Factors That Help In Deciding Where To Inject Insulin
There are a few factors that should be kept in mind while you inject insulin. It is important to inject the insulin injections in the right area so that you can avoid pain while taking these injections. Following are a few factors to be considered before taking insulin injections:
- The most important factor is the presence of fatty tissue or those areas where there is a decent quantity of fat.
- Accessibility of the area is another factor to be considered
- The rate and speed in which the hormone insulin is absorbed in the body. According to the Joslins Diabetes Deskbook, the rate in which the hormone is absorbed is different in different areas. It is most quickly absorbed in the abdomen followed by the arms, thighs, and finally the buttocks.
Basis the above factors, the following are the guidelines as to which can be the best place to inject insulin.
Insulin For Type 2 Diabetes
If you have type 2 diabetes and your doctor thinks insulin can help you, it doesnt mean you now have type 1 diabetes. You still have type 2 diabetes, but you’ve changed treatment.
If you have type 2 diabetes, you may not need to use insulin straight away. But some people have very high blood sugar levels when they are first diagnosed. Insulin can be used as a short-term treatment to help quickly bring down your blood sugar levels.
Some people may need to take insulin for a particular reason, like during pregnancy or a severe illness, or after surgery. But you may also need to start it as a treatment if other medications havent helped managed your blood sugar levels or are not appropriate for you.
If you need insulin it isnt your fault and it doesnt mean you havent managed your diabetes well. It’s simply another medication that can help to keep you as healthy as possible. Managing blood sugars effectively is really important in reducing your risk of future diabetes complications and insulin may be the most appropriate treatment choice for you. Many people with type 2 diabetes need to use it as treatment at some point.
Its still important to keep going to your appointments and manage your condition with healthy lifestyle choices. Staying active and eating a healthy diet will reduce the risk of complications from your diabetes.
Why You Should Rotate Your Insulin Injections
Every time you inject insulin into a certain area of your body, that location of skin and body fat is injured and has to heal. Over the course of years injecting insulin into your body, scar tissue will develop.
You may not see evidence of that scar-tissue on the outside of your body, but its there on the inside.
The more you inject insulin into the back of your arm, the more scar tissue will develop there. As people with diabetes, its very easy to get into the habit of injecting into the same spot over and over because its easy to reach and comfortable to access in the middle of a restaurant, for example.
But scar tissue will significantly affect your bodys ability to absorb the insulin from that last injection, and you could end up needing more insulin to do the same job even though your insulin needs didnt change. Instead, its just scar-tissue built-up and interfering with the absorption of your insulin dose.
Rotating your injection sites is critical.
- If you used your left arm for your lunchtime injection, you should use your right arm for your dinnertime injection.
- If you used the left side of your bum for your long-acting insulin injection last night, you should use your right side for tonights injection.
The more you can rotate the areas of your body and the exact spots on each area, the less scar-tissue will build-up and the more easily your body will absorb that insulin.
You May Like: Sx Of High Blood Sugar
Rotation Schemes An Example
In cooperation with people affected by diabetes, our specialists have developed site rotation schemes for the generally favored injection areas: the abdomen and the thighs. If you operate with long and short acting insulin, you can combine these injection areas perfectly.
- Start at either side of your navel.
- Work your injections in a line from the top to the bottom of your abdomen.
- Each day, you skip a little more away from your navel and start a new line.
- Use the whole surface of your abdomen. Depending on your fat layer, the last line could start almost at your flank.
- Leave as much space as possible between the injection spots. The more spacious the surface of your abdomen is, the more generous you may place your injections.
- When no more space is left to inject into, change to the other side of your navel and follow the same procedure.
Thighs
- Start with your left leg.
- Think of two lines down your thigh.
- In the morning, inject into the outer line and in the evening inject into the inner line.
- The next day, you move downwards to your knee and repeat the procedure.
- Stay approximately handbreadth clear of your knees.
- When you are done with one leg, proceed to the other one and repeat the procedure.
Rotate injection sites and injection areas to avoid lipos.
Rotating is key to maintaining predictable blood glucose levels.
Regularly check for lipos. If you detect any anomalies, please contact your physician.
Disposing Of Needles Syringes And Lancets
In the United States, people use more than 3 billion needles and syringes each year, according to the Environmental Protection Agency. These products are a risk to other people and should be disposed of properly. Regulations vary by location. Find out what your state requires by calling the Coalition for Safe Community Needle Disposal at 1-800-643-1643, or visiting their site at .
You arent alone in treating your diabetes. Before beginning insulin therapy, your doctor or health educator will show you the ropes. Remember, whether youre injecting insulin for the first time, running into problems, or just have questions, turn to your healthcare team for advice and instruction.
Recommended Reading: Symptoms Of High And Low Blood Sugar
Where Can Intravenous Injections Be Administered
An IV injection is usually given by a healthcare professional. A small plastic tube called a catheter is typically inserted into the vein for an IV injection to be administered through, especially when more than one injection is required. IV catheters are best placed where they are easy to access and the blood flow is good.
An IV catheter is most commonly placed into a vein in the:
- Forearm
- Antecubital fossa – the depression on the inside of the elbow joint
- Ankle, close to the foot – for small patients such as babies and neonates
When selecting a site to place an IV catheter its important to avoid infected areas of skin and placing a catheter in a flexible joint where it may bend. Injured or sore areas, and stiff or very thin veins should also be avoided.
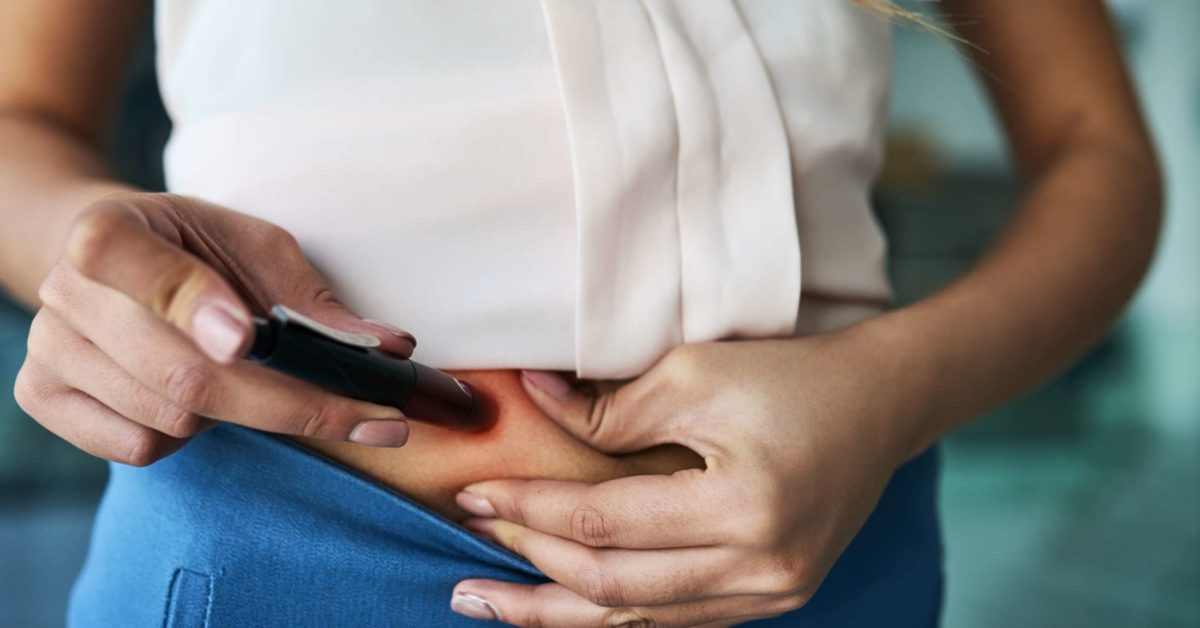
How Do I Inject The Insulin With A Syringe
- Wash your hands with soap and water. This will help prevent an infection. Dry your hands with a clean towel or paper towel.
- Clean the skin where you will inject the insulin. You can use an alcohol pad or a cotton swab dipped in alcohol.
- Grab a fold of your skin. Gently pinch the skin and fat between your thumb and first finger.
- Insert the needle straight into your skin. Do not hold the syringe at an angle. Make sure the needle is all the way into the skin. Let go of the pinched tissue.
- Push down on the plunger to inject the insulin. Press on the plunger until the insulin is gone. Keep the needle in place for 5 seconds after you inject the insulin.
- Pull out the needle. Press on your injection site for 5 to 10 seconds. Do not rub. This will keep insulin from leaking out.
- Throw away your used insulin syringe as directed. Do not recap the syringe before you throw it away.
Don’t Miss: How Can You Tell If Your Sugar Is High
Medications Given Using A Subcutaneous Injection
Medications administered by subcutaneous injection include drugs that can be given in small volumes . Insulin and some hormones are commonly administered as subcutaneous injections.
Other drugs that need to be given very quickly can also be administered via subcutaneous injection. Epinephrine comes in an automated injector form, called an EpiPen, thats used to quickly treat severe allergic reactions. While its intended to be given intramuscularly, epinephrine will also work if given subcutaneously.
Some pain medications like morphine and hydromorphone can be given this way as well. Drugs that prevent nausea and vomiting like metoclopramide or dexamethasone can also be given via subcutaneous injection.
Some vaccines and allergy shots are administered as a subcutaneous injection. Many other vaccines are administered as an intramuscular injection into muscle tissue rather than under the skin.
Rotating Injections At The Same Site
To prevent the development of fatty deposits and hard lumps in an injection site, it is vital that you place your injections in different areas at any given injection site. Follow these rules:
- Try to imagine your abdomen as being a clock. Inject along the clock so you remember where to inject the next dose of insulin
- Switch sides within a given area. If you inject your nighttime insulin into the right side of the abdomen on one night, inject it on the left side of your abdomen on the next night.
If, for example, you need to inject your insulin 4 times daily and decide to put all of the injections into your abdomen, pretend that your abdomen is a clock and inject your noontime dose at the 12 oclock position. Your next dose should then be at the 1 oclock position and the one after that should be at the 2 oclock position. Go around the clock so that you arent injecting the 12 oclock position until 4 days later. This allows that spot to have a rest.
You May Like: Diabetic Rash On Chest
Can I Reuse My Syringe
You may increase your risk for a bacterial infection when you reuse syringes. Ask your healthcare provider if it is safe for you to reuse a syringe. Do not reuse a syringe if you have an open wound, trouble seeing, or have an infection. The following are tips on how to safely reuse a syringe:
- Recap the needle as soon as you are done using it. Place the cap on a table or hard surface and slide the needle into the cap.
- Do not let the needle touch anything but clean skin or the top of the insulin bottle.
- Never share syringes with anyone.
- Do not clean your needle with alcohol. This will remove the coating that helps your needle slide easily into your skin.
- Throw out any syringe that bends or touches anything other than clean skin.
What Is Insulin Made Of
Insulin is made in different ways. You and your healthcare team will discuss which insulin you can take.
- Human insulin this is synthetic and made in a laboratory to be like insulin made in the body.
- Analogue insulin the insulin molecule is like a string of beads. Scientists have managed to alter the position of some of these beads to create genetically engineered insulin known as analogues.
- Animal insulin This isnt used much anymore, but some people find that insulin from animals works best for them. It is usually from a cow or pig.
You May Like: Pita Bread Good For Diabetics
Best Place To Inject And Absorption
The best place to inject insulin will depend on what type of insulin you are using and when you are using it. Your body absorbs insulin differently depending on where it is injected. Typically, insulin absorption is fastest in the abdomen, somewhat less quickly in the upper arms, slower in the thighs, and slowest in the buttocks.
You Can Become An Expert At Insulin Injections And Avoid Site Bruising With These Techniques Which Include Icing Places To Avoid Etc

Integrated Diabetes Services provides detailed advice and coaching on diabetes management from certified diabetes educators and dieticians. Insulin Nation IDS answers to questions submitted from the Type 1 diabetes community.
Q: Is it common to get bruises at the site of injection? What can you do about that?
A: There are many reasons that an injection site might develop a bruise. Try some of these techniques to decrease the chances of bruising:
Read Also: How Do You Know If You Have Type 1 Diabetes
Local Degradation At The Injection Site
Little is known about the fate of the insulin that does not reach the systemic circulation after injection into the SC tissue. Insulin degradation presumably takes place at the injection site, but the reported extent of degradation varies considerably between the few, mostly older studies that have been conducted so far . Nevertheless, insulin bioavailability varies for different types of insulin preparations indicating that some degradation occurs in the SC tissue. Insulin bioavailability has, for example, been estimated to be similar for human insulin and analogues in rapid-acting insulin preparations, whereas it is lowest for insulin suspensions and biphasic insulin mixtures, decreasing with the crystal-to-soluble ratio and with increasing concentrations . This may partly be explained by activation of the local immune response by insulin crystals: whereas degradation of soluble insulin preparations is assumed to occur enzymatically, invading macrophages are believed to play a major role in the degradation of insulin crystals . Consequently, besides affecting insulin absorption in general, SBF also influences bioavailability of crystalline insulin, specifically. This is probably due to a high sensitivity of crystalline insulin to blood flow changes, since higher SBF increases the dissolution of crystals and consequently decreases the time available for macrophage degradation .
Where Can Subcutaneous Injections Be Administered
If youre prescribed an injection that you have to administer yourself at home then its likely itll be a SC injection. This type of injection is used to administer medications like insulin for diabetes, hormone injections for fertility treatment and blood thinning agents to prevent blood clots.
SC injections need to be injected into an area on the body with subcutaneous fat. It is recommended that you inject a SC injection into:
- The lower abdomen , except for the 2 inches area around the navel
- The front or outer sides of the thighs
- The upper area of the buttock
- The upper outer area of the arms
When selecting an injection site take care to avoid areas where the skin is sunken or lumpy, or areas where you might inject into a muscle rather than subcutaneous tissue. Also avoid sites where the skin is injured or damaged.
Read Also: What Happens When You Take Metformin And Eat Sugar
General Tips For Administering An Insulin Shot
- Allow the insulin to come to room temperature before injecting, to avoid pain.
- Always use a new syringe and needle or pen needle.
- Always remove the needle before storing your insulin pen.
- Keep your insulin away from extreme hot or cold temperatures and store according to the manufacturers recommendations.
- Check your insulin vial for particles or anything that doesnt look right.
- Dispose of used needles safely.
- Create a plan for rotating injection sites.
Dont:
- Inject close to your belly button, near bony areas, or where you have a mole, scar, or wound.
- Use the same exact spot repeatedly to inject insulin.
- Let yourself run out of supplies. Always bring extra when traveling.
- Try to use expired insulin, as it may not work effectively.
- Forget to wear a medic alert ID in case you have a hypoglycemic event and cant speak for yourself.
- Forget to carry a rapid source of glucose.
Since insulin is a glucose-lowering medication, you should always be prepared in the event you need to treat a low blood sugar by carrying a rapid acting source of glucose with you, like a juice box, glucose tabs, or hard candy.
Principles For Teaching Patients
Some patients do not remember being taught all the aspects of injection technique when they started insulin therapy. It is therefore essential to review injection technique regularly nurses should not assume that patients injecting insulin are doing it correctly either from the start or over a period of time. The following should be revisited at least every year:
- Injection technique
- Correct technique for lifted skin fold if needed
- Site rotation
- Ability to check for lipohypertrophy
- Ability to re-suspend insulin correctly before injection
- Disposal of sharps.
You May Like: Metformin Dose Range
Protect Your Skin Rotate
The target of site rotation is to never inject into the same spot within a short time. There are many ways to rotate and various assistive devices you can use. You first select your injection area which needs to have an adequate layer of fat for example the abdomen, the thighs and the buttocks. Within your preferred area, you follow a rotation scheme. Please remember that it is best to adhere to one scheme.
General rules
- Never use the same injection spot more than once consecutively.
- Place the injections 1-2 centimeters apart.
- Never inject close to your navel.

