How Long Can You Live With Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes doesnt have to be a chronic condition. To the contrary, a type 2 diabetes diagnosis is the moment to begin changing habits and working towards a healthier and longer life. What you do every day can make a difference, says Dr. Christofides. Park at the far-end of the lot. Try taking the stairs. Consider buying only fresh foods and avoiding things in packages.
There is no one best type 2 diabetes diet. Focus on fresh, and focus on balance. Include vegetables, lean proteins , whole grains, nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole fruits.
Get moving. Exercise is one of the most important things you can do for overall health, including mental well-being. Fitness is also one of the best ways to keep weight off once youve lost it.
Find activities you enjoy and try sharing those with friends and family. Exercise doesnt have to happen in the gym. Grab a friend and go for a fast walk through the neighborhood or take a hike in the park. The vitamin D will give you an extra boost of health and well-being.
How Is The Pancreas Linked With Diabetes
Diabetes is characterized by high blood sugar. This results from insufficient insulin production or function, which can be one effect of problems with the pancreas.
People with diabetes experience high or low blood sugar levels at different times, depending on what they eat, how much they exercise, and whether they take insulin or diabetes medication.
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes both involve the pancreas.
What’s It Like For Teens With Type 2 Diabetes
Sometimes people who have diabetes feel different from their friends because they need to think about how they eat and how to control their blood sugar levels every day.
Some teens with diabetes want to deny that they even have it. They might hope that if they ignore diabetes, it will just go away. They may feel angry, depressed, or helpless, or think that their parents are constantly worrying about their diabetes management.
If you’ve been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, it’s normal to feel like your world has been turned upside down. Your diabetes care team is there to provide answers and support. Don’t hesitate to ask your doctors, dietitian, and other treatment professionals for advice and tips. It also can help to find support groups where you can talk about your feelings and find out how other teens cope.
Diabetes brings challenges, but teens who have it play sports, travel, date, go to school, and work just like their friends.
Recommended Reading: Does Losing Weight Lower A1c
Will I Need Medication Or Insulin For Type 2 Diabetes
Some people take medication to manage diabetes, along with diet and exercise. Your healthcare provider may recommend oral diabetes medications. These are pills or liquids that you take by mouth. For example, a medicine called metformin helps control the amount of glucose your liver produces.
You can also take insulin to help your body use sugar more efficiently. Insulin comes in the following forms:
- Injectable insulin is a shot you give yourself. Most people inject insulin into a fleshy part of their body such as their belly. Injectable insulin is available in a vial or an insulin pen.
- Inhaled insulin is inhaled through your mouth. It is only available in a rapid-acting form.
- Insulin pumps deliver insulin continuously, similar to how a healthy pancreas would. Pumps release insulin into your body through a tiny cannula . Pumps connect to a computerized device that lets you control the dose and frequency of insulin.
What Happens If I Have Too Much Insulin
If a person accidentally injects more insulin than required, e.g. because they expend more energy or eat less food than they anticipated, cells will take in too much glucose from the blood. This leads to abnormally low blood glucose levels . The body reacts to hypoglycaemia by releasing stored glucose from the liver in an attempt to bring the levels back to normal. Low glucose levels in the blood can make a person feel ill.
The body mounts an initial ‘fight back’ response to hypoglycaemia through a specialised set of of nerves called the sympathetic nervous system. This causes palpitations, sweating, hunger, anxiety, tremor and pale complexion that usually warn the person about the low blood glucose level so this can be treated. However, if the initial blood glucose level is too low or if it is not treated promptly and continues to drop, the brain will be affected too because it depends almost entirely on glucose as a source of energy to function properly. This can cause dizziness, confusion, fits and even coma in severe cases.
Some drugs used for people with type 2 diabetes, including sulphonylureas and meglitinides , can also stimulate insulin production within the body and can also cause hypoglycaemia. The body responds in the same way as if excess insulin has been given by injection.
Also Check: Does Black Coffee Increase Blood Sugar
To What Extent Is Type 2 Diabetes A Genetic Disease
An individuals risk of developing T2D is determined by a complex interplay between genetic and environmental/lifestyle factors. Genotype clearly plays an important role: prospective studies of monozygotic twins have shown a 76 % concordance rate for T2D, and a 96 % concordance rate for impaired glucose tolerance . Furthermore, a family history of T2D more than doubles an individuals risk of developing the disease . But at the same time the epidemiological evidence shows a dramatic rise in T2D rates over the past 60 years that clearly cannot be due to genetic change, but is associated with alterations in diet and behavior, including a more sedentary lifestyle and increased consumption of calorie-dense foods .
T2D risk may also be influenced by epigenetic changes, which are heritable alterations affecting cell function which do not involve changes in the DNA sequence. These are largely determined by environmental factors, such as parental nutrition. Recent evidence suggests that -cells from T2D patients show altered DNA methylation with changes in gene expression profiles . Rodent studies have shown that suboptimal maternal or paternal nutrition can influence chromatin modifications and gene expression in -cells of subsequent offspring, consistent with epigenetic transmission . In humans maternal and early-life nutrition is known to influence the risk of T2D in offspring . Further studies will be needed to clarify the emerging role of epigenetics in the etiology of T2D.
Peace Of Mind With Life Line Screening
At Life Line Screening, we have years of experience helping people prevent major medical issues with vital early detection services, including A1C screenings. In fact, screenings are our specialty. We partner with community centers to help people get quick, easy access to the screenings they want to stay on top of their health. No lengthy doctor’s visits, no complicated insurance to deal with, just convenient screenings for health-conscious people conducted by trained professionals.
Learn more or schedule a screening today at lifelinescreening.comâ or give us a call at . We’d love to help.
Recommended Reading: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
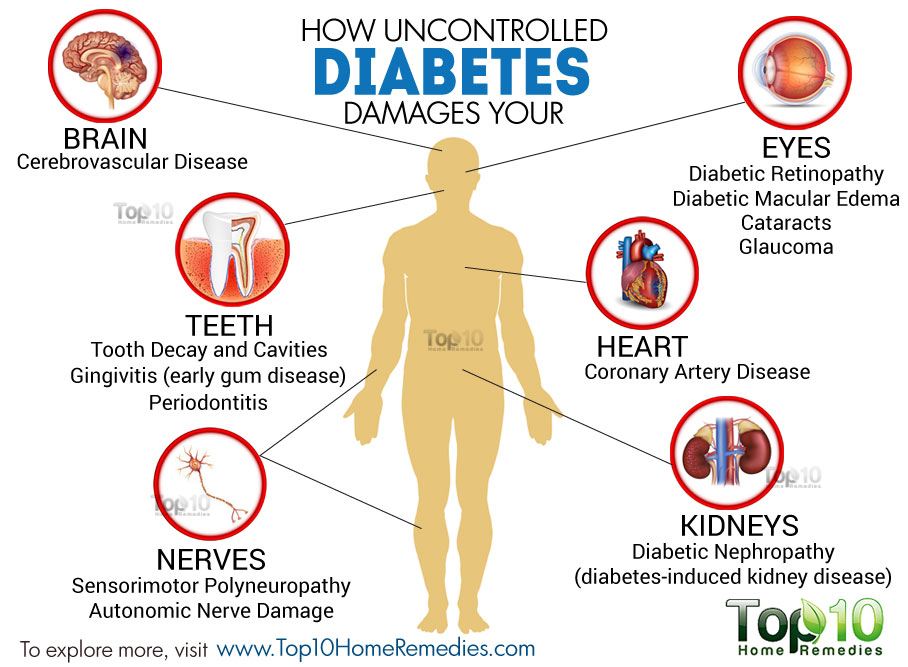
How Does Type 2 Diabetes Affect The Pancreas
Chronic inflammation of the pancreas can damage the cells that produce insulin. That can lead to diabetes. Pancreatitis and type 2 diabetes share some of the same risk factors. Observational studies indicate that people with type 2 diabetes may have a two- to threefold increased risk of acute pancreatitis.
You Say Sugar I Say Glucose
Glucose
Sucrose
Fructose
Is sugar in a doughnut the same as blood sugar? Lets clear up the confusion: Sugar can have many different names, with different meanings.
When doctors and scientists talk about sugar in the blood, they often use the word glucose. Glucose is a simple carbohydrate, also known as a monosaccharide . This can also be called blood sugar.
Unlike sucrose or fructose , you wont be able to find glucose in the grocery store.
Read Also: Metformin And A1c Levels
Can Obesity Cause Type 2 Diabetes
How we understand obesity and type 2 diabetes matters as they are the most widespread metabolic disorders. Though theyre separate conditions, they often overlap.
Weight and nutrition specialist Caroline Apovian MD explains, Although lifestyle is very important for both obesity treatment and diabetes, there are people who never develop obesity, and there are people who do have obesity for whom lifestyle changes dont always work, because obesity is a disease and the body defends a higher body weight set point. Even after weight loss, the hormonal changes involved in obesity can force a patient to regain the weight.
Type 2 diabetes patients did not bring it on themselves, emphasizes diabetes and metabolism expert Elena Christofides MD. This is not a moral failing.
But both the prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes is increasing. Why? Researchers believe its our environment. There has been an increased availability of high-fat, high-sugar, highly processed foods. These foods often contain other non-food items.
Some of these ingredients have been found to act as endocrine disrupters and change the way our bodies store fat and process energy. While there have not been sufficient studies to prove a causal relationship, most doctors and nutritionists recommend avoiding them.
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed
Doctors can say for sure if a person has diabetes by testing blood samples for glucose. Even if someone doesn’t have any symptoms of type 2 diabetes, doctors may order blood tests to check for it if the person has certain risk factors .
Some kids and teens with diabetes may go to a pediatric endocrinologist â a doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating children and teens living with diseases of the endocrine system, such as diabetes and growth problems.
p
Read Also: Metformin Safe Dose Range
Overweight Obesity And Physical Inactivity
You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you are not physically active and are overweight or obese. Extra weight sometimes causes insulin resistance and is common in people with type 2 diabetes. The location of body fat also makes a difference. Extra belly fat is linked to insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and heart and blood vessel disease. To see if your weight puts you at risk for type 2 diabetes, check out these Body Mass Index charts.
Are Other Islet Cell Types Involved In The Pathogenesis Of Type 2 Diabetes
It is now well established that T2D is not caused simply by lack of insulin and that impaired glucagon secretion from pancreatic -cells also plays a pivotal role. Glucagon elevates blood glucose by stimulating gluconeogenesis and glucose output from liver hepatocytes. In T2D there is a marked increase in glucagon secretion at high glucose, which exacerbates the hyperglycemic effects of insulinopenia . There is also too little glucagon secretion at low glucose, which may precipitate fatal hypoglycemia .
Glucagon, a long-neglected player in glucose homeostasis and T2D, has recently taken center stage. The spectacular finding that the complete destruction of the -cells by streptozotocin does not result in hyperglycemia in mice in which the glucagon receptor has been genetically ablated , whereas wild-type mice are severely diabetic following -cell ablation, underscores the importance of glucagon in glucose homeostasis. Because expression of the glucagon receptor in the liver alone is sufficient to produce severe diabetes in glucagon receptor-null mice lacking functional -cells , suppression of glucagon-induced hepatic glucose output would appear to be a good target for T2D therapy.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take To Lower Blood Sugar
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Managed
Theres no cure for Type 2 diabetes. But you can manage the condition by maintaining a healthy lifestyle and taking medication if needed. Work with your healthcare provider to manage your:
- Blood sugar: A blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring can help you meet your blood sugar target. Your healthcare provider may also recommend regular A1c tests, oral medications , insulin therapy or injectable non-insulin diabetes medications.
- Blood pressure: Lower your blood pressure by not smoking, exercising regularly and eating a healthy diet. Your healthcare provider may recommend blood pressure medication such as beta blockers or ACE inhibitors.
- Cholesterol: Follow a meal plan low in saturated fats, trans fat, salt and sugar. Your healthcare provider may recommendstatins, which are a type of drug to lower cholesterol.
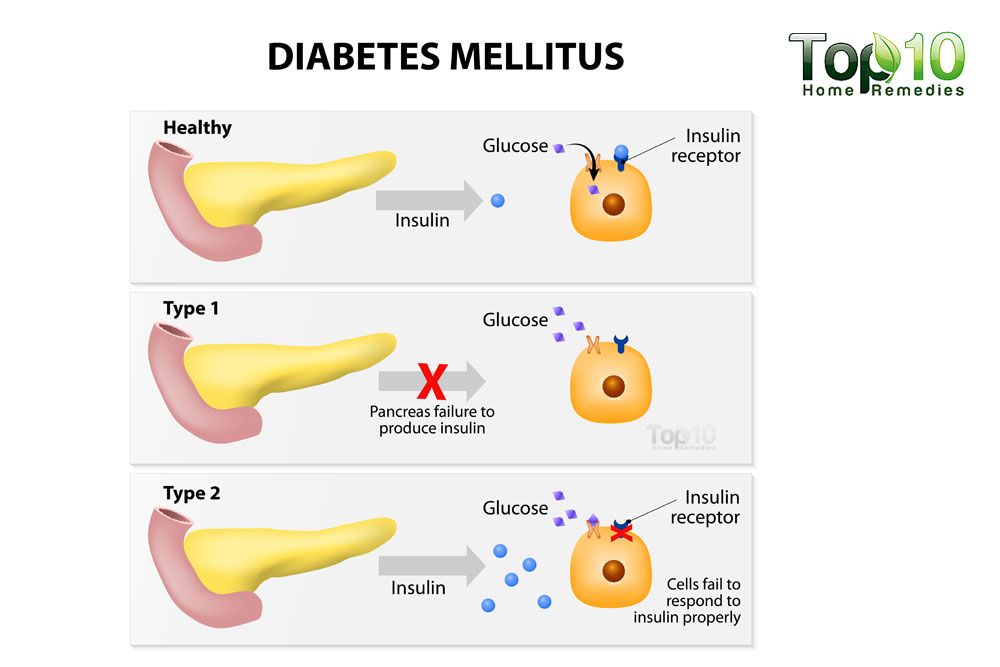
What Are The Differences Between The Causes Of Type 1 And Type 2
Type 1 diabetes causes
Type 1 diabetes is believed to be due to an autoimmune process, in which the body’s immune system mistakenly targets its own tissues . In people with type 1 diabetes, the beta cells of the pancreas that are responsible for insulin production are attacked by the misdirected immune system. This tendency for the immune system to destroy the beta cells of the pancreas is likely to be, at least in part, genetically inherited, although the exact reasons that this process happens are not fully understood.
Exposure to certain viral infections or other environmental toxins have been suggested as possible reasons why the abnormal antibody responses develop that cause damage to the pancreas cells.
Type 2 diabetes causes
Both diabetes type 1 and diabetes type 2, require good control over their diet by eating foods that help regulate blood sugar, exercise, and in most patients, medical treatments to allow the patient to remain in good health.
You May Like: Acanthosis Nigricans In Skinny Person
Insulin Resistance And Insufficient Insulin Production
Insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes means the signal insulin gives to a cell is weakened. This results in less glucose uptake by muscle and fat cells and a reduction in insulin mediated activities inside cells. Compounding this problem of resistance, there is additional defect in insulin production and secretion by the insulin producing cells, the beta cells in the pancreas.
As a group, everyone with with type 2 diabetes has both insulin resistance and an inability to overcome the resistance by secreting more insulin. But any given individual with type 2 may have more resistance than insulin insufficiency or the opposite, more insulin insufficiency than resistance. And the problems may be mild or severe. It is believed that the wide range of clinical presentation is because there are many, many genetic causes and combinations of genetic causes of type 2 diabetes. At present there is no single genetic test for type 2 diabetes. The diagnosis is made on the basis of the individual having clinical features consistent with type 2 diabetes, and by excluding other forms of diabetes.
What Is Type 1 Diabetes
An absolute lack of insulin, usually due to destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas, is the main problem in type 1 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes was formerly referred to as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus . Its causes are different from type II diabetes, as will be reviewed in this article.
Don’t Miss: Can Diabetics Eat Macaroni And Cheese
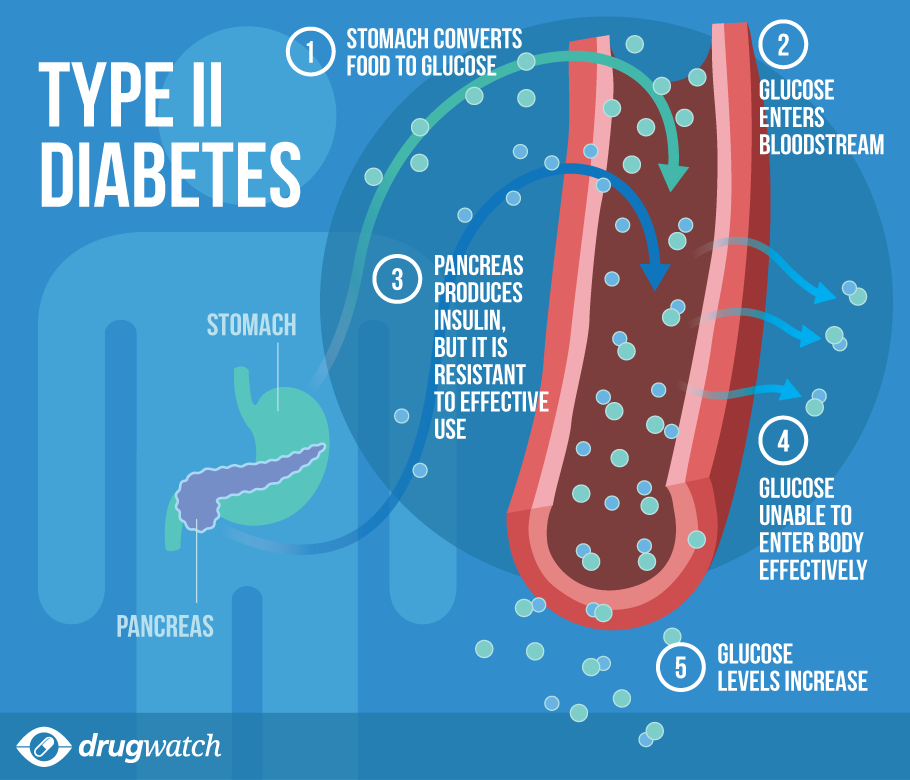
Insulin Blood Sugar And Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin is a key player in developing type 2 diabetes. This vital hormoneyou cant survive without itregulates blood sugar in the body, a very complicated process. Here are the high points:
- The food you eat is broken down into blood sugar.
- Blood sugar enters your bloodstream, which signals the pancreas to release insulin.
- Insulin helps blood sugar enter the bodys cells so it can be used for energy.
- Insulin also signals the liver to store blood sugar for later use.
- Blood sugar enters cells, and levels in the bloodstream decrease, signaling insulin to decrease too.
- Lower insulin levels alert the liver to release stored blood sugar so energy is always available, even if you havent eaten for a while.
Thats when everything works smoothly. But this finely tuned system can quickly get out of whack, as follows:
- A lot of blood sugar enters the bloodstream.
- The pancreas pumps out more insulin to get blood sugar into cells.
- Over time, cells stop responding to all that insulintheyve become insulin resistant.
- The pancreas keeps making more insulin to try to make cells respond.
- Eventually, the pancreas cant keep up, and blood sugar keeps rising.
The Pancreas And Insulin
The pancreas is responsible for producing insulin. The cells which produce insulin are beta cells. These cells are distributed in a cluster of cells in the pancreas called the Islets of Langerhans, named after the anatomist who discovered them
Insulin is a hormone that helps to regulate blood sugar levels by assisting the transport of glucose from the blood into neighbouring cells.
You May Like: What Cells Secrete Glucagon
What Are The Risk Factors For Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Risk factors for type 1 diabetes include:
- Family history: People with a parent or sibling with type 1 diabetes have a higher risk of developing it themselves.
- Age: Type 1 diabetes can appear at any age, but its most common among children and adolescents.
- Geography: The prevalence of type 1 diabetes increases the farther away you are from the equator.
- Genetics: The presence of certain genes points to an increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
Youre at risk of developing type 2 diabetes if you:
- have prediabetes, or slightly elevated blood sugar levels
- are carrying excess weight or have obesity
- are Black, Hispanic, American Indian, or Alaska Native
- have an immediate family member with type 2 diabetes
Faq: Frequently Asked Questions
Is type 2 diabetes genetic?
Over 75% of kids with type 2 diabetes also have a relative with the condition. But this could be due to similar lifestyles in the family rather than genetic factors. Like any condition, some people have a genetic predisposition towards both insulin insensitivity and type 2 diabetes, but the primary factor governing type 2 diabetes is lifestyle.
How often do I need to monitor my blood sugar if I have type 2 diabetes?
You and your healthcare provider should decide when and how often you need to check your blood sugar. You can keep a record in a smart phone app or on paper so you can easily chart your variations. Doctors recommend that diabetes patients get an A1C test at least two times a year.
How has type 2 diabetes changed over time?
Type 2 diabetes used to be called adult-onset diabetes or non-insulin dependent diabetes because it was diagnosed mainly in adults who did not require insulin to manage their condition. However, because more children are starting to be diagnosed with T2D, and insulin is used more frequently to help manage type 2 diabetes, referring to the condition as adult-onset or non-insulin dependent is no longer accurate or used.
Can type 2 diabetes be cured?
Yes! Your greatest opportunity to reverse type 2 diabetes is early detection and intervention.
You May Like: Do Bananas Affect Blood Sugar

