The Real Question Isnt Whether Insulin Stops You From Burning Fat Its Whether Insulin Stops You From Losing Fat
Here’s what we can say with confidence: There’s zero scientific evidence to suggest you’ll gain weight if your energy intake is less than your energy expenditure.
Or put another way: Insulin itself doesn’t cause weight gain. You also need to eat more calories than you expend.
Remember, in healthy people, the increase in insulin after a meal only lasts a few hours. Then it returns to baseline, allowing fat burning to throttle up again.
If energy intake is lower than energy expenditure, insulin will stay low for long periods throughout the day and night. This permits fat burning to occur at full effect despite short periods of fat-burning inhibition.
So, if you initiate a diet to lose fat, you can accomplish that with or without carbs.20
Instead Of Thinking About The Effects Of Insulinor Any Of These Hormonesas An On
Your body is constantly adjusting its hormonal dials, not based solely on food intake, but also on thousands of other inputs and processes you aren’t even aware of.
The upshot: When your insulin levels are high, you’ll burn less fat for energy than when your insulin levels are low. But you won’t stop burning fat altogether.
You’ll preferentially burn carbohydrates for energy instead.
So…
Elevated Insulin Concentrations Impair Cellular Functionsinsulin Toxicity
There is ample evidence that transient increases of metabolic or immune mediator levels are benign physiological responses to biochemical challenges, such as the rise of systemic glucose or cytokines following meals. However, chronic elevations of such mediators, even when modest in amplitude, are usually detrimental to cellular functions . In the case of glucose, the term glucose toxicity was coined to describe this phenomenon . Prolonged conditions of elevated glucose concentrations cause dysfunction of numerous cell types in the body, including beta cells, neurons, and the endothelium, via several pathways, including increased oxidative stress and activation of the sorbitol pathway . As described below, there seems to be a similar detrimental outcome of long-term elevated insulin concentrations on cellular functions, a corresponding term would be insulin toxicity.
For Moderate To Severe Insulin Overdoses: Blood Sugars Below 50 Mg/dl
There are two things you can and should do if you feel you’ve taken a significant overdose of insulin or you’re suffering from severe hypoglycemia:
Use a glucagon kit
Aglucagon kit can save your life and is prescribed by your doctor. Be sure to keep it in an easy-to-reach location that others in your household or office know about. A glucagon kit works by giving you an injection of glucagon which is a hormone that tells your liver to release stored glucose . This large dump of glucose from your liver can save your life, or at least prevent seizures in someone who is already unconscious.
If you’ve taken a serious overdose of insulin or your blood sugar is crashing and you do not have a glucagon kit, call 911 immediately. If you’re caring for someone else who has taken an overdose of insulin and they are unresponsive and unable to chew or swallow, you absolutely need to call 911. The emergency medics will give dextrose intravenous to hopefully revive the person suffering from a severe insulin overdose.
If you take insulin, you are at risk of experiencing an insulin overdose nearly every day of the week because juggling insulin doses with the many other variables that affect blood sugar levels is a complicated game. The more you observe how much insulin you need with certain meals and with meals that occur right before exercise, the more you can prevent overdosing.
It Doesnt Matter What You Believe About Insulin Carbohydrates Or Fat

That might sound extreme, but what you believe doesn’t change what’s needed to lose fat and keep it off :
- Eat less energy than you expend
- Develop eating, exercise, and stress-management habits that are sustainable long-term
If a low-carb diet helps you do that, great.
If a low-fat diet helps you do that, right on.
If a diet with a relatively equal balance of carbs, fat, and protein suits you better, that works too.
Paleo, plant-based, Meditteranean, keto, you name it: They’re all viable and can be effective, depending on your personal preferences, lifestyle, and needs.
Detrimental Combination Of Hyperinsulinemia With Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is defined as an attenuated effect of insulin on blood glucose homeostasis, primarily by less efficient export of glucose from the blood into skeletal muscle, adipose, and liver tissue. Permanently elevated insulin concentrations in the blood are often considered as an attempt to overcome insulin resistance. Indeed, induction of insulin resistance by genetic disruption of insulin signaling, as well as by increased growth hormone levels or an inflammatory milieu, causes hyperinsulinemia . The opposite causality is of more relevance. Hyperinsulinemia during insulin infusion in humans leads to systemic insulin resistance , while in vitro, high ambient insulin concentrations cause an increase in insulin resistance in isolated adipocytes . A summary analysis of nine studies in rodents and seven trials in humans confirmed that the first detectable change in the fasting state, after feeding a high caloric diet for several days, is an increase of basal insulin concentrations, but not of blood glucose concentrations or insulin resistance . Both increased secretion of insulin by ß cells and decreased insulin clearance in the liver contribute to elevated insulin levels post-meal, the latter being of primary importance in the case of carbohydrate-rich food .
You can also search for this author inPubMed
Chronically Elevated Insulin Concentrations Impair Body Functions
Longevity
Insulin, IGF-1, and hybrid insulin/IGF-1 receptors share signaling via PI3K and AKT. The subsequent activation of the protein kinase mTORC1 is a major pathway for supporting somatic growth, protein synthesis, and fertility, while impeding autophagy and lifespan. Suppression of mTOR signaling by treatment with rapamycin prolongs life in model organisms and mice . In humans, hyperinsulinemia in type 2 diabetes is associated with increased mTORC1 activity which may have a negative impact on beta cell survival, healthspan, and longevity . In the Leiden Longevity Study, follow-up of nonagenarians for 10?years showed a strong association of low insulin and glucose levels with healthy aging .
Since both IGF-1 and insulin employ PI3K and AKT for signal transduction, it is difficult to disentangle the contribution of insulin versus IGF-1 to the modulation of longevity. In animal models, selective downregulation of circulating insulin levels improved the lifespan of mice, and in elderly persons of the Leiden Longevity Study, only insulin and glucose, but not IGF-1, consistently met all four pre-defined criteria of healthy aging . Therefore, it may be concluded that low circulating insulin concentrations are not only a marker of longevity but are causally involved in promoting healthspan or lifespan extension.
For Mild Insulin Overdoses: Blood Sugars Between 50 To 70 Mg/dl
If you are able to feed yourself food or drink, treat your low blood sugar with 5 to 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrate like:
- Glucose tabs
- Honey
- Syrup
A small percentage of people can lose consciousness at 50 mg/dL. While this is less common, it’s important to know what your personal tolerance is for hypoglycemia. If you’ve lost consciousness before at a blood sugar level at or just below 50 mg/dL, you should treat this more seriously with a glucagon kit or calling 911 for emergency help.
Treat with 5 to 15 grams of carbs and then…wait.
Some mild lows may only need 5 grams of carbohydrate to correct back to a healthy blood sugar level. Others may need 15 grams or more. Either way, try to eat that fast-acting carbohydrate source and then be patient. Check your blood sugar again in 15 minutes to see if you’re coming back up. The symptoms of a low — like cravings for more food — can persist long after your blood sugar has returned to a safe level.
It’s very easy to binge-eat during hypoglycemia, but this can become a vicious cycle. There’s a simple look at the binge-eating cycle around low blood sugars in my book, .
Be prepared: keep fast-acting carbohydrates in easy-to-reach locations.
As a person taking insulin, you should have fast-acting carbohydrate sources stored in a few places, like:
- Your purse
- Your office desk
- Your partner’s car
Choose foods that will not melt, freeze, or rot since they’ll likely be kept in places that can get very hot or very cold.
How Do You Know If You Suffer From Insulin Resistance
Most people with insulin resistance have extra fat around the middle.
You may be tall, thin, short, fat, or any combination of these and still have insulin resistance. The only way to know for sure is to take an insulin response test, which measures blood sugar and insulin while you are fasting and one and two hours after you consume a 75-gram sugar drink. Just measuring blood sugar alone isn’t enough. You have to measure insulin — this is something that many doctors miss.
Fortunately, balancing blood sugar and correcting insulin resistance are well within our reach. Scientific advances of the last few decades show us how. While some medications can help with insulin resistance, such as Glucophage, Avandia and Actos, they have side effects and are only a Band-aid unless they are used along with a comprehensive nutrition, exercise and stress management plan like the one described below.
Ways To Reset Your Metabolism For Optimal Blood Sugar
My goal is to make your metabolism more efficient, to make your cells more intelligent and cooperative, not resistant. In other words, you will need much less insulin to accomplish the task of balancing your blood sugar.
You can achieve this by resetting your metabolism of sugar and insulin. To do this, you have to eliminate the things that are knocking you out of balance and provide your body the things it needs to reestablish optimal balance and thrive.
Here’s what to do:
Just try these suggestions for one week and see how you feel — you may be shocked at how quickly your body can recover.
The Danger Of Giving Diabetic Cats Too Much Insulin
If your cat is diagnosed with diabetes, you may soon find you’re required to give the cat insulin injections once or twice a day, which can lead to an accidental overdose. Keep reading to learn what to do if your cat has received too much insulin.
Insulin overdose can cause your cat to use too much of its body’s blood sugar. This is a condition called hypoglycemia, and it can become fatal very quickly.
What Would Cause Someone To Forget To Take Insulin
Literally anything can cause someone to forget to take their insulin: traveling, time-changes, sleepovers, the weather, falling asleep before a scheduled dose, an interruption such as a phone call or text message, spontaneous meals or snacks, or even just being forgetful are common reasons.
This is perfectly normal and happens to everyone. Do not guilt yourself or feel down if you forget to take your insulin from time to time. It may happen, but these strategies can help.
When To Seek Medical Care For An Insulin Reaction

Most people with diabetes have experienced an insulin reaction early after their initial diagnosis as diet and medication or insulin dosing is being adjusted to fit into their lifestyle.
Whenever a person is unconscious, regardless of the cause, call 911 or your local emergency telephone number to activate emergency medical service responses.
If the affected individual remains confused, even after eating or drinking to correct a low blood sugar, he or she should receive medical care.
People with diabetes who take sulfonylurea oral hypoglycemic medications, like glipizide , glyburide , or glimepiride , should contact their health care practitioner or seek urgent medical care if they experience an insulin reaction. These medications can remain active in the body for a prolonged period of time, and observation in a hospital setting may be necessary.
Insulin reactions, especially those that occur at night or early morning should be reported to your health care practitioner. People with diabetes should keep a record of their blood sugar readings as it is an important tool to help keep blood sugars under good control and decrease the risk of long-term complications of diabetes.
Insulin Overdose: Causes Symptoms And What To Do
Everybody needs insulin to survive! Without enough or any insulin, your body cannot use the food you eat for energy, and blood sugar levels rise to dangerous and eventually fatal levels.
This makes insulin one of the most important hormones in your body, but just as too little insulin can be life-threatening, too much insulin — an insulin overdose — is equally dangerous.
In this article, we will look at how to spot the warning signs of an insulin overdose, how to treat it, and how to prevent it from occurring in the first place.
What Happens If You Take Lantus Twice Dont Worry
After reading about the effects of hypoglycemia, you may be worried. However, all of these may not happen to you. And even if they do, they generally aren’t very severe.
The reason is that Lantus is a long-acting insulin. It does not dissolve at normal physiological pH of 7.4. It has an isoelectric pH of 6.7. So, it crystallizes upon entry on the subcutaneous tissue where it is administered. Then, it is released slowly over time.
So, the drug gets to the bloodstream slowly. This results in a more continuous supply of insulin to your body. Thus, there is no sharp rise in insulin levels. And so, there is no sharp decline in blood glucose.
For this reason, you’ll not be severely hypoglycemic if you’ve taken Lantus twice. The extra Lantus will get to the bloodstream. So, you’ll have a prolonged but mild to moderate episode of hypoglycemia. This type of hypoglycemia isn’t life-threatening. Thus, you can rest assured.
Risk Factors Of Elevated Insulin In Vacaville Ca
These are the factors that have the possibility to mae you have increased insulin levels in the blood:
- Early puberty – girls who reached their puberty earlier are found to have increased insulin levels.
- If you’re lacking from sleep on a regular basis, you will build up insulin resistance over time thus leading to excess insulin production.
- The stress hormone known as cortisol can make insulin resistance as one of its side effects. It blocks the insulin receptor that indirectly leads to excess insulin production.
- Metabolic syndrome – a combination of hypertension, obesity, and high blood cholesterol levels – can lead to hyperinsulinemia.
Signs that you have hyperinsulinemia
If you have high insulin levels in your blood, these are the symptoms that are commonly experienced:
- Fatigue
- Lack of focus or motivation
- Weight gain, especially in the waist, that forms an apple shape
Adverse effects of high insulin levels
If you’ve been using external insulin for too long or you have high levels in the blood, it can create side effects on your different body parts which are as follows:
Schedule Today!
Schedule an appointment with our team at Absolute Integrative Physical Medicine in Vacaville today!
OFFICE HOURS
Whats The Link Between Diabetes And Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is most common, by far, in people with diabetes. Treatment for the diseaseoften involves taking medication to increase insulin. Hypoglycemia can develop if things like food, exercise and diabetes medications are out of balance.
Common pitfalls for people with diabetes include:
- Being more active than usual.
- Drinking alcohol without eating.
- Eating late or skipping meals.
- Not balancing meals by including fat, protein and fiber.
- Not eating enough carbohydrates.
- Not timing insulin and carb intake correctly .
Also, if someone with diabetes uses the wrong insulin, takes too much or injects it incorrectly, that can cause hypoglycemia.
What Is The Outlook For People With Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia can be managed when you and your healthcare provider understand what causes your blood sugar to go down. Give your healthcare provider as much information as possible about any hypoglycemic episodes. Fixing the problem may be as simple as changing the times you take medication, eat and exercise. Minor changes to the types of food you eat may also help.
The Question Is: Does It Hold Up Scientifically
In this article, we’ll walk you through the science of how the carb-insulin relationship works—for both health and fat loss—and answer these questions:
PN coach roundtable: Robin Beier discusses the truth about insulin, carbs and weight loss with Helen Kolias and Brian St. Pierre.
What Happens If You Havehigh Levels Of Insulin
Insulin is a hormone that’s produced by the pancreas to transport the glucose from the blood to the cells. It helps in maintaining the normal levels of your blood sugar.
When you have , your insulin levels are below normal value. But if you have type 2 diabetes, your insulin levels spike to overpower the insulin resistance. Diabetes is a major concern in today’s population and for the high sugar levels in the blood to be managed, insulin levels need to be increased either through direct injections or by using drugs to promote its production. Also, when you’re pregnant or have pancreatic tumors, your insulin levels become high.
The long-term use of insulin and its excess production can result in unwanted effects in your system. Take a look at these effects brought by hyperinsulinemia and how you could manage it.
What should the healthy numbers be?
Insulin can be measured in either mcU/ml or mIU/ml . The normal insulin levels in the blood of a healthy individual can vary with and without food.
- The fasting value is <25 mIU/L
- After 30 minutes of eating foods, the value is 30 to 230 mIU/L
- After 1 hour of eating foods, the value is 18 to 276 mIU/L
- After 2 hours of eating foods, the value is 16 to 166 mIU/L
If ever the insulin levels are beyond the values mentioned, then it can be considered as hyperinsulinemia.
What Should Be The Numbers In A Healthy Person
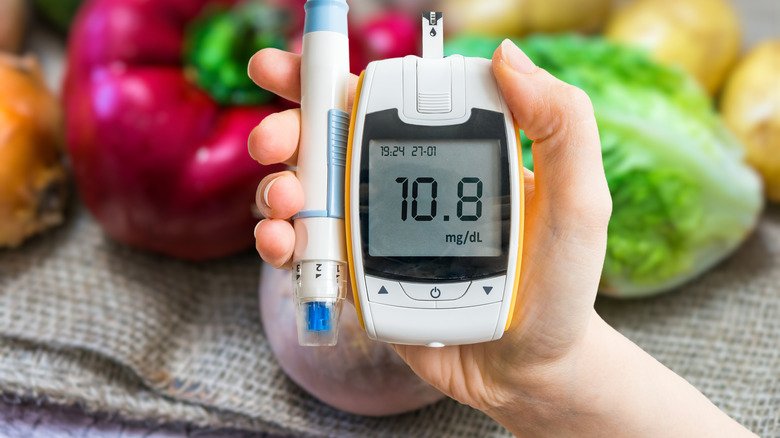
Insulin is measured in MCU/ml or mIU/ml . The normal levels of insulin in the blood of a healthy person vary with and without food.
-
The fasting value is < 25 mIU/L
-
After 30 minutes of food intake, the value is 30-230 mIU/L
-
After 1 hour of food intake, the value is 18-276 mIU/L
-
After 2 hours of food intake, the value is 16-166 mIU/L
If the levels of insulin are higher than these normal values, then it is considered as hyperinsulinemia.
What Are The Risk Factors For Elevated Insulin
The following factors can increase your chance of having excess insulin levels in the blood
-
Early puberty – Girls who attain early puberty are found to have elevated insulin levels.
-
Lack of sleep if happens on a regular basis can lead to insulin resistance which over time leads to the excess insulin production as a feedback mechanism.
-
The stress hormone ‘Cortisol’ causes insulin resistance as one of the side effects, by blocking the insulin receptor which indirectly leads to excess insulin production.
-
The metabolic syndrome which is a combination of obesity, hypertension, and high blood cholesterol levels can lead to hyperinsulinemia .
Too Much Insulin How To Reset Your Metabolism
Are your hormones out of balance? Does your life feel like a song played badly out of tune? If so, the problem may have to do with imbalances in your hormones, which are wreaking havoc on your body and mind.
Today I want to focus on the most common — and therefore the most problematic — of hormonal problems in Americans today: too much insulin.
When you eat too much sugar, flour and white rice, your insulin levels spike. When this happens, your cells become resistant to its effects. So you pump out more and more insulin, become even more resistant to its effects, and end up in the vicious cycle of insulin resistance.
Insulin resistance can cause energy and mood swings — and it can take you down the slippery road toward high blood pressure, heart disease, obesity, cancer, brain aging, dementia, and more.
Between 80 and 100 million Americans suffer from insulin resistance. It is not exactly the same in everyone, but the ultimate consequences can be similar.
How To Monitor Your Insulin & Glucagon Levels
Although you can’t directly monitor your insulin and glucagon levels at home, you can monitor your glucose levels with a continuous glucose monitor , providing you with the data you need to understand if there is a problem with these hormones.Â
Continuous glucose monitoring enables you to track your glucose levels in real-time. It can help you to identify if your glucose levels are significantly high or low and take the right steps to find out why. Wearing a CGM helps you take charge of your metabolic health and make positive changes to ensure your glucose levels remain stable.Â
It can seem a bit daunting to start monitoring your own glucose levels, but the NutriSense Continuous Glucose Health Program simplifies it. It provides you with a CGM, accompanying CGM phone app, and personalized support from Registered Dietitians to help you decipher your data. If you have any concerns about your glucose levels, why not give it a try?
�
Does Everyone Have Symptoms From Hypoglycemia
Some people don’t have symptoms or don’t notice them. Healthcare providers call that situation hypoglycemia unawareness. People with such a challenge aren’t aware when they need to do something about their blood sugar. They’re then more likely to have severe episodes and need medical help. People with hypoglycemia unawareness should check their blood sugar more often.
How Can I Be Better Prepared For Hypoglycemia
You can take some steps to be ready for hypoglycemia:
- Be aware of the symptoms and treat them early.
- Carry some fast-acting carbs with you all the time.
- Check your glucose levels frequently, especially around meals and exercise.
- Inform family, friends and co-workers so they know what do if you need help.
- Talk to your healthcare provider regularly to make and update your plan.
- Wear a medical bracelet that lets people know you have diabetes. Carry a card in your purse or wallet with instructions for hypoglycemia.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Hypoglycemia is quite common in people with diabetes. If not treated, it can cause troubling symptoms, and even serious health problems. Fortunately, you can avoid hypoglycemic episodes by monitoring your blood sugar. You can also make small adjustments to eating and exercising routines.
What Not To Do If You Forget To Dose Insulin
While it’s important to be action-oriented, here are some things you should never do if you forget to dose insulin:
- Blame yourself
- Go to sleep immediately
- Not take a correction dose of insulin at all
- Not tell anyone about the missed dose
- Bolus like normal for the number of carbohydrates you ate, even if you ate several hours before realizing you missed a dose
- Take double the amount of insulin for carbohydrates eaten and high blood sugar, without factoring in the time that has passed, carbohydrates already digested, or your blood sugar correction factor
What Happens If You Dont Have Enough Insulin
Too little insulin is a problem usually seen in people with diabetes. They can have problems producing insulin or using insulin effectively. In type 2 diabetes, the body can still make insulin, but it may not make enough, and/or insulin resistance has developed.
With type 1 diabetes, a person may make very little or no insulin whatsoever. Without enough insulin, your body can’t move glucose from the bloodstream into the cells. This results in high blood sugar levels and a lack of energy in the cells.Â
Symptoms of low insulin in type 1 diabetes can include weight loss, fatigue, dehydration, and confusion. Therefore, people with type 1 diabetes need to inject insulin to prevent these symptoms, which can be life-threatening.Â

