What Is The Normal Range For Blood Sugar Levels And What Blood Sugar Level Constitutes A True Emergency
Dr. Horton answers the question: ‘Normal Range For Blood Sugar Levels?’
? — Question:What is the normal range for blood sugar levels, and what blood sugar level constitutes a true emergency?
Answer:Now, in a normal individual we measure blood sugar under different circumstances. What we call fasting blood sugar or blood glucose levels is usually done six to eight hours after the last meal. So it’s most commonly done before breakfast in the morning; and the normal range there is 70 to 100 milligrams per deciliter.
Now when you eat a meal, blood sugar generally rises and in a normal individual it usually does not get above a 135 to 140 milligrams per deciliter. So there is a fairly narrow range of blood sugar throughout the entire day.
Now in our diabetic patients we see both low blood sugar levels that we call hypoglycemia, or elevated blood sugars, hyperglycemia. Now, if the blood sugar drops below about 60 or 65 milligrams per deciliter, people will generally get symptoms, which are some shakiness, feeling of hunger, maybe a little racing of the heart and they will usually be trenchant or if they eat something, it goes away right away. But if blood sugar drops below 50 and can get down as low as 40 or 30 or even 20, then there is a progressive loss of mental function and eventually unconsciousness and seizures. And of course that is very dangerous and a medical emergency.
How Does Canada Compare To Other Countries In Terms Of Numbers Of People With Diabetes
According to the World Health Organization, approximately 422 million people around the world have diabetes. The prevalence varies somewhat among countries, though:
- 3 million people in Canada have diabetes
- 4 million people in the United Kingdom have diabetes
- 69 million people in India have diabetes
- 30 million people in the United States have diabetes
How Do I Prepare For The Plasma Glucose Level Test And How Are The Results Interpreted
To get an accurate plasma glucose level, you must have fasted for at least 8 hours prior to the test. When you report to the clinic or laboratory, a small sample of blood will be taken from a vein in your arm. According to the practice recommendations of the American Diabetes Association, the results of the blood test are interpreted as follows:
Fasting blood glucose level
- If your blood glucose level is 70 to 99* mg/dL . . .
- What it means: Your glucose level is within the normal range
*Values between 50 and 70 are often seen in healthy people
**The condition of “prediabetes” puts you at risk for developing Type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and blood lipid disorders
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 02/21/2018.
References
How Can Continuous Glucose Monitoring Help You Maintain Optimal Glucose Levels
It is not uncommon for your glucose levels to increase after a meal: you just ate food that may contain glucose, and now your body is working on getting it out of the bloodstream and into the cells. We know that we want to prevent excessive spiking of glucose levels because studies show that high post-meal glucose spikes over 160 mg/dl are associated with higher cancer rates. Spikes are also associated with heart disease. Repeated high glucose spikes after meals contribute to inflammation, blood vessel damage, increased risk of diabetes, and weight gain. Additionally, the data shows that the big spikes and dips in glucose are more damaging to tissues than elevated but stable glucose levels. Therefore, you should strive to keep your glucose levels as steady as possible, at a low and healthy baseline level, with minimal variability after meals.
Keeping your glucose levels constant is more complicated than just following a list of “eat this, avoid that” foods. Each person has an individual response to food when it comes to their glucose levels; studies have shown that two people can have different changes in their glucose levels after eating identical foods. The difference can be quite dramatic. One study found that some people had equal and opposite post-meal glucose spikes in response to the same food.
Are There Different Recommendations For Blood Sugar Levels In Other Countries
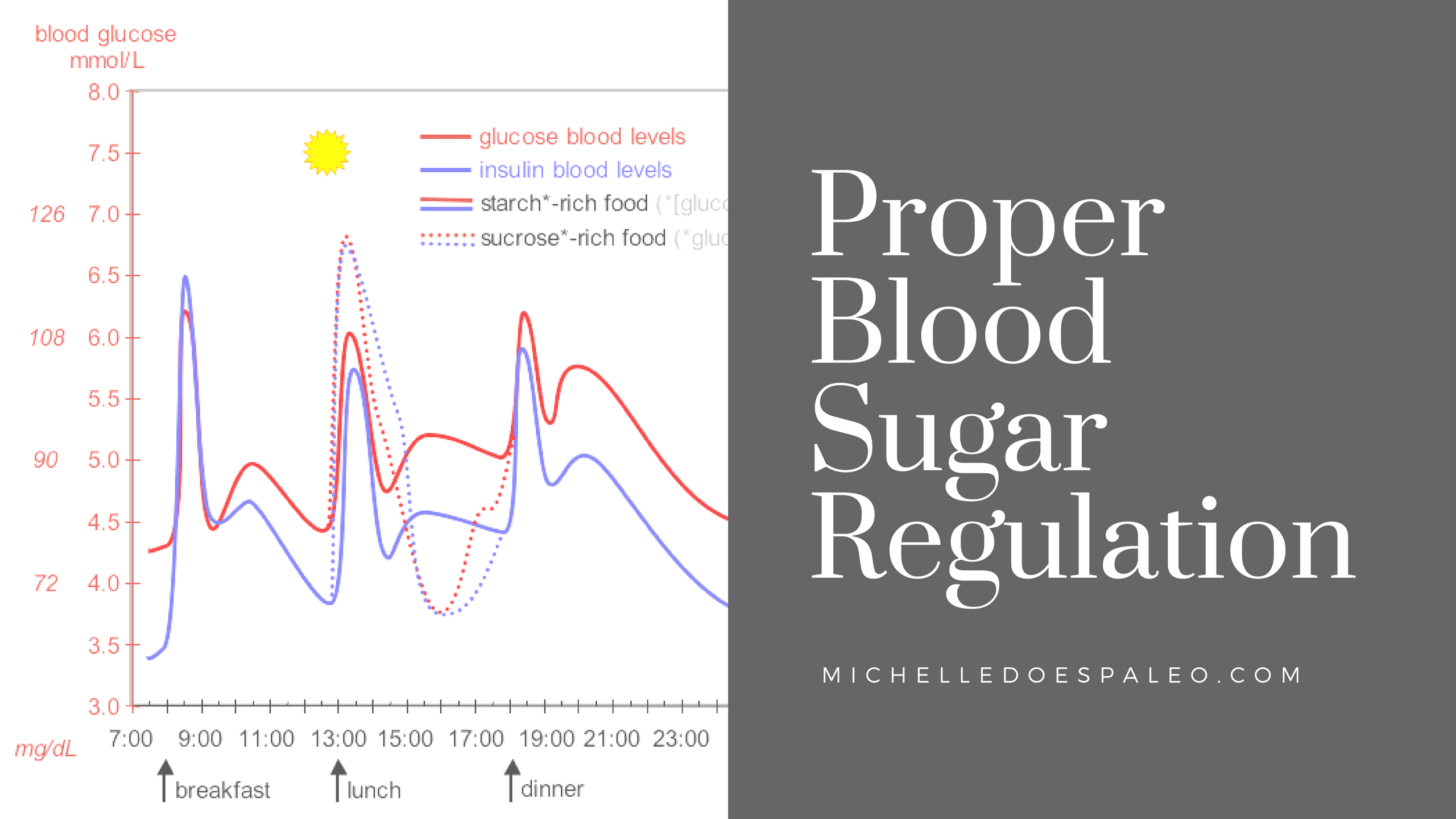
The recommended blood sugar level ranges in countries around the world are very similar. However, there are two different units of measurement that are used when referring to blood sugars, depending on where you live: millimoles per litre and milligrams per decilitre .
The mmol/L measurement is used here in Canada, as well as England, Australia and China, while mg/dL is used in such countries as the United States, France, Japan, Israel and India.
To convert mmol/L to mg/dl, simply multiply by 18. For example, a blood sugar level of 5.0 mmol/L would mean a level of 90 mg/dL .
Here are blood sugar recommendations from some countries other than Canada:
| Country | Blood sugar before a meal | Blood sugar two hours after the start of a meal |
| India | 80 to 110 mg/dL | 120 to 140 mg/dL |
| United Kingdom | 4 to 7 mmol/L | Type 1 diabetes: less than 9 mmol/L
Type 2 diabetes: less than 8.5mmol/L |
| United States | 80 to 130 mg/dL | Less than 180 mg/dL |
Are Some Canadians At Higher Risk For Elevated Blood Sugar Levels Than Others
You may have a higher risk for elevated blood sugars and type 2 diabetes if you:
- Are 40 or years of age or older
- Have a close relative with diabetes
- Are of African, Arab, Asian, Hispanic, Indigenous or South Asian descent
- Are overweight
- Have been diagnosed with prediabetes
Some medical conditions can also increase your risk of type 2 diabetes, such as:
- High blood pressure or cholesterol levels
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Psychiatric disorders
- Sleep apnea
Read more about diabetes risk factors here.
Beyond Normal Goals: Whats An Optimal Glucose Level And Why Does It Matter
Exact numbers for what is considered “optimal” glucose levels to strive for while using CGM to achieve your best health are not definitively established; this is a question that is individual-specific and should be discussed with your healthcare provider. With that said, research shows that there is an increased risk of health problems as fasting glucose increases, even if it stays within the “normal” range, making finding your “optimal” glucose levels all the more important.
While the International Diabetes Federation and other research studies have shown that a post-meal glucose spike should be less than 140 mg/dL in a nondiabetic individual, this does not determine what value for a post-meal glucose elevation is truly optimal for your health. All that number tells us is that in nondiabetics doing an oral glucose tolerance test, researchers found that these individuals rarely get above a glucose value of 140 mg/dL after meals.
So, while this number may represent a proposed upper limit of what’s “normal,” it may not indicate what will serve you best from a health perspective. Many people may likely do better at lower post-meal glucose levels. Similarly, while the ADA states that a fasting glucose less than 100 mg/dL is normal, it does not indicate what value is optimal for health.
The following is a summary of insights from our review of research. You should consult with your doctor before setting any glucose targets or changing dietary and lifestyle habits.
Blood Sugar Levels: What’s Normal What’s Not And How To Measure Them
What blood glucose levels mean and what range is healthy.
Sugar can lead to high blood sugar and contributes to the development of diabetes.
We all want to keep track of our health in every way we can — you may weigh yourself daily, measure your waist-to-hip ratio, keep track of your blood pressure or monitor your resting heart rate. But how close of an eye do you keep on your blood sugar?
People with diabetes are all too familiar with their blood sugar levels, but the rest of us might not even think about them. However, consistently high blood sugar levels can coexist with Type 2 diabetes and cause serious health conditions like kidney disease, nerve problems or stroke.
Our Health & Wellness newsletter puts the best products, updates and advice in your inbox.
I hope I haven’t scared you away, but when it comes to our health it’s important to know exactly what’s going on inside of our bodies. Without further ado, let’s get into what blood sugar means, how to measure it and everything else you need to know.
Read more: How to eat less sugar without feeling deprived
Now That Youre Checking Your Blood Glucose What Do The Numbers Mean
Depending on your diabetes treatment plan, your doctor or diabetes educator may advise you to check once a week, once a day or up to 10 times a day . But what does it mean when you see a 67, 101 or 350 on your meter? And what is a “normal” blood sugar, anyway? Great questions! After all, if you don’t know what the numbers on your meter mean, it’s hard to know how you’re doing.
The American Diabetes Association provides guidelines for blood glucose goals for people with diabetes, and the goals vary depending on when you’re checking your glucose:
• Fasting and before meals: 80–130 mg/dl
• Postprandial : Less than 180 mg/dl
Your blood glucose goals may be different, however. If you’re younger, have had diabetes for a shorter amount of time or are not taking any medicine for your diabetes, your glucose goals might be a little “tighter,” or lower. Likewise, your blood glucose goals may be higher than what ADA recommends if you’re older, have diabetes complications, or don’t get symptoms when your blood glucose is low.
Bottom line: talk with your health-care provider about the following:
• When to check your blood glucose• How often to check your blood glucose• What your blood glucose goals are
Symptoms Signs Causes Of Levels Of High Blood Sugar In The Blood
High blood sugar or hyperglycemia is an abnormally high blood sugar level in the blood. Hyperglycemia is a hallmark sign of diabetes and prediabetes.
Signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia include blurred vision, headaches, hunger, and …
The normal ranges for blood sugar levels in adults who do not have diabetes before eating or fasting the range begins at 72-99mg/dL while fasting ranges for those being treated for type 1 or type 2 diabetes range from 80 -130 mg/dL. According to the American Diabetes Association normal blood sugar levels before and after eating should be 80-130 mg/dL before eating a meal , and less than 180 mg/dL about 1-2 hours after eating a meal
High blood sugar ranges for people who don’t have diabetes begins at 140 mg/dL or greater while for those being treated for diabetes, the high range begins at 180 mg/dL , called hypoglycemia.
The 411 On A1c: Normal A1c Levels And 15 Ways To Lower High A1c
SingleCare TeamLindsey Hudson, APRN, NP-C, CDCES
The hemoglobin A1C test is the closest thing to a diabetes scorecard you can find. Whether someone has had diabetes mellitus for years or if they have just been diagnosed, they have probably heard about this test. Unlike blood sugar meters people use at home, the A1C measures an average blood sugar level over the past several months by analyzing how many of a patient’s hemoglobin cells have glucose attached to them. The test results keep track of how well a person is managing his or her diabetes.
Recommended Blood Sugar Targets For Most People With Diabetes*
Your targets may not be the same as the examples in this chart. Your targets are important and should be specific to you.
| A1C** | |
| 4.0 to 7.0 | 5.0 to 10.0 |
* This information is based on the Diabetes Canada 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Canada and is a guide.** A1C is a measurement of your average blood sugar control for the last two to three months and approximately 50 per cent of the value comes from the last 30 days.
What Are Normal Blood Glucose Levels In Healthy Individuals
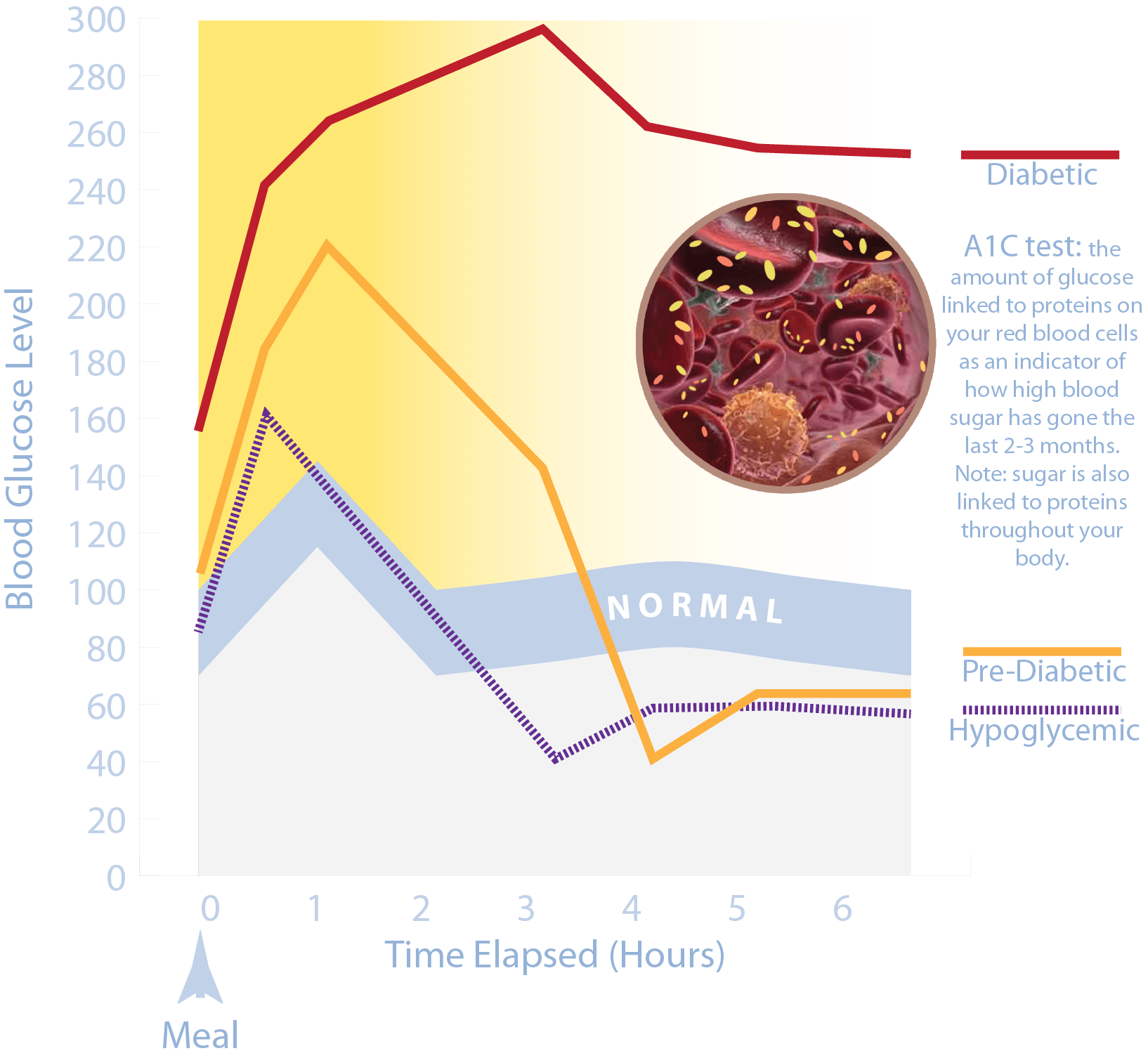
Blood sugar levels can either be normal, high, or low, depending on how much glucose someone has in their bloodstream. Glucose is a simple sugar that’s present in the bloodstream at all times. Normal blood glucose levels can be measured when someone fasts, eats, or after they’ve eaten. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, who haven’t eaten for at least eight hours is less than 100 mg/dL. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, two hours after eating is 90 to 110 mg/dL.
Many factors affect blood sugar levels throughout the day:
- Type of food consumed, how much, and when
- Physical activity
- Menstrual periods
- Alcohol
An ideal blood sugar level for anyone without diabetes or prediabetes, regardless of age, in the morning should be less than 100 mg/dL. Remember, blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day as a result of the factors previously mentioned.
What Are Target Blood Sugar Levels For People With Diabetes
A target is something that you aim for or try to reach. Your health care team may also use the term goal. People with diabetes have blood sugar targets that they try to reach at different times of the day. These targets are:
- Right before your meal: 80 to 130
- Two hours after the start of the meal: Below 180
Talk with your health care team about what blood sugar numbers are right for you.
How To Calculate Your Blood Sugar Level: The Complete Guide
To get an accurate reading of your blood sugar level, the best and most effective method is using a glucose meter. This will involve a small prick in your finger so receive a blood sample. The strip is then inserted into the meter and tested.
You may be wondering what your reading should be. There is no ‘normal’ reading, an ideal reading differs from person to person. Everyone will get different readings at different times of the day. However, there is a rough range to determining a low, normal and high blood sugar level. Blood sugar level is read in mmol/L, which stands for millimoles per liter. Here is a guide as to what an ideal reading is for each diabetic type and non-diabetic patients:
| Child | |
| 4 – 5.9 mmol/L<7.8 mmol/L | 4 – 5.9 mmol/L<7.8 mmol/L |
It is advised to check it regularly if you are concerned, show regular symptoms or have diabetes. You should check before meals, exercise, before bedtime and after driving. Everyone is different so it is best to ask your doctor if you are unsure how many times and when you should check your blood sugar levels.
Research shows that over 50% who try to estimate their blood sugar level reading are incorrect. This may be due to over underlying medical conditions that did not know they had or poor lack of judgement. Therefore, this suggests it is very important to test at home to check in on your levels regularly to avoid any unnecessary future complications.
Target Blood Sugar Ranges For Pregnant People With Diabetes
Blood sugar targets during pregnancy are lower due to hormonal influences. The ADA, AACE, and Joslin Diabetes Center have slightly different guidelines for target blood sugar levels during pregnancy. In general, pregnant women with diabetes will want to follow individual guidelines provided by their endocrinologist.
The ADA recommends maintaining blood sugar levels of 95-140 mg/dL for pregnant women. However, some providers recommend an even tighter goal of blood glucose levels below 89 mg/dL before a meal and below 120 mg/dL after a meal.
To keep close tabs on levels, most diabetes specialists recommend that women with diabetes during pregnancy check their blood sugar:
- First thing in the morning
- Before all meals
Track your own personal ranges with our free weekly and monthly blood sugar charts >
Target Blood Sugar Levels For Pregnant Women With Diabetes
It’s possible for diabetes to cause problems during pregnancy. For example, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, women with type 1 and type 2 diabetes who have uncontrolled blood sugar levels could experience an increased risk of having a premature baby, needing a C-section and more.
Gestational diabetes — a type of diabetes that occurs in a pregnant woman who has never been diagnosed with diabetes before — can also cause complications. These include giving birth to a baby who is larger than average and an increased risk of needing a C-section. The ADA suggests that pregnant women shoot for a target fasting blood sugar level of 95 mg/dL or less before a meal.
Read more:Do Oranges Raise Your Blood Sugar?
High Blood Sugar In The Morning: Is It The Dawn Phenomenon
If you have high blood sugar levels in the morning, you may be experiencing the dawn phenomenon, the name given to an increase in blood sugar that usually occurs between 2 a.m. and 8 a.m., according to the Mayo Clinic. One reason this occurs: During the early hours of the morning, our bodies secrete higher levels of a hormone called cortisol, says Dr. Spratt. When cortisol levels are high, it can make you more resistant to insulin, a hormone that helps regulate your blood sugar levels.
“Some people have a striking dawn phenomenon,” says Dr. Spratt. “You can look at their continuous glucose tracing and see that their blood sugar level suddenly goes up at 3 a.m.” If this is the case for you, your doctor may adjust your insulin medication or suggest you use an insulin pump .
Recommended Blood Glucose Targets For People With Diabetes
| AIC* | Fasting blood glucose/ blood glucose before meals | Blood glucose two hours after start of meal |
| Target for most patients with diabetes | ?7.0% | |
| If A1C targets not being met** | 4.0 to 5.5 | 5.0 to 8.0 |
*An A1C is an average of your blood glucose levels over the past three months. Learn more about the A1C here.
**Must be balanced against the risk of hypoglycemia
How Can One Tell If I Have Diabetes By Examining My Blood
Your body converts sugar, also called glucose, into energy so your body can function. The sugar comes from the foods you eat and is released from storage from your body’s own tissues.
Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas. Its job is to move glucose from the bloodstream into the cells of tissues. After you eat, the level of glucose in the blood rises sharply. The pancreas responds by releasing enough insulin to handle the increased level of glucose — moving the glucose out of the blood and into cells. This helps return the blood glucose level to its former, lower level.
If a person has diabetes, two situations may cause the blood sugar to increase:
- The pancreas does not make enough insulin
- The insulin does not work properly
As a result of either of these situations, the blood sugar level remains high, a condition called hyperglycemia or diabetes mellitus. If left undiagnosed and untreated, the eyes, kidneys, nerves, heart, blood vessels and other organs can be damaged. Measuring your blood glucose levels allows you and your doctor to know if you have, or are at risk for, developing diabetes.
Much less commonly, the opposite can happen too. Too low a level of blood sugar, a condition called hypoglycemia, can be caused by the presence of too much insulin or by other hormone disorders or liver disease.
Change Your Life Today And Reduce Your Risk Of Diabetes

Diabetes can be a massive burden on both your health and your wallet. But, maintaining normal blood sugar levels, managing your weight, and staying physically active are great ways to reduce your risk of developing diabetes.
If you are looking to improve your health and monitor your risk factors for disease, getting covered is a great way to relieve the financial pressures of looking after yourself.
Why not contact us today at Insurdinary for a free, personalized, no-obligation quote from some of the best health care providers in Canada!
What Are Abnormal Glucose Levels And Why Do They Matter
Why is it unhealthy for glucose levels to be too high or too low ?
Hyperglycemia refers to elevated blood glucose levels. This usually occurs because the body does not appropriately remove glucose from the blood; this can happen due to many complex reasons. Elevated glucose levels can damage blood vessels and nerves over time; this can then lead to problems in the eyes, kidneys, and heart, as well as numbness in the hands and feet. Very high levels can lead to coma and even death in some cases. People with fasting glucose levels higher than 100 mg/dl have impaired glucose tolerance and should speak with their healthcare provider.
Some people may think that to avoid all these issues, they should just keep their blood glucose levels as low as possible. If too high is bad, then low must be good, right? Not exactly. When glucose gets too low, it’s called hypoglycemia. The threshold for hypoglycemia is typically thought to be when glucose falls below 70 mg/dl. When this happens, the body may release epinephrine , the “fight or flight” hormone, which can lead to a fast heart rate, sweating, anxiety, blurry vision, and confusion, but also helps the body mobilize glucose into the blood. If blood glucose levels stay too low for too long, it can cause seizures, coma, and in very rare instances, death.
What Else Can I Do To Help Manage My Blood Sugar Levels
Eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular physical activity can all help. Other tips include:
- Keep track of your blood sugar levels to see what makes them go up or down.
- Eat at regular times, and don’t skip meals.
- Choose foods lower in calories, saturated fat, trans fat, sugar, and salt.
- Track your food, drink, and physical activity.
- Drink water instead of juice or soda.
- Limit alcoholic drinks.
- For a sweet treat, choose fruit.
- Control your food portions .
Q What Is The Blood Sugar Level For A 72 Year Old Woman
Answer:If you are aged but completely healthy, then you are likely to have your blood glucose at a standard level. But generally, aged people are more or less vulnerable to diseases. Though it is preferable to have blood sugar in between 100-120 mg/dl rising up to 140mg/dl is acceptable in certain conditions.
What If I Have Trouble Getting To My Blood Sugar Goals
There may be times when you have trouble reaching your blood sugar goals. This does not mean that you have failed. It means that you and your health care team should see if changes are needed. Call your health care team if your blood sugar is often too high or too low. Taking action will help you be healthy today and in the future.
Agree On Specific Target Ranges With The Diabetes Team
Sit down with a member of your diabetes health care team and discuss a range of blood glucose targets that are considered reasonable and realistic, given age, lifestyle and health considerations.
You should have a clear understanding of which numbers are considered too high or too low. It should also be clear what actions need to be taken if these numbers occur.

