What Is Type 1 Diabetes
An absolute lack of insulin, usually due to destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas, is the main problem in type 1 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes was formerly referred to as juvenile or insulin-dependent mellitus . Its causes are different from type II , as will be reviewed in this article.
How Does Diabetes Affect The Body
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2.
Both types of are chronic diseases that affect the way your body regulates blood sugar, or . Glucose is the fuel that feeds your bodys cells, but to enter your cells it needs a key. is that key.
People with type 1 diabetes dont produce insulin. You can think of it as not having a key.
People with type 2 diabetes dont respond to insulin as well as they should and later in the disease often dont make enough insulin. You can think of it as having a broken key.
People with type 1 and type 2 diabetes may also experience irritability, mood changes, and unintentional weight loss.
People with type 1 and type 2 diabetes may also have numbness and tingling in their hands or feet. Good glucose management significantly reduces the risk of developing numbness and tingling in someone with type 1 diabetes, according to the American Diabetes Association .
Although many of the symptoms of type 1 and type 2 diabetes are similar, they present in very different ways.
Many people with type 2 diabetes wont have for many years, and their symptoms often develop slowly over the course of time. Some people with type 2 diabetes have no symptoms at all and dont discover they have the condition until complications arise.
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes may have similar names, but theyre different diseases with unique .
Which Is Worse Type 1 Or 2 Diabetes
It really is hard to distinguish which one is worse as each case is unique. What you need to keep in mind is that type 1 needs insulin to live.
People with type 1 diabetes need to have a regular insulin shot or else may lead to emergency situation and even death.
On the other hand, people with type 2 diabetes need an enormous amount of insulin because their body is resistant to it. Type 1 diabetes is easily diagnosed whereas people with type 2 can go undiagnosed for years.
Do Type 2 diabetics take insulin?
People with diabetes type 2 usually manage their blood glucose level with oral medication and lifestyle modification such as losing weight, quit smoking, and regular exercise.
However, there will come to a point when they will eventually need insulin shots such as in the case of people with symptomatic hyperglycemia, as the beta cell reserve gets depleted after many years of diagnosis with type 2 diabetes, multiple intakes of diabetes medication, and uncontrolled diabetes during pregnancy.
We Know Some People Get Confused Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes And Were Often Asked About The Differences Between Them
Although type 1 and type 2 both have stuff in common, there are lots of differences. Like what causes them, who they affect, and how you should manage them. There are other types of diabetes like and . But this page is mainly about the differences between type 1 and type 2.
For a start, type 1 affects 8% of everyone with diabetes. While type 2 diabetes affects about 90%.
Lots of people get confused between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. This can mean you have to explain that what works for one type doesn’t work for the other, and that there are different causes.
The main thing to remember is that both are as serious as each other. Having high blood glucose levels can lead to serious health , no matter whether you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes. So if you have either condition, you need to take the right steps to manage it.
What Happens When You Have Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
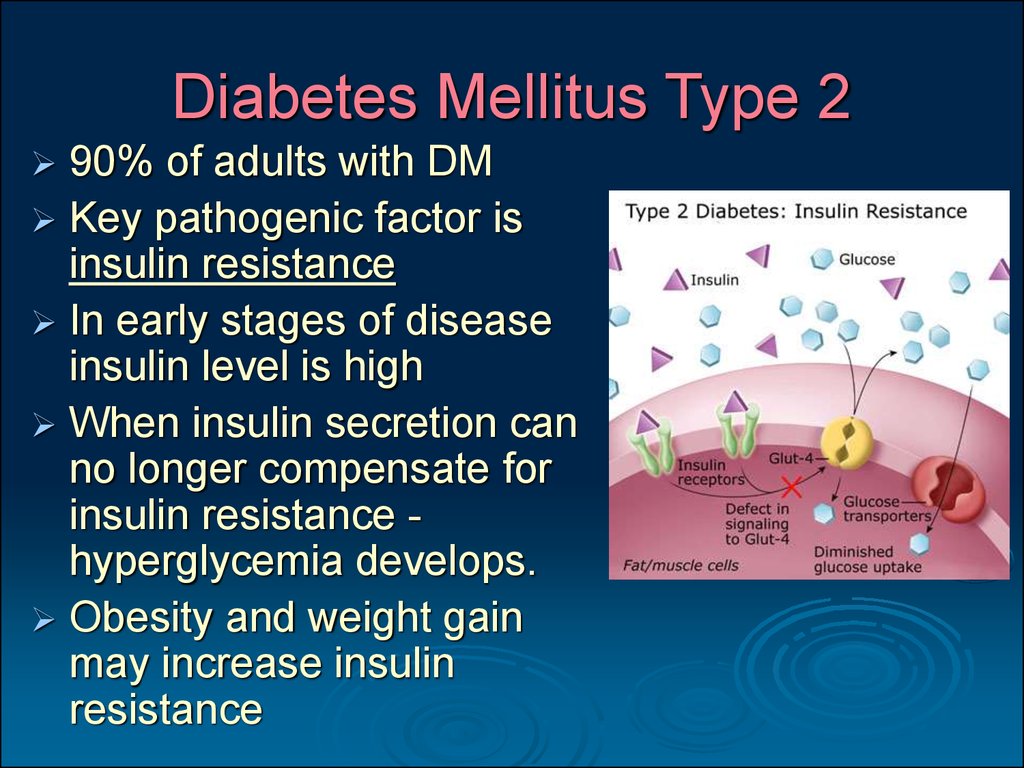
If you have either type 1 or type 2 diabetes, it means you have too much glucose in your blood. This is the same for both types. But the difference between them is how this happens.
If you have type 1 diabetes, it means you have an autoimmune condition. This means your body has attacked and destroyed the cells that make a hormone called insulin. So you cant make insulin anymore.
We all need insulin as it helps take the glucose from our blood into our bodys cells. We then use this glucose for energy. Without insulin, the glucose level in your blood gets too high.
Type 2 diabetes is different. If youve got type 2, either your body doesnt make enough insulin, or your insulin doesnt work properly. This is known as insulin resistance. Like type 1, this means the level of glucose in your blood is too high.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus type 1 is the bodys lack of ability to produce insulin. Those who have type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every single day. That is why type 1 diabetes is called insulin dependent diabetes mellitus.
It is once known as juvenile diabetes because it usually appears during childhood. It has no cure. The best way to deal with type 1 diabetes is to religiously manage the level of blood sugar through insulin, diet and lifestyle modification, and preventing possible complications.
What Causes Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes develops when the pancreas makes less insulin than the body needs, and the body cells stop responding to insulin. They dont take in sugar as they should. Sugar builds up in your blood. When cells dont respond to insulin, this is called insulin resistance. It’s usually caused by:
- Lifestyle factors, including obesity and a lack of exercise.
- Genetics, or abnormal genes, that prevent cells from working as they should.
What Is The Prognosis Of Diabetes
Diabetes is a leading cause of death in all industrialized nations. Overall, the risk of premature death of people with diabetes is twice that of people without diabetes. Prognosis depends on the duration of diabetes, degree of blood sugar control, and development of complications.
Type 1 diabetes
About 15% of people with T1D die before age 40 years, which is about 20 times the rate of this age group in the general population.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis , kidney failure, and heart disease compose the most common causes of death related to T1D.
- The good news is prognosis improves with good sugar control. Maintaining tight blood sugar control prevents, slows the progression of, and can improve established complications of T1D.
Type 2 diabetes
The life expectancy of people who are diagnosed with T2D during their 40s decreases by five to 10 years because of the disease.
- Heart disease leads the causes of death related to T2D.
- Aim for excellent glycemic control, tight blood pressure control, keeping the “bad” level at the recommended level below 100 mg/dL , and keeping the “good” cholesterol as high as possible. When indicated, can prevent, slow the progression of, and improve established complications related to diabetes.
Symptoms Of Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is often asymptomatic. Therefore, an oral glucose tolerance test is recommended during the 24th to 28th week of pregnancy. Untreated gestational diabetes can lead to developmental problems in the fetus, which results in increased birth weight , respiratory distress syndrome, and . In emergency cases, the fetus may suffer from diabetic embryopathy.
During pregnancy, due to hydramnios, in which the fetus is larger than average, urinary tract infections and preeclampsia can be noticed. Usually, in gestational diabetes, type 2 DM occurs as the hormonal changes lead to insulin resistance in 35% of females. In rare cases, pregnancy may trigger type 1 DM.
What Are The Types Of Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes
The body produces little or no insulin to regulate blood glucose level.
- T1D affects about 10% of all people with diabetes in the United States.
- T1D is typically diagnosed during childhood or adolescence. In the past T1D was called juvenile-onset diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
- Insulin deficiency can occur at any age due to destruction of the pancreas by , disease, or removal by surgery.
- T1D results from progressive destruction by the immune system of the pancreatic beta cells, the only cell type that produces significant amounts of insulin.
- People with T1D require daily insulin treatment to sustain life.
Type 2 diabetes
Although the pancreas still secretes insulin in someone with T2D, the bodys tissues are partially or completely incapable of responding to insulin. This is often referred to as insulin resistance. The pancreas tries to overcome this resistance by secreting more and more insulin. People with insulin resistance develop T2D when they fail to secrete enough insulin to cope with their body’s demands.
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a form of diabetes that occurs during the second half of .
- Although gestational diabetes typically resolves after delivery of a baby, a woman who develops gestational diabetes is more likely than other women to develop T2D later in life.
- Women with gestational diabetes are more likely to have large , complicated pregnancies, and complicated deliveries.
Metabolic syndrome
Prediabetes
Symptoms Of Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms of Type 1 diabetes include increased thirst and urination, constant hunger, weight loss, blurred vision and extreme tiredness.
Type 2 symptoms appear gradually and are more subtle than those seen with type 1. This makes catching the onset of type 2 diabetes harder to recognize for early treatment. Symptoms include unexpected weight loss, blurred vision, feeling tired or sick more frequently, more frequent urination . Higher levels of thirst, frequent infections and slower healing of cuts and scrapes.
Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
An ever-increasing number of children are developing diabetes. Very young children who develop the disease are most likely to be diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus, a lifelong illness characterized by the body’s inability to produce insulin, resulting in high blood sugar levels. Type2 diabetes is often seen in older children and adults whose bodies do not produce insulin, do not produce enough insulin, or do not use insulin effectively.
Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes Different
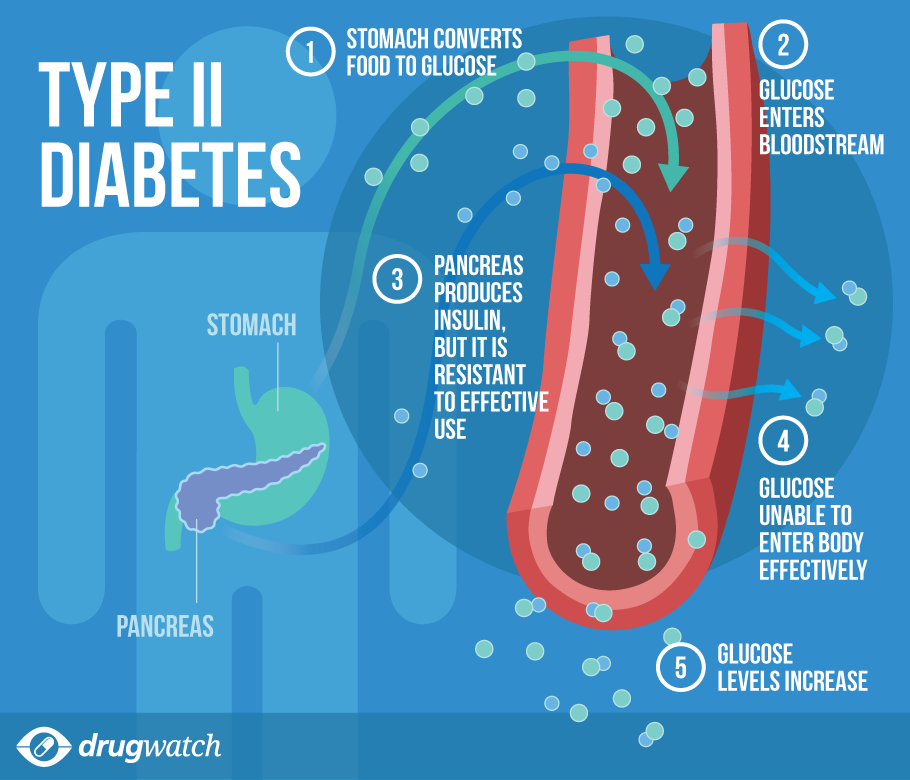
The first symptoms of type 1 diabetes appear when blood sugar gets too high. Symptoms include thirst, hunger, fatigue, frequent urination, weight loss, tingling or numbness in the feet, and blurred vision. Very high blood sugar can cause rapid breathing, dry skin, fruity breath, and nausea.
Meanwhile, the first symptoms of type 2 diabetes may not show up for many years meaning the disease can ravage a persons body without them realizing it. Early symptoms include frequent infections, fatigue, frequent urination, thirst, hunger, blurred vision, erectile dysfunction in men, and pain or numbness in the hands or feet. Drincic notes that “symptoms of type 2 diabetes don’t start as suddenly as symptoms of type 1 diabetes.”
Research Design And Methods
The original study population included 211 type 1 diabetic subjects, 1,059 type 2 diabetic subjects, and 1,373 corresponding nondiabetic subjects. A detailed description of study participants has been published previously . The selection of the diabetic study cohort was based on a drug reimbursement registry maintained by the Social Insurance Institution. All participants were aged 4564 years. Diabetic participants fulfilled the World Health Organization diagnostic criteria for diabetes . Their age at onset of diabetes was >30 years. Type 1 diabetes was verified by the performance of glucagon-stimulated C-peptide measurement, with the 6-min stimulated level <0.20 nmol/l. A random control population sample of nondiabetic subjects matched for age was invited to participate in the study. The ethics committees of the Kuopio University Hospital and the Turku University Central Hospital approved the study. All study participants gave informed consent.
Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes Onset In An Infant Or Child
The young child who is urinating frequently, drinking large quantities, losing weight, and becoming more and more tired and ill is the classic picture of a child with new-onset type 1 diabetes. If a child who is potty-trained and dry at night starts having accidents and wetting the bed again, diabetes might be the culprit.
Although it is easy to make the diagnosis diabetes in a child by checking blood sugar at the doctors office or emergency room, the tricky part is recognizing the symptoms and knowing to take the child to get checked. Raising the awareness that young children, including infants, can get type 1 diabetes can help parents know when to check for type 1 diabetes.
Sometimes children can be in diabetic ketoacidosis when they are diagnosed with diabetes. When there is a lack of insulin in the body, the body can build up high levels of an acid called ketones. DKA is a medical emergency that usually requires hospitalization and immediate care with insulin and IV fluids. After diagnosis and early in treatment, some children may go through a phase where they seem to be making enough insulin again. This is commonly called the honeymoon phase. It may seem like diabetes has been cured, but over time they will require appropriate doses of insulin to keep their blood sugar levels in the normal range.
What Is The Significance Of A Blood Glucose
It is the primary source of energy. If you eat foods, the pancreas produces a hormone insulin which transports glucose from the food to the cells to be used as an energy.
If the body has problems with insulin production the glucose will stay in the blood and will not be utilized by the cells. Too much glucose in the blood leads to diabetes.
There are four types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, gestational, and other types .
The most common types are the type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Regardless of the type, they share common symptoms. What are the common signs of diabetes?
- Frequent urination
- Burn out/easily gets tired
- Wounds/cuts/sores that do not heal properly
In this article, we are going to dig deeper into the two most common types of diabetes: diabetes type 1 and 2.
We are going to distinguish which is worse type 1 or 2 diabetes including the differences and similarities between type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
What Is Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a disorder of blood glucose . Its mechanisms are deficient insulin production and/or a blunted response of cells to insulin. The effect it has on the maintenance of equilibrium causes glucose in the blood to be elevated. Other than gestational diabetes there are two main types of diabetes mellitus.
An expert panel, with input from the American Diabetic Association and World Health Organization , made changes to the system for classifying and naming diabetes in 1997. It eliminated confusing terms and replaced Roman numerals with regular numbers.
As a result of the changes type 1 diabetes mellitus is now the accepted term for what used to be termed type I, juvenile-onset, or insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus . By the same token, type 2 diabetes mellitus is now the approved term for type II, adult-onset, or non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus .
Will I Need Medication Or Insulin For Type 2 Diabetes
Some people take medication to manage diabetes, along with diet and exercise. Your healthcare provider may recommend oral diabetes medications. These are pills or liquids that you take by mouth. For example, a medicine called metformin helps control the amount of glucose your liver produces.
You can also take insulin to help your body use sugar more efficiently. Insulin comes in the following forms:
- Injectable insulin is a shot you give yourself. Most people inject insulin into a fleshy part of their body such as their belly. Injectable insulin is available in a vial or an insulin pen.
- Inhaled insulin is inhaled through your mouth. It is only available in a rapid-acting form.
- Insulin pumps deliver insulin continuously, similar to how a healthy pancreas would. Pumps release insulin into your body through a tiny cannula . Pumps connect to a computerized device that lets you control the dose and frequency of insulin.
Are There Support Groups And Counseling For People With Diabetes
Consider joining a support group to share your experiences and learn from others. The American Diabetes Association, Hormone Health Network, and local chapters of Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation International are excellent resources. Your health care team will have information about local groups in your area. The following groups also provide support:
American Association of Diabetes Educators100 W Monroe, Suite 400Chicago, IL 60603
Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
There are important differences between type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes . Other types, such as unusual forms of , also exist. Diagnosing the type of diabetes is important for appropriate medical treatment.
| Juvenile Onset or Dependent | Adult Onset or Noninsulin Dependent Diabetes | |
| Who is diagnosed? |
Children and teens, usually with healthy body weight, but also diagnosed in adults. These individuals may be the only ones in their family with the disease. |
Usually diagnosed in adults who are or but also diagnosed in children. These individuals often have relatives with diabetes. |
| What causes it? | The individuals immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the . The pancreas can no longer produce , a needed for controlling blood . | These individuals can still produce insulin but the body becomes resistant to its effects. Over time, the pancreas eventually stops producing insulin. |
| How is it detected? |
The same diagnostic criteria are used for both types of diabetes. However, blood tests may help clarify whether a patient has type 1 versus type 2 diabetes. |
|
| How is it treated? | Patients with type 1 diabetes need to take | Some patients with type 2 diabetes can control their blood glucose by reducing their weight and changing their diet. Most others are treated with , injectable medicines, or insulin. |
Explore more articles:
Foods to EatGlycemic Controlheart attackhigh glucoseMeal PlanningNational Diabetes MonthNutrition Labels
What Types Of Health Care Professionals Treat Diabetes
![[Full text] Continual evolution of type 2 diabetes: an ... [Full text] Continual evolution of type 2 diabetes: an ...](https://www.livingwithdiabetes.info/wp-content/uploads/full-text-continual-evolution-of-type-2-diabetes-an.jpeg)
Most primary care providers have experience managing diabetes, including internists, gynecologists, and family practitioners. Specialists in diabetes care are called endocrinologists or diabetologists. You can locate endocrinologists using the “Find an Endocrinologist” search engine online at the Hormone Health Network. You can locate a pediatric endocrinologist for diabetic youth using the “Find a Doctor” search engine of the Pediatric Endocrine Society.
Can You Be Born With Diabetes Is It Genetic
You arent born with diabetes, but Type 1 diabetes usually appears in childhood. Prediabetes and diabetes develop slowly over time years. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy.Scientists do believe that genetics may play a role or contribute to the development of Type 1 diabetes. Something in the environment or a virus may trigger its development. If you have a family history of Type 1 diabetes, you are at higher risk of developing Type 1 diabetes. If you have a family history of prediabetes, Type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes, youre at increased risk of developing prediabetes, Type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes.
Why Is My Blood Glucose Level High How Does This Happen
The process of digestion includes breaking down the food you eat into various different nutrient sources. When you eat carbohydrates , your body breaks this down into sugar . When glucose is in your bloodstream, it needs help a “key” to get into its final destination where it’s used, which is inside your body’s cells . This help or “key” is insulin.
Insulin is a hormone made by your pancreas, an organ located behind your stomach. Your pancreas releases insulin into your bloodstream. Insulin acts as the key that unlocks the cell wall door, which allows glucose to enter your bodys cells. Glucose provides the fuel or energy tissues and organs need to properly function.
If you have diabetes:
- Your pancreas doesnt make any insulin or enough insulin.
Or
- Your pancreas makes insulin but your bodys cells dont respond to it and cant use it as it normally should.
If glucose cant get into your bodys cells, it stays in your bloodstream and your blood glucose level rises.
What Tests Do Health Care Professionals Use To Diagnose Diabetes
Doctors use common tests to diagnose diabetes and monitor blood sugar control.
The health care professional will take a history including information about the patient’s symptoms, risk factors for diabetes, past medical problems, current medications, allergies to medications, family history of diabetes, or other medical problems , and personal habits and lifestyle.
Various laboratory tests can confirm the diagnosis of diabetes.
Fingerstick blood glucose at the point of care. This rapid test may be performed anywhere, including community-based screening programs.
- Although not as accurate as testing blood in a hospital laboratory, a fingerstick blood glucose test is easy to perform, and the adequate result is available quickly.
- The test involves sticking the patient’s finger for a tiny blood sample. The blood drop is placed on a strip to be inserted into a machine that reports the blood sugar level. These portable machines are accurate to within about 10%-20% of true laboratory values.
- Fingerstick blood glucose values tend to be most inaccurate at very high or very low levels. Abnormally low or high results should be confirmed by repeat testing. Point-of-care testing is how most people with diabetes monitor their blood sugar levels at home.
Oral glucose tolerance test. After fasting for at least six hours, the health care professional draws blood to measure plasma glucose before and at two hours after drinking a specific sweet drink .
Causes Of Type 1 Diabetes
The bodys immune system is responsible for fighting off foreign invaders, such as harmful viruses and bacteria.
In people with type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakes the bodys own healthy cells for foreign invaders. The immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the . After these beta cells are destroyed, the body is unable to produce insulin.
Researchers dont know why the immune system sometimes attacks the bodys own cells. It may have something to do with genetic and environmental factors, such as exposure to viruses. Research into autoimmune diseases is ongoing.
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Managed
Theres no cure for Type 2 diabetes. But you can manage the condition by maintaining a healthy lifestyle and taking medication if needed. Work with your healthcare provider to manage your:
- Blood sugar: A blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring can help you meet your blood sugar target. Your healthcare provider may also recommend regular A1c tests, oral medications , insulin therapy or injectable non-insulin diabetes medications.
- Blood pressure: Lower your blood pressure by not , exercising regularly and eating a healthy diet. Your healthcare provider may recommend blood pressure medication such as beta blockers or ACE inhibitors.
- Cholesterol: Follow a meal plan low in saturated fats, trans fat, salt and sugar. Your healthcare provider may recommend, which are a type of drug to lower .
What Are The Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms of Type 2 diabetes tend to develop slowly over time. They can include:
- Urinary tract infections and bladder infections.
Rarely, Type 2 diabetes leads to a condition called diabetic ketoacidosis . DKA is a life-threatening condition that causes your blood to become acidic. People with Type 1 diabetes are more likely to have DKA.
Who Gets Diabetes What Are The Risk Factors
Factors that increase your risk differ depending on the type of diabetes you ultimately develop.
Risk factors for Type 1 diabetes include:
- Having a family history of Type 1 diabetes.
- Injury to the pancreas .
- Presence of autoantibodies .
- Physical stress .
- Exposure to illnesses caused by viruses.
Risk factors for prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American, Asian-American race or Pacific Islander.
- Being overweight.
Risk factors for gestational diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American or Asian-American.
- Being overweight before your pregnancy.
- Being over 25 years of age.

