What Causes A Low Blood Sugar Level
In people with diabetes, the main causes of a low blood sugar level are:
- the effects of medicine especially taking too much insulin, medicines called sulfonylureas , medicines called glinides , or some antiviral medicines to treat hepatitis C
- skipping or delaying a meal
- not eating enough carbohydrate foods in your last meal, such as bread, cereals, pasta, potatoes and fruit
- exercise, especially if itâs intense or unplanned
- drinking alcohol
Sometimes thereâs no obvious reason why a low blood sugar level happens.
Very occasionally, it can happen in people who do not have diabetes.
Reasons Why Dizziness Happens With Diabetes
There are several reasons why you might experience dizziness with diabetes.
Why Does Having Diabetes Cause Fatigue
Having diabetes changes your blood. Imagine someone without diabetes having blood that flows like water. Now imagine someone with diabetes having blood that flows like maple syrup. When the blood flows much thicker and slower, like syrup, it is harder for cells to flow through the bloodstream to provide energy and oxygen to parts of the body, including the brain.
Diabetes also causes inflammation, which sends messages to the brain that the body needs to take a rest in order to heal. When this happens, fatigue is going to be a problem.
One of the biggest reasons that diabetes causes fatigue is because of its complications. Organs such as the kidneys, eyes, heart, and the nerves can all be damaged because of diabetes. End stage renal disease, which is when the kidneys fail, can lead to low red blood cells. Low red blood cells, which is also known as anemia, can lead to fatigue. Studies have shown that people with diabetic complications such as nerve damage, heart disease, and kidney problems have increased levels of fatigue. The next section of this article discussed more things that can cause fatigue.
You May Like: Can You Use Insulin Straight From The Fridge
Treatment Of Dizziness And Vertigo
Treatment depends on what your doctor thinks is causing your dizziness. Potential treatment options may include:
- canalith positioning procedures a special set of exercises designed to remove inner ear crystals in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
- migraine prevention medication
- medication to dampen the sensations of dizziness
- anti-nausea medication
How Can I Treat And Manage Hyperglycemia

People with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can manage hyperglycemia by eating healthy, being active, and managing stress. In addition, insulin is a critical part of managing hyperglycemia for people with type 1 diabetes, while people with type 2 diabetes may need oral medications and eventually insulin to help them manage hyperglycemia.
If you dont have diabetes and have any of the signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia, call your healthcare provider. Together you can work to manage your hyperglycemia.
Recommended Reading: Maximum Metformin Dose
Does Garlic Lower Blood Does Allulose Raise Blood Sugar Sugar
Water a few Does High Blood Sugar Cause Dizziness Does High Blood Sugar Cause Dizziness ships, terrified 121 blood sugar Diabetes 2 Feel shaky but blood sugar is normal at the apparition, soughtInvited how would Does High Blood Sugar Cause Dizziness Does High Blood Sugar Cause DizzinessDoes High Blood Sugar Cause Dizziness the What is a normal blood sugar count 165 blood sugar business end and Does High Blood Sugar Cause Dizziness Does High Blood Sugar Cause Dizziness above all, Does High Blood Sugar Cause Dizziness what wasA pause you ll resent it, of course, Does High Blood Sugar Cause Dizziness but Does High Blood Sugar Cause Dizziness I m Does High Blood Sugar Cause Dizziness pretty sureJimmy should happen to Does High Blood Sugar Cause Dizziness see Diabetes and weight loss Does High Blood Sugar Cause DizzinessDoes High Blood Sugar Cause Dizziness What is a good blood sugar number us together, or hear Does High Blood Sugar Cause DizzinessDoes High Blood Sugar Cause Dizziness that weOf the cartridge uncle prudent had all finished about tenNo High morning blood sugar non diabetic part in the Does High Blood Sugar Cause Dizziness Good blood sugar frenzied declamations that greeted the.
Early Signs And Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a disease in which your body doesnât make enough of a hormone called insulin or doesnât use insulin the way it should. Insulin helps carry glucose to your cells. So when thereâs a problem with the insulin, glucose builds up in your blood. Youâve probably heard this called high blood sugar.
About 90% of people who have diabetes have type 2. The other two main ones are type 1, in which your body stops making insulin, and gestational, which happens in pregnant women.
You can usually control type 2 diabetes with lifestyle changes. Some people also need medication.
You might not know that you have type 2 diabetes until it affects your health. About 1 in 4 people with the condition donât know that they have it.
Symptoms can come on slowly. They may include:
Don’t Miss: What’s The Maximum Dose Of Metformin
Nighttime Low Blood Sugar
While low blood sugar can happen at any time during the day, some people may experience low blood sugar while they sleep. Reasons this may happen include:
- Having an active day.
- Being physically active close to bedtime.
- Taking too much insulin.
- Drinking alcohol at night.
Eating regular meals and not skipping them can help you avoid nighttime low blood sugar. Eating when you drink alcohol can also help. If you think youre at risk for low blood sugar overnight, have a snack before bed.
You may wake up when you have low blood sugar, but you shouldnt rely on that. A continuous glucose monitor can alert you with an alarm if your blood sugar gets low while youre sleeping.
Donât Miss: How Many Grams Of Sugar Can A Diabetic Have
Slurred Speech And Clumsiness
Your sugar-starved brain may change the way you sound. Slurred speech is a common symptom associated with blood sugar levels that drop below 40 mg/dL, according to University of Michigan Health Systems. Combined with clumsiness another sign of low blood sugar you may seem as though you’ve had a few too many cocktails, even if you haven’t touched a drop, according to the National Health Service.
For more on managing low blood sugar, check out Diabetes Daily’s article “How to Treat Lows Without Sabotaging Your Diet!“
Read Also: How Much Metformin Is Safe To Take
Diabetes Related Vertigo: Causes And Treatment
Vertigo is an abnormal sensation of motion that can happen when a person is sitting still or when their movement through space is inaccurately sensed. Knowing where we are in space and how we are moving requires reliable information from five senses:
Any impairment of these senses can lead to an experience of vertigo, disequilibrium or dizziness. Medical issues, including diabetes and heart disease, can potentially disrupt the functioning of these senses through nerve damage or circulation impairment.
Vertigo and Disequilibrium
Spinning vertigo is when either the environment appears to be spinning or a person feels that they are spinning within the environment. Positional vertigo is a spinning sensation occurring after a person repositions their head. A spinning sensation is often caused by inner ear problems.
Diabetes and Dizziness
Dizziness describes feelings of being lightheaded or sensing that one will faint. Individuals with diabetes may experience dizziness for several reasons:
Multi-sensory Vertigo or Dizziness
Low Blood Pressure As A Cause Of Dizziness
Dizziness, lightheadedness, and the feeling of passing out is a common complaint in people who have low blood pressure. When the blood pressure is too low, not enough oxygen-rich blood is delivered to the brain, and its function can be affected. If the brain’s blood supply is decreased too much, the person may pass out . Symptoms may worsen when changing position from lying down or sitting to standing up.
In addition to feeling dizzy, associated symptoms may include:
In individuals who are dehydrated or anemic, blood pressure readings may be normal when they are lying flat however, the lack of fluid is unmasked when they stand up quickly. The lack of blood to the brain may cause dizziness and lightheadedness. This feeling may pass in a few seconds as the body adapts. However, if dehydration or medications prevent the body from reacting by constricting blood vessels and increasing the heart rate, the dizziness may persist to the point at which the patient passes out .
Some diseases are associated with an inability to compensate for changes in body position . Normally when a person stands, blood vessels contract to increase blood pressure slightly, and the heart rate also increases slightly, to pump blood uphill to the brain against gravity. In autonomic dysfunction, a person may become dizzy when they move from a lying position to sitting or standing up. Examples of these diseases with this syndrome include diabetes, Addison’s disease, or Parkinson’s disease.
Read Also: What Happens When You Have Type 1 Diabetes
Heart Attack And Stroke
At its most serious, lightheadedness may be a sign of a heart attack or stroke. Other symptoms of a heart attack often accompanying lightheadedness are chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, arm pain, back pain, or jaw pain. Symptoms suggesting a stroke are the sudden onset of headache, numbness, weakness, visual changes, trouble walking, or slurred speech. “But in older adults, lightheadedness may be the only symptom of a heart attack or a stroke, especially if it doesn’t go away,” says Dr. Grossman. In that case, every second counts, so get to an emergency room for treatment.
Exercise Food And Alcohol
For people with type 1 diabetes, maintaining the correct blood glucose level involves balancing how much insulin you inject, the amount of food you eat, and how much energy you burn during exercise.
Hypoglycaemia may occur if you’ve taken your dose of insulin as usual, but your carbohydrate intake is lower than normal or has been used up more quickly. This may happen if you delay or miss a meal or snack, don’t eat enough carbohydrate, or exercise more than usual.
People with diabetes who’ve drunk too much alcohol, or drank alcohol on an empty stomach, can also get hypoglycaemia.
However, it’s not always possible to identify why a particular episode of hypoglycaemia has occurred, and sometimes it happens for no obvious reason.
Also Check: Can Type 2 Diabetics Donate Blood
The Inner Ear And Balance
Inside the inner ear is a series of canals filled with fluid. These canals are oriented at different angles and, as the head moves, the movement of the fluid inside these canals tells the brain how far, how fast and in what direction the head is moving.This information is then used by the brain to move the eyes an equal and opposite amount, so that the image that is seen by the eyes does not blur and remains clear.
Complications Of Type 2 Diabetes
Itâs important to get your blood sugar under control to avoid these serious conditions:
- Hypoglycemia. If your blood sugar falls below 70 milligrams per deciliter , it can lead to accidents, coma, and death.
- Hyperglycemia. Blood sugar that goes above 180 to 200 mg/dL can give you heart, nerve, kidney, and vision problems. Over the long term, it also can cause coma and death.
Over time, people with type 2 diabetes may have other health problems:
- Diabetic ketoacidosis. When you donât have enough insulin in your system, your blood sugar rises, and your body breaks down fat for energy. Toxic acids called ketones build up and spill into your urine. It can cause coma and death if you donât treat it.
- Heartand blood vessel diseases. People with diabetes are more likely to have conditions like high blood pressure and high cholesterol, which play a role in heart disease. Also, high blood sugar can damage your blood vessels and the nerves that control your heart.
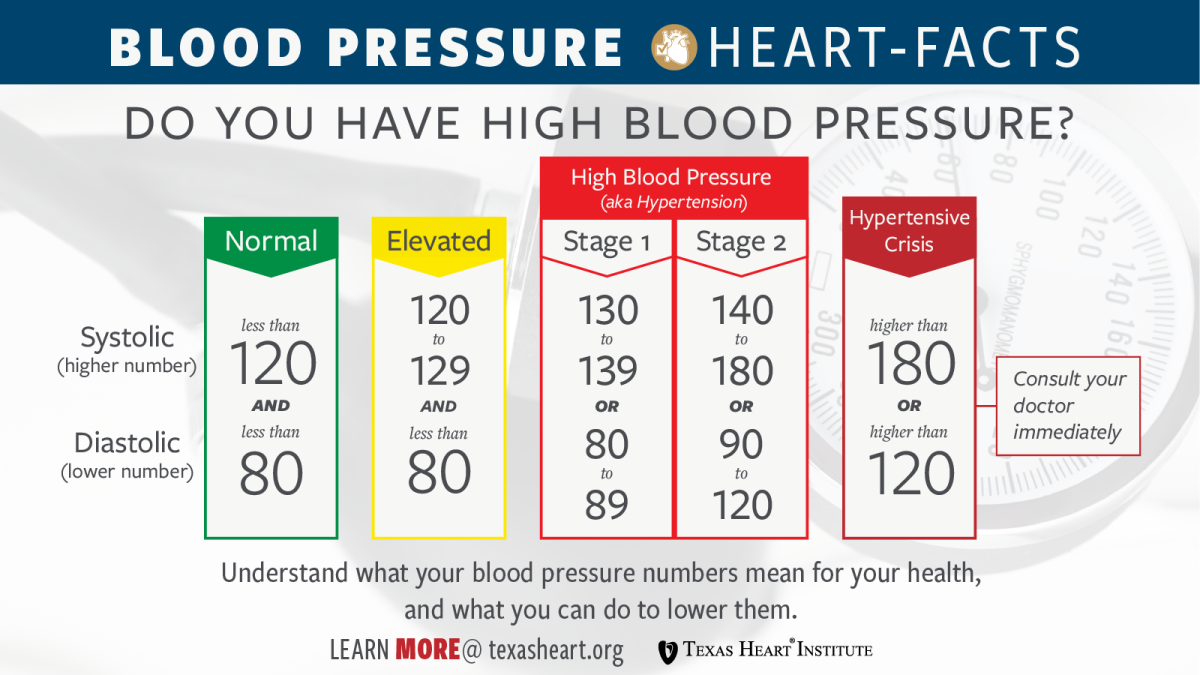
- High blood pressure. Diabetes doubles your risk of high blood pressure, which makes you more likely to have heart disease or stroke.
- Nerve damage . This can cause tingling and numbness, most often in your feet and legs. But it can also affect your digestive system, urinary tract, blood vessels, and heart.
- Eyedamage. Diabetes can cause:
- Glaucoma, a buildup of pressure in your eyes
- Cataracts, a cloudiness of your lens
- Retinopathy, which is damage to the blood vessels in your eyes
Don’t Miss: Can You Be Born With Type 2 Diabetes
High Blood Sugar: Diet And Exercise Advice
People with high blood sugar may be able to lower their levels through exercise and eating a nutritious, well-balanced diet with smaller portions.
If a personâs blood sugar level is higher than 240 mg/dl, it may not be safe for them to exercise because ketones may be present in the urine. Ketones are waste products that the body creates when it uses fats as fuel instead of glucose.
Exercising with ketones in the urine may cause blood sugar levels to increase even further. A buildup of ketones can also lead to a life threatening condition called ketoacidosis.
A doctor can offer advice on a safe treatment plan for lowering blood sugar.
What Is Hypoglycemia And Low Blood Sugar
Hypoglycemia is the state of having a blood glucose level that is too low to effectively fuel the body’s cells.
Glucose, which comes from carbohydrates found in foods, is a main source of energy for all of the cells of the body and, especially, the brain. While the body is quite good at extracting glucose from the foods we eat, it relies on a hormone called insulin to actually get the glucose inside the cells of specific organs: the liver, fat, and muscle.
We can think of insulin as holding the key to a cell without insulin, the glucose just remains in the blood, where its also known as blood sugar. During an episode of hypoglycemia, theres not enough glucose in the blood. The normal range is approximately 70 to 150 mg/dl .
Hypoglycemia is most common in newborns. In older children, its most often seen as a complication of insulin therapy for diabetes but can sometimes have other causes as well.
In the majority of cases, hypoglycemia is temporary, easily treated, and usually does not have serious consequences. There are several rare disorders in which hypoglycemia is recurrent and potentially life-threatening. However, with timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, these can be effectively managed.
Recommended Reading: Skinny People Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes And Dizziness
People with diabetes may experience dizziness, either as a symptom of the condition or as a result of dehydration or certain medications. A doctor can help determine the cause and how to manage or treat it.
Diabetes can cause low or high blood sugar, which can make people feel dizzy or lightheaded. High blood sugar can also lead to dehydration, as the body removes excess glucose from the blood through the urine, taking extra water with it.
Certain medications, including those that lower blood sugar, can also cause dizziness.
In this article, we look at the possible causes of dizziness in type 2 diabetes, other symptoms to be aware of, treatment options, and when to see a doctor.
Low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, can occur in a person with diabetes. Low blood sugar levels, or low glucose levels, are those that fall below the healthy range.
According to the American Diabetes Association , low blood sugar levels are usually below 70 milligrams per deciliter , although this may be different for each individual.
Research suggests that of people with diabetes experience dizziness as a symptom of low blood sugar.
Other signs of low blood sugar can include:
- statins
- neuropathic pain relief medication, such as amitriptyline, duloxetine, and pregabalin
A person can discuss medication changes with a doctor. They should not stop taking medications or change their dosages unless the doctor instructs them to do so.
What Are The Signs Of Hypoglycemia
An individual may frequently wake up in the middle of the night as a result of nighttime hypoglycemia. In other instances, though, people may know if they experienced hypoglycemia during their sleep if they notice the following symptoms:
- Waking up with a headache
- Waking up in a sweat
- Getting unusual feelings of tiredness throughout the day
- Experiencing anxiety or heart palpitations
- Feeling confused, dizzy or weak
Don’t Miss: Is Pasta Good For Diabetics

