Expert Advice: If Blood Sugar Suddenly Increases After Eating Then Know How To Control
Whatever diet we take, it plays an important role in controlling the level of blood sugar. An increase in blood sugar levels after a meal is called postprandial or hyperglycemia. This spike is affected by several factors such as the amount of food, the timing of the meal, the timing of your medication, and the foods you are eating. Recently, Nutritionist Namami Aggarwal shared some tips on controlling blood sugar levels after meals in her question and answer series on Instagram. Here are some such tips-
Postprandial Blood Sugar Few Of Those With Diabetes Know Why It Is So Important
Blood sugar after a meal is referred to as postprandial blood sugar. So the opposite, namely before a meal, is called preprandial. The American Diabetes Association advises keeping your blood sugar levels before meals between 80–130 mg/dl and your levels 1–2 hours after meals under 180.
Usually, blood sugar begins to rise 10-15 minutes after a meal and reaches its peak after an hour. However, it is important to note that these are just approximate guidelines as postprandial glucose depends on several factors, such as the type of food consumed.
Influence on HbA1c
Research has shown that postprandial blood sugar levels are significant for HbA1c. Even if glucose spikes after eating are only brief, they still have the potential to raise HbA1c over the course of the day. Most people with diabetes check their blood sugar before a meal but not afterwards or they leave it until the next mealtime. This can lead to glucose spikes being undetected and remaining high for a long period of time.
How to deal with high postprandial blood sugar levels
Be sure to check your levels at least 90 minutes after a meal. Why? By that time rapid acting analogue insulin has reached its maximum effect .
If it’s still too high then you should look into the causes such as:
-
what type of food did I eat?
-
did I correctly estimate my carbs?
-
is my insulin-to-carb ratio correct?
-
and is the injection-meal interval correct?
Featured Posts
/8the Right Time To Test Your Blood Sugar And The Correct Way To Do It
According to the International Diabetes Federation, 42.5 crore people are dealing with diabetes globally. The number is expected to increase to 62.9 crores by 2045.
The data is shocking and alarming because not just the elderly, even kids as young as 6 months old are getting diagnosed with the disease.
High Calorie Foods May Or May Not Cause The Blood Sugar Level To Rise
Many people think that all high-calorie foods raise blood sugar level, but this is not always the case.
In general, foods that cause blood sugar level to rise the most are those that are high in carbohydrates, which are quickly converted into energy, such as rice, bread, fruits and sugar. Next are foods high in protein, such as meats, fish eggs, milk and dairy products, and oily foods. However, even though carbohydrates affect blood sugar levels, if you don’t eat them your diet will be unbalanced and you won’t feel satisfied after your meal, which can lead to excessive consumption of foods rich in protein and fat.
Food containing three major nutrients
| Carbohydrates |
|---|
/8different Times When You Should Check Your Blood Sugar Levels
– If you are someone who is newly diagnosed with high blood sugar, it’s important for you to take the blood sugar test more often. Note down this data and share with the doctor, it will help him shape an appropriate treatment plan for you.
– If you take insulin, doctors will recommend you to take three or more blood sugar readings throughout the day.
Recommended Blood Sugar Targets For Most People With Diabetes*
Your targets may not be the same as the examples in this chart. Your targets are important and should be specific to you.
| A1C** | |
| 4.0 to 7.0 | 5.0 to 10.0 |
* This information is based on the Diabetes Canada 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Canada and is a guide.** A1C is a measurement of your average blood sugar control for the last two to three months and approximately 50 per cent of the value comes from the last 30 days.
Measuring Carbs And Insulin For Blood Sugar Level After Eating
Reaching those target levels is definitely easier said than done. To get greater control of blood sugar after eating, we should think about it in a comprehensive way. First, let’s look at food in relation to insulin.
Food is where it all begins; make sure you are eating fibrous and nutritious kinds of carbohydrates. Examples of food containing the kind of carbohydrates which are beneficial are whole-grain bread or pasta, legumes like chickpeas and lentils, grapefruit, pears, apples, and potatoes.
See our Nutrition and Health Consultant’s post about food and diabetes for more information!
But how does a person with diabetes control what their body does with that food? Getting the right amount of insulin is important. While insulin injections are usually a matter for those with type 1 diabetes, many with type 2 also benefit from insulin treatment. Understanding insulin injections is helpful for all people with diabetes, and people in their support network.
The insulin dosage taken at a mealtime is called a bolus. The calculations for the bolus vary from person to person – this is where a doctor will help. The insulin to carbohydrate ratio will be established. This will help you understand how many grams of carbohydrates are covered by one unit of rapid-acting insulin.
Hedia’s page about our app, “Carb Calculator and Diabetes“ gives explanations for these calculations. Find a snippet of that page below for the calculation of the 500 rule.
Acceptable Blood Sugar Levels 2 Hours After Eating Breakfast
As food digests, sugar molecules circulate through the bloodstream and provide energy for the body. But having too much sugar in the blood can be dangerous, sometimes leading to diabetes and other health concerns. Knowing the acceptable blood sugar target range after eating can help you determine whether your blood sugar levels are stable and healthy or unstable and dangerous.
What To Do If Your Blood Sugar Levels Are Higher Than Normal
If your fasting or post-meal blood sugar readings are consistently higher than normal, you may have prediabetes or diabetes. If you suspect you have diabetes or prediabetes, you should see your healthcare provider as soon as possible.
Symptoms of diabetes, beyond elevated blood sugars, may include increased thirst and urination, severe fatigue and excessive hunger. For more details, see our guide to common .
How To Test Your Blood Sugar Accurately In An Empty Stomach
What do diabetics need to know when to monitor their blood sugar on an empty stomach? Diabetes: How does glucose meters work? This article will help you test blood sugar with Blood Glucose meters?
1. The time on an empty stomach to reach 8 hours
Many people with diabetes think they don’t eat when they get up in the morning, and the result of blood sugar monitoring is fasting blood sugar, but that’s not the case, diabetics need to fast for eight hours to get the right fasting blood sugar before they can count as fasting blood sugar.
2. Blood sugar needs to be monitored between 6:00 a.m. and 8:00 a.m
Many people with diabetes think that getting up in the morning and not eating for blood sugar monitoring is what they want fasting blood sugar, but most people do not know that the best time to measure fasting blood sugar is 6:00 a.m. to 8:00 a.m., not too early and not too late, so diabetics should adjust the time to eat the night before according to the time to measure blood sugar in the morning.
3. To ensure that sleep is normal:
Some people with diabetes have the habit of often staying up late, and staying up late will make their sleep quality lower, will let oneself appear sleep deprivation phenomenon, and sleep easy to have a certain impact on blood sugar, when sleep is insufficient or sleep quality is not good will lead to the 2nd sky abdominal blood sugar blood sugar value also followed by errors.
4. Get up to take sugar-lowering drugs
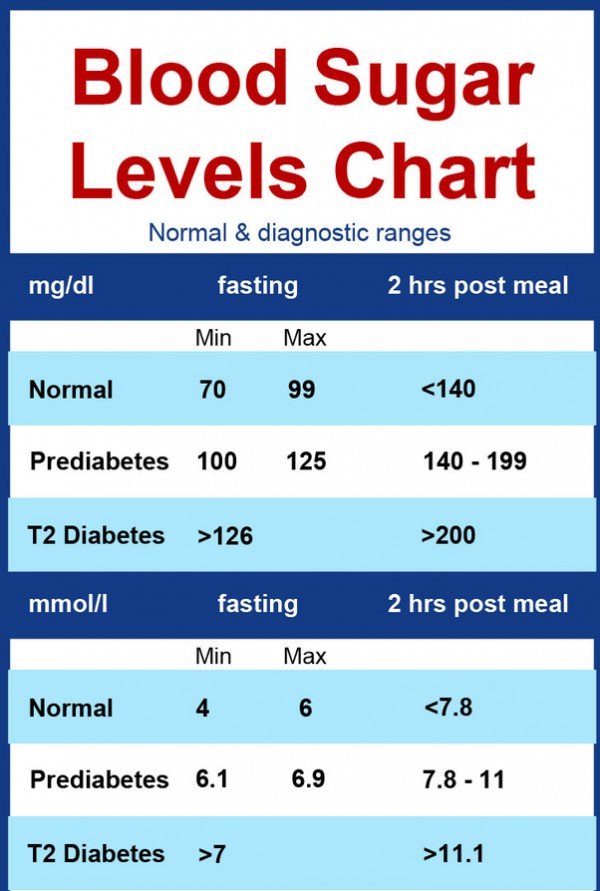
What Are Normal Blood Glucose Levels In Healthy Individuals
Blood sugar levels can either be normal, high, or low, depending on how much glucose someone has in their bloodstream. Glucose is a simple sugar that’s present in the bloodstream at all times. Normal blood glucose levels can be measured when someone fasts, eats, or after they’ve eaten. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, who haven’t eaten for at least eight hours is less than 100 mg/dL. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, two hours after eating is 90 to 110 mg/dL.
Many factors affect blood sugar levels throughout the day:
- Type of food consumed, how much, and when
- Physical activity
- Menstrual periods
- Alcohol
An ideal blood sugar level for anyone without diabetes or prediabetes, regardless of age, in the morning should be less than 100 mg/dL. Remember, blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day as a result of the factors previously mentioned.
What To Do If Your Blood Sugar Levels Are Lower Than Normal
Blood sugar levels that are below 70 mg/dL are known as hypoglycemia. Symptoms of hypoglycemia include heart palpitations and feeling lightheaded, jittery, irritable, fatigued, or sweaty.9
Low fasting blood sugar levels can occur if you have diabetes and your medication does not match your carbohydrate intake. So it’s very important to let your healthcare provider know you’re following a low-carb diet so they can adjust your medication to match your carb intake.
In people who do not have diabetes, low fasting blood sugar levels may be the result of a serious underlying medical condition such as an eating disorder or a tumor. If your fasting blood sugar is low and you do not take diabetes medications, see your healthcare provider.
Low blood sugar levels after eating are often called reactive hypoglycemia. This can occur in people with diabetes, as well as those with normal fasting blood sugars. How it should be treated depends on what the underlying cause is. But if you have low blood sugar and experience symptoms, you can remedy this in the short term by eating something with carbs or sugar.
High-carb intake may cause reactive hypoglycemia in people who are very insulin sensitive or have experienced massive weight loss.10 A low-carb, high-protein diet has been found to improve reactive hypoglycemia in adults who have undergone weight-loss surgery.11
What Are Target Blood Sugar Levels For People With Diabetes
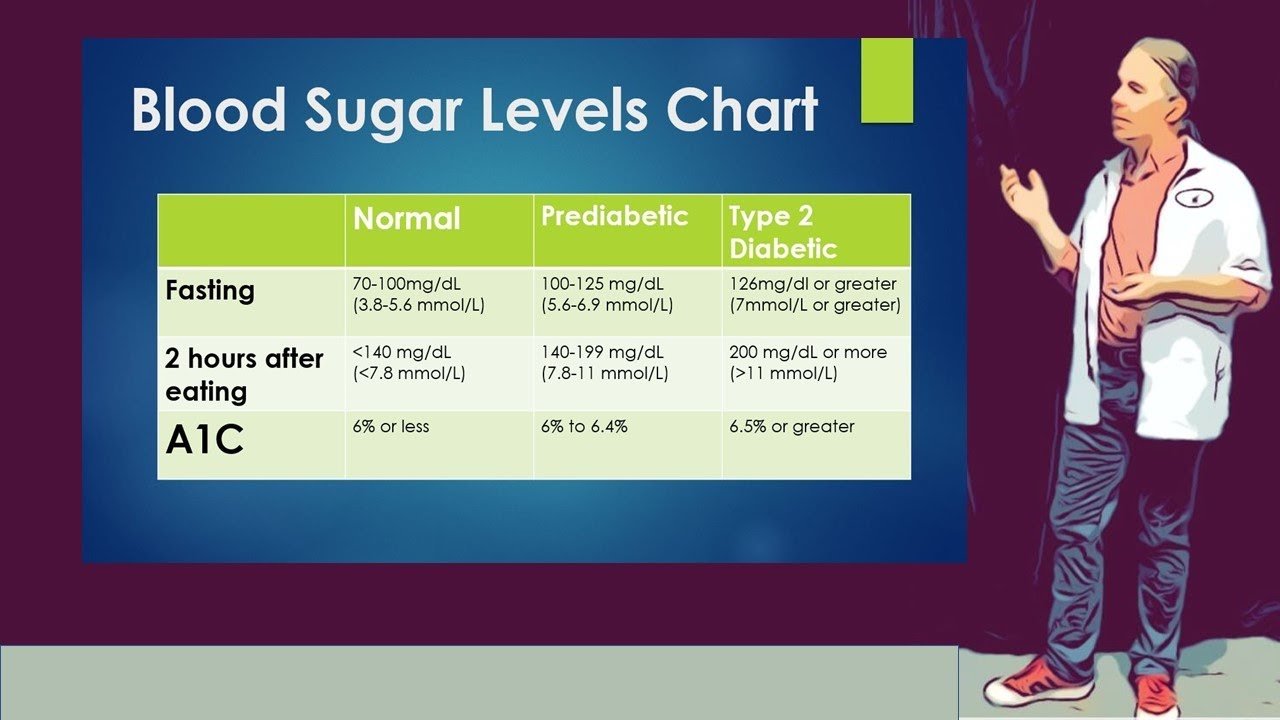
A target is something that you aim for or try to reach. Your health care team may also use the term goal. People with diabetes have blood sugar targets that they try to reach at different times of the day. These targets are:
- Right before your meal: 80 to 130
- Two hours after the start of the meal: Below 180
Talk with your health care team about what blood sugar numbers are right for you.
Different Approaches To Managing Blood Sugar After Eating
Each person’s body is different, and responds to insulin in a different way. There is no one-size-fits-all insulin treatment.
So, even after you’ve counted your carbs and figured out how much to inject, there is still another way to influence your blood sugar level after eating. Namely, try different methods and time-periods for injecting.
The common method is to inject before eating. Rapid-acting insulin requires injections 5-15 minutes before eating. Those minutes are the time it takes for insulin to enter the bloodstream. That way, your body will be ready for digestion once eating has begun.
After entering the bloodstream, rapid-acting insulin peaks after 1 hour – this is when it is most effective at lowering the blood sugar level after eating.
This insulin will remain effective for 2-4 hours in the body. Find out whether those minutes and hours work best for you by trial-and-error and consulting with a doctor.
If not, splitting the bolus is another route to more efficient insulin treatment. This is especially useful if eating fatty food, such as takeaway pizza or curry.
This means taking a portion of the insulin before eating, and a portion after eating. Again, this is trial-and-error. Experiment and speak to a doctor.
It’s always good for a person with diabetes to know what is going on with their body. So, when trying different methods, remember to keep testing. And keep testing even when sticking to the same routine.
How Long After Eating Does Blood Sugar Return To Normal
The blood sugar level falls back to a normal level around 1-2 hours after taking food. During this time digestion slows down and the sugar is absorbed by the tissue.
In diabetics, there can be a sudden spike in blood sugar after eating causing headache, dizziness and discomfort. This is called a post-prandial reaction. Normally, taking prescribed insulin medication can help mediate this problem.
What Else Can I Do To Help Manage My Blood Sugar Levels
Eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular physical activity can all help. Other tips include:
- Keep track of your blood sugar levels to see what makes them go up or down.
- Eat at regular times, and don’t skip meals.
- Choose foods lower in calories, saturated fat, trans fat, sugar, and salt.
- Track your food, drink, and physical activity.
- Drink water instead of juice or soda.
- Limit alcoholic drinks.
- For a sweet treat, choose fruit.
- Control your food portions .
Still Frustrated With Your Blood Sugar And A1c Results
Your blood sugars and your insulin or medication needs never stay in one place. If you gain weight or lose weight, your insulin and medication needs will change. If you become more active or less active, your needs will change. If you make drastic or even small changes to your nutrition, your needs will change!
Working with your diabetes healthcare team, and diabetes coaches who can teach you how to make changes in your overall diabetes management plan are essential. Diabetes is a lifelong learning process.
Take a deep breath and be patient. If you don’t like what you’re seeing on your glucose meter, don’t get mad…get studying! Take good notes and work with your team to make changes to reach your goals.
Read more about improving your A1c in DiabetesStrong’s guide, How to Lower Your A1c.
If you liked this guide to normal blood sugar levels, please sign up for our newsletter using the form below. We send out a weekly newsletter with the latest posts and recipes from Diabetes Strong.
Should I Test My Blood Sugar 1 Or 2 Hours After Eating
Testing too soon after you’ve had a meal or a snack will give you results that are probably too high. The solution for better diabetes control: Test fasting blood sugar, and test every time before you eat. Wait two hours after eating to get the best reading.
READ: What is Ronald Reagan best known for?
What If I Have Trouble Getting To My Blood Sugar Goals
There may be times when you have trouble reaching your blood sugar goals. This does not mean that you have failed. It means that you and your health care team should see if changes are needed. Call your health care team if your blood sugar is often too high or too low. Taking action will help you be healthy today and in the future.
Personalizing Your Diet Based On Blood Sugar Response
In addition to seeing your healthcare provider, there are steps you can take to reduce your blood sugar levels. If you check your blood sugar after meals and keep track of those measurements, along with the types and amounts of food you ate, you may be able to see which foods are problematic.
Although an increase in blood sugar is usually due to eating high-carb foods, all carbs are not the same when it comes to raising blood sugar. Because starchy foods digest down to glucose very quickly, some starchy foods may end up having a much greater impact on blood sugar than you might expect.
For instance, even though a banana tastes sweeter than a baked potato, the potato may actually have a bigger impact on blood sugar.13
Because high-carb foods have the biggest impact on blood sugar levels, it makes sense to reduce them, no matter what type of diet you follow. The American Diabetes made this point in a 2019 paper on nutrition for people with diabetes.14
Sometimes making gradual changes can work best. Our guide, Eating better: six steps down carb mountain, can help you lower your carb intake, one step at a time.
If you’ve been diagnosed with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, our guide to the best foods for diabetes can help you make choices that may reduce your need for blood sugar control medications.
If a food or beverage seems to be causing your blood sugar to rise too much, try leaving it out of your diet for a few days to see if you notice a difference.
Gaining Insights From Routine Blood Glucose Testing
Day-to-day blood sugar checks can give you a good idea of how you’re doing at this moment, and they can be reviewed overall to see trends. They can help answer questions such as:
- Are your medications working as they should?
- How does the type or amount of food you eat affect your blood sugar?
- How does activity or stress affect your blood sugar?
Your Blood Sugar Isnt Just Because Of What You Eat
Mainstream media would have you believe that your blood sugar levels are impacted only by what you eat and how much you exercise, but people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes who test their blood sugars frequently could tell you otherwise.
It’s especially important to keep this mind when looking at your own blood sugars and your goals because there are certain variables and challenges that impact blood sugar levels that you can’t always control.
For example:
- Menstrual cycles: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- Adrenaline rushes from competitive sports, heated arguments, rollercoaster rides: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- The common cold and other illnesses: usually raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- Hormonal changes due to puberty and healthy growth in young adults: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- An injury which raises overall inflammation levels: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- Glucogenesis during anaerobic exercise: raises blood sugar
While you can’t necessarily prevent these factors that affect your blood sugar from occurring, you can work with your diabetes healthcare team to adjust your insulin, other diabetes medications, nutrition and activity levels to help compensate for them when they do occur.
For example, when engaging in anaerobic exercise — like weightlifting — many people with type 1 diabetes find it necessary to take a small bolus of insulin prior to or during their workout because anaerobic exercise can actually raise blood sugar.
Diagnosing Prediabetes Type 2 And Type 1 Diabetes
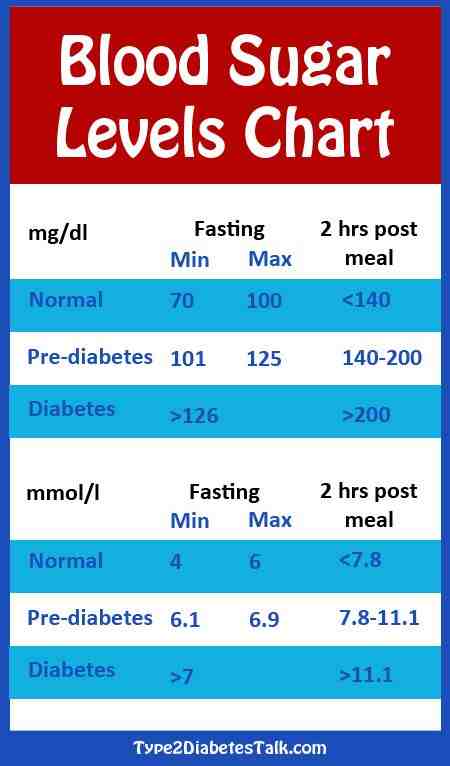
Depending on which country or medical organization you ask, the qualifying numbers for “normal” versus “prediabetes” versus diagnosed type 1 or type 2 diabetes can vary slightly. The following blood sugar and A1c the general results are used to diagnosed prediabetes and diabetes according to sources including the American Diabetes Association and Diabetes UK:
Prediabetes
- HbA1c: 5.7 to 6.4 percent
- Fasting: 100 to 125 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 140 mg/dL to 199 mg/dL
Type 1 or 2 diabetes
- HbA1c: 6.5 percent or higher
- Fasting: 126 mg/dL or higher
- 2 hours after a meal: 200 mg/dL or higher
Please note: Type 1 diabetes tends to develop very quickly which means that by the time symptoms are felt, blood sugar levels are generally well above 200 mg/dL all the time. For many, symptoms come on so quickly they are dismissed as the lingering flu or another seemingly ordinary virus.
Read more about ketones at diagnosis in Diabetes Strong’sDiabetic Ketoacidosis Guide.
Why Do You Check Blood Sugar 2 Hours After Eating
This means your blood sugar levels are too high, and over time this can lead to serious health problems including heart, nerve, kidney, and eye damage. Postprandial means after a meal. This test is done to see how your body responds to sugar and starch after you eat a meal.
Blood Sugar After Eating How To Manage It Better
Hi. My name is Christina and I am a nurse specialized in diabetes and also one of the co-founders of Hedia. Let me give you my advice on how to manage blood sugar after eating in this short video – or check out my more detailed advice below the video.
As a nurse, and as a family member of a person with diabetes, I have seen first-hand how much must be considered with managing blood sugar after eating.
From that experience, I also know that diabetes doesn’t need to take over your life. I have studied the importance of taking a positive approach to diabetes; I want you to know that everything with diabetes can be tackled.
This includes blood sugar after eating. Understanding why you might have high blood glucose/sugar after eating is a hurdle that others without diabetes might not need to think about.
However, once you have that knowledge under your belt, you will have the confidence to know that you control your diabetes – not the other way round!
To get control of that blood sugar level after eating, we should first look at what happens with the body. From this we can get an understanding of different approaches to handling that after-meal spike, as well as some often overlooked aspects.
/8the Right Time To Check Your Blood Sugar Levels
The perfect time to check the fasting glucose levels is right after your wakeup. And the right time to check postprandial glucose levels is two hours after you have your meals.
A gap of two hours after a meal must be maintained to get the correct reading.
This helps you choose the right foods and medication. When you test before your meal, it tells you how much medication you need and when you test two hours after eating, you know if your medicines are working fine for you.
What Should I Do If My Blood Sugar Gets Too High
High blood sugar is also called hyperglycemia . It means that your blood sugar level is higher than your target level or over 180. Having high blood sugar levels over time can lead to long-term, serious health problems.
If you feel very tired, thirsty, have blurry vision, or need to pee more often, your blood sugar may be high.
Check your blood sugar and see if it is above your target level or over 180. If it is too high, one way to lower it is to drink a large glass of water and exercise by taking a brisk walk. Call your health care team if your blood sugar is high more than 3 times in 2 weeks and you don’t know why.
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Eating
Your blood sugar level is influenced by several factors, including the food you eat. During digestion, carbohydrates are converted into sugar which your body uses as an energy source. Excess sugar from any source is stored in your cells for later use. When your cells contain too much sugar, though, it can lead to type 2 diabetes. This is why eating a balanced diet to maintain a normal blood sugar range is important.
Blood sugar levels can vary based on many factors, including age and life expectancy, comorbidities like heart disease, stress, and lifestyle factors like physical activity, smoking, or drinking alcohol.

