Part 1: What Is Insulin Resistance
Insulin is a hormone that is produced by the pancreas and tells the cells in the liver, muscles and fat to absorb glucose in the blood, particularly after a meal. Your body needs insulin to aid in nutrient uptake in the cells, and without this hormone, your cells would starve.
The primary stimulator for insulin release is glucose in the blood stream.
Glucose levels rise in response to food and stress, and the main job of insulin is to lower blood sugar by getting the extra glucose to the cells, where they are burned for energy or stored as fat.
The problem is that when insulin is repeatedly secreted in large quantities over time, your cells can become less sensitive to its signals.
Think of the FIRST time you ever changed a VERY dirty diaper. When you first smell that dirty diaper, you’re VERY aware of the stench. The smell is strong. One whiff makes you gag, right?! But over time, and after several dirty diapers, you become more accustomed to the smell of a dirty diaper, it begins to make you gag less and less, and eventually- you don’t even realize it stinks that much at all!
This is what happens to your cells when they become insulin resistant.
They no longer respond to insulin the same way. They become accustom to the insulin and are less sensitive to the signals it is sending.
Conditions Associated With Insulin Resistance
The following health conditions are associated with insulin resistance:
Guide Many people come to Diet Doctor because they are looking for help to lose weight or reverse type 2 diabetes. But did you know that almost all the symptoms of a common female condition called Polycystic Ovary Syndrome respond very well to a low-carb or ketogenic diet, too?
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease — Called NAFLD, this is where there is too much fat stored in the liver. It may be the result of chronically high insulin levels and it may contribute to insulin resistance. While it is more common in individuals who are obese, have metabolic syndrome, or have type 2 diabetes, it has been found to be associated with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia in lean individuals with normal glucose tolerance. Some people with NAFLD go on to develop liver problems, such as inflammation, scarring, and cirrhosis as well as liver failure.
- Cancer — Insulin resistance is associated with an increase in risk of colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, pancreatic cancer, and breast cancer. It is not clear whether it is the insulin resistance itself or its relationship to other risk factors, such as obesity and high blood glucose, that contributes to the increased cancer risk. However, it is thought that chronically high levels of insulin may promote cancer growth and that reducing insulin levels may slow cancer growth, although more data are needed in this area to draw firm conclusions.
What Foods Help Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
Foods that are particularly helpful for people trying to prevent type 2 diabetes and maintain a healthy weight are similar to the low glycemic index foods described above:
- Vegetables and fruits provide fiber and .
- Fat-free or low-fat dairy products provide calcium and strengthen bones. Avoid full-fat dairy products, as high-fat foods can worsen insulin resistance.
- Whole-grain products have a lower glycemic index than refined grains and are rich in fiber.
- Nuts contain fiber, protein, and healthy fats.
- Some fish can be a source of “good” fats, such as salmon, herring, mackerel, or sardines.
- Lean meats or beans are an excellent source of protein.
Several studies have confirmed that weight loss — and even aerobic exercise without weight loss — increases the rate at which muscle cells take glucose from the blood as a result of improved sensitivity to insulin.
> Blood Tests For Insulin Resistance
Keep in mind that the typical tests for diabetes often don’t pick up insulin resistance. Nor does a fasting insulin. This is especially true in women who are mildly insulin resistance as well as women with “lean” PCOS. The following information was adapted from Dr. Fiona McCullough, PCOS expert. to bring to your next doctor’s appointment. Even if you don’t have PCOS, the chart can be helpful. BEST TESTS FOR DIABETESFasting glucose: done after an overnight fast. Normal range is < 99 mg/dl Glucose intolerance or prediabetes is 100-124. Over 124 is diabetes. Many individuals with insulin resistance have normal glucoseHbA1c: done anytime. Normal range is < 5.7. Interpretation: An HbA1c of 5.7-6.4 indicates pre-diabetes and 6.5 and higher is diabetes. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, if blood tests indicate prediabetes, insulin resistance most likely is present. However a normal test does not mean you are NOT insulin resistant!
C peptide: done after an overnight fast C- peptide is not often tested except in those suspected of having type 1 diabetes however it can also be a surrogate marker of insulin resistance as levels can be higher than normal.Normal values : range from 0.51 – 2.72 ng/mLElevated levels suggest insulin resistance, however it is not diagnostic for insulin resistance.
BEST TEST FOR INSULIN RESISTANCE:
How Do I Know If A Mole Is Cancer

The vast majority of moles are not dangerous. Moles that are more likely to be are those that look different than other existing moles or those that first appear after age 25. If you notice changes in a mole’s color, height, size, or shape, you should have a dermatologist evaluate it. You also should have moles checked if they bleed, ooze, itch, or become tender or painful.
Examine your skin with a mirror or ask someone to help you. Pay special attention to areas of the skin that are often exposed to the sun, such as the hands, arms, chest, neck, face, ears, legs, and back.
If a mole does not change over time, there is little reason for concern. If you see any signs of change in an existing mole, if you have a new mole, or if you want a mole to be removed for cosmetic reasons, talk to your dermatologist.
The following ABCDEs are important characteristics to consider when examining moles. If a mole displays any of the signs listed below, have it checked immediately by a dermatologist. It could be cancerous.
- Asymmetry. One half of the mole does not match the other half.
- Border. The border or edges of the mole are ragged, blurred, or irregular.
- Color. The color of the mole is not the same throughout or has shades of tan, brown, black, blue, white, or red.
- Diameter. The diameter of a mole is larger than the eraser of a pencil.
- Evolution. The mole is changing in size, shape, or color.
Can You Reverse Insulin Resistance
On the bright side, there are ways you can help improve insulin sensitivity and reverse insulin resistance:
- Engage in at least 30 minutes of physical activity most days of the week. Exercise is one of the fastest and most effective ways to reverse insulin resistance.
- Lose weight, especially around the middle. Losing weight around the abdomen not only improves insulin sensitivity but also lowers your risk of heart disease.
- Adopt a high-protein, low-sugar diet. Protein helps keep your body’s blood sugar levels stable, whereas high-sugar diets can cause spikes in blood sugar that only make insulin resistance worse. Even though being insulin resistant doesn’t necessarily mean you have diabetes, following a meal plan recommended by the American Diabetes Association can help improve insulin sensitivity.
Hyperinsulinemia & Insulin Resistance Causes More Death Than Ww1 And Ww2 Combined
When you’re more insulin resistant, your body requires MORE insulin from your pancreas to push glucose and energy into cells.
High insulin may not cause all chronic disease. But at the very least it exacerbates them. Having persistently high fasting insulin levels is called hyperinsulinemia. It usually goes hand in hand with insulin resistance.
If you have insulin resistance, you’re at risk for chronic disease. There’s no chronic disease that’s not related to insulin resistance:
- Heart disease
- A waist larger than 35” for women or 40” for men
- A fasting insulin level above 5
Here Are Some Ways To Determine If You Have Insulin Resistance:
Find your waist to hip ratio.
Measure yourself around your natural waist and also around the widest part of your hips. Divide your waist measurement by your hip measurement. For women, the ratio should be no greater than 0.8. If you are above that, it means that you are at risk for insulin resistance. The number for men is 1.0.
Get a fasting insulin test
Ask your doctor to order a blood glucose and insulin test. Typically, you fast for 12 hours and then have your first blood draw. Then you will eat a meal and get a second blood draw two hours after your meal. Fasting blood glucose levels should be under 90 mg/dL. If your levels are 100 to 125 mg/dL you are considered in the pre-diabetes range and are insulin resistant. Fasting insulin levels should be around 5 mcU/ml Anything higher indicates insulin resistance.
Get your cholesterol checked
Abnormal blood cholesterol in addition to abnormal fasting insulin and blood glucose may indicate that you have insulin resistance, especially if you have low HDL and high triglycerides. Typically fasting triglycerides should be below 150. But, more importantly, you want to look for a 1:2 ratio of triglycerides to cholesterol.
Do a skin check
A skin condition called acanthosis nigricans is associated with insulin resistance. Look for darkened skin patches on your neck, elbows, knees, and armpits. Skin tags are also a sign of insulin resistance.
What Happens When Insulin Resistant Diabetes Forms
Insulin resistance is a huge health threat in America, even for men and women who believe they’re perfectly healthy. It’s estimated that more than 30% of the U.S. population may be insulin resistant, but the symptoms can take years to manifest in a way that can’t be ignored.
Insulin resistance creates a destructive cycle that starts and ends with high blood glucose. When your body becomes resistant to insulin, the pancreas produces even more insulin in an attempt to lower blood glucose levels. That doesn’t help at all. Instead, it causes stronger insulin resistance, which in turn allows blood glucose levels to rise even higher.
Insulin and blood glucose levels may rise for months or years until the pancreas becomes too damaged to produce high levels of insulin. The result of low insulin production and minimal insulin response creates the perfect storm for blood glucose levels to surge out of control and trigger immeasurable health consequences. In other words, uncontrolled type 2 diabetes.
Why Does Insulin Resistance Happen
Genetic risk factors, environmental risk factors, and lifestyle factors have all been found to contribute to the development of insulin resistance.
While some people may be genetically more likely to develop insulin resistance, the biggest impact has perhaps come from the change in our food environment in recent decades. Greater availability of cheap, energy-dense food and drinks may have led whole populations to adopt an unhealthy lifestyle, characterized by consumption of high levels of sugar and other refined carbohydrates. These simple carbohydrates are converted into large amounts of glucose that we may not need for energy, often resulting in much of it being stored in our cells or stored as fat.
Scientists have elucidated many mechanisms and pathways that contribute to the development of insulin resistance. Interestingly, although we often think of insulin resistance in terms of the effect of insulin on glucose metabolism, one of the major causes is actually disordered fatty acid metabolism.
Scientific evidence suggests that fatty acids inappropriately accumulate in muscle and liver which then interferes with their cells’ ability to respond to insulin and take up glucose. One of the main questions, therefore, is how do excess fatty acids invade muscle and liver cells?
What Is Insulin Resistance
resistance is when cells in your muscles, , and don’t respond well to insulin and can’t use glucose from your for energy. To make up for it, your makes more insulin. Over time, your blood sugar levels go up.
Insulin resistance syndrome includes a group of problems like , high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and type 2 diabetes. It could affect as many as 1 in 3 Americans. You might also hear it called metabolic syndrome.
Get Off Your Ass And Exercise
If you want to be healthy, you need to get off of your ass. You need to try to mimic your hunter gatherer ancestors as much as possible. But still continue to follow me on Twitter, even though they didn’t…
Unfortunately, most people today are sitting down and eating all day. Most people are cramped in a cubicle surrounded by snacks. You want to do the exact opposite. Move around as much as possible throughout the day.
And most importantly for insulin resistance, conduct high intensity exercise.
Other than consuming red meat, exercise is the fastest way to reduce insulin resistance. Just one single bout of high intensity training can increase insulin sensitivity 40%
This study below showed that just 6 weeks of training, with one set of 8 exercises improved insulin sensitivity. You don’t need to go out and run a marathon.
Just lift heavy weights.
Steak + deadlifts are a magical combination.
Obesity is also highly correlated to insulin resistance, which rises linearly with BMI . If you’re insulin resistant and obese, you need to cut your BMI.
Lastly, lean muscle mass is associated with better insulin sensitivity . Lean muscle is like a glucose sink. It sucks up any and all glucose available in your blood stream.
Insulin Resistance Causes And Symptoms
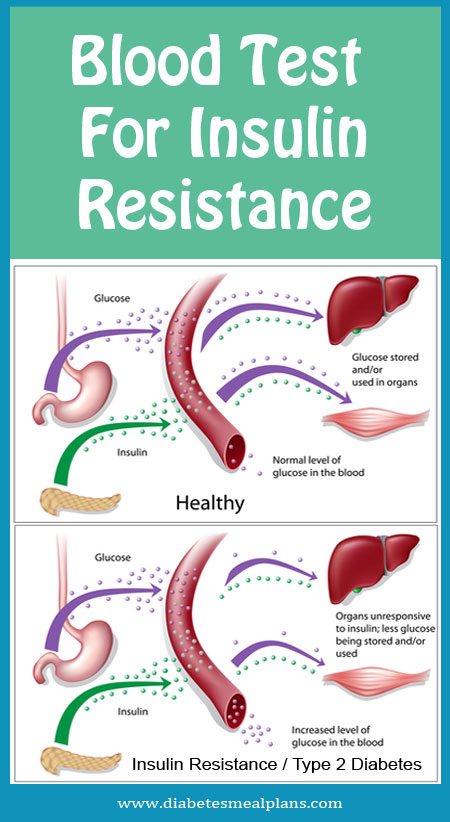
One in three Americans—including half of those age 60 and older1— have a silent blood sugar problem known as insulin resistance. Insulin resistance increases the risk for prediabetes, type 2 diabetes and a host of other serious health problems, including heart attacks, strokes2 and cancer.3
What is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin resistance is when cells in your muscles, body fat and liver start resisting or ignoring the signal that the hormone insulin is trying to send out—which is to grab glucose out of the bloodstream and put it into our cells. Glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the body’s main source of fuel. We get glucose from grains, fruit, vegetables, dairy products, and drinks that bring break down into carbohydrates.
How Insulin Resistance Develops
While genetics, aging and ethnicity play roles in developing insulin sensitivity, the driving forces behind insulin resistance include excess body weight, too much belly fat, a lack of exercise, smoking, and even skimping on sleep.4
Signs and Symptoms of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is usually triggered by a combination of factors linked to weight, age, genetics, being sedentary and smoking.
– You have additional signs of metabolic syndrome. According to the National Institutes of Health,7 in addition to a large waist, if you have three or more of the following, you likely have metabolic syndrome, which creates insulin resistance.
Health Conditions Related to Insulin Resistance
How Can I Prevent Or Reverse Insulin Resistance And Prediabetes
Physical activity and losing weight if you need to may help your body respond better to insulin. Taking small steps, such as eating healthier foods and moving more to lose weight, can help reverse insulin resistance and prevent or delay type 2 diabetes in people with prediabetes.
The National Institutes of Health-funded research study, the Diabetes Prevention Program , showed that for people at high risk of developing diabetes, losing 5 to 7 percent of their starting weight helped reduce their chance of developing the disease.3 That’s 10 to 14 pounds for someone who weighs 200 pounds. People in the study lost weight by changing their diet and being more physically active.
The DPP also showed that taking , a medicine used to treat diabetes, could delay diabetes. Metformin worked best for women with a history of gestational diabetes, younger adults, and people with obesity. Ask your doctor if metformin might be right for you.
Making a plan, tracking your progress, and getting support from your health care professional, family, and friends can help you make lifestyle changes that may prevent or reverse insulin resistance and prediabetes. You may be able to take part in a lifestyle change program as part of the National Diabetes Prevention Program.
Reducing Your Risk For Insulin Resistance
The best way to prevent and treat insulin resistance or metabolic syndrome is to lose weight if you’re overweight, and exercise. The composition of your diet is important too. Processed carbohydrates that are low in fiber stimulate more insulin release and worsen the problem – so can eating white potatoes and white rice.
The best diet to treat insulin resistance is one that emphasizes lean protein sources, especially fish, fiber-rich carbs from vegetables and moderate amounts of healthy fats like the monounsaturated fats in nuts and olive oil and omega-3s in fatty fish. It’s also important to eat magnesium-rich foods like seafood, nuts, and lentils since low magnesium levels may worsen insulin resistance.
Exercise not only helps insulin-resistant people lose weight, but it also increases the sensitivity of cells to insulin. A combination of strength training and high-intensity interval cardio exercises is ideal for improving insulin sensitivity and reducing abdominal fat.
Don’t underestimate the importance of sleep. Skimping on sleep reduces insulin sensitivity and makes it harder to control your weight. Seven to eight hours is the amount most people need for optimal insulin sensitivity and health.
What Does Insulin Do In The Body
Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate your blood sugar and is made by an organ known as the pancreas that sits behind your stomach. Your pancreas sends insulin into your bloodstream after you eat or if it detects that your blood sugar levels are high.
Once insulin enters your blood, it has 2 major jobs:
What Are The Symptoms Of Insulin Resistance And Prediabetes
Insulin resistance and prediabetes usually have no symptoms. Some people with prediabetes may have darkened skin in the armpit or on the back and sides of the neck, a condition called acanthosis nigricans. Many small skin growths called skin tags often appear in these same areas.
Even though blood glucose levels are not high enough to cause symptoms for most people, a few research studies have shown that some people with prediabetes may already have early changes in their eyes that can lead to . This problem more often occurs in people with diabetes.
Insulin Resistance In The Bipoc Community
according to a March 2019 study in Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.according to a systematic review and meta-analysis in Diabetes Care.
- 5 percent of non-Hispanic whites
- 2 percent of Asian Americans
- 7 percent of non-Hispanic blacks
- 5 percent of Hispanics
- 7 percent of American Indians/Alaskan Natives
More on Health Disparities Affecting BIPOC Individuals
Carbs And Fat Together Make You As Fat As Possible
And because sugar and fat are burned reciprocally, if you combine them it makes you as fat as possible. All the fat just goes straight to storage.
Nutritional scientists have discovered this and actually use this methodology to fatten up rats. Researchers created an “obesogenic rat chow” made up of 14% protein, 45% fat and 40% carbohydrates.
Well, thanks to the USDA, our basic dietary recommendations are basically the same obesogenic rat chow.
The fat and sugar accumulate in your bloodstream, causing more futile insulin secretion. When your insulin levels are chronically elevated, this is called hyperinsulinemia.
Unsubstantiated evidence led experts to substitute saturated fats for poisonous carbohydrates. Now hundreds of millions of people around the globe are insulin resistant today.
Every time you eat carbohydrates — especially refined, high glycemic carbs — your body goes to war with itself. And you lose.
Ancel Keys’ Junk science has destroyed your health.
Insulin Takes Sugar Out Of Your Blood And Sends It Into Your Cells To Be Used For Energy
When you eat a meal with carbohydrates , you often get a burst of energy. Well, your cells get energy from sugar too, but how does the sugar get into the cells? That’s where insulin comes in.
Most of the cells in your body contain insulin receptors. Think of an insulin receptor like a lock and the insulin hormone like a key. When the key opens the lock—or when insulin binds to the insulin receptor—the cell opens to let sugar in. By attaching to insulin receptors, insulin helps take sugar out of the blood and sends it into cells to be put to good use. As a result, your blood sugar levels should return to normal.
Is There An Insulin Resistance Test

Unfortunately, there is no insulin resistance test that is commonly used in medicine. Your doctor can use a blood glucose test or hemoglobin A1C test to evaluate your blood sugar levels. But remember that in the early stages of insulin resistance, your blood sugar levels may still appear normal, so a blood glucose or A1C test is not always a reliable test of insulin resistance.
How Do I Know If I’m Insulin Resistant
Here’s the problem. Most people who have insulin resistance don’t know they have it.
One third of Americans have insulin resistance, according to the Centers for Disease Control . But four out of five people who have insulin resistance don’t know they have it. While insulin resistance may cause symptoms in the early stages, such as low energy, many people will not notice symptoms. But that doesn’t mean insulin resistance isn’t causing damage in the body. The only way to know if you have insulin resistance is to test for it.
Why A Fasting Glucose Test Isnt Enough
Most people who are insulin resistant – – don’t realize it. That’s because most doctors don’t routinely check glucose levels, and if they do, they only test fasting glucose, which doesn’t show the full picture.
As a doctor with insulin resistance myself, and as someone who has helped hundreds of patients lower their blood glucose and insulin levels, I recommend doing a fasting glucose test, an oral glucose tolerance test, and an insulin test.
Let me share an example to illustrate my point. A patient of mine was concerned about diabetes. Why? He was slightly overweight, he had family members with diabetes, and his father had died of a heart attack. He told me his family doctor checked his fasting glucose once a year and it always came back normal.
So I ran the tests. His fasting glucose indeed came back normal, at 88mg/DL. But when we did an oral glucose tolerance test, his sugar levels were through the roof: at 291mg/Dl at the two-hour mark. . As you can see, fasting glucose doesn’t tell the whole story. Some people can bring their sugars down to normal levels over time but the worrying part is that it takes them too long to do so. The sugar in their bloodstream can still cause damage. This is especially common in prediabetes and early diabetes.
Â
Youve Developed Dark Velvety Patches In The Folds Of Your Skin
These could be under your arms or on the back of your neck. The proper name for them is acanthosis nigricans. It’s caused when insulin-like growth factor stimulates the cells in the skin to produce more keratin and dermal fibroblasts.
Studies have shown that insulin resistance is not the only reason that these patches develop. However, they are still a potential indicator of it.
What Is Insulin And How Does It Work
Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas. Its main job is to manage how your body uses glucose for energy. When blood sugar levels rise after a meal, your pancreas releases insulin to help your body’s cells — especially cells in the liver and muscles — absorb glucose. Your liver converts stored glucose to glycogen for future use.
When blood sugar levels are too low, your pancreas releases a hormone called glucagon. Glucagon forces the liver to convert glycogen back to glucose, which causes your blood sugar to rise.
You always have low levels of insulin circulating in your body. When insulin is out of balance, the result is abnormal blood sugar levels. High insulin levels can make you feel tired, bloated and cause sugar cravings. And, the more insulin you have circulating in your body, the harder it becomes to lose weight and burn fat.

