diabetes, according to the American Diabetes Association .
Although many of the symptoms of type 1 and type 2 diabetes are similar, they present in very different ways.
Many people with type 2 diabetes wont have symptoms for many years, and their symptoms often develop slowly over the course of time. Some people with type 2 diabetes have no symptoms at all and dont discover they have the condition until complications arise.
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes may have similar names, but theyre different diseases with unique causes.
Read Also: How To Protect Kidneys From Diabetes
Faqs: Frequently Asked Questions
Why did type 1 diabetes used to be called juvenile diabetes?
Most people with type 1 diabetes are diagnosed as children, although in rare cases some are not diagnosed until they are adults.
Are type 1 diabetes symptoms in adults different than in children?
No, adults and children experience the same symptoms.
Is there a type 1 diabetes cure?
Type 1 diabetes can be managed with insulin, but there is no cure.
In type 1 diabetes vs type 2, is diet as important?
Even though diet and lifestyle changes cannot reverse type 1 diabetes, and they have the potential of reversing type 2, learning what, how much, and when to eat can still help you have the most effective type 1 diabetes diet to manage your condition.
What type of doctor is best for type 1 diabetes treatment?
Even though an ER doctor or your primary care physician will likely be the one to first diagnose your type 1 diabetes, an endocrinologist is the best doctor to help you learn how to monitor your blood sugar and manage your condition.
How Common Is Type 1 Diabetes
Well, its a lot less common than type 2. According to the American Diabetes Association, 1.6 million Americans have type 1 diabetes, including 187,000 children and adolescents. Type 1 diabetes makes up between 5 and 10% of total diabetes cases in the United States, while type 2 diabetes covers the other 90 to 95%.
Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed before the age of 40, although occasionally people have been diagnosed later after an illness causes an immune response that triggers it. In the US, most type 1 diabetes diagnoses occur in children between the ages of 4 and 14 years old.
Also Check: How To Increase Blood Flow To Feet For Diabetics
Diabetes: 12 Warning Signs That Appear On Your Skin
Diabetes can affect many parts of your body, including your skin. When diabetes affects the skin, its often a sign that your blood sugar levels are too high. This could mean that:
-
You have undiagnosed diabetes, or pre-diabetes
-
Your treatment for diabetes needs to be adjusted
If you notice any of the following warning signs on your skin, its time to talk with your doctor.
Causes Of Type 1 Diabetes
There is no known direct cause of type 1 diabetes, but scientists think genes may play an important factor, as well as viruses and infections that can trigger your bodys immune system.
Ineffective immune system
Scientists currently believe that type 1 diabetes occurs when your bodys immune system, which normally fights off infections, instead attacks and destroys cells in your pancreas that produce insulin.
Insulin is a hormone that moves glucose into cells for energy. Without sufficient insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream. Elevated glucose remains in the blood, eventually causing severe complications with the kidneys, heart, nerves, eyes, gums and even teeth.
Genetics
Some people may have a genetic predisposition to develop type 1 diabetes. Although this may make them more likely to develop the disease, many people never do develop it, because most people who are at risk do not develop diabetes.
Recommended Reading: What Are The First Signs Of Diabetes
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. They have similar symptoms, and over time, they can lead to many of the same complications. However, they are very different diseases.
Type 1 diabetes is the result of the body not producing insulin on its own. Taking insulin is necessary for survival, to move glucose from the bloodstream into the bodys cells.
For people with type 2 diabetes, the cells have stopped responding well to insulin. The body struggles to move glucose from the blood into the cells, despite adequate levels of the hormone. Eventually, their bodies may stop making adequate insulin entirely.
Type 1 diabetes develops very quickly, and symptoms are obvious. For people with type 2 diabetes, the condition can develop over many years. In fact, a person with type 2 diabetes may not know they have it until they have a complication.
Newly Diagnosed With Type 1 Diabetes
It can be difficult to know where to get started with your new type 1 diagnosis, but were here to help you find the information you need.
As well as reading through the guidance and advice on this page, why not try our Learning Zone? With videos, quizzes and interactive tools tailored just for you, its the perfect way to discover more about your diabetes.
“She made me feel normal, when my normal had completely changed.”
– Laura, on being diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. Read her story.
Don’t Miss: How To Determine If You Have Diabetes
How Is Type 1 Diabetes Diagnosed
Doctors can say for sure if a person has diabetes by testing blood samples for glucose. If the doctor suspects that a kid or teen has diabetes, he or she may send the person to see a pediatric endocrinologist a doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating children and teens living with diseases of the endocrine system, such as diabetes and growth problems.
How Is Type 1 Diabetes In Children Managed
Type 1 diabetes is managed by monitoring glucose levels. In addition, the child will need to:
- Check blood sugar levels a few times a day
- Give themselves insulin injections or use an insulin pump
- Eat a balanced, healthy diet
- Get regular exercise
- Work closely with healthcare providers and family to control diabetes
- Follow treatment plan created by healthcare provider
- Take the A1C blood test to check how well diabetes is being managed
Recommended Reading: Does Drinking Water Lower Blood Sugar
Type 1 Diabetes And Pregnancy
Pregnant women with type 1 diabetes need to be extra careful to maintain good blood sugar control. If blood sugar runs too high during pregnancy, there is an increased risk of complications including having a very large baby, having the baby too early, and having preeclampsia, a condition that can be life threatening to the mother and baby. You can minimize the risk for complications by paying close attention to blood sugar, eating a low-glycemic diet, and staying regularly active.
What Causes Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes occurs when your immune system, the bodys system for fighting infection, attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas. Scientists think type 1 diabetes is caused by genes and environmental factors, such as viruses, that might trigger the disease. Studies such as TrialNet are working to pinpoint causes of type 1 diabetes and possible ways to prevent or slow the disease.
Also Check: Why Does Blood Sugar Go Up At Night

