We Know Some People Get Confused Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes And Were Often Asked About The Differences Between Them
Although type 1 and type 2 diabetes both have stuff in common, there are lots of differences. Like what causes them, who they affect, and how you should manage them. There are other types of diabetes like gestational and MODY. But this page is mainly about the differences between type 1 and type 2.
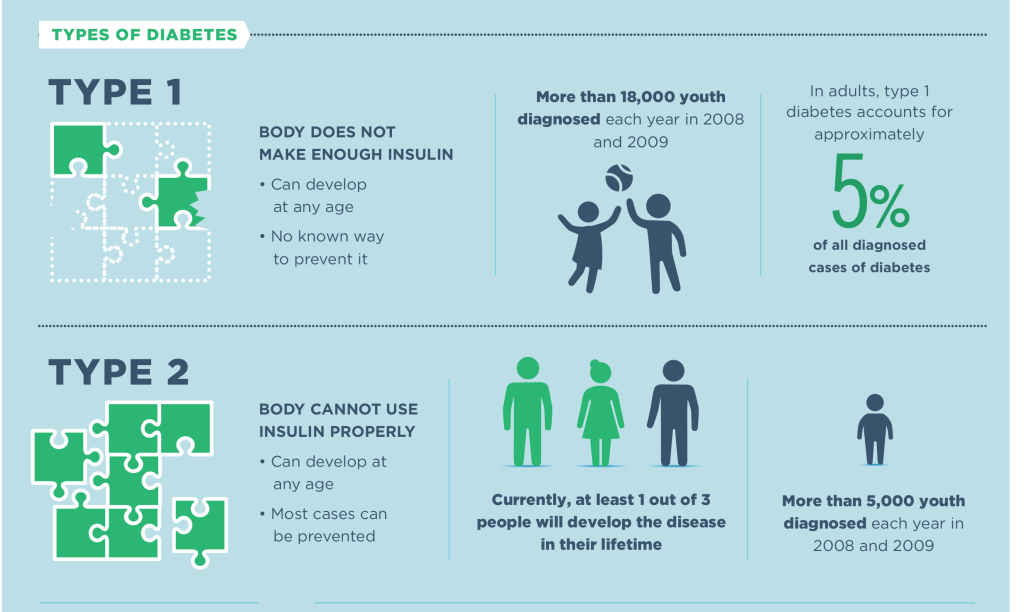
For a start, type 1 affects 8% of everyone with diabetes. While type 2 diabetes affects about 90%.
Lots of people get confused between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. This can mean you have to explain that what works for one type doesn’t work for the other, and that there are different causes.
The main thing to remember is that both are as serious as each other. Having high blood glucose levels can lead to serious health complications, no matter whether you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes. So if you have either condition, you need to take the right steps to manage it.
Because Of Their Different Causes The Treatment Plans For Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Are Also Slightly Different
“People with type 1 diabetes need multiple insulin injections a day or a continuous infusion through an insulin pump,” O’Malley says. They also need to check their blood sugar regularly, usually by pricking a finger and using a glucose monitor to test a drop of blood. “Type 1 is not yet reversible; people with type 1 diabetes need to be on insulin for the rest of their lives,” O’Malley says.
In both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, regular exercise and a balanced diet are also important for keeping blood sugar levels relatively steady, according to the American Diabetes Association. People with diabetes should work with a registered dietitian to find a sustainable way of eating that balances carbohydrate intake throughout the day.
In type 2 diabetes, it’s possible for some patients to manage the condition with diet alone, O’Malley says. In fact, type 2 diabetes is sometimes reversible with proper diet and weight maintenance. But, O’Malley says this reversal can be difficult to maintain long-term. “I focus on how to control diabetes, as opposed to reversing it.”
Although some people with type 2 diabetes might use insulin injections for treatment , this isn’t common. Instead, patients are often prescribed medications meant to keep blood sugar levels low and/or improve insulin sensitivity.
Ultimately The Goal In Managing Both Types Of Diabetes Is To Keep Blood Sugar Levels Steady Over Time
The goal of diabetes treatment-whether through insulin injections, medication or proper diet-is to keep blood sugar levels as steady as possible to minimize potential complications. All people with diabetes should see a doctor for an A1C test two to four times a year, according to the NIDDK. The test results show average blood glucose level over the past three months, and the goal for many people with diabetes is for that level to remain below 7%.
Diabetes is a chronic condition, and both types of diabetes require long-term treatment. But with proper management, patients can lead long, healthy lives.
What Are The Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar Difference Between Diabetes 1 And 2
Symptoms include blurred vision, dry mouth, quick or irregular heart beat, headache, dizziness, fatigue, constipation, and swollen feet or hands. You might also experience indigestion, regular urination, restlessness, fatigue, irritation, insomnia, and chills. See a medical professional instantly if you experience any of these signs. These signs may also show other conditions, so it is very important to have your physician inspect you out completely.
Concerned That You Might Have Type 1 Or Type 2 Diabetes Please Come See Us
If you have diabetes, either type 1 or type 2, or are worried that you’re at risk of developing it and would like guidance about managing this condition, please call 232-1919 to make an appointment with one of our Westchester Health endocrinologists. We’ll examine you, evaluate your symptoms, possibly perform some tests, and together with you, decide on the best course of treatment and lifestyle changes that can improve your health and reduce your risk of complications. Whenever, wherever you need us, we’re here for you.
In Type 2 Diabetes Your Body Produces Insulin But It Doesn’t Work Properly
“In type 2 diabetes, you produce insulin, but the main issue is that the rest of your body does not listen to it,” O’Malley explains. “We call this insulin resistance.” When blood sugar is high and insulin is released, your body ignores it. Just like in type 1 diabetes, your blood sugar stays high, your liver releases even more glucose, and other cells don’t get the energy they need.
“With time, some patients with type 2 diabetes may start to produce less insulin, but not to the same extent as with type 1,” O’Malley says.
Although some people are genetically predisposed to developing type 2 diabetes, lifestyle factors also play a role. According to the NIDDK, a person is more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if they are overweight or obese, have high blood pressure, have high cholesterol or are not physically active. People over the age of 45, or with a history of heart attack or stroke, are also more likely to develop the disease.
Although people with type 2 diabetes sometimes experience the same symptoms as those with type 1 diabetes prior to diagnosis, many have no symptoms at all . Doctors routinely test for diabetes using blood glucose tests in patients over 45, or patients with two or more other risk factors, according to the NIDDK. As in type 1 diabetes, glucose levels of 126 or above for the fasting plasma glucose test, or 200 or above for the oral glucose tolerance or random plasma glucose tests, are indicative of diabetes.
What Are The Chances Of Developing Diabetes If You Have Prediabetes
If you have prediabetes, you are at risk of developing diabetes. Your degree of risk depends on where your glucose and A1C levels fall within the ranges in the table above. If your numbers are toward the lower end of the range, you are at a lower risk of developing diabetes. If your numbers are toward the higher end of the range, you are at a higher risk of developing diabetes.
There is no reliable way to tell how fast you could progress from prediabetes to diabetes. It depends on your body, diet, level of activity, and the severity of disease.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention refers to a prediabetes diagnosis as “your chance to prevent type 2 diabetes.” Many people who find out they have prediabetes take their diagnosis as a warning to make lifestyle changes in order to reverse their prediabetes diagnosis and avoid developing diabetes.
The ADA offers an online type 2 diabetes risk test that you can take to find out what your risk is.
Both Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Have To Do With The Hormone Insulin
Without getting too deep in biochemistry, it’s important to know that insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas when levels of blood glucose in the body are high-that is, right after a meal or snack that contains carbohydrates, which are made of glucose and other sugars. In a nutshell, insulin tells your body to shuttle glucose to cells for energy, and to store glucose in the liver and other tissues. When this happens, your blood sugar levels lower, your body gets the energy it needs, and any leftover glucose is stored and saved for when you need energy between meals.
Read more:12 Healthy Ways to Lower Your Blood Sugar
How Do Diet And Exercise Effect Type1 And Type2 Diabetes Mellitus
The food choices one make will affect the blood sugar control of a person with either type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Eating foods very high in sugar or simple carbohydrates will raise blood sugar significantly. A person needs to eat a balanced diet that includes some carbohydrates along with protein and fat. Proteins and fats eaten along with carbohydrates will slow the absorption for a less significant blood sugar rise. A nutritionist may be able to help create a food plan that will be beneficial.
Exercise is an important component of diabetes treatment. While helping to keep the cardiovascular system healthy, exercise can also lower blood sugar. For children, exercise can simply be outdoor games, dancing, or sports.
What Are The Differences Between The Causes Of Type 1 And Type 2
Type 1 diabetes causes
Type 1 diabetes is believed to be due to an autoimmune process, in which the body’s immune system mistakenly targets its own tissues . In people with type 1 diabetes, the beta cells of the pancreas that are responsible for insulin production are attacked by the misdirected immune system. This tendency for the immune system to destroy the beta cells of the pancreas is likely to be, at least in part, genetically inherited, although the exact reasons that this process happens are not fully understood.
Exposure to certain viral infections or other environmental toxins have been suggested as possible reasons why the abnormal antibody responses develop that cause damage to the pancreas cells.
Type 2 diabetes causes
Both diabetes type 1 and diabetes type 2, require good control over their diet by eating foods that help regulate blood sugar, exercise, and in most patients, medical treatments to allow the patient to remain in good health.
What Does Treatment Look Like With Prediabetes And Diabetes
In most cases, the first treatment recommendations for prediabetes will be lifestyle changes. Your healthcare provider will likely recommend improving your diet and exercising more. Reducing your sugar intake can help lower your blood sugar. Physical activity makes the cells of your body more sensitive to the effects of insulin. This means insulin can more effectively remove sugar from your blood and give it to cells to be used as energy. Many healthcare providers will recommend following an ADA meal plan and being physically active for at least 30 minutes a day, 5 days a week.
In some cases, a healthcare provider may recommend taking if you are diagnosed with prediabetes. Metformin is an effective diabetes medication that lowers the amount of sugar your liver makes and keeps sugar in your diet from being absorbed into the bloodstream. Metformin may help keep your prediabetes from turning into diabetes.
If you are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, your treatment will depend on how severe your condition is. Most people with type 2 diabetes will take metformin. Your healthcare provider may also prescribe other oral and injectable diabetes medications. People who have uncontrolled diabetes for a long time may eventually need to take insulin to make up for the insulin their bodies are no longer producing.
–––
The Difference Between Type 1 Diabetes And Type 2 Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes is a chronic condition in which blood sugar levels become too high due to the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin.
- Type 2 Diabetes is a chronic condition in which blood sugar levels become too high due to the body developing resistance to insulin.
This question, along with many others, is typical of proceedings at our First Aid course in Robina. Our trainers work hard to fill the knowledge gaps for soon-to-be certified students of First Aid from Varsity Lakes and surrounding Robina suburbs.
First Aiders need to be able to deal with a medical emergency involving Diabetes. In Australia, people are diagnosed with Diabetes at a rate of one every 5 minutes.
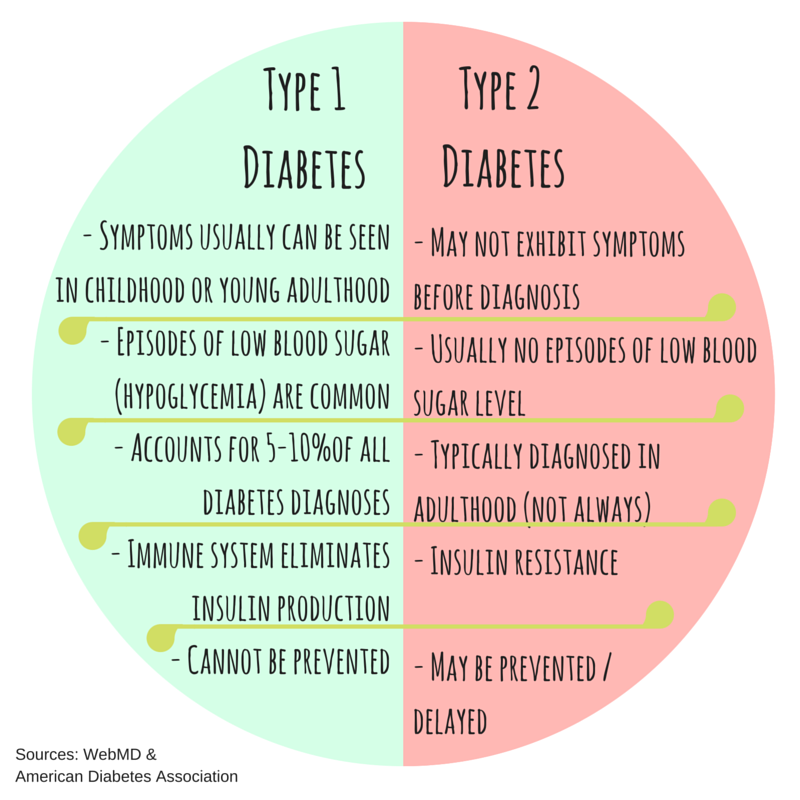
- Type 1 accounts for 10% of Diabetes in Australia and is increasing
- Type 2 accounts for 85% of Diabetes in Australia and is increasing
Let’s dig a little deeper into the mysteries of Diabetes, including talk of a Type 3 Diabetes.
What Is The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Glucose is a type of sugar. It comes from food and also is created in the liver. Glucose travels through the body in the blood. It moves from the blood to cells with the help of a hormone called insulin. Once glucose is in those cells, it can be used for energy. Diabetes mellitus is a condition that causes a buildup of glucose in the blood and makes it difficult for the body’s cells to get enough energy. There are two primary kinds of diabetes mellitus, type 1 and type 2.
In short, both types result in high levels of blood glucose. Type 1 is an autoimmune disease, caused by genetic and environmental factors, that results in too little insulin being produced by the body. Type 2 is influenced by lifestyle choices and results in the body not being able to use its insulin efficiently. According the Centers for Disease Control , “Type 2 diabetes accounts for about 90% to 95% of all diagnosed cases of diabetes, and type 1 diabetes accounts for about 5%.”
What Are The Risk Factors For Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Risk factors for type 1 diabetes include:
- Family history: People with a parent or sibling with type 1 diabetes have a higher risk of developing it themselves.
- Age: Type 1 diabetes can appear at any age, but it’s most common among children and adolescents.
- Geography: The prevalence of type 1 diabetes increases the farther away you are from the equator.
- Genetics: The presence of certain genes points to an increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
You’re at risk of developing type 2 diabetes if you:
- have prediabetes, or slightly elevated blood sugar levels
- are carrying excess weight or have obesity
- are Black, Hispanic, American Indian, or Alaska Native
- have an immediate family member with type 2 diabetes
The Difference Between Type1 And Type2 Diabetes Mellitus
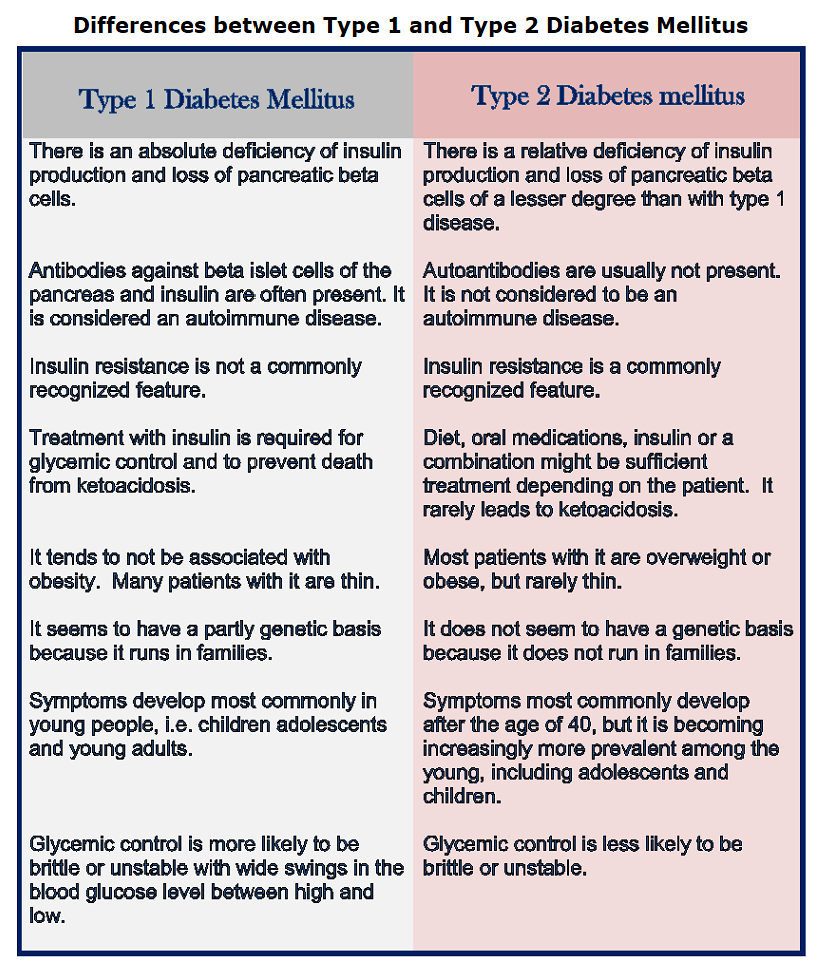
There are several differences between type1 and type2 diabetes mellitus. First, type 1 diabetes most often develops in young children while type2 diabetes can occur at any age. Additionally, type1 patients are dependent on insulin because their pancreas does not produce any. Those with type2 may produce some insulin in their pancreas, but they do not produce enough, or it is not used efficiently in their bodies.
Another difference between the two types is that those with type one can experience episodes of low blood sugar as well as high levels while those with type2 rarely do. Moreover, type1 diabetes cannot be prevented, but, in many cases, type2 can be avoided. Finally, there are many more cases of type2 diabetes are documented.
Whats The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that impacts 1.25 million American children and adults. For type 1, the immune system destroys the cells that release insulin, eventually leading to the complete inability to produce insulin in the body. Type 1 generally manifests at a young age and lasts a lifetime.
Type 2 diabetes has multiple contributing factors including genetics and lifestyle factors such as obesity and inactivity. The disease generally arises during adulthood and oftentimes can be reversed or controlled through diet and exercise. 90-95% of those diagnosed with diabetes have type 2.
Differences Between Type 1 Diabetes And Type 2 Diabetes
| Type 1 diabetes | |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Former names | |
|
|
Can You Manage Your Diabetes With Diet Plan And Workout
Yes, you definitely can. Diet and workout not only help control your weight, however they likewise assist manage your blood sugar level. Exercise helps increase your metabolic process and help you burn more energy. These two aspects integrate to give you more endurance and increased ability to manage your diabetes.
What Are The Complications Of Prediabetes And Diabetes
The main complication of prediabetes is developing type 2 diabetes. Diabetes is not just an inconvenient condition. Over time, having too much sugar in the blood can lead to serious cardiovascular complications, including:
Keeping your blood sugar controlled is the most effective way to prevent complications of type 2 diabetes. But don’t forget about blood pressure and cholesterol, too. Your risk of complications increases if you have high blood pressure and high cholesterol in addition to diabetes.
What Happens When You Have Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
If you have either type 1 or type 2 diabetes, it means you have too much glucose in your blood. This is the same for both types. But the difference between them is how this happens.
If you have type 1 diabetes, it means you have an autoimmune condition. This means your body has attacked and destroyed the cells that make a hormone called insulin. So you can’t make insulin anymore.
We all need insulin as it helps take the glucose from our blood into our body’s cells. We then use this glucose for energy. Without insulin, the glucose level in your blood gets too high.
Type 2 diabetes is different. If you’ve got type 2, either your body doesn’t make enough insulin, or your insulin doesn’t work properly. This is known as insulin resistance. Like type 1, this means the level of glucose in your blood is too high.
In Type 1 Diabetes Your Body Doesn’t Produce Insulin
“Type 1 diabetes is due to not producing any insulin,” says Grenye O’Malley, M.D., an endocrinologist at the Mount Sinai Diabetes Center and an assistant professor at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. “The most common cause is an autoimmune process in which your body attacks your own pancreas.” Without insulin, your body doesn’t know to use glucose for energy , even after you’ve eaten and there’s plenty of glucose in your blood. In fact, your liver ends up releasing more glucose into your blood-because glucose isn’t being shuttled to your liver for energy and storage, it thinks you’re starving. So, your blood sugar stays high , and other cells don’t get the energy they need, which can lead to serious health problems.
“Type 1 is typically diagnosed at a younger age, but it can be diagnosed at any age,” O’Malley says. Doctors and scientists aren’t exactly sure what causes type 1 diabetes, but it’s likely a genetic condition, and it isn’t caused by diet or other lifestyle factors. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases , a patient with type 1 will experience symptoms like increased hunger and thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, numbness or tingling in the hands and feet, sores that don’t heal, and unexplained weight loss.
Type 1 And Type 2 Affect Different Groups Of People
Type 1 diabetes used to be called “Juvenile Onset Diabetes” because, although it can affect anyone, it most often strikes kids aged four to six and those aged 10 to 14.
Type 2 diabetes, originally called adult-onset diabetes, mostly affects adults, but the age at diagnosis is getting younger.
“There’s been more of a gray area within the last decade or so, where you see an older onset of what actually is type 1 and a younger onset of type 2 diabetes,” says Gonzalvo. “There has been more of a merging rather than a separation.”
Other distinctions remain. “Type 1 diabetes tends to be diagnosed in younger individuals of normal weight, though they may have a personal or family history of autoimmune disease,” Deena Adimoolam, MD, a specialist in endocrinology and preventative medicine, who practices in New Jersey, tells Health. “Type 2 diabetes tends to be diagnosed in older individuals who are overweight or obese.”
The Emotional Impact Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Living with type 1 or type 2 diabetes can sometimes feel overwhelming.
Both types are different but feeling down or anxious because of your diabetes can affect anyone. It is important to understand that a long-term condition can come with an emotional impact, no matter how it has been caused or how you treat it.
If you’re struggling with your diabetes, remember that you’re not alone.
There is lots of support available to you, like our helpline. There you can speak to our highly trained advisors about how you’re feeling. And you can also speak to people who are going through similar experiences on our forum. There are lots of things you can do to help yourself and it’s just about finding what works for you.
It can be frustrating to explain the differences between type 1 and type 2.
Both types face confusion over what causes the condition and how it can be treated. This will be slightly different whether you’re type 1 or the more common type 2. Just because something is more common, doesn’t mean it is understood.
And while it is emotionally draining to constantly correct people, you should also know that you’re not alone. There are many people living with diabetes facing similar questions and struggles, regardless of type. You can reach out to them to give or receive support in the forum and at local groups.
Type 1 & 2 What Is The Difference Between The Two
Diabetes – Can It Be Prevented? How Is Treated?
Our bodies cells and organs need energy in order to perform various functions. Although many tissues use fat or proteins as a source of energy, some organs such as the brain and red blood cells rely on glucose for energy needs. A hormone called insulin, produced by the beta cells of the pancreas helps to convert blood sugar into usable energy, it also helps to control blood sugar levels and keep them in the normal range. Sometimes the pancreas is unable to produce enough or any insulin or fails to use insulin well, this results in an increase in the blood glucose levels.
Prediabetes Vs Diabetes: Whats The Real Difference
Megan N. Freeland, PharmD, RPh
Have you ever been told you have borderline diabetes? What about actual diabetes? Terms like prediabetes, borderline diabetes, and type 1 and type 2 diabetes can be confusing and overwhelming. In this post, we’ll compare prediabetes and diabetes. Is there a difference between them, and if so, what is it?
The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
How many times have you read an article that said “avoid these foods if you have diabetes” or “if you are prediabetic?” The truth is, almost all of this information is referencing type 2 diabetes, as it’s more common than type 1. In fact, of the 30.3 million Americans who have diabetes, an estimated 90 to 95 percent of these individuals have type 2. However, each type requires different treatment and management.
To explain the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, we consulted endocrinologist Dr. Kathleen Wyne of The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, so you never confuse the two ever again.

