What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Dka
The symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis usually don’t develop all at once they usually come on slowly over several hours. People who have DKA may:
- feel really tired
- feel really thirsty or pee way more than usual
- have a dry mouth and signs of dehydration
These symptoms are caused by the high blood sugar levels that usually happen before someone develops DKA. If the person doesn’t get treatment, these signs of DKA can happen:
- abdominal pain
- unconsciousness
For Moderate To Severe Insulin Overdoses: Blood Sugars Below 50 Mg/dl
There are two things you can and should do if you feel youve taken a significant overdose of insulin or youre suffering from severe hypoglycemia:
Use a glucagon kit;
Aglucagon kit can save your life and is prescribed by your doctor. Be sure to keep it in an easy-to-reach location that others in your household or office know about. A glucagon kit works by giving you an injection of glucagon which is a hormone that tells your liver to release stored glucose . This large dump of glucose from your liver can save your life, or at least prevent seizures in someone who is already unconscious.;
or get someone to drive you to the ER immediately
If youve taken a serious overdose of insulin or your blood sugar is crashing and you do not have a glucagon kit, call 911 immediately. If youre caring for someone else who has taken an overdose of insulin and they are unresponsive and unable to chew or swallow, you absolutely need to call 911. The emergency medics will give dextrose intravenous to hopefully revive the person suffering from a severe insulin overdose.
If you take insulin, you are at risk of experiencing an insulin overdose nearly every day of the week because juggling insulin doses with the many other variables that affect blood sugar levels is a complicated game. The more you observe how much insulin you need with certain meals and with meals that occur right before exercise, the more you can prevent overdosing.
If Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar Return
-
Always keep a source of fast-acting sugar with you. At the first sign of low blood sugar, eat or drink 15 to 20 grams of fast-acting sugar. Examples include:
-
3 to 4 glucose tablets or glucose gel. These are sold at most drugstores.
-
4 ounces of regular soda
-
4 ounces of fruit juice
-
2 tablespoons of raisins
-
1 tablespoon of honey
-
Check your blood sugar 15 minutes after treating yourself. If it’s still low, take another 15 to 20 grams of fast-acting sugar. Test again in 15 minutes. If its still low, go to an emergency room.
-
Once your blood sugar is normal again, eat a snack or meal with protein to keep your blood sugar in a safe range.
In the future, you may need to lower your insulin dose if you aren’t able to eat your normal amount at each meal because of illness or vomiting. Call your healthcare provider right away. Ask him or her about changing your dose for a little bit.
Check your blood sugar every 4 to 6 hours. Do this until you can start eating normal amounts again.
Wear a medical alert bracelet or necklace or carry a card in your wallet that says you have diabetes. It will help healthcare providers give you correct care if you have a severe low blood sugar reaction and can’t tell them you have the disease.
Read Also: How Long Does It Take To Lower Blood Sugar
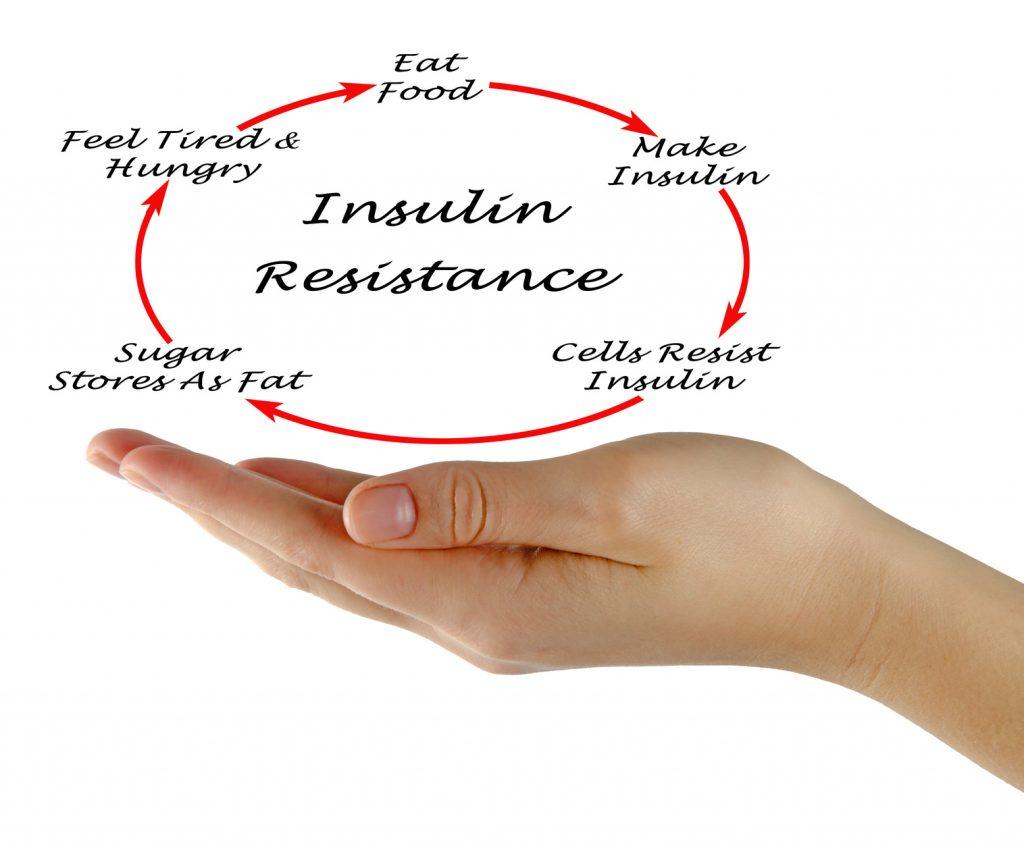
Signs Of Insulin Resistance
Most people think about diabetics when they see the word insulin, but problems with insulin can occur in a number of different conditions, in people with normal blood sugar. You have probably heard of insulin resistance; it is a significant health problem because it’s associated with an increased risk of obesity, heart attacks, polycystic ovarian syndrome, cancer and other serious conditions. People with insulin resistance usually have excessively high levels of this hormone, because it doesn’t work properly. We are seeing an increasing number of patients who have been diagnosed with insulin resistance by their own doctor, yet they don’t fully understand what this term means.
How would you know if your insulin level is too high?
There is a blood test that can measure your fasting insulin, but it isn’t always reliable and many doctors are not willing to order this test. This is a shame because elevated insulin is bad for your health and shortens your lifespan.
Insulin has many important roles in your body. People with too much insulin in their bloodstream are said to have insulin resistance, syndrome X, metabolic syndrome or pre-diabetes. They are all interchangeable terms.
Knowing whether or not you have too high insulin is important because it can allow you to make some changes and avoid some serious health problems in the future. Luckily there are several tell tale signs or clues that your body gives you, alerting you to this problem.
The role of insulin in your body
What Happens If I Have Too Little Insulin
People with diabetes have problems either making insulin, how that insulin works or both. The main two types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2 diabetes, although there are other more uncommon types.
People with type 1 diabetes produce very little or no insulin at all. This condition is caused when the beta cells that make insulin have been destroyed by antibodies , hence they are unable to produce insulin. With too little insulin, the body can no longer move glucose from the blood into the cells, causing high blood glucose levels.;If the glucose level is high enough, excess glucose spills into the urine.;This drags extra water into the urine causing more frequent urination and thirst.;This leads to dehydration, which can cause confusion. In addition, with too little insulin, the cells cannot take in glucose for energy and other sources of energy are needed to provide this energy.;This makes the body tired and can cause weight loss. If this continues, patients can become very ill. This is because the body attempts to make new energy from fat and causes acids to be produced as waste products.;Ultimately, this can lead to coma and death if medical attention is not sought. People with type 1 diabetes will need to inject insulin in order to survive.
Read Also: Are Pumpkin Seeds Good For Diabetics
What Happens If You Take Too Much Humalog Insulin
4.3/5insulintoo muchIt
If you take too much Humalog, your blood sugar may fall too low . If you forget to take your dose of Humalog, your blood sugar may go too high .
Also Know, can insulin overdose be detected in autopsy? Four cases of self-injected insulin overdose in nondiabetic individuals are presented. Included are two cases of presumed insulin overdose , one case with elevated vitreous insulin , and one case with elevated postmortem blood insulin and low blood C peptide .
Also Know, what to do if you take too much fast acting insulin?
What to Do If You Have an Insulin Overdose
How much insulin can you take in a day?
Eventually, many people with Type 2 diabetes will require 12 units of insulin for every kilogram of body weight; that is, an 80-kilogram person will require at least 80 units of insulin each day. To start, however, your doctor may begin by prescribing 0.15 units of insulin per kilogram.
Effects Of Excess Insulin
As a diabetic patient who is dependent on insulin, you must measure your requirements for the same very carefully and consider your food intake and level of activity. If you take insulin but eat insufficient amounts of food, your body will use high levels of glucose from your blood resulting in hypoglycemia.
On the other hand, if you are a non-diabetic who takes insulin then the extra amounts of insulin in your body will eliminate the glucose already present in the blood causing your blood sugar level to fall considerably. In some cases the level falls so much that it can even prove fatal for the person. Hence, it is necessary to avoid taking medicines when not advised and also to follow proper dosage, as advised.
Recommended Reading: Why Does My Blood Sugar Go Up At Night
What Is Insulin And Why Do I Need It
Insulin is a hormone that controls the level of blood sugar in your body. People with diabetes may not have enough insulin or may not be able to use it properly. The sugar builds up in the blood and overflows into the urine, passing out of your body unused. Over time, high blood sugar levels can cause serious health problems.
All people with type 1 diabetes, and some people with type 2 diabetes, need to take insulin to help control their blood sugar levels. The goal in treating diabetes is to keep the blood sugar level within a normal range.
How To Prevent Insulin Overdoses
- Take care when calculating meal time insulin. Taking an extra couple of minutes to be sure of your dose will save the time and hassle of an overdose.
- Never be tempted to delay your meal or snack if you have injected.
- Dont inject whilst doing other tasks, such as watching the TV, holding a conversation or performing another task as this raises the chance that you may forget your injection has been done. Concentrate solely on giving the injection
- Be careful of injecting insulin when you are hypo as mistakes are more likely to be made. Ideally, ensure your blood glucose has risen to safe levels and then put in your scheduled insulin dose.
- Ask for help if you have difficulty seeing the numbers or gradations on your insulin pen or syringe. See also our page on diabetes and visual impairment which lists a number of injection aids for people that have visual impairments
Don’t Miss: How Long Can You Live With Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms Of An Insulin Overdose
Early symptoms of an insulin overdose are the same as symptoms of low blood sugar.
The American Diabetes Association lists the following as symptoms of low blood sugar:
- Feeling shaky
- Color draining from the skin
- Feeling Sleepy
- Feeling weak or having no energy
- Blurred/impaired vision
- Tingling or numbness in the lips, tongue, or cheeks
- Headaches
- Nightmares or crying out during sleep
Severe hypoglycemia from an insulin overdose can lead to:;
- Being unable to talk, chew, or swallow
- Losing consciousness because your brain isnt getting the glucose it needs to function
- Seizures because your brain isnt getting the glucose it needs to function
- Death because every part of your part requires glucose in order to function
Could Your Patient Be On Too Much Insulin
Jay H. Shubrook, DO; Sandhya Manivannan, MD
Jay H. Shubrook, DO: Hello. I am Jay Shubrook, DO, professor in the Department of Primary Care at Touro University California College of Osteopathic Medicine in Vallejo, California. Today we are going to be talking about insulin and how you know that you are on too much insulin. Our guest today is Sandhya Manivannan, MD, family medicine diabetologist.
Primary care providers have become pretty comfortable with using basal insulin, and lots of people are taking insulin. How do you know when someone is on too much insulin? What are the signs that I should be looking for as a busy clinician?
Dr Shubrook: I don’t have many patients who come to me and say that they are having hypoglycemic episodes. How do I start that conversation with them?
Dr Manivannan: One thing that can give you a hint is their glycated hemoglobin . You can check their A1c, and if it’s almost too good, meaning 6.5% or under, they might be having undetected serum glucose lows. Although their average A1c may look good, they may have unaccounted for lows and highs. When someone’s A1c may be too good to be true, you can have your patient check their blood sugar at nightset an alarm and check their blood sugar around 3:00 AM or 4:00 AMand see if they are having dips in the night that are going undetected.
Dr Shubrook: You talked about glucose being a way to help identify that. What is the pattern that should alert me that my patient could be dropping low at night?
Also Check: How Are Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Similar
What Happens If You Stop Taking Insulin Suddenly
Very quickly, severe hyperglycemia sets in. That is high blood sugar that leads to a state called DKA, short for diabetic ketoacidosis, which untreated leads to death. If you have any residual insulin at all in your system, it can help hold off DKA even when your blood sugar level is high, according to Dr.
Weight Loss Improves Insulin Sensitivity

Scientists arent sure exactly why the cells become less sensitive to insulin. However, being overweight is a major risk factor. Getting your weight down should be your primary focus if you’re overweight or obese. Losing weight will not only increase insulin sensitivity, it will lower your risk for other chronic conditions, like high blood pressure and elevated cholesterol.
You don’t need to lose a ton of weight to improve glucose balance. Losing just 5 percent of your body weight, if you’re obese, significantly improves insulin sensitivity in fat cells, muscle and the liver, reported a study published in Cell Metabolism in February 2016. Thats just 9 pounds if you weigh 180 pounds.
You May Like: Why Do You Draw Up Regular Insulin First
What Causes Insulin Shock
Having too much insulin in your blood can lead to having too little glucose. If your blood sugar falls too low, your body no longer has enough fuel to carry out its regular functions. In insulin shock, your body becomes so starved for fuel that it begins to shut down.
If you have diabetes and use insulin to help control your blood sugar, you can end up with excess amounts in your blood if you inject too much insulin or miss a meal after injecting insulin.
Other possible causes include:
- irritability
- rapid pulse
At this stage, you can usually take immediate steps to recover. Eating 15 grams of quick-acting carbohydrates such as glucose tablets or high-sugar options like fruit juice, raisins, honey, or candy can help stabilize your blood sugar and reduce symptoms.
After 15 minutes, test your blood sugar. If your blood sugar has improved, youll want to eat a small smack to help your body fully recover but otherwise you should be fine.
If your blood sugar isnt increasing, try eating another 15 grams of carbohydrates, followed by a meal. If you blood sugar is not increasing after repeating this step again, contact your doctor or visit the emergency room.
Plummeting blood sugar can also cause:
- headaches
How Does Insulin Work
Receiving the diagnosis of diabetes in the life of any person is a life-changing moment. Suddenly life revolves only around your blood sugar levels. To maintain these blood glucose levels, one must maintain a healthy lifestyle and insulin.
If you have type 1 diabetes youre insulin-dependent. Most of the time you use long-acting insulin and rapid-acting insulin. You must be very careful with your dosages. Although there are different insulin pumps and pens available on market it can be a bit difficult to make sure you take your insulin injection on time and make sure the insulin dose is correct.
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas. When you eat something, insulin gets the sugar from carbohydrates in your food. This way your body gets the energy it needs or stores energy for later. It regulates your blood sugar levels, makes sure it doesn’t go too high or too low . Without a working pancreas, your body starts using fat to produce energy but also produces keto acids. When these keto acid levels are too high you can get into diabetic ketoacidosis.;
Also Check: How High Can Your Blood Sugar Go
What Is High Blood Sugar
The is the amount of glucose in the blood. Glucose is a sugar that comes from the foods we eat, and it’s also formed and stored inside the body. It’s the main source of energy for the cells of our body, and it’s carried to each cell through the bloodstream.
Hyperglycemia is the medical word for high blood sugar levels. High blood sugar levels happen when the body either can’t make insulin or can’t respond to insulin properly . The body needs insulin so glucose in the blood can enter the cells of the body where it can be used for energy. In people who have developed diabetes, glucose builds up in the blood, resulting in hyperglycemia.
Having too much sugar in the blood for long periods of time can cause serious health problems if it’s not treated. Hyperglycemia can damage the vessels that supply blood to vital organs, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke, kidney disease, vision problems, and nerve problems. These problems don’t usually show up in kids or teens who have had the disease for only a few years. But they can happen in adulthood in some people with diabetes, particularly if they haven’t managed or controlled their diabetes well.
Blood sugar levels are considered high when they’re above your target range. Your diabetes health care team will let you know what your target blood sugar levels are.
page 1

