Problems With The Pancreas
If there is a problem with the pancreas, it can affect the entire body. This can affect the amount of digestive enzymes that are produced by the pancreas. In case there is not enough digestive enzymes being produced, food will not be properly absorbed. This may lead to health complications such as diarrhea and weight loss. The pancreatic islets are responsible for producing the hormone insulin. People with type 1 diabetes do not produce any insulin. This is because the insulin producing beta cells are mistakenly attacked by the immune system. When we eat carbohydrates, the amount of glucose in the bloodstream tends to rise. Glucose is a form of sugar which is one of the biggest sources of fuel for the body.
An increase in blood sugar will stimulate the pancreas to release the hormone insulin, which helps to regulate blood sugar levels. As a result of beta cells dying, the pancreas in people with type 1 diabetes will struggle to secrete enough insulin. This leads to a build up of blood sugar levels which, if not treated, can lead to serious health problems like nerve and kidney damage. To prevent this risk, people with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections to keep their blood sugar levels normal.
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed
Doctors can say for sure if a person has diabetes by testing blood samples for glucose. Even if someone doesn’t have any symptoms of type 2 diabetes, doctors may order blood tests to check for it if the person has certain risk factors .
Some kids and teens with diabetes may go to a pediatric endocrinologist â a doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating children and teens living with diseases of the endocrine system, such as diabetes and growth problems.
p
Exocrine Function Of Pancreas
Enzymes break down food by cleaving specific chemical compounds in food so that the molecules are smaller and can easily be absorbed through the intestinal wall and into the blood. The various enzymes are different from each other by cleaving different chemical compounds.
The enzyme-producing part of the pancreas is called the exocrine section. This part of the gland works closely with the liver and gall bladder, both of which secrete substances that are important for digestion of food.
It can occur in both acute and chronic pancreatitis . Often these diseases are associated with prolonged and excessive alcohol intake. Acute pancreatitis can be life threatening. Chronic pancreatitis results in decreased production of enzymes. Thus, the food is not break down in the intestine sufficiently Many of nutrients are without being absorbed in the blood, when the food passes through the digestive system.
You May Like: What Is The Ribbon Color For Type 1 Diabetes
What Is The Function Of The Pancreas
A pancreas that is functioning normally produces chemicals which are responsible for digesting food that we eat. The pancreas plays a role in two different systems, that is the exocrine system and the endocrine system. The exocrine tissue in the pancreas secretes an alkaline fluid that consists of several enzymes. These enzymes work by breaking down the food we eat into small particles that can be absorbed by the intestines.
Organ Of The Body That Produces Insulin Codycross
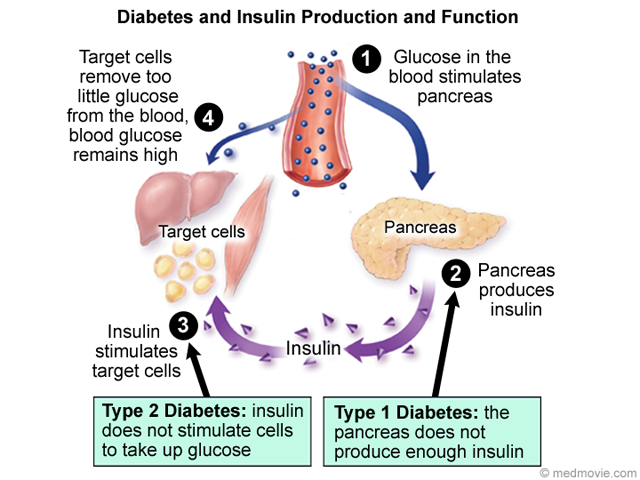
Key points :
Striving for the right answers? Lucky You! You are in the right place and time to meet your ambition. In fact, this topic is meant to untwist the answers of CodyCross Organ of the body that produces insulin. Accordingly, we provide you with all hints and cheats and needed answers to accomplish the required crossword and find a final word of the puzzle group.
You May Like: What Medications Can Raise Blood Sugar Levels
How Our Bodies Turn Food Into Energy
All parts of the body need energy to work. This energy comes from the food we eat.
Our bodies digest the food we eat by mixing it with fluids in the stomach. When the stomach digests food, the carbohydrate in the food breaks down into another type of sugar, called glucose.
The stomach and small intestines absorb the glucose and then release it into the bloodstream. Once in the bloodstream, glucose can be used immediately for energy or stored in our bodies, to be used later.
However, our bodies need insulin in order to use or store glucose for energy. Without insulin, glucose stays in the bloodstream, keeping blood sugar levels high.
The Pancreas And Type 1 Diabetes
In type 1 diabetes , the beta cells that produce insulin are attacked by the bodys immune system.
As more beta cells get killed off, the pancreas struggles to produce enough insulin to keep blood sugar levels down and the symptoms of diabetes begin to appear.
Research has shown that whilst many beta cells are killed off, the body can continue to produce very small amounts of insulin even after decades have passed.
Don’t Miss: Metformin Side Effects Skin Rash
Understanding Insulin And Diabetes
- The pancreas maintains the bodys blood glucose balance.
- Primary hormones of the pancreas include insulin and glucagon, and both regulate blood glucose.
- Diabetes is the most common disorder associated with the pancreas.
Anatomy of the Pancreasspineislets of LangerhansHormones of the Pancreas
- Gastrin: This hormone aids digestion by stimulating certain cells in the stomach to produce acid.
- Glucagon: Glucagon helps insulin maintain normal blood glucose by working in the opposite way of insulin. It stimulates your cells to release glucose, and this raises your blood glucose levels.
- Insulin: This hormone regulates blood glucose by allowing many of your bodys cells to absorb and use glucose. In turn, this drops blood glucose levels.
- Somatostatin: When levels of other pancreatic hormones, such as insulin and glucagon, get too high, somatostatin is secreted to maintain a balance of glucose and/or salt in the blood.
- Vasoactive intestinal peptide : This hormone helps control water secretion and absorption from the intestines by stimulating the intestinal cells to release water and salts into the intestines.
Diseases and Disorders of the Pancreas
What Causes Too Much Insulin In Body
4.6/5Causescauseinsulinbodyinsulininsulinexcessiveinsulincomplete answer
A rare tumor of the pancreas can cause you to produce too much insulin, resulting in hypoglycemia. Other tumors also can result in too much production of insulin-like substances. Enlargement of cells of the pancreas that produce insulin can result in excessive insulin release, causing hypoglycemia.
Beside above, what are the symptoms of too much insulin? The list of symptoms below are symptoms of hypoglycemia which can result from an insulin overdose:
- Depressed mood.
- Irritability.
Also, what is it called when your body produces too much insulin?
The pancreas is an organ in the abdomen. Tumors of the pancreas that produce too much insulin are insulinomas. Insulinomas keep making insulin, and can make your blood sugar drops too low . A high blood insulin level causes a low blood sugar level .
Can you have too much insulin?
When there is too much insulin in the blood, the cells absorb more sugar than they need to, leaving less sugar in the blood. Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can occur as a result. When the blood sugar levels are too low, the body cannot function properly. The symptoms of an insulin overdose are those of hypoglycemia.
Also Check: Low A1c Symptoms
Components Of Pancreatic Juice
The pancreatic juice consists of a clear, alkaline solution of 750-1500 ml/d containing digestive enzymes.
PH of pancreatic juice: 7.5~8.4.
Pancreatic juice contains: water and electrolytes HCO3, others like Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, HPO42+, and a variety of digestive enzymes.
Pancreatic juice enzymes: also called pancreatic digestive enzymes, including:
Balancing Insulin And Blood Sugar For Energy
The rise and fall in insulin and blood sugar happens many times during the day and night. The amount of glucose and insulin in our bloodstream depends on when we eat and how much. When the body is working as it should, it can keep blood sugar in target range, which is between 70 and 140 milligrams per deciliter. However, even in people without diabetes, blood sugar levels can go up as high as 180 during or right after a meal. Within two hours after eating, blood sugar levels should drop to under 140. After several hours without eating, blood sugar can drop as low as 70.
Using glucose for energy and keeping it balanced with just the right amount of insulin not too much and not too little is the way our bodies maintain the energy needed to stay alive, work, play, and function even as we sleep.
Don’t Miss: Diabetes Mac And Cheese
What Tests Will Be Done To Evaluate Insulin Resistance
Your healthcare provider may order the following blood tests to diagnose insulin resistance and/or prediabetes or diabetes:
- Glucose: A fasting plasma glucose or a glucose tolerance test may be used to screen for, diagnose and/or monitor prediabetes, type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes.
- Glycated hemoglobin A1c : This test reveals your average blood glucose levels over the past three months.
- Lipid panel: This is a group of tests that measure specific lipids in your blood, such as total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
Your healthcare provider may also order tests that can help diagnose other conditions that are associated with insulin resistance, such as metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease and polycystic ovary syndrome .
What Is The Difference Between Insulin Resistance And Diabetes
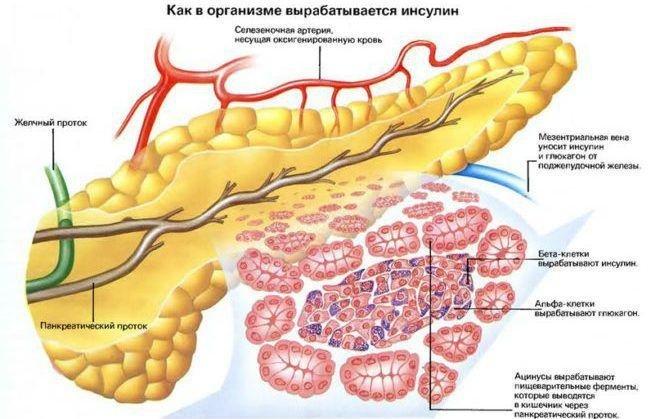
Anyone can develop insulin resistance temporarily or chronically. Over time, chronic insulin resistance can lead to prediabetes and then Type 2 diabetes if its not treated or able to be treated.
Prediabetes happens when your blood glucose levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. Prediabetes usually occurs in people who already have some insulin resistance.
Prediabetes can lead to Type 2 diabetes , the most common type of diabetes. T2D happens when your pancreas doesnt make enough insulin or your body doesnt use insulin well , resulting in high blood glucose levels.
Type 1 diabetes happens when your bodys immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas for an unknown reason. T1D is an autoimmune and chronic disease, and people with T1D have to inject synthetic insulin to live and be healthy. While T1D is not caused by insulin resistance, people with T1D can experience levels of insulin resistance in which their cells dont respond well to the insulin they inject.
Gestational diabetes is a temporary form of diabetes that can happen during pregnancy. Its caused by insulin resistance thats due to the hormones the placenta makes. Gestational diabetes goes away once you deliver your baby. Approximately 3% to 8% of all people who are pregnant people in the United States are diagnosed with gestational diabetes.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If You Have High Blood Sugar
What Are The Target Cells Of Glucagon
The target organ of the glucagon signaling pathway that produces the above metabolic effects is the liver, which removes the liver or blocks the blood flow of the liver , and these effects disappear. In addition, the glucagon signaling pathway promotes the secretion of insulin and islet somatostatin.
What Is The Prognosis For Insulin Resistance
The prognosis of insulin resistance depends on several factors, including:
- The cause of insulin resistance.
- The severity of insulin resistance.
- How well your insulin-producing cells are working.
- How susceptible you are to developing complications from insulin resistance.
- Adherence to treatment and your bodys response to treatment.
People can have mild insulin resistance that never turns into prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes. People can also have insulin resistance thats reversible or very manageable with lifestyle changes. For some people who have inherited conditions that cause severe insulin resistance, it can be life-threatening or lead to death.
If you have insulin resistance, ask your healthcare provider about what you can expect and how best to manage it.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Side Effects Of Metformin 500mg
Produced In The Pancreas
When you eat, food travels to your stomach and small intestines, where its broken down into nutrients that include glucose. The nutrients are absorbed and distributed via your bloodstream.
The pancreas is a gland located behind your stomach that performs an essential role in the digestion process. It creates enzymes that break down the fat, starches, and sugar in the food. It also secretes insulin and other hormones into your bloodstream.
Insulin is created in the beta cells of the pancreas. Beta cells comprise about 75% of pancreatic hormone cells.
Other hormones produced by the pancreas are:
- glucagon, which alerts your liver to raise your blood sugar if it gets too low
- gastrin, which stimulates the production of gastric acid in your stomach
- amylin, which helps control your appetite
You Say Sugar I Say Glucose
Glucose
Sucrose
Fructose
Is sugar in a doughnut the same as blood sugar? Lets clear up the confusion: Sugar can have many different names, with different meanings.
When doctors and scientists talk about sugar in the blood, they often use the word glucose. Glucose is a simple carbohydrate, also known as a monosaccharide . This can also be called blood sugar.
Unlike sucrose or fructose , you wont be able to find glucose in the grocery store.
Also Check: Contraindications For Metformin
What Is Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance, also known as impaired insulin sensitivity, happens when cells in your muscles, fat and liver dont respond as they should to insulin, a hormone your pancreas makes thats essential for life and regulating blood glucose levels. Insulin resistance can be temporary or chronic and is treatable in some cases.
Under normal circumstances, insulin functions in the following steps:
- Your body breaks down the food you eat into glucose , which is your bodys main source of energy.
- Glucose enters your bloodstream, which signals your pancreas to release insulin.
- Insulin helps glucose in your blood enter your muscle, fat and liver cells so they can use it for energy or store it for later use.
- When glucose enters your cells and the levels in your bloodstream decrease, it signals your pancreas to stop producing insulin.
For several reasons, your muscle, fat and liver cells can respond inappropriately to insulin, which means they cant efficiently take up glucose from your blood or store it. This is insulin resistance. As a result, your pancreas makes more insulin to try to overcome your increasing blood glucose levels. This is called hyperinsulinemia.
As long as your pancreas can make enough insulin to overcome your cells weak response to insulin, your blood sugar levels will stay in a healthy range. If your cells become too resistant to insulin, it leads to elevated blood glucose levels , which, over time, leads to prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes.
How Is The Pancreas Linked With Diabetes
Diabetes is characterized by high blood sugar. This results from insufficient insulin production or function, which can be one effect of problems with the pancreas.
People with diabetes experience high or low blood sugar levels at different times, depending on what they eat, how much they exercise, and whether they take insulin or diabetes medication.
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes both involve the pancreas.
Recommended Reading: Is Diabetes Mellitus–an Autoimmune Disease
Regulator Of Endocannabinoid Metabolism
Insulin is a major regulator of endocannabinoid metabolism and insulin treatment has been shown to reduce intracellular ECs, the 2-arachidonoylglycerol and anandamide , which correspond with insulin-sensitive expression changes in enzymes of EC metabolism. In insulin-resistant adipocytes, patterns of insulin-induced enzyme expression is disturbed in a manner consistent with elevated EC synthesis and reduced EC degradation. Findings suggest that insulin-resistant adipocytes fail to regulate EC metabolism and decrease intracellular EC levels in response to insulin stimulation, whereby obese insulin-resistant individuals exhibit increased concentrations of ECs. This dysregulation contributes to excessive visceral fat accumulation and reduced adiponectin release from abdominal adipose tissue, and further to the onset of several cardiometabolic risk factors that are associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Hypoglycemia, also known as “low blood sugar”, is when blood sugar decreases to below normal levels. This may result in a variety of symptoms including clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, loss of consciousness, seizures or death. A feeling of hunger, sweating, shakiness and weakness may also be present. Symptoms typically come on quickly.
Main Organs Involved In Glucose Homeostasis
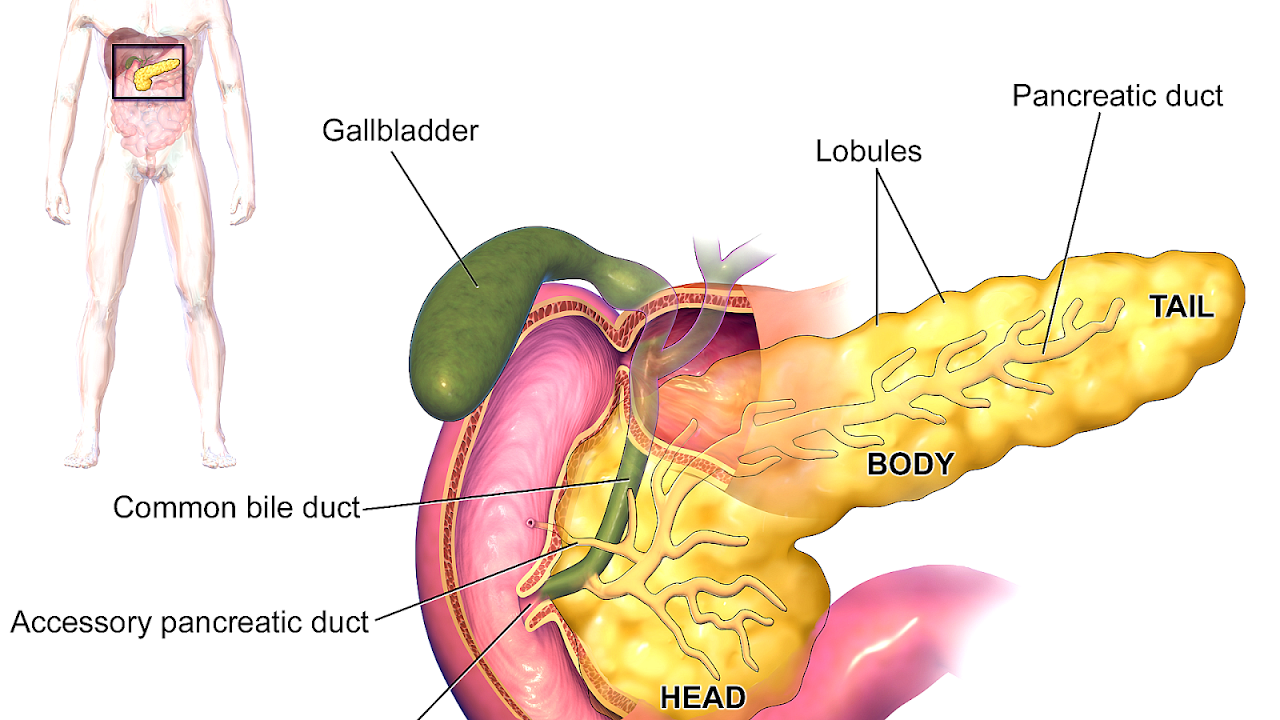
Although some organs need fatty acids to carry out their metabolic processes, most tissues in the human body use glucose as their main source of energy. Good glucose utilization depends on keeping blood glucose levels within range at all times and on the proper functioning of the glucose homeostatic mechanism. Several complementary physiological processes are involved in the glucose homeostatic mechanism. The gastrointestinal tract is responsible to produce and absorb glucose, the liver carries out biochemical reactions such as glycogenolysis, glycolysis, and gluconeogenesis, the kidneys filter, reabsorb, and in some cases excrete glucose, and they also produce glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors. The role of the main organs involved in the glucose regulation cycle is described below.
Don’t Miss: Insulin Secretion Would Be Highest
Health Risks Of Insulin Resistance
People with insulin resistance are at greater risk of developing prediabetes, Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
People with insulin resistance are more likely to have a history of being obese and physically inactive. They are also likely to have other cardiovascular risk factors such as too much LDL cholesterol, not enough HDL cholesterol, high triglycerides and high blood pressure.
Thats why its important to be aware of diabetes risk factors and take steps to prevent diabetes.
How Common Is Insulin Resistance
Since there arent any common tests to check for insulin resistance and there arent any symptoms until it turns into prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes, the best way to measure the prevalence of insulin resistance is through the number of prediabetes cases. More than 84 million adults in the United States have prediabetes. Thats about 1 out of every 3 adults.
You May Like: What Level Of A1c Requires Insulin

