How Can I Manage My Type 2 Diabetes
Managing your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol, and quitting smoking if you smoke, are important ways to manage your type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle changes that include planning healthy meals, limiting calories if you are overweight, and being physically active are also part of managing your diabetes. So is taking any prescribed medicines. Work with your health care team to create a diabetes care plan that works for you.
Type 2 Diabetes Management
Youâll need to make lifestyle changes to help you successfully manage type 2 diabetes.
- Weight loss. Losing 5% to 10% of your body weight — thatâs less than 20 pounds if you weigh 180 — can lower your A1c levels and your risk for cardiovascular disease. It may help you cut back on medications to treat diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. Weight loss can also ease symptoms of depression and help with sleep apnea.
- Healthy diet. There’s no one-size-fits-all diabetes diet. You’ll need to pay attention to carbs, fiber, fat, and salt to manage your blood sugar and avoid complications of diabetes. How much and when you eat are important, too. Talk to your diabetes team or a registered dietitian to help you plan your meals and snacks.
- Physical activity. From working out to doing chores, activity lowers your blood sugar. It helps your cells use insulin. It also helps your muscles use glucose. Make sure you check your blood sugar before and after exercise.
- Better sleep. Not getting enough sleep can raise your odds of getting type 2 diabetes in the first place. The length of time you sleep and the quality of sleep can raise A1c levels, a test doctors use to check your average blood sugar levels over 3 months. That means improving your sleep can lead to lower blood sugar readings.
Understanding Diabetes Is The First Step Toward Managing It
Learn what diabetes is and how it affects your body, what kind of diabetes you have, and how to manage your health.
Understanding diabetes is the first step toward managing it. So what do you need to know? First, you need to know what diabetes is and how it affects your body. And youll need to know what kind of diabetes you have. Next you have to know how to maintain your health, treat your diabetes, know when your treatment is successful and what to do when its not.
This section will take you through the answers to these first questions, and give you important information that will help you live a healthy life with diabetes.
Recommended Reading: Articles On Diabetes Mellitus
Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Managing type 2 diabetes requires teamwork. Youll need to work closely with your doctor, but a lot of the results depend on your actions.
Your doctor may want to perform periodic blood tests to determine your blood glucose levels. This will help determine how well youre managing the disease. If you take medication, these tests will help gauge how well its working.
Because diabetes increases your risk of cardiovascular disease, your doctor will also monitor your blood pressure and blood cholesterol levels.
If you have symptoms of heart disease, you may need additional tests. These tests may include an electrocardiogram or a cardiac stress test.
Follow these tips to help manage your diabetes:
- Maintain a balanced diet that includes non-starchy vegetables, whole-grains fiber, lean proteins, and unsaturated fats. Avoid unhealthy fats, sugars, and simple carbohydrates.
- Achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
- Exercise daily.
- Take all your medication as recommended.
- Use a home monitoring system to test your own blood glucose levels between visits to your doctor. Your doctor will tell you how often you should do that and what your target range should be.
It may also be helpful to bring your family into the loop. Educate them about the warning signs of blood glucose levels that are too high or too low so that they can help in an emergency.
Risk Factors For Type 2 Diabetes
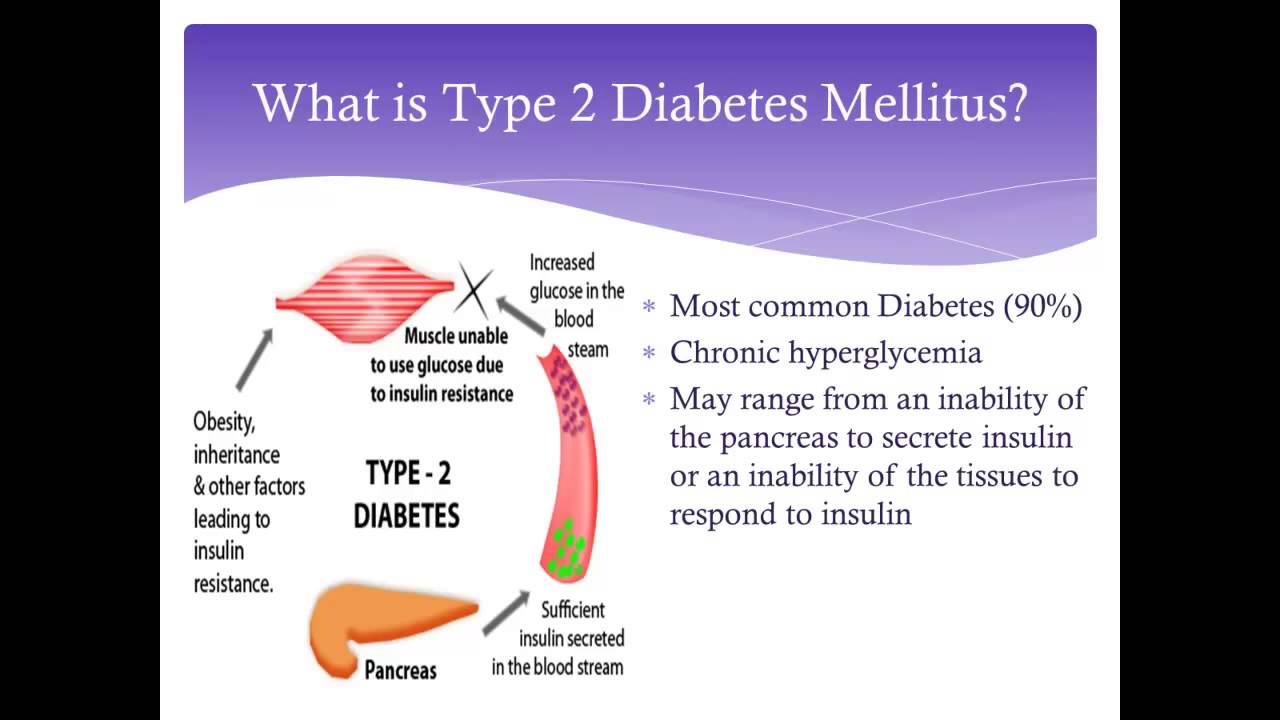
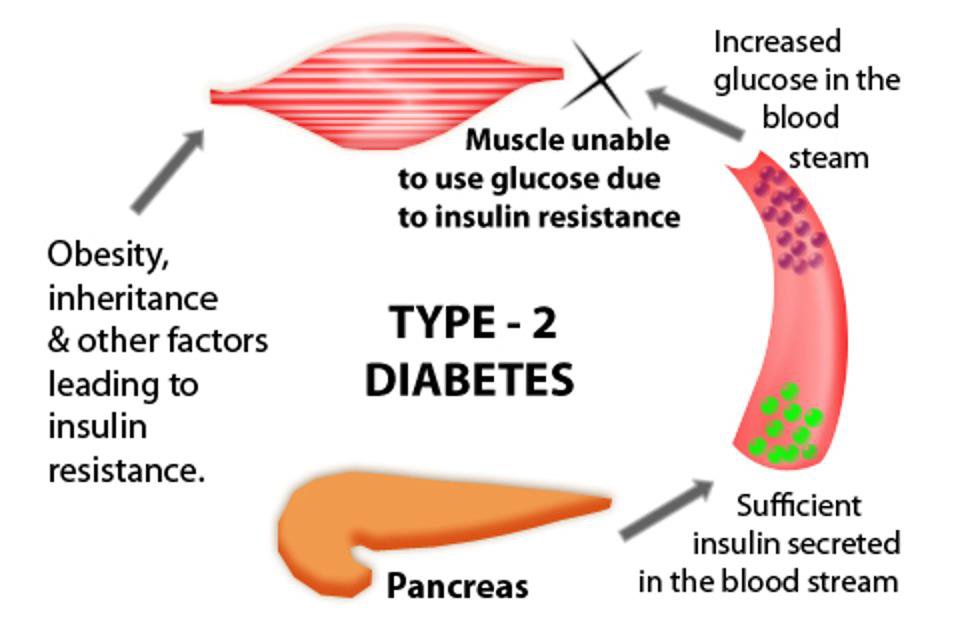
We may not understand the exact causes of type 2 diabetes, but we do know that certain factors can put you at increased risk.
Certain factors are out of your control:
- Your risk is greater if you have a brother, sister, or parent who has type 2 diabetes.
- You can develop type 2 diabetes at any age, but your risk increases as you get older. Your risk is particularly high once you reach 45 years old.
- African-Americans, Hispanic-Americans, Asian-Americans, Pacific Islanders, and Native Americans are at higher risk than Caucasians.
- Women who have a condition called polycystic ovarian syndrome are at increased risk.
You may be able to change these factors:
- Being overweight means that you have more fatty tissue, which makes your cells more resistant to insulin. Extra fat in the abdomen increases your risk more than extra fat in the hips and thighs.
- Your risk increases if you have a sedentary lifestyle. Regular exercise uses up glucose and helps your cells respond better to insulin.
Youre also at increased risk if youve had gestational diabetes or prediabetes, two conditions caused by elevated glucose levels. Learn more about the factors that can increase your risk for diabetes.
Also Check: Can Diabetics Eat Macaroni And Cheese
Causes Of Type 1 Diabetes
The bodys immune system is responsible for fighting off foreign invaders, such as harmful viruses and bacteria.
In people with type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakes the bodys own healthy cells for foreign invaders. The immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. After these beta cells are destroyed, the body is unable to produce insulin.
Researchers dont know why the immune system sometimes attacks the bodys own cells. It may have something to do with genetic and environmental factors, such as exposure to viruses. Research into autoimmune diseases is ongoing.
Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors:
Your risk of developing type 2 diabetes is higher if your diet is high in carbs and fat but low in fiber, if you’re not very physically active and/or if you have high blood pressure. High alcohol consumption and age are also risk factors. Though genes do play a role in the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes, it can be prevented with the right lifestyle choices, unlike type 1.
Read Also: Insulin Release From Beta Cells
Which Diets Are Recommended For Diabetes
Nutritional management is an important part of life for people with diabetes.
If you have type 1 diabetes, work with your doctor to identify how much insulin you may need to inject after eating certain types of food.
For example, carbohydrates can cause blood sugar levels to quickly increase in people with type 1 diabetes. Youll need to counteract this by taking insulin, but youll need to know how much insulin to take. Learn more about type 1 diabetes and diet.
People with type 2 diabetes need to focus on healthy eating. Weight loss is often a part of type 2 diabetes treatment plans, so your doctor may recommend a low-calorie meal plan. This could mean reducing your consumption of animal fats and junk food.
What Is The Treatment For Type 2 Diabetes
Treatment for this type of diabetes can include:
- Diabetic eating plan
- Foot problems such as wounds that don’t heal, loss of feeling, or pins and needles sensations
- Neuropathy or nerve pain especially in the legs and feet
- Sexual issues such as erectile dysfunction, inability to orgasm or feel full sensation
- Urinary frequency
- Unusual odor to urine
If you have diabetes, you have a higher risk of heart disease and heart attack. Because of this, it is important to control cholesterol and high blood pressure in addition to blood sugar. The good news is that all of these diseases are responsive to healthy lifestyle changes.
You May Like: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
Treatments For Type 2 Diabetes
There are a number of different ways you can treat type 2 diabetes, such as making healthy lifestyle choices, using insulin or taking medication. Your healthcare team will help you to find the right treatment for you. This can reduce your risk of developing complications and help you to live well with diabetes.
Learn more about diabetes treatments.
Medications For Type 2 Diabetes
In some cases, lifestyle changes are enough to keep type 2 diabetes under control. If not, there are several medications that may help. Some of these medications are:
- metformin, which can lower your blood glucose levels and improve how your body responds to insulin its the preferred treatment for most people with type 2 diabetes
- sulfonylureas, which are oral medications that help your body make more insulin
- meglitinides, which are fast-acting, short-duration medications that stimulate your pancreas to release more insulin
- thiazolidinediones, which make your body more sensitive to insulin
- dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, which are milder medications that help reduce blood glucose levels
- glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, which slow digestion and improve blood glucose levels
- sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors, which help prevent the kidneys from reabsorbing glucose into the blood and sending it out in your urine
Each of these medications can cause side effects. It may take some time to find the best medication or combination of medications to treat your diabetes.
If your blood pressure or cholesterol levels are a problem, you may need medications to address those needs as well.
If your body cant make enough insulin, you may need insulin therapy. You may only need a long-acting injection you can take at night, or you may need to take insulin several times per day. Learn about other medications that can help you manage diabetes.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Determining If You Have Borderline Diabetes
Prediabetes is a silent condition, so getting a regular wellness checkup is important for early detection. If you think you might have borderline diabetes, discuss your concerns with your doctor.
If your doctor is concerned you may have prediabetes, theyll most likely perform a hemoglobin A1c test or oral glucose tolerance test .
HbA1c is an indicator of your blood sugar patterns over the last two to three months, so its often a better overall picture than a single fasting blood sugar check. An HbA1c level between 5.7 and 6.4 indicates prediabetes.
Preeclampsia And Gestational Hypertension
A population-based, retrospective cohort study of 1,010,068 pregnant women examined the association between preeclampsia and gestational hypertension during pregnancy and the risk of developing diabetes post partum. Results showed the incidence rate of diabetes per 1000 person-years was 6.47 for women with preeclampsia and 5.26 for those with gestational hypertension, compared with 2.81 in women with neither condition. Risk was further elevated in women with preeclampsia or gesntational hypertension comorbid with gestational diabetes.
Read Also: Normal A1c For Non Diabetics
Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors
Certain things make it more likely that youâll get type 2 diabetes. The more of these that apply to you, the higher your chances of getting it are. Some things are related to who you are:
- Age. 45 or older
- Family. A parent, sister, or brother with diabetes
- Ethnicity. African American, Alaska Native, Native American, Asian American, Hispanic or Latino, or Pacific Islander American
Risk factors related to your health and medical history include:
- Prediabetes
- Sleeping too little or too much
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes: Whats The Difference
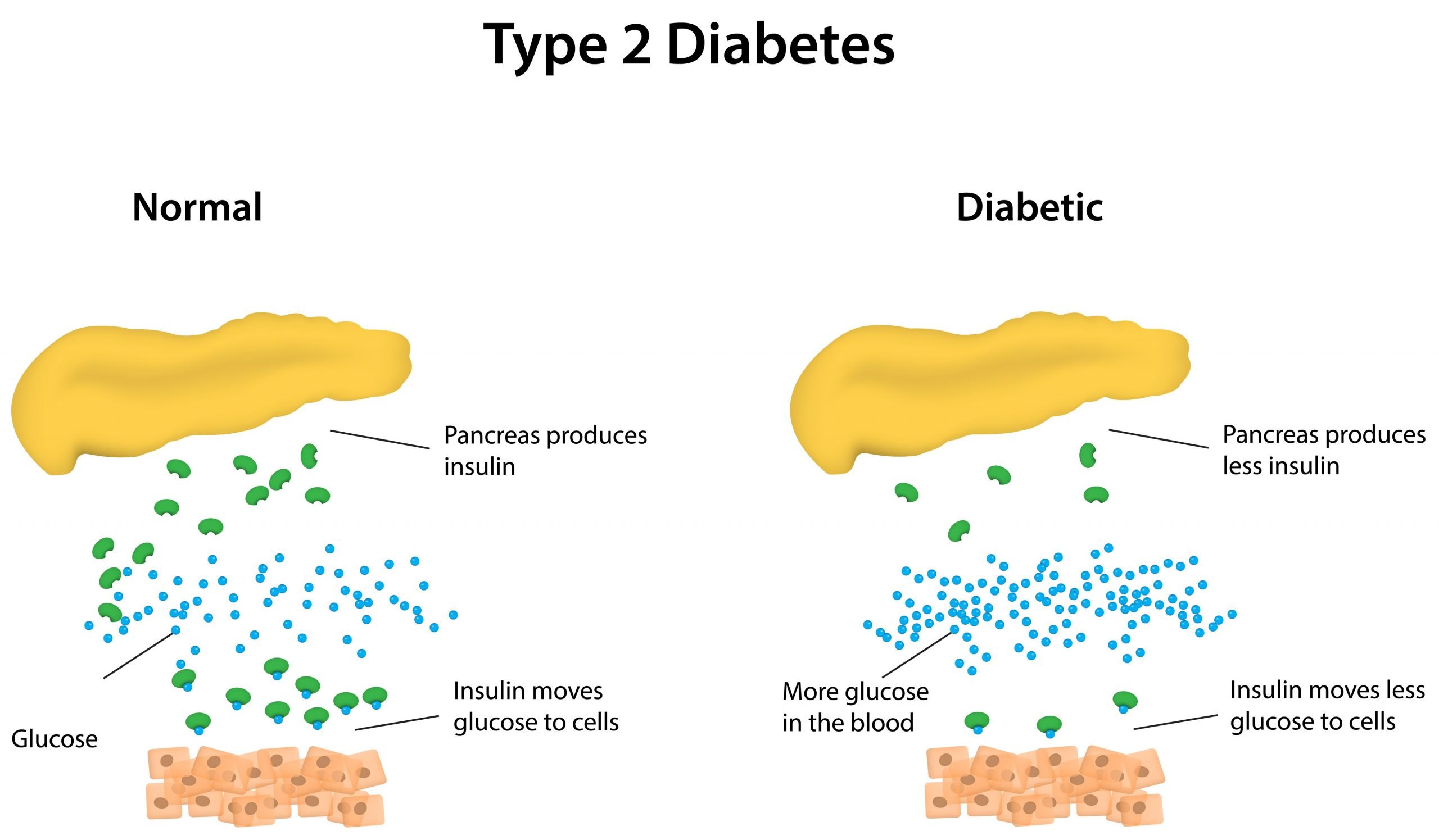
Type 2 diabetes is not the same as Type 1 diabetes. In Type 1 diabetes, your pancreas doesnt make any insulin. In Type 2, your pancreas doesnt make enough insulin, and the insulin it is making doesnt always work as it should. Both types are forms of diabetes mellitus, meaning they lead to hyperglycemia .
Type 2 diabetes usually affects older adults, though its becoming more common in children. Type 1 diabetes usually develops in children or young adults, but people of any age can get it.
Also Check: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Oral Medications Can Help
If diet and exercise canât get your blood sugar under control, your doctor may add medication. There are many types of diabetes pills available. Theyâre often combined. Some work by telling your pancreas to make more insulin. Others help your body use it better or block the digestion of starches. Some slow insulin breakdown. Newer oral drugs help your body pee out more sugar.
Impact Of Type 2 Diabetes
As stated above, type 2 diabetes can lead to a greater chance of health problems which could in some cases affect your ability to work and could therefore affect your personal income.
Another factor to bear in mind is that increased care may be needed, from your family or from a carer, particularly as you get older.
With the right support and good diabetes management, the potential negative effects of type 2 diabetes can be minimised.
Don’t Miss: What Happens If A Non Diabetic Takes Insulin
Type 2 Diabetes In Children
Type 2 diabetes in children is a growing problem. According to the American Diabetes Association , around 193,000 Americans under age 20 have type 1 or type 2 diabetes. One study found that the incidence of type 2 diabetes in youth has increased to about 5,000 new cases per year. Another study showed a significant increase, particularly in minority races and ethnic groups.
The reasons for this are complex, but risk factors for type 2 diabetes include:
- being overweight, or having a body mass index above the 85th percentile
- having a birth weight of 9 pounds or more
- being born to a mother who had diabetes while she was pregnant
- having a close family member with type 2 diabetes
- having a sedentary lifestyle
- being African-American, Hispanic American, Asian-American, Native American, or a Pacific Islander
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes in children are the same as those in adults. They include:
- excessive thirst or hunger
See your childs doctor immediately if they have these symptoms.
In 2018, the ADA recommended that all children who are overweight and have additional diabetes risk factors be tested for prediabetes or type 2. Untreated diabetes can lead to serious and even life-threatening complications.
A random blood glucose test may reveal high blood glucose levels. A hemoglobin A1C test can provide more information about average blood glucose levels over a few months. Your child may also need a fasting blood glucose test.
Risk Factors Of Type 2 Diabetes
There are several factors that can affect your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Because the symptoms of type 2 diabetes are not always obvious, its really important to be aware of these risk factors. They can include:
- your age
- if you have a parent, brother, sister or child with diabetes
- your ethnicity
Don’t Miss: Metformin Dosing
Monitoring Your Own Blood Glucose
If you have type 2 diabetes, as well as having your blood glucose level checked by a healthcare professional every two to six months, you may be advised to monitor your own blood glucose levels at home.
Even if you have a healthy diet and are taking tablets or using insulin therapy, exercise, illness and stress can affect your blood glucose levels.
Other factors that may affect your blood glucose levels include drinking alcohol, taking other medicines and, for women, hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle.
A blood glucose meter is a small device that measures the concentration of glucose in your blood. It can be useful for detecting high blood glucose or low blood glucose .
If blood glucose monitoring is recommended, you should be trained in how to use a blood glucose meter and what you should do if the reading is too high or too low.
Blood glucose meters aren’t currently available for free on the NHS but, in some cases, blood monitoring strips may be. Ask a member of your diabetes care team if you’re unsure.
Read about diabetic eye screening.
Occurrence In The United States
A 2017 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report estimated that in the United States, as of 2015, 30.3 million persons of all ages, or 9.4% of the population, had diabetes and 84.1 million adults had prediabetes.
Prediabetes, as defined by the American Diabetes Association, is that state in which blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. It is presumed that most persons with prediabetes will subsequently progress to diabetes. In 2015, according to the CDC report, prediabetes was present in 23.1 million persons aged 65 years or older .
A study by Andes et al using a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey indicated that in the United States, prediabetes exists in approximately 1 out of 5 adolescents and 1 out of 4 young adults.
As estimated for 2015, diabetes occurred in 4.6 million adults aged 18-44 years , 14.3 million aged 45-64 years , and 12.0 million aged 65 years or older . Of those adults with diabetes, however, 7.2 million did not know or did not report that they had the disease.
In 2014, the CDC reported that about 40% of US adults will develop diabetes, primarily type 2, in their lifetime, and more than 50% of ethnic minorities will be affected. This is substantially higher than previous estimates. The central reason for the increase is obesity.
Don’t Miss: What To Do If A Diabetic Feels Dizzy

