My Mom Has Been A Type 1 Diabetic For 40 Years Recently She Tested My Four Year Old Son And His Blood Sugar Was 129 Mg/dl I Did Two Fasting Blood Sugars And They Were 79 Mg/dl And 90 Mg/dl Our Pediatrician Did An A1c And It Was 56 He Said That Was Within Normal Range But My Moms Diabetic Doctor Says Thats High Normal And That We Should Be Concerned What Is The A1c Range For A Juvenile Non
Answer:
A typical A1c for a non-diabetic is between 4.5 and 5.5. Your child’s A1c is still close to normal. The best way to watch for diabetes is to monitor carefully for the symptoms of diabetes such as excessive thirst, excessive hunger, frequent urination and weight loss. Doing random blood sugars on a home glucometer is not as helpful and frequently only cause parents to worry.
MSB
An A1c Goal Of Between 7% And 8% Is Reasonable And Beneficial For Most Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
…though if lifestyle changes can get that number lower, then go for it. For patients who want to live a long and healthy life and try to avoid the complications of diabetes, they will need to keep their blood sugars as normal as possible — that means an A1c under 6.5%. However, studies show that using medications to achieve that goal significantly increases the risk of harmful side effects like hypoglycemia and weight gain. To live longer and healthier and avoid both the complications of diabetes as well as the risks of medications, there’s this amazing thing called lifestyle change. This involves exercise, healthy diet, weight loss, and not smoking. It is very effective. Lifestyle change also can help achieve healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels, which in turn reduce the risk for heart disease. And heart disease is a serious and common complication of diabetes.
Lifestyle change should be the cornerstone of treatment for type 2 diabetes. The recommendations go on to say that for patients who achieve an A1c below 6.5% with medications, we should decrease or even discontinue those drugs. Doing so requires careful monitoring to ensure that the person stays at the goal set with his or her doctor, which should be no lower than 7%, for the reasons stated above.
Doctors And Patients Should Discuss Goals Of Treatment Together And Come Up With An Individual Plan
Blood sugar goals should take into account a patient’s life expectancy and general health, as well as personal preferences, and include a frank discussion of the risks, benefits, and costs of medications. This is a big deal because it reflects a change in how we think about blood sugar control. It’s not a simply number to aim for; it’s a discussion. Diabetes medications have many potential side effects, including dangerously low blood sugar and weight gain . Yes, uncontrolled blood sugars can lead to very bad things, but patients should get all the information they need to balance the risks and benefits of any blood sugar control plan.
Stick To A Regular Schedule So You Can More Easily Follow Your Healthy Diet And Lifestyle
, letting too much time pass between meals, or eating too much or too often can cause your blood sugar levels to fall and rise too much, the ADA points out. This is especially true if you are taking insulin or certain diabetes drugs. Your doctor can help you determine the best meal schedule for your lifestyle.
So What If Your Test Says You Have A Higher Level Of A1c But You Do Not Have Diabetes

Yes, some conditions may raise the level of A1C in your blood, but that does not mean you have diabetes. According to a study by Elizabeth Selvin, a single elevated A1C level greater than 6% was found in the general population with no history of diabetes. Such adults may have compromised fasting glucose or other cardiovascular diseases. Other factors that contribute to higher levels of A1C in no-diabetic patients are:
For Those Diagnosed With Diabetes You Can Reduce The Risk Of Complications:
- Monitor blood glucose levels with appropriate testing and an A1C blood test every three months to measure the average amount of sugar in your blood
- If you smoke, it’s never too late to quit
- Be physically active
- Examine feet and skin every day
- Have an eye exam at least once a year
- Have a kidney function test at least once a year
- Visit your healthcare provider regularly
Hemoglobin A1c Levels In Children And Adolescents With Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract Hemoglobin A1c was measured as an indicator of glucose control in 180 children and adolescents with diabetes mellitus who received two daily injections of insulin as part of a highly structured treatment program. A total of 426 HbA1c determinations was made in the group of 180 patients. HbA1c values were elevated in most patients despite the aggressive treatment. The HbA1c level was very elevated at diagnosis, fell to near normal after 60-90 days of insulin therapy, increased gradually, and reached a plateau after approximately 4 yr duration . Mean insulin dose paralleled both HbA1c and duration of diabetes. The relationship between endogenous insulin secretion and glucose control was examined in those patients with diabetes for longer than 5 yr. Patients were separated into three groups based on HbA1c levels: those with HbA1c less than 9% , between 9 and 11% , and greater than 11% . Serum C-peptide and glucose concentrations were measured 2 h after a standard breakfast in those patients in the “low” and “high” HbA1c groups . C-peptide was detectable in all patients and the mean C-peptide levels did not differ significantly in the two groups, although postprandial glucose concentrations were significantly lower in the “low” HbA1c group .Continue reading >>
What Tools Are Available If An A1c Test Is Not Accurate Or Sufficient
Besides A1c tests, the most common measures of blood sugar are the oral glucose tolerance test , CGM, and self-monitored blood glucose tests.
The OGTT is a diagnostic tool diabetes and prediabetes, assessing a person’s response to consuming a fixed amount of sugar. After taking the sugar drink, blood sugar levels are measured two hours later. Below 140 mg/dl is considered “normal,” between 140 mg/dl and 200 mg/dl points to prediabetes or impaired glucose tolerance, and above 200 mg/dl indicates diabetes. It is not useful for tracking diabetes management.
For those with established diabetes, CGM has the advantage of monitoring blood sugar levels consistently throughout the day , providing more detailed insight into time spent in-range, low blood sugars, and high blood sugars. Examples of CGM include:
-
Senseonics implantable Eversense CGM
If CGM is not available, taking frequent fingersticks with a blood glucose meter – when waking up, before and after meals, and before bed – can also indicate when blood sugar levels are going low, high, and staying in range.
Follow The Diabetes Treatment Plan Your Healthcare Team Recommends
Diabetes treatment is very individualized, noted an article published in May 2014 in Diabetes Spectrum. After all, factors including how long you’ve lived with the disease, your socioeconomic status, and any other conditions you’re living with can play a role in the best treatment approach for you.
Your healthcare team will help you determine the steps you need to take to successfully manage diabetes. Always talk to your doctor before making any changes, such as starting a very-low-carbohydrate diet or beginning a new exercise regimen, and especially before making any medication or insulin changes.
RELATED:
Finally: A1c Is Also Defined As Estimated Average Glucose Or Eag
Another term you may come across when finding out your A1C is eAG. Your doctor might report your A1C results as eAG. eAG is similar to what you see when monitoring your blood sugar at home on your meter. However, because you are more likely to check your blood sugar in the morning and before meals, your meter readings will likely be lower than your eAG.
The 411 On A1c: Normal A1c Levels And 15 Ways To Lower High A1c
SingleCare TeamLindsey Hudson, APRN, NP-C, CDCES
The hemoglobin A1C test is the closest thing to a diabetes scorecard you can find. Whether someone has had diabetes mellitus for years or if they have just been diagnosed, they have probably heard about this test. Unlike blood sugar meters people use at home, the A1C measures an average blood sugar level over the past several months by analyzing how many of a patient’s hemoglobin cells have glucose attached to them. The test results keep track of how well a person is managing his or her diabetes.
Elevated A1c In Adults Without A History Of Diabetes In The Us
https://doi.org/10.2337/dc08-1699
Recommended Blood Sugar Targets For Most People With Diabetes*
Your targets may not be the same as the examples in this chart. Your targets are important and should be specific to you.
| A1C** | |
| 4.0 to 7.0 | 5.0 to 10.0 |
* This information is based on the Diabetes Canada 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Canada and is a guide.** A1C is a measurement of your average blood sugar control for the last two to three months and approximately 50 per cent of the value comes from the last 30 days.
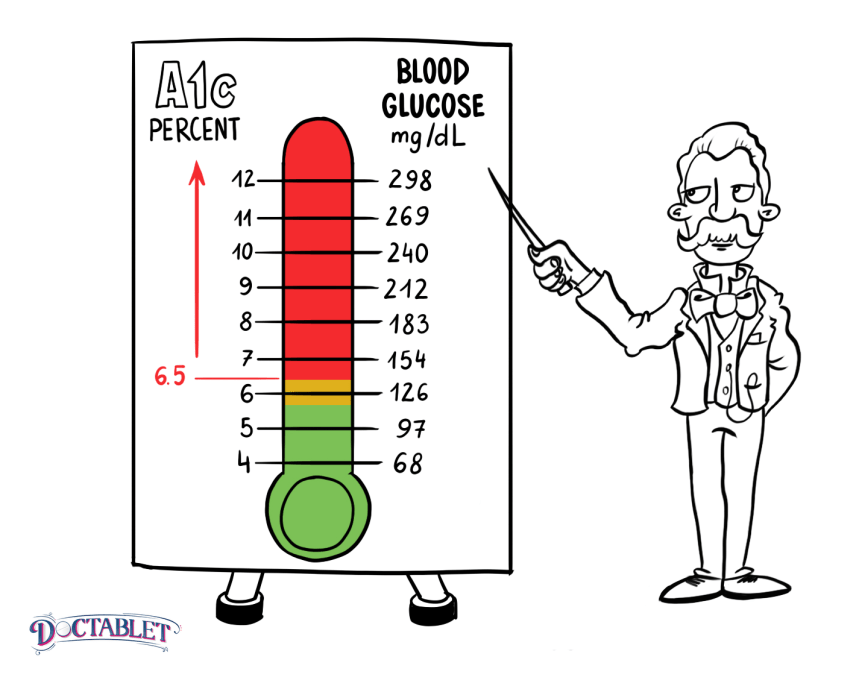
What Are Normal A1c Levels For People Who Don’t Have Diabetes
Generally, high A1c values indicate high average blood sugar levels and that a person might be at risk for or may have diabetes. The American Diabetes Association has established the following cutoffs:
|
A1c Level |
|
|
“Prediabetes,” meaning at risk for developing type 2 diabetes |
|
|
6.5% or greater |
Diagnosed diabetes |
Make sure you get a regular A1c test, especially if you think you might be at risk for diabetes.
Interestingly Your Ethnicity Can Also Affect Your A1c Result
Everyone has a different type of hemoglobin, depending on their ethnicity. A1C test works best with type A hemoglobin. Hemoglobin variants such, C, D or E, can affect the precision of A1C as well .
It is crucial to note that the A1C test is not always accurate. Repeated checks can give higher or lower measurements for the same blood samples. Doctors rely on other tests as well called fructosamine blood tests. This test gives an extended-term assessment of your sugar level.
To view the list of factors that may cause a high A1C result, please click here.
Do you need more information on the Haemoglobin A1C blood test, please click here
Check Your Blood Sugar Levels As Your Doctor Has Directed
Work with your doctor to determine if, and how often, you should check your blood sugar. You may be tempted to pick up an A1C home testing kit, but Dowdell does not recommend doing that. As he mentions, day-to-day fluctuations in your blood sugar can be masked by an A1C result that is at your goal level. Instead, if you have a personal continuous glucose monitor, such as a Dexcom G6 or a Freestyle Libre , Dowdell recommends checking your “time in range” to see if you are at the optimal level. For many people that is 70 to 180 milligrams per decilter , according to ADA guidelines. Having your A1C checked by your healthcare provider every three to six months is sufficient, he adds.
Understanding your A1C levels is an important part of your overall diabetes management. If you have any questions about your A1C levels or what they mean, don’t hesitate to ask your doctor.
Additional reporting by Mikel Theobald.
What Are Common Complications From Living With Diabetes
Cardiovascular Disease
- Over time, diabetes can damage arteries, which may result in high blood pressure.
- If not controlled, this can lead to stroke, heart failure or heart attack.
- People with diabetes need to keep their blood pressure and cholesterol under control.
Kidney Disease
- Kidney damage can develop in some people with diabetes.
- If left untreated, this can lead to more severe kidney damage or kidney failure.
- If you have diabetes, you should have your kidney function tested regularly.
Did You Know?
A healthcare provider can help with monitoring blood glucose levels, as well as ensuring that necessary preventive care treatments and advice are received in a timely manner.
Vision Loss
- Diabetic eye disease can lead to loss of vision and blindness.
- Regular eye exams can help find problems that can be treated if found early.
Lower Limb Amputation
- Over time, diabetes can damage sensory nerves, especially in the hands and feet.
- As a result, people with diabetes may not feel a foot injury, such as a blister or cut. Even a small injury, if left untreated, can quickly become infected. This can lead to serious complications such as amputation.
- People with diabetes should regularly check their feet and skin for ulcers and wounds .
Other Complications
People with diabetes are likely to develop other conditions such as dental disease and mental illness .
Q What Is The Blood Sugar Level For A 72 Year Old Woman
Answer:If you are aged but completely healthy, then you are likely to have your blood glucose at a standard level. But generally, aged people are more or less vulnerable to diseases. Though it is preferable to have blood sugar in between 100-120 mg/dl rising up to 140mg/dl is acceptable in certain conditions.
Still Frustrated With Your Blood Sugar And A1c Results
Your blood sugars and your insulin or medication needs never stay in one place. If you gain weight or lose weight, your insulin and medication needs will change. If you become more active or less active, your needs will change. If you make drastic or even small changes to your nutrition, your needs will change!
Working with your diabetes healthcare team, and diabetes coaches who can teach you how to make changes in your overall diabetes management plan are essential. Diabetes is a lifelong learning process.
Take a deep breath and be patient. If you don’t like what you’re seeing on your glucose meter, don’t get mad…get studying! Take good notes and work with your team to make changes to reach your goals.
Read more about improving your A1c in DiabetesStrong’s guide, How to Lower Your A1c.
If you liked this guide to normal blood sugar levels, please sign up for our newsletter using the form below. We send out a weekly newsletter with the latest posts and recipes from Diabetes Strong.
We Dont Even Need To Follow The A1c For Some Patients
Elderly patients, and those with serious medical conditions, will benefit from simply controlling the symptoms they have from high blood sugars, like frequent urination and incontinence, rather than aiming for any particular A1c level. Who would be included in this group? People with a life expectancy of less than 10 years, or those who have advanced forms of dementia, emphysema, or cancer; or end-stage kidney, liver, or heart failure. There is little to no evidence for any meaningful benefit of intervening to achieve a target A1c in these populations; there is plenty of evidence for harm. In particular, diabetes medications can cause low blood sugars, leading to weakness, dizziness, and falls. There is the added consideration that elderly and sick patients often end up on a long list of medications that can interact, causing even more side effects.
How Often Should You Check Your Hemoglobin A1c Levels
The American Diabetes Association suggests if people with diabetes want to reduce their hemoglobin A1c levels quickly, they should get their hemoglobin A1c levels checked every three months until they reach their treatment goals.
People with diabetes who are meeting treatment goals and have stable blood control are recommended to check their hemoglobin A1c every six months according to the ADA.
Tracking hemoglobin A1c levels allows an individual and their health-care professional to determine how well the person is controlling their blood sugar levels over time. However, they are not a substitute for daily glucose monitoring.
Start An Exercise Plan You Enjoy And Do It Regularly
Find something you enjoy doing that gets your body moving — take your dog for a walk, play a sport with a friend, or ride a stationary bike indoors or a regular bike outdoors.
A good goal is to get 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, recommends Jordana Turkel, a registered dietitian and certified diabetes educator at Park Avenue Endocrinology and Nutrition in New York City. This is also what the ADA recommends. Different types of exercise can lower your A1C by making the body more sensitive to insulin, Turkel says. She encourages her patients not to go more than two days in a row without exercising, and to aim for two days of strength training.
Be sure to check with your healthcare provider before embarking on an exercise plan, though. He or she can come up with an individualized plan for you.
And if you monitor your blood sugar daily, check it before and after exercise. As the Joslin Diabetes Center at Harvard Medical School explains, exercise can cause your blood sugar to rise, as more is released from the liver, and blood sugar to fall, due to increase insulin sensitivity. Fluctuations in your blood sugar levels can result if you aren’t careful. This is particularly important if you are on insulin or another diabetes medication that causes insulin secretion, such as include sulfonylureas, such as Amaryl , and glinides, such as Prandin and Starlix .
Testing Hba1c Levels Vs Blood Glucose Finger Prick
The typical fasting blood glucose finger prick shows your blood sugar levels right at that moment.
These are measured in mmol/L or mg/dL.
Measuring HbA1c levels instantly provides a bigger picture view, kind of like an average of your blood sugar levels over the past 3 months.
It’s usually taken from your regular arm blood test rather than the finger prick.
This HbA1c chart shows how the different tests correlate with one another. HbA1c levels are shown at the top, and blood glucose is shown below:
As an example, if your average blood glucose reading in the finger prick tests is around 10.0 mmol/L, then your HbA1c level will be about 8%.
Said another way, if you get a HbA1c of 9% then we know your average blood glucose level is about 11.8 mmol/L for the past few months.
Here’s another HbA1c chart that shows those comparisons side-by-side:
|
HbA1c levels |
|
|
42 |
7 |
Summary: The blood glucose finger prick shows your current blood sugar levels, whereas HbA1c is representative of your previous 3-month average.
Your Blood Sugar Isnt Just Because Of What You Eat
Mainstream media would have you believe that your blood sugar levels are impacted only by what you eat and how much you exercise, but people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes who test their blood sugars frequently could tell you otherwise.
It’s especially important to keep this mind when looking at your own blood sugars and your goals because there are certain variables and challenges that impact blood sugar levels that you can’t always control.
For example:
- Menstrual cycles: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- Adrenaline rushes from competitive sports, heated arguments, rollercoaster rides: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- The common cold and other illnesses: usually raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- Hormonal changes due to puberty and healthy growth in young adults: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- An injury which raises overall inflammation levels: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- Glucogenesis during anaerobic exercise: raises blood sugar
While you can’t necessarily prevent these factors that affect your blood sugar from occurring, you can work with your diabetes healthcare team to adjust your insulin, other diabetes medications, nutrition and activity levels to help compensate for them when they do occur.
For example, when engaging in anaerobic exercise — like weightlifting — many people with type 1 diabetes find it necessary to take a small bolus of insulin prior to or during their workout because anaerobic exercise can actually raise blood sugar.
Diagnosing Prediabetes Type 2 And Type 1 Diabetes
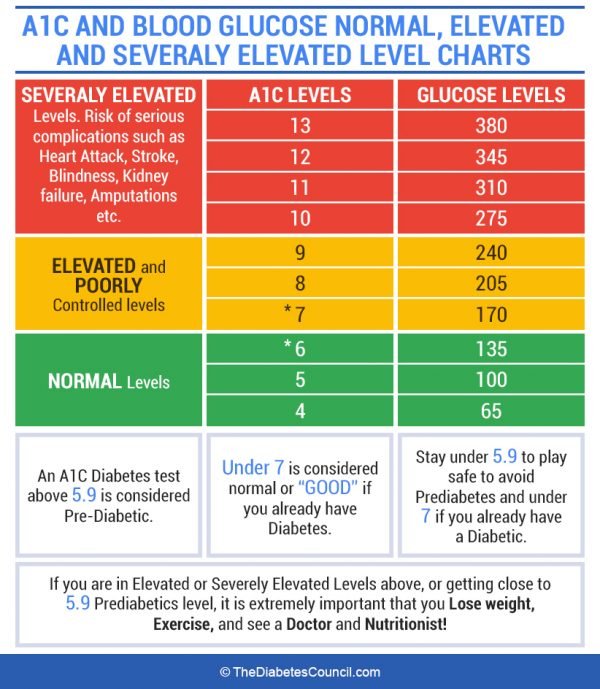
Depending on which country or medical organization you ask, the qualifying numbers for “normal” versus “prediabetes” versus diagnosed type 1 or type 2 diabetes can vary slightly. The following blood sugar and A1c the general results are used to diagnosed prediabetes and diabetes according to sources including the American Diabetes Association and Diabetes UK:
Prediabetes
- HbA1c: 5.7 to 6.4 percent
- Fasting: 100 to 125 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 140 mg/dL to 199 mg/dL
Type 1 or 2 diabetes
- HbA1c: 6.5 percent or higher
- Fasting: 126 mg/dL or higher
- 2 hours after a meal: 200 mg/dL or higher
Please note: Type 1 diabetes tends to develop very quickly which means that by the time symptoms are felt, blood sugar levels are generally well above 200 mg/dL all the time. For many, symptoms come on so quickly they are dismissed as the lingering flu or another seemingly ordinary virus.
Read more about ketones at diagnosis in Diabetes Strong’sDiabetic Ketoacidosis Guide.
Laboratory Measurement Of A1c And Plasma Glucose
A1C measurements for NHANES 1999–2004 were performed by the Diabetes Diagnostic Laboratory at the University of Missouri-Columbia using Primus CLC330 and Primus CLC 385 instruments . A1C measurements in NHANES 2005–2006 were performed by the Diabetes Laboratory at the University of Minnesota using a Tosoh A1c 2.2 Plus Glycohemoglobin Analyzer . Both assays use a high-performance liquid chromatography system . All A1C measurements were standardized to the reference method used for the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. The plasma glucose concentration was determined by a hexokinase enzymatic method .
Can People With Diabetes Have A Normal A1c Level
In recent years, I have come across numerous social media posts about people with diabetes having A1c levels that are “too low.” In particular, I was floored by posts about medical practitioners automatically telling their patients that their normal A1c levels were unsafe and that they should aim higher.
Time and time again, I have seen stories of endocrinologists and general practitioners discouraging patients from an A1c level in the 4.5-5.5% range, with some even advocating for an A1c level of no lower than 6% or even 7%! Moreover, I have seen such reports from pregnant women, which is astounding, since optimizing blood glucose control is especially critical during pregnancy.
So why is this occurring and can you actually have an A1c level that is too low?
I’d like to think that a truly knowledgeable endocrinologist would never give bad advice about blood glucose targets. I imagine that upon being confronted with a normal A1c level in a patient with diabetes, the practitioner would evaluate how frequently hypoglycemia occurs and how severe it is. In other words, is the patient successfully achieving a normal blood glucose levels for a vast majority of the time, or are they swinging wildly above and below their optimal range to achieve a normal average?
Graphic by Maria Muccioli
Image by Maria Muccioli
What Is The Normal Blood Sugar Level For Seniors
We, humans, get our energy from food. Our body converts food into a sugar called glucose with the help of insulin and supplies the necessary energy required to continue our daily activities.
Is it okay to have a random level of blood glucose? No! Definitely not!
Blood sugar has also got an optimum level. What is it then? Thus, this is our topic today. Here in this article, I will give you a brief idea about the normal blood sugar levels in our body. But my main focus will be on the geriatric or older adult citizens as altered blood glucose level or diabetes is the most prevalent amongst them. So, let’ dig into the topic quickly!
Table of Content

