What Insulin Medications Are Approved To Treat Diabetes
There are many types of insulins for diabetes. If you need insulin, you healthcare team will discuss the different types and if they are to be combined with oral medications. To follow is a brief review of insulin types.
- Rapid-acting insulins: These insulins are taken 15 minutes before meals, they peak at one hour and work for another two to four hours. Examples include insulin glulisine , insulin lispro and insulin aspart .
- Short-acting insulins: These insulins take about 30 minutes to reach your bloodstream, reach their peak effects in two to three hours and last for three to six hours. An example is insulin regular .
- Intermediate-acting insulins: These insulins reach your bloodstream in two to four hours, peak in four to 12 hours and work for up to 18 hours. An example in NPH.
- Long-acting insulins: These insulins work to keep your blood sugar stable all day. Usually, these insulins last for about 18 hours. Examples include insulin glargine , insulin detemir and insulin degludec .
There are insulins that are a combination of different insulins. There are also insulins that are combined with a GLP-1 receptor agonist medication .
Can Diabetes Cause Headaches Or Dizziness
Yes, its possible to develop headaches or dizziness if your blood glucose level is too low usually below 70 mg/dL. This condition is called hypoglycemia. You can read about the other symptoms hypoglycemia causes in this article.Hypoglycemia is common in people with Type 1 diabetes and can happen in some people with Type 2 diabetes who take insulin or medications such as sulfonylureas.
What Are The Complications Of Diabetes
If your blood glucose level remains high over a long period of time, your bodys tissues and organs can be seriously damaged. Some complications can be life-threatening over time.
Complications include:
- Dental problems.
Complications of gestational diabetes:
In the mother:Preeclampsia , risk of gestational diabetes during future pregnancies and risk of diabetes later in life.
In the newborn: Higher-than-normal birth weight, low blood sugar , higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes over time and death shortly after birth.
Don’t Miss: What Happens If You Stop Taking Diabetes Medication
Structural Analysis And Synthesis
Purified animal-sourced insulin was initially the only type of insulin available for experiments and diabetics. John Jacob Abel was the first to produce the crystallised form in 1926. Evidence of the protein nature was first given by Michael Somogyi, Edward A. Doisy, and Philip A. Shaffer in 1924. It was fully proven when Hans Jensen and Earl A. Evans Jr. isolated the amino acids phenylalanine and proline in 1935.
The amino acid structure of insulin was first characterized in 1951 by Frederick Sanger, and the first synthetic insulin was produced simultaneously in the labs of Panayotis Katsoyannis at the University of Pittsburgh and Helmut Zahn at RWTH Aachen University in the mid-1960s.Synthetic crystalline bovine insulin was achieved by Chinese researchers in 1965. The complete 3-dimensional structure of insulin was determined by X-ray crystallography in Dorothy Hodgkin‘s laboratory in 1969.
Two other Nobel Prizes have been awarded for work on insulin. British molecular biologist Frederick Sanger, who determined the primary structure of insulin in 1955, was awarded the 1958 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.Rosalyn Sussman Yalow received the 1977 Nobel Prize in Medicine for the development of the radioimmunoassay for insulin.
What Happens If I Have Too Little Glucagon
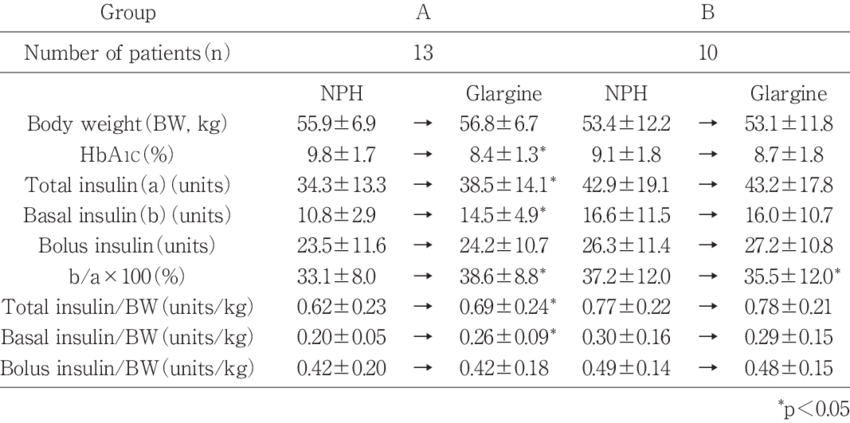
Unusual cases of deficiency of glucagon secretion have been reported in babies.;This results in severely low blood glucose which cannot be controlled without administering glucagon.;
Glucagon can be given by injection to restore blood glucose lowered by insulin .;It can increase glucose release from glycogen stores more than insulin can suppress it. The effect of glucagon is limited, so it is very important to eat a carbohydrate meal once the person has recovered enough to eat safely.
Don’t Miss: Thin Type 2 Diabetes
Regulation Of Proinsulin Folding In Health And Diabetes
Proinsulin folding in the ER involves the establishment of three disulfide bonds, two interchain between the B and A chains and one intrachain within the A chain . Altered cysteine pairing, such as upon mutations of C96 in the A chain, causes misfolding, accumulation and toxic aggregation of proinsulin in the ER leading to permanent neonatal diabetes or mature-onset diabetes of the young . Recent studies in a human-derived induced pluripotent stem cell model of neonatal diabetes with a C96R mutation, and in the Akita mouse model of diabetes, in which one Ins2 allele carries a C96Y replacement, suggest that proinsulin misfolding reduces beta cell proliferation and mass due to downregulation of mTOR signalling during pancreas development , rather than beta cell apoptosis, as it is commonly assumed.
History Or How This Came About
The history of the insulin Unit has been well reviewed elsewhere,, but it is, in short, a history of change. Originally defined as the amount of insulin required to cause convulsive hypoglycemia in a fasted 2kg rabbit, standards for potency have changed with improvements in the preparation and stabilization of insulin in solution. Where potency was defined in the 1920s as 8IU/mg of insulin, this definition was revised upward in 1959 by the World Health Organization Expert Committee on Biological Standardizations Fourth International Standard to 24IU/mg. It was revised upward again by the same committee in the 1986 to 26IU/mg., This value remains the standard to date, with the latest updates made in 2010.
However, as the 1986 standard contains some water and salts, amino acid analysis gives a corrected potency of 6 nmol per 1IU., If instead, anhydrous insulin is considered, the 6 nmol per 1IU potency is equivalent to 28.8IU/mg, or 0.0347mg/IU. This latter potency is more common and has been referred to as the established standard.
As a result, there is one standard, but two human insulin potencies due to improvements in the quality of insulin preparation. The conversion factors arising from these different potencies are given in . The conversion factor resulting from the Fourth International Standard was calculated as per, and can still be occasionally found .
Read Also: Why Eat Sugar After Giving Blood
Insulin And The Bloodbrain Barrier
Insulin levels in cerebrospinal fluid are much lower than plasma insulin levels, but are highly correlated with them , which suggests that brain insulin originates predominantly from circulating pancreatic insulin that crosses the bloodbrain barrier . The cerebral BBB is established by tight junctions between endothelial cells and serves to protect the brain from diffusion of neuroactive nutrients , infectious agents, inflammatory molecules, and other substances in the systemic circulation. The BBB allows passive diffusion of water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and highly lipid-soluble molecules, whereas glucose, amino acids, hormones such as insulin, and most other peptide, free fatty acids, and carbohydrate entities cross via selective transporters. Insulin crosses the BBB primarily via selective receptor-mediated transport . Insulin binding receptors located on capillary endothelial cells are presumed to be the same as those involved in canonical insulin signaling, but whether the insulin-binding transporter is the same gene product or an isoform remains to be established.
N.B. Panda, … A. Swain, in, 2017
Can Diabetes Cause Hearing Loss
Scientists dont have firm answers yet but there appears to be a correlation between hearing loss and diabetes. According to the American Diabetes Association, a recent study found that hearing loss was twice as common in people with diabetes versus those who didnt have diabetes. Also, the rate of hearing loss in people with prediabetes was 30% higher compared with those who had normal blood glucose levels. Scientists think diabetes damages the blood vessels in the inner ear, but more research is needed.
Also Check: How Much Fruit Can A Diabetic Eat
How Often Do I Need To See My Primary Diabetes Healthcare Professional
In general, if you are being treated with insulin shots, you should see your doctor at least every three to four months. If you are treated with pills or are managing diabetes through diet, you should be seen at least every four to six months. More frequent visits may be needed if your blood sugar is not controlled or if complications of diabetes are worsening.
What Oral Medications Are Approved To Treat Diabetes
Over 40 medications have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of diabetes. Its beyond the scope of this article to review all of these drugs. Instead, well briefly review the main drug classes available, how they work and present the names of a few drugs in each class. Your healthcare team will decide if medication is right for you. If so, theyll decide which specific drug are best to treat your diabetes.
Diabetes medication drug classes include:
Many oral diabetes medications may be used in combination or with insulin to achieve the best blood glucose control. Some of the above medications are available as a combination of two medicines in a single pill. Others are available as injectable medications, for example, the GLP-1 agonist semaglutide and lixisenatide .
Always take your medicine exactly as your healthcare prescribes it. Discuss your specific questions and concerns with them.
Recommended Reading: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
What Should My Blood Glucose Level Be
Ask your healthcare team what your blood glucose level should be. They may have a specific target range for you. In general, though, most people try to keep their blood glucose levels at these targets:
- Before a meal: between 80 and 130 mg/dL.
- About two hours after the start of a meal: less than 180 mg/dL.
How Is Diabetes Managed
Diabetes affects your whole body. To best manage diabetes, youll need to take steps to keep your risk factors under control and within the normal range, including:
- Keep your blood glucose levels as near to normal as possible by following a diet plan, taking prescribed medication and increasing your activity level.
- Maintain your blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels as near the normal ranges as possible.
- Control your blood pressure. Your blood pressure should not be over 140/90 mmHg.
You hold the keys to managing your diabetes by:
- Planning what you eat and following a healthy meal plan. Follow a Mediterranean diet or Dash diet. These diets are high in nutrition and fiber and low in fats and calories. See a registered dietitian for help understanding nutrition and meal planning.
- Exercising regularly. Try to exercise at least 30 minutes most days of the week. Walk, swim or find some activity you enjoy.
- Losing weight if you are overweight. Work with your healthcare team to develop a weight-loss plan.
- Taking medication and insulin, if prescribed, and closely following recommendations on how and when to take it.
- Quitting smoking .
You have a lot of control on a day-to-day basis in managing your diabetes!
Recommended Reading: Life Expectancy With Type 2 Diabetes
Physiologic Effects Of Insulin
Stand on a streetcorner and ask people if they know what insulin is, and many will reply, “Doesn’t it have something to do with blood sugar?” Indeed, that is correct, but such a response is a bit like saying “Mozart? Wasn’t he some kind of a musician?”
Insulin is a key player in the control of intermediary metabolism, and the big picture is that it organizes the use of fuels for either storage or oxidation. Through these activities, insulin has profound effects on both carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, and significant influences on protein and mineral metabolism. Consequently, derangements in insulin signalling have widespread and devastating effects on many organs and tissues.
The Insulin Receptor and Mechanism of Action
Like the receptors for other protein hormones, the receptor for insulin is embedded in the plasma membrane. The insulin receptor is composed of two alpha subunits and two beta subunits linked by disulfide bonds. The alpha chains are entirely extracellular and house insulin binding domains, while the linked beta chains penetrate through the plasma membrane.
Insulin and Carbohydrate Metabolism
It should be noted here that there are some tissues that do not require insulin for efficient uptake of glucose: important examples are brain and the liver. This is because these cells don’t use GLUT4 for importing glucose, but rather, another transporter that is not insulin-dependent.
Insulin and Lipid Metabolism
Other Notable Effects of Insulin
Regulation Of Blood Glucose
Regulation of glucose in the body is done autonomically and constantly throughout each minute of the day. Normal BG levels should be between 60 and 140 mg/dL in order to supply cells of the body with its required energy. Brain cells dont require insulin to drive glucose into neurons; however, there must still be normal amounts available. Too little glucose, called hypoglycemia, starves cells, and too much glucose creates a sticky, paralyzing effect on cells. Euglycemia, or blood sugar within the normal range, is naturally ideal for the bodys functions. A delicate balance between hormones of the pancreas, intestines, brain, and even adrenals is required to maintain normal BG levels.
You May Like: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Can Diabetes Cause Hair Loss
Yes, its possible for diabetes to cause hair loss. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to persistently high blood glucose levels. This, in turn, leads to blood vessel damage and restricted flow, and oxygen and nutrients cant get to the cells that need it including hair follicles. Stress can cause hormone level changes that affect hair growth. If you have Type 1 diabetes, your immune system attacks itself and can also cause a hair loss condition called alopecia areata.
Can Diabetes Kill You
Yes, its possible that if diabetes remains undiagnosed and uncontrolled it can cause devastating harm to your body. Diabetes can cause heart attack, heart failure, stroke, kidney failure and coma. These complications can lead to your death. Cardiovascular disease in particular is the leading cause of death in adults with diabetes.
You May Like: Which Jonas Brother Is Diabetic
Are There Other Treatment Options For Diabetes
Yes. There are two types of transplantations that might be an option for a select number of patients who have Type 1 diabetes. A pancreas transplant is possible. However, getting an organ transplant requires taking immune-suppressing drugs for the rest of your life and dealing with the side effects of these drugs. However, if the transplant is successful, youll likely be able to stop taking insulin.
Another type of transplant is a pancreatic islet transplant. In this transplant, clusters of islet cells are transplanted from an organ donor into your pancreas to replace those that have been destroyed.
Another treatment under research for Type 1 diabetes is immunotherapy. Since Type 1 is an immune system disease, immunotherapy holds promise as a way to use medication to turn off the parts of the immune system that cause Type 1 disease.
Bariatric surgery is another treatment option thats an indirect treatment for diabetes. Bariatric surgery is an option if you have Type 2 diabetes, are obese and considered a good candidate for this type of surgery. Much improved blood glucose levels are seen in people who have lost a significant amount of weight.
Of course other medications are prescribed to treat any existing health problems that contribute to increasing your risk of developing diabetes. These conditions include high blood pressure, high cholesterol and other heart-related diseases.
How Can Type 2 Diabetes Be Cured Permanently
Although theres no cure for type 2 diabetes, studies show its possible for some people to reverse it. Through diet changes and weight loss, you may be able to reach and hold normal blood sugar levels without medication. This doesnt mean youre completely cured. Type 2 diabetes is an ongoing disease.
Also Check: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Talk With Your Doctor
Knowing how your body works can help you stay healthy. Insulin and glucagon are two critical hormones your body makes to keep your blood sugar levels balanced. Its helpful to understand how these hormones function so you can work to avoid diabetes.
If you have more questions about insulin, glucagon, and blood glucose, talk to your doctor. Questions you have might include:
- Is my blood glucose at a safe level?
- Do I have prediabetes?
What Is Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome

Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome develops more slowly than diabetic ketoacidosis. It occurs in patients with Type 2 diabetes, especially the elderly and usually occurs when patients are ill or stressed.If you have HHNS, you blood glucose level is typically greater than 600 mg/dL. Symptoms include frequent urination, drowsiness, lack of energy and dehydration. HHNS is not associated with ketones in the blood. It can cause coma or death. Youll need to be treated in the hospital.
Read Also: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
How Does Diabetes Lead To Amputation
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to poor blood flow . Without oxygen and nutrients , you are more prone to the development of cuts and sores that can lead to infections that cant fully heal. Areas of your body that are farthest away from your heart are more likely to experience the effects of poor blood flow. So areas of your body like your toes, feet, legs and fingers are more likely to be amputated if infection develops and healing is poor.
What Types Of Healthcare Professionals Might Be Part Of My Diabetes Treatment Team
Most people with diabetes see their primary healthcare provider first. Your provider might refer you to an endocrinologist/pediatric endocrinologist, a physician who specializes in diabetes care. Other members of your healthcare team may include an ophthalmologist , nephrologist , cardiologist , podiatrist , neurologist , gastroenterologist , registered dietician, nurse practitioners/physician assistants, diabetes educator, pharmacist, personal trainer, social worker, mental health professional, transplant team and others.
Read Also: Do You Give Insulin Or Dextrose First For Hyperkalemia

