Blood Sugar Levels: What’s Normal What’s Not And How To Measure
What do blood glucose levels mean and what range is healthy? Here’s what you need to know.
Sugar can lead to high blood sugar and contributes to the development of diabetes.
We all want to keep track of our health in every way we can — you may weigh yourself, keep track of your blood pressure or monitor your resting heart rate. But how close of an eye do you keep on your blood sugar?
People with diabetes are all too familiar with their blood sugar levels, but the rest of us might not even think about it much. However, consistently high blood sugar levels can coexist with Type 2 diabetes and cause serious health conditions like kidney disease, nerve problems or stroke.
While that’s no reason to panic, when it comes to our health, it’s important to know exactly what’s going on inside of our bodies. Without further ado, let’s get into what blood sugar means, how to measure it and everything else you need to know.
Our Health & Wellness newsletter puts the best products, updates and advice in your inbox.
Recommended Blood Sugar Targets
For people with type 1 diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends that blood sugar targets be based on a person’s needs and goals. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about these goals. A general guideline is:
Before meals, your blood sugar should be:
- From 90 to 130 mg/dL for adults
- From 90 to 130 mg/dL for children, 13 to 19 years old
- From 90 to 180 mg/dL for children, 6 to 12 years old
- From 100 to 180 mg/dL for children under 6 years old
After meals , your blood sugar should be:
- Less than 180 mg/dL for adults
At bedtime, your blood sugar should be:
- From 90 to 150 mg/dL for adults
- From 90 to 150 mg/dL for children, 13 to 19 years old
- From 100 to 180 mg/dL for children, 6 to 12 years old
- From 110 to 200 mg/dL for children under 6 years old
For people with type 2 diabetes, the American Diabetes Association also recommends that blood sugar targets be individualized. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about your goals.
In general, before meals, your blood sugar should be:
- From 70 to 130 mg/dL for adults
After meals , your blood sugar should be:
- Less than 180 mg/dL for adults
Normal Fasting Blood Sugar For Person Without Diabetes
A normal fasting blood glucose for someone who does not have diabetes ranges from 70 to 99 mg/dl. The American Diabetes Association recommends a routine screening for type 2 diabetes starting at age 45. If the results are normal, the screening should be repeated every 3 years.
If have diabetes risk factors, which include being overweight or obese, having a family history of type 2 diabetes, having a history of gestational diabetes, or being of a certain race/ethnicity , you should be screened for diabetes sooner than age 45.
Children and adolescents who have diabetes symptoms or who are overweight and have a family history of type 2 diabetes, are of African American, Latino, Asian American, Native American or Pacific Islander descent, who have signs of prediabetes or a mother who had gestational diabetes should be tested beginning at age 10 and then every 3 years thereafter.
A fasting blood sugar of 100 to 125 mg/dl is indicative of prediabetes, which is a condition where blood sugar levels are above normal but not high enough to be considered diabetes. Prediabetes is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, heart disease and stroke. Its managed by lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication.
Read Also: Symptoms Of Diabetes Mellitus Type 1
Who Should Get An A1c Test And When
Testing for diabetes or prediabetes:Get a baseline A1C test if youre an adult over age 45or if youre under 45, are overweight, and have one or more risk factors for prediabetes or type 2 diabetes:
- If your result is normal but youre over 45, have risk factors, or have ever had gestational diabetes, repeat the A1C test every 3 years.
- If your result shows you have prediabetes, talk to your doctor about taking steps now to improve your health and lower your risk for type 2 diabetes. Repeat the A1C test as often as your doctor recommends, usually every 1 to 2 years.
- If you dont have symptoms but your result shows you have prediabetes or diabetes, get a second test on a different day to confirm the result.
- If your test shows you have diabetes, ask your doctor to refer you to diabetes self-management education and support services so you can have the best start in managing your diabetes.
Managing diabetes:If you have diabetes, get an A1C test at least twice a year, more often if your medicine changes or if you have other health conditions. Talk to your doctor about how often is right for you.
How Can I Pay For Tests And Diabetes Supplies
Medicareexternal icon, Medicaid, and most private insurance plans pay for the A1C test and fasting blood sugar test as well as some diabetes supplies. Check your plan or ask your health care team for help finding low-cost or free supplies, and see How to Save Money on Diabetes Care for more resources.
Don’t Miss: Not Taking Insulin Side Effects
Why Do I Need To Know My Blood Sugar Numbers
Your blood sugar numbers show how well your diabetes is managed. And managing your diabetes means that you have less chance of having serious health problems, such as kidney disease and vision loss.
As you check your blood sugar, you can see what makes your numbers go up and down. For example, you may see that when you are stressed or eat certain foods, your numbers go up. And, you may see that when you take your medicine and are active, your numbers go down. This information lets you know what is working for you and what needs to change.
Random Plasma Glucose Test
Random blood sugar testing is used in people who have symptoms of diabetes. A random blood sugar test can be done at any time of day. The test looks at blood sugar without considering your last meal.
No matter when you last ate, a random blood sugar test of 200 mg/dL or above suggests that you have diabetes. This is particularly true if you already have symptoms of diabetes.
Your doctor will go over your results with you. Heres what your test results could mean:
- random blood sugar of 200 mg/dL or more = diabetes
- random blood sugar level between 140 and 199 mg/dL = prediabetes
- random blood sugar less than 140 mg/dL = normal
Recommended Reading: Is Metformin Addictive
Is Diabetes Diagnosed The Same Way In Every Country
There are four methods of diagnosing diabetes, which are used around the world. They are:
Low Blood Sugar Symptoms
Hypoglycemia happens when blood glucose levels drop too low. Low blood sugar can be caused by many things including the two different types of diabetes, certain medications, alcohol, endocrine disorders, eating disorders, pregnancy , and disorders of the liver, kidneys, or heart.
Here are some of the most common symptoms that someone with low blood sugar might experience:
- Lightheadedness
- Fainting
- Tingling lips
If your blood sugar is low you might start to feel some of the first signs of hypoglycemia like dizziness, lightheadedness, or sweating. The only way to know for sure if your blood sugar is low is to test it with a glucose meter or other glucose monitoring device.
If you dont have access to these tools and start to feel the symptoms of low blood sugar, consume 15 grams of carbs or take a quick dissolve glucose tablet to raise your blood sugar levels and avoid further symptoms, according to the American Diabetes Association . Once your blood sugar is back in its target range, you can have a snack or meal to make sure it doesnt drop again.
Here are some other lifestyle and medicinal treatments that can help treat hypoglycemia:
- Eat a healthy diet full of whole foods that are minimally processed.
- Take prediabetes or diabetes medications as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Use a glucagon kit in emergencies. Glucagon is a hormone that raises blood sugar levels quickly.
Don’t Miss: Metformin Highest Dose
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Your blood sugar levels are a critical part of your overall health and your bodys ability to function properly on a daily basis. For those of us with diabetes, striving to achieve normal blood sugar levels is a constant, hour-by-hour pursuit. And it isnt easy.
In this article, well look at normal blood sugar levels and goal ranges for a non-diabetics body, and realistic blood sugar goals for people with prediabetes, type 1, and type 2 diabetes.
How Do You Know What Your Blood Glucose Level Is
For the most part, you cant feel what your blood glucose level is unless its fairly high or its low. You may not even always have symptoms of either high or low blood glucose in fact, many people with type 2 diabetes dont have the usual symptoms of high blood glucose, and for this reason, its not uncommon for people to go undiagnosed for many years.
The best way to know your blood glucose level is to check it with a glucose meter. This means doing a fingerstick with a lancet and getting a drop of blood onto a test strip, then inserting the strip into the meter for a reading. Your doctor may be able to give you a meter free of charge, but youll likely need to pay for test strips and lancets. But check with your health plan, as there are likely one or two preferred meters that they want you to use.
Another way to know what your glucose levels are up to is to use a continuous glucose monitor, or CGM, which reads glucose in the interstitial fluid about every 5 minutes. Continuous glucose monitoring is expensive and may or may not be covered by your health plan.
Read Also: Side Effects Of 70 30 Insulin
Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart For Diabetic Adults Age Wise
| Chart of Normal Blood Sugar Levels for Diabetic Adults |
|---|
| Age |
| 100 to 140 mg/dL |
Healthy blood sugar levels in diabetic adults age wise:
Summary
Healthy diabetic adults should maintain a blood sugar level of 70 to 130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL after 2 hours of meals. Pregnant women should maintain a blood sugar level of 95-140 mg/dL to avoid complications. This can be done with the right habits in place that help you maintain your sugar level without getting stressed about it.
Are Low Blood Sugar Levels Dangerous

Yes, low blood sugar symptoms can cause problems such as hunger, nervousness, perspiration, dizziness and even confusion if untreated, low blood sugar may result in unconsciousness, seizures, coma, or death. Low blood sugar levels begin at 70 mg/dL or less. People with diabetes who take too much medication or take their usual amount but then eat less or exercise more than usual can develop hypoglycemia. Although much rarer, hypoglycemia may develop in some people without diabetes when they take someone elses medication, have excessive alcohol consumption, develop severe hepatitis, or develop a rare tumor of the pancreas . The treatment for hypoglycemia is oral glucose intake (15. 0 grams of sugar, for example, 1 tablespoon of sugar, honey, corn syrup, or IV fluids containing glucose. Recheck your blood sugar levels in about 15 minutes after treatment is advised.
Don’t Miss: Glucose Over 400
A1c Goals Should Be Individualized
A1c goals should be individualized based on the individual capabilities, risks, and prior experiences, explains Gary Scheiner, MS, CDE, founder of Integrated Diabetes, and author of Think Like a Pancreas.
For example, we generally aim for very tight A1c levels during pregnancy and more conservative targets in young children and the elderly.
However, Scheiner highlights important factors that could justify aiming for a higher A1c, like hypoglycemia unawareness, which is described as when a person with diabetes no longer feels the oncoming warning signs of low blood sugar. This can put you at significant risk for severe low blood sugars resulting seizures or death. To reduce that risk, you would aim for higher target blood sugar ranges.
Someone with significant hypoglycemia unawareness and a history of severe lows should target higher blood glucose levels than someone who can detect and manage their lows more effectively, adds Scheiner. And certainly, someone who has been running A1cs in double digits for quite some time should not be targeting an A1c of 6% better to set modest, realistic, achievable goals.
Learn how to lower your A1c in DiabetesStrongsA1C Guide.
Are The Test Results Ever Wrong
Initially, your test results may vary. For instance, a blood sugar test may show that you have diabetes but an A1C test may show that you dont. The reverse can also be true.
How does this happen? It could mean that youre in an early stage of diabetes, and your blood sugar levels may not be high enough to show on every test.
The A1C test can be wrong in some people of African, Mediterranean, or Southeast Asian heritage. The test can be too low in people with anemia or heavy bleeding, and too high in people with iron deficiency anemia. Dont worry your doctor will repeat the tests before making a diagnosis.
Recommended Reading: Signs Of High Or Low Blood Sugar
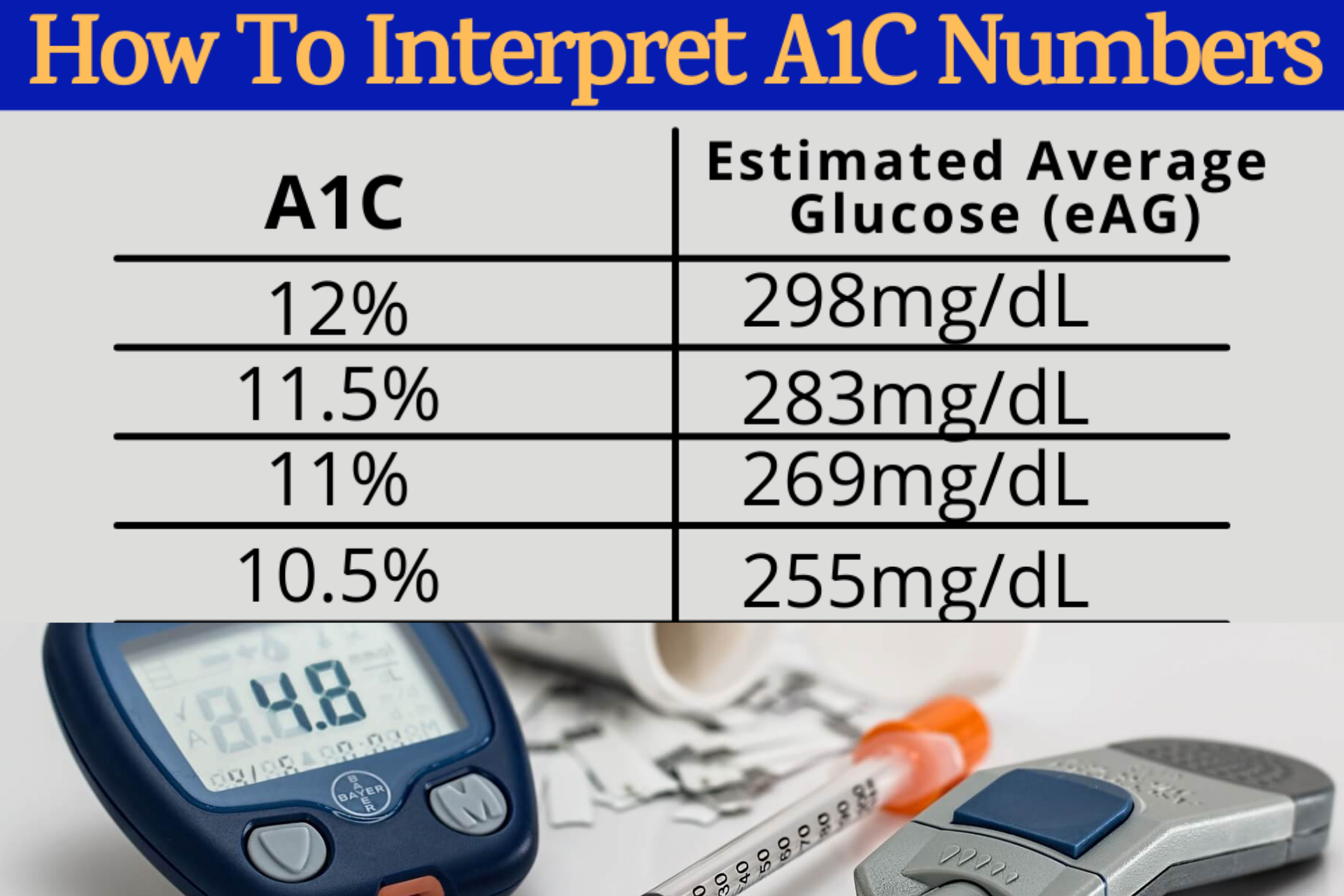
Official Hba1c Ada Recommendation For Someone With Diabetes
The American Diabetes Association recommends an HbA1C of less than 7% for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. A lower goal, such as less than 6.5%, may be appropriate for some people who have had diabetes for a shorter amount of time, for younger people, for those without heart disease, and/or for those with type 2 diabetes treated with lifestyle or metformin only. A higher HbA1C goal, such as less than 8%, may be appropriate for people with a history of severe hypoglycemia, a limited life expectancy, advanced diabetes complications, other illnesses, or for whom a lower HbA1C goal is difficult to achieve. Its important that people with diabetes discuss their target blood sugar goals with their healthcare provider.
HbA1C levels should be checked between two to four times per year in people who have diabetes.
Official Fasting Blood Sugar Ada Recommendation For Someone With Diabetes
The American Diabetes Association recommends a fasting blood sugar target of 80 to 130 mg/dl for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. However, the fasting blood sugar target may need to be individualized for certain people based on such factors as duration of diabetes, age and life expectancy, cognitive status, other health conditions, cardiovascular complications, and hypoglycemia unawareness. Its important that people with diabetes discuss their target blood sugar goals with their healthcare provider.
Also Check: Does Metformin Cause Gas
Living With Type 1 Diabetes:
Life with type 1 diabetes poses lifelong challenges for every member of the family.
People with type 1 diabetes should:
- Test blood glucose levels three or more times per day and adjust their insulin through injections or an insulin pump.
- Ensure insulin doses are balanced with food intake and level of daily activity. People with type 1 diabetes may experience low and high blood sugar levels, which should be carefully monitored and managed.
While living with type 1 diabetes requires a certain amount of daily structure, newer pumps and insulin products have provided more flexibility in the management of this condition.
A healthcare provider can provide advice to help properly manage blood glucose levels.
Whats My Target Range
You might be asking, what’s the normal range for blood sugar levels? The answer is, there is a healthy range that you should ideally be aiming for. The infographics above show the general guidelines, but your individual target range for your blood sugar levels may be different. Youll healthcare team will agree with you what it is.
Youll get different readings at different times of the day, depending on things like what youve eaten and how much you are moving around. Heres a guide to help you get started on finding your target range:
If youre a child with Type 1 diabetes
- when you wake up and before meals: 4 to 7mmol/l
- after meals: 5 to 9mmol/l
If youre an adult with Type 1 diabetes
- when you wake up and before meals: 5 to 7mmol/l
- before meals at other times of the day: 4 to 7mmol/l
If you have Type 2 diabetes
- before meals: 4 to 7mmol/l
- two hours after meals: less than 8.5mmol/l
Recommended Reading: Diabetic Reaction To Too Much Sugar

