What Is Genetic Engineering
- Genetic engineering, sometimes called genetic modification, is the process of altering the DNA in an organisms genome.
- This may mean changing one base pair , deleting a whole region of DNA, or introducing an additional copy of a gene.
- It may also mean extracting DNA from another organisms genome and combining it with the DNA of that individual.
- Genetic engineering is used by scientists to enhance or modify the characteristics of an individual organism.
- Genetic engineering can be applied to any organism, from a virus to a sheep.
- For example, genetic engineering can be used to produce plants that have a higher nutritional value or can tolerate exposure to herbicides.
Isolation Of Insulin Gene
insulin is a small protein . the first challenge was to isloate the insulin gene from the rest of the DNA in the human cell. But there was a problem doing so directly, instead the mRNA carrying the code for synthesizing insulin was extracted from the cells in the pancreas that produces insulin, called B-cells.
then the mRNA was left in incubation with reverse transcriptase, reverse transcriptase is a special retrovirus, it does the opposite of transcription i.e codes for DNA from RNA, this newly coded DNA is called complimentary DNA or simply cDNA. at first single stranded molecules were formed, which then turned in double helix. these DNA molecules carried the code for human insulin. these DNA molecules then needed to be stuck to other DNA strands, & so they were given sticky ends by adding lenghts of single stranded DNA made up of guanine nucleotide to each end using enzyymes.
If you need assistance with writing your essay, our professional essay writing service is here to help!
Biotechnological Applications In Agriculture
- Let us take a look at the three options that can be thought for increasing food production
- Plants, bacteria, fungi and animals whose genes have been altered by manipulation are called Genetically Modified Organisms . GM plants have been useful in many ways. Genetic modification has:
You May Like: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
A Timeline Of Genetic Modification In Agriculture
A Timeline of Genetic Modification in Modern Agriculture
Circa 8000 BCE Humans use traditional modification methods like selective breeding and cross-breeding to breed plants and animals with more desirable traits.
1866 Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk, breeds two different types of peas and identifies the basic process of genetics.
1922 The first hybrid corn is produced and sold commercially.
1940 Plant breeders learn to use radiation or chemicals to randomly change an organisms DNA.
1953 Building on the discoveries of chemist Rosalind Franklin, scientists James Watson and Francis Crick identify the structure of DNA.
1973 Biochemists Herbert Boyer and Stanley Cohen develop genetic engineering by inserting DNA from one bacteria into another.
1982 FDA approves the first consumer GMO product developed through genetic engineering: human insulin to treat diabetes.
1986 The federal government establishes the Coordinated Framework for the Regulation of Biotechnology. This policy describes how the U.S. Food and Drug Administration , U.S. Environmental Protection Agency , and U.S. Department of Agriculture work together to regulate the safety of GMOs.
1992 FDA policy states that foods from GMO plants must meet the same requirements, including the same safety standards, as foods derived from traditionally bred plants.
2005 GMO alfalfa and sugar beets are available for sale in the United States.
2017 GMO apples are available for sale in the U.S.
What Are The Latest Scientific Advances In Plant And Animal Breeding

Scientists are developing new ways to create new varieties of crops and animals using a process called genome editing. These techniques can make it easier and quicker to make changes that were previously done through traditional breeding.
There are several genome editing tools, such as CRISPR. Scientists can use these newer genome editing tools to make crops more nutritious, drought tolerant, and resistant to insect pests and diseases.
You May Like: What Can Diabetes Do To You
Structure And Function Of Insulin
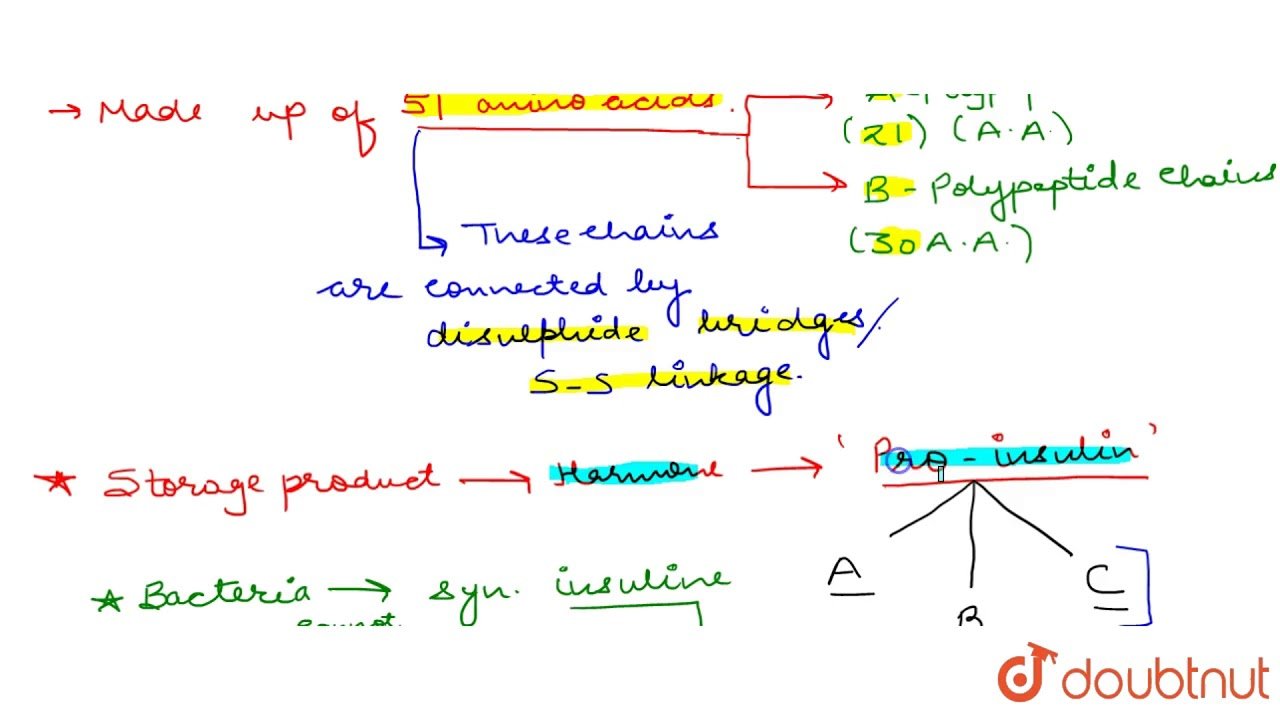
The human insulin is comprised of 51 amino acids and has a molecular weight of 5808 Da. It is produced by beta cells of the pancreas and plays a key role in regulating carbohydrate and fat metabolism in the body. Insulin is synthesized as a single polypeptide known as preproinsulin in pancreatic beta cells. Preproinsulin harbours a 24-residue signal peptide, which directs the nascent polypeptide to the endoplasmic reticulum. The signal peptide is cleaved as the polypeptide is translocated into the human of the endoplasmic reticulum resulting in the formation of proinsulin. In the Endoplasmic reticulum, the proinsulin is folded in proper confirmation with the formation of 3 disulphide bonds. Folded proinsulin is then transported to the trans-Golgi network, where it is converted into active insulin by cellular endopeptidases called as prohormone convertases and exoprotease carboxypeptidase E. The endopeptidases cleaves at two positions, resulting in the release of a fragment termed as C-peptide. The mature insulin, thus formed consists of an A-chain with 21 aminoacids and a B-chain containing 30 aminoacids and both polypeptides linked together by two disulphide bonds. Besides, the A-chain has an intrachain disulphide bond .
Genetically Modified Organisms Examples
In traditional animal husbandry production, crop cultivation, and even domestic breeding, there is a practice of breeding specific individuals of a species to produce offspring with long-desired traits. However, in genetic modification, recombination genetic techniques are used to generate organisms whose genome has been properly modified at the molecular level, usually by incorporating features encoded by genes from unrelated biological species. , And features encoded by these features are traditional selection reproduction is not easy to achieve.
Read Also: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
Yeast Expression System For The Production Of Insulin
Yeast is a preferred host for expression of various heterologous proteins that require post-translational modifications for its biological activity. Yeast cell has the ability to carry out numerous post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation, O-linked glycosylation, N-linked glycosylation, acetylation and acylation. Recombinant proteins are expressed in soluble form in yeast and properly folded in functionally active form. Production of biopharmaceuticals using yeast expression system is also very cost effective and is amenable to scale up using large bioreactors. However, one major concern for producing therapeutic glycoprotein for human application is that yeast N-glycosylation is of the high-mannose type, which confers a short half-life in vivo and hyperâimmunogenicity and thus render the therapeutic glycoprotein less effective. Various attempts have been made to humanize yeast N-glycosylation pathways in order to produce therapeutic glycoproteins with humanized N-glycosylation structure .
Introduction To Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering refers to the direct manipulation of DNA to alter an organisms characteristics in a particular way. This may mean changing one base pair , deleting a whole region of DNA, or introducing an additional copy of a gene. It may also mean extracting DNA from another organisms genome and combining it with the DNA of that individual. It has been used by scientists to enhance or modify the characteristics of an individual organism from a virus to sheep, to possibly humans. For example, genetic engineering can be used to produce plants that have a higher nutritional value or can tolerate exposure to herbicides.
We can change an organisms characteristics by introducing new pieces of DNA into their genomes. This could be:
- DNA from the same species.
- DNA from a different species.
- DNA made synthetically in the lab.
There are several techniques that can be used to modify a genome, including:
Recommended Reading: How Long Do Type 1 Diabetics Live
What Is The Main Advantage Of Producing Genetically Engineered Insulin
Insulin was the first human protein to be produced via genetic engineering and is still produced this way today. As insulin used to be harvested from pigs and cows, genetic-engineered insulin has the advantages of being cheaper and more ethical to create, and of having fewer adverse reactions in patients.
Are Genes And Dna Safe To Eat
Virtually everything we eat comes from a plant, animal, or fungal source. That means it either has genes in it or if it was highly processed, such as oil and sugars which no longer contain DNA, it was extracted from an organism that had genes. This means we are constantly eating genes , whether modified by traditional breeding methods, natural mutations or genetic engineering. Our digestive tract breaks down DNA in the same way, regardless of the source and regardless of the DNA sequence.
Nonetheless, proteins produced by the new genes, and the resultant crop products, must be tested for safety. For this reason, whenever a new plant variety is created using genetic engineering in the U.S., the new variety undergoes rigorous testing for allergens, toxins and modified nutritional content, based on FDA and international food safety standards. All GM products currently on the market have been approved by and are regulated by the FDA. For a greater understanding of testing genetic engineered plants, see a discussion by Professor Robert Hollingworth from the Michigan State University Center for Research on Ingredient Safety .
Don’t Miss: Can Type 2 Diabetics Eat Bananas
How Are Gmos Made
GMO has become the common term consumers and popular media use to describe foods that have been created through genetic engineering. Genetic engineering is a process that involves:
- Identifying the genetic informationor genethat gives an organism a desired trait
- Copying that information from the organism that has the trait
- Inserting that information into the DNA of another organism
- Then growing the new organism
Humulin N Nph Human Insulin Isophane Suspension
- Description
- Humulin is human insulin used for treating diabetes. Prior to its development, diabetics used insulin isolated from pig and cow pancreases. Developed by Genentech, the first American biotechnology company, Humulin was licensed to Eli Lilly and became the first marketable product created through recombinant DNA technology. Its licensing by the FDA in October 1982 also made it the first recombinant pharmaceutical approved for use in the United States.
- Recombinant pharmaceuticals are created by inserting genes from one species into a host species, often yeast or bacteria, where they do not naturally occur. The genes code for a desired product, and therefore the genetically modified host organisms can be grown and used as a kind of living factory to produce the product. In this case, genes coding for human insulin are inserted into bacteria. Bacteria produce insulin, which is harvested and used as the active ingredient in Humulin.
- Humulin N is formulated to have a slower onset of action than regular insulin and a longer duration of activity .
- Object consists of a white cardboard box with black and red printing. Box contains two product inserts and one clear round glass bottle with an orange plastic cap and a white label. Bottle contains a pinkish substance suspended in a clear solution.
- Location
Recommended Reading: What Is A High Blood Sugar Reading
Can Synthetic Biology Make Insulin Faster Better And Cheaper
Rising insulin prices have become a dangerous norm for diabetics. Whether on Twitter, TV, or public … radio, the insulin market has the worlds attention and for all the wrong reasons.
Getty
He lost his insurance and turned to a cheaper form of insulin. It was a fatal decision.
Rising insulin prices have become a dangerous norm for diabetics. Whether on Twitter, TV, or public radio, the insulin market has the worlds attention and for all the wrong reasons.
Insulin prices are not only skyrocketing lack of access is killing Americans. People with Type 1, Type 2, and even gestational diabetes need to take insulin to regulate their blood sugar levels. Insulin is the signal that tells our cells to take in glucose and convert it to energy. Without this molecule, glucose builds up in the bloodstream and can cause serious complications, including cardiovascular disease.
We are at the precipice of a profound public health crisis. If insulin has been around for nearly fifty years, and production has become cheaper over time, how did we get here? And what can synthetic biology do about these circumstances?
The cost burden of insulin
NBC News
In the early 1900s, Frederick Banting and Charles Best, two scientists at the University of Toronto, found that insulin extracted from dogs pancreases could effectively regulate blood glucose levels. The discovery was earth-shattering, marking the first hope of a feasible treatment for diabetics.
GettySynBioBeta
Insertion Of Gene Into A Vector
for the human insulin gene to be inserted into a bacterium, there has to be an intermediate carrier of the gene called a vector & this was a plasmid. plasmids are small circular pieces of DNA found in many bacteria. plasmids can freely move into bacterium cells and if we are able to insert the human DNA inside the plasmid & then insert plasmid into a bacterium. To obatin the plasmids from the bacteria containing them, these bacteria frist had to be mixed with enzymes to dissolve their cell walls. then centrifuged so that large organelles e.g chromosomes & small ones like plasmids would be seperated. restriction enzymes were used to slice open the the circular DNA making up the plasmid. sticky ends were added again but this time the nucleotide used to make them conatined cytosine & guanine bases on their ends paired up. DNA ligase was then used to link the nucleotide backbone together so that the human insulin gene became part of tthe plasmid. this was the manufacture of recombinant DNA.
Recommended Reading: What Is A High Blood Sugar Reading
What Are Genetically Modified Organisms
Genetically modified organisms are any plant, animal, or bacteria that has been altered at the genetic level in a laboratory. These organisms do not occur naturally. Genetic scientists can take genes from one organism and add them to another, or they can remove genetic material to get rid of undesired traits.
Creating GMOs
Genetically modified organisms are created for a variety of applications. Scientists have created crops that are more resistant to weather, pests, and chemicals, all while providing higher yields. Theyre also working toward increasing the nutritional content of food, especially for foods sent to impoverished nations. For example, a new type of rice called golden rice is being developed to supply nutrition-poor areas with a reliable source of vitamin A.
GMOs are also used to make a variety of biofuels like corn-derived ethanol and algae biodiesel, as well as numerous medical products like growth hormones and insulin.
Genetically modified animals also exist. Examples include goats that create spider silk proteins in their milk, fish that glow in the dark under ultraviolet light, and sheep that glow green.
Notable uses of GMOs
GMOs were once used to prevent the destruction of an entire industry. In the 1990s, the Hawaiian papaya was saved from a devastating virus, thanks to the creation of a genetically modified papaya that was resistant to the virus.
GMO safety
Avoiding GMO foods
The debate on GMOs
An Example Of Genetic Engineering: Insulin Production
Normally, insulin is produced in the pancreas, but in people with type 1 diabetes, there is a problem with insulin production. People with diabetes, therefore, have to inject insulin to control their blood sugar levels. Genetic engineering has been used to produce a type of insulin in yeast and in bacteria like E. coli that is very similar to our own. This genetically modified insulin, Humulin was licensed for human use in 1982.
To produce genetically-engineered insulin, a small, circular DNA called a plasmid is extracted from the bacteria or yeast cell. A small section is then cut out of the circular plasmid by restriction enzymes that act as molecular scissors. The gene for human insulin is inserted into the gap in the plasmid, creating a genetically modified plasmid.
This genetically modified plasmid is introduced into a new bacteria or yeast cell. This cell divides rapidly and starts making insulin. To create large amounts of the cells, the genetically modified bacteria or yeast are grown in large fermentation vessels that contain all the nutrients they need. The more the cells divide, the more insulin is produced. When fermentation is complete, the mixture is filtered to release the insulin. The insulin is then purified and packaged into bottles and insulin pens for distribution to patients with diabetes.
Mosquitos and the Lethal Gene
For another example of genetic engineering, check out HHMI Biointeractives Genetically Modified Mosquitos video.
Recommended Reading: Low A1c In Nondiabetic
How The Insulin Project Started
Significant advances resulting from the somatostatin and insulin projects.
After Itakura worked for about a year to make the lac operator DNA using his phosphotriester method, it was found that the final product was not adequately pure as measured by binding to the lac repressor, so we needed a way to further enrich for the correct, functional sequence. At this time, it was not possible to purify DNA according to a base sequence, but, driven by necessity, we realized that cloning, using methods very recently developed by Herbert Boyer , and then screening for the correct sequence would function to purify and then produce the desired DNA fragment. This led to a collaboration with Herbert W. Boyer and Herbert Heyneker, a postdoctoral fellow in Boyers laboratory. Heyneker was quickly successful in cloning the chemically synthesized lac operator and showing, for the first time, that cloned, chemically synthesized DNA could function in vivo as a ligand for its protein target .

