Insulin Analogs Are Now Replacing Human Insulin In The Us
Insulins are categorized by differences in onset, peak, duration, concentration, and route of delivery.
Human Insulin and Insulin Analogs are available for insulin replacement therapy. Insulins also are classified by the timing of their action in your body specifically, how quickly they start to act, when they have a maximal effect and how long they act.Insulin analogs have been developed because human insulins have limitations when injected under the skin. In high concentrations, such as in a vial or cartridge, human clumps together. This clumping causes slow and unpredictable absorption from the subcutaneous tissue and a dose-dependent duration of action . In contrast, insulin analogs have a more predictable duration of action. The rapid acting insulin analogs work more quickly, and the long acting insulin analogs last longer and have a more even, peakless effect.
What Are The 6 Different Types Of Insulin
If you need insulin, your doctor will recommend a specific type depending on your lifestyle, the type of diabetes you have, and your blood sugar levels at different times of the day. You may need more insulin coverage at mealtimes, overnight, or throughout the entire day. Currently, there are 5 types of injectable insulins and 1 inhaled insulin.
Types of insulin and how they work in your body
| How long it takes to start working | How long it lasts |
|---|
By signing up, I agree to GoodRx’sterms of service andprivacy policy, and to receive marketing messages from GoodRx.
How Many Types Of Diabetes Are There
There are a lot of types of diabetes. Some of these diabetes are type 1 and type 2 and others. Diabetes mellitus is a major problem that significantly affects the health of humans. It may result in a range of complications which can cause disability, and reduce peoples quality of life and life expectancy.
Read Also: What Happens If You Stop Taking Diabetes Medication
Faq: Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is insulin so expensive?
Though reforms are underway in many parts of the US, insulin costs are still prohibitively expensive for many people with diabetes. Reasons include the complexity of the pharmaceutical supply chain and lack of generic substitutes.
2. What is sliding scale insulin?
Sliding scale therapy is a regimen that prescribes a progressive increase in insulin doses before meals and at bedtime, based on your blood sugar levels.
3. What is an insulin index?
The insulin index gives foods a rating based on how much your blood insulin concentration rises in the two hours after consumption.
4. What is an insulin resistance diet?
An insulin resistance diet incorporates foods that will help maintain your bodys balance of insulin and blood sugar. Think nourishing calories from veggies, fruit, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
What Is Insulin Used For
Insulins main job is to keep your blood sugar levels from getting too high. After a meal, your pancreas releases the hormone insulin into your bloodstream. Insulin travels through your body where it helps take sugar out of your blood and move it into cells for energy.
In some cases, your body may not make or respond to its own natural insulin the way it should. Therefore, you may need to use an insulin medication to manage your blood sugar levels.
Also Check: What Does Diabetic Mean
Type 1 Diabetes: Types Of Insulin
Insulin therapy is essential for everyone who has type 1 diabetes and some people who have type 2 diabetes. Various types of insulin are available. They differ in terms of how quickly and how long they are effective, as well as in their chemical structure.
Some types of insulin work quickly , while others only start to work after a certain amount of time, and then work over a longer time period .
Insulin can be extracted from the pancreas cells of pigs or cattle and prepared for use in humans. But nowadays most people use genetically engineered insulin for the treatment of diabetes. There are two types of genetically engineered insulin, known as human insulin and insulin analogues. Human insulin is similar to the insulin made in the human body. Insulin analogues have a different chemical structure, but they have a similar effect.
How Should I Store My Insulin
- Keep current insulin at room temperature to help alleviate injection discomfort.
- Insulin can usually be stored at room temperature for about a month. Once in use, insulin pens should be stored at room temperature. Expiration dates of insulin pens can vary depending upon the type of insulin. For disposable pens, you should discard the entire device when empty or when you reach the expiration date.
- Store extra insulin in the refrigerator.
- Dont expose insulin to excessive cold or heat.
You May Like: Basal Insulin Side Effects
Structural Analysis And Synthesis
Purified animal-sourced insulin was initially the only type of insulin available for experiments and diabetics. John Jacob Abel was the first to produce the crystallised form in 1926. Evidence of the protein nature was first given by Michael Somogyi, Edward A. Doisy, and Philip A. Shaffer in 1924. It was fully proven when Hans Jensen and Earl A. Evans Jr. isolated the amino acids phenylalanine and proline in 1935.
The amino acid structure of insulin was first characterized in 1951 by Frederick Sanger, and the first synthetic insulin was produced simultaneously in the labs of Panayotis Katsoyannis at the University of Pittsburgh and Helmut Zahn at RWTH Aachen University in the mid-1960s.Synthetic crystalline bovine insulin was achieved by Chinese researchers in 1965. The complete 3-dimensional structure of insulin was determined by X-ray crystallography in Dorothy Hodgkin‘s laboratory in 1969.
Two other Nobel Prizes have been awarded for work on insulin. British molecular biologist Frederick Sanger, who determined the primary structure of insulin in 1955, was awarded the 1958 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.Rosalyn Sussman Yalow received the 1977 Nobel Prize in Medicine for the development of the radioimmunoassay for insulin.
How Do I Take It
Many people get insulin into their blood using a needle and syringe, a cartridge system, or pre-filled pen systems.
The place on the body where you give yourself the shot may matter. You’ll absorb insulin the most evenly when you inject it into your belly. The next best places to inject it are your arms, thighs, and buttocks. Make it a habit to inject insulin at the same general area of your body, but change up the exact injection spot. This helps lessen scarring under the skin.
Inhaled insulin, insulin pumps, and a quick-acting insulin device are also available.
Recommended Reading: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
What Type Of Insulin Is Best For My Diabetes
Your doctor will work with you to prescribe the type of insulin that’s best for you and your diabetes. Making that choice will depend on many things, including:
- How you respond to insulin.
- Lifestyle choices. The type of food you eat, how much alcohol you drink, or how much exercise you get will all affect how your body uses insulin.
- Your willingness to give yourself multiple injections per day
- Your age
- Your goals for managing your blood sugar
Your doctor may prescribe more than one type. You might need to take insulin more than once daily, to space your doses throughout the day, or to add other medicines.
Afrezza, a rapid-acting inhaled insulin, is FDA-approved for use before meals for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The drug peaks in your blood in about 15-20 minutes and it clears your body in 2-3 hours. It must be used along with long-acting insulin in people with type 1 diabetes.
The chart below lists the types of injectable insulin with details about onset , peak and duration . These three things may vary. The final column offers some insight into the “coverage” provided by the different insulin types in relation to mealtime.
| Type of Insulin & Brand Names | Onset |
| 30 min.-2 1/2 hours | 16-20 hours |
| *Premixed insulins combine specific amounts of intermediate-acting and short-acting insulin in one bottle or insulin pen. |
Regulator Of Endocannabinoid Metabolism
Insulin is a major regulator of endocannabinoid metabolism and insulin treatment has been shown to reduce intracellular ECs, the 2-arachidonoylglycerol and anandamide , which correspond with insulin-sensitive expression changes in enzymes of EC metabolism. In insulin-resistant adipocytes, patterns of insulin-induced enzyme expression is disturbed in a manner consistent with elevated EC synthesis and reduced EC degradation. Findings suggest that insulin-resistant adipocytes fail to regulate EC metabolism and decrease intracellular EC levels in response to insulin stimulation, whereby obese insulin-resistant individuals exhibit increased concentrations of ECs. This dysregulation contributes to excessive visceral fat accumulation and reduced adiponectin release from abdominal adipose tissue, and further to the onset of several cardiometabolic risk factors that are associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Hypoglycemia, also known as “low blood sugar”, is when blood sugar decreases to below normal levels. This may result in a variety of symptoms including clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, loss of consciousness, seizures or death. A feeling of hunger, sweating, shakiness and weakness may also be present. Symptoms typically come on quickly.
You May Like: What Cells Release Glucagon
Insulin Activity And Duration
Insulin has a period of activity that affects when it must be injected and how long it will continue to work in the dog’s body. Insulin also has a peak of activity, making it critical that the dog be fed at an appropriate time in order for there to be enough sugars in the dog’s system for the insulin to burn, avoiding hypoglycemic reactions. The broadest selection of insulin activity and duration is found in Novolin, providing short, intermediate, mixed and long-term activity insulin. Vetsulin/Caninsulin currently offer intermediate-acting insulin.
Short duration insulin reaches its peak activity in a very short period of time and drops off to no activity very quickly. Short-acting insulin is frequently mixed with intermediate or long-acting insulin to provide peaks of activity at meal times. Short-acting insulin can also be used to control high blood sugars that can occur when a dog is sick.
Mature Onset Diabetes Of The Young
Mature Onset Diabetes of the Young is a rare form of diabetes which is different from both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, but is genetic and runs in families.
MODY is caused by a mutation in a single gene. If a parent has this gene mutation, their children have a 50% chance of inheriting the gene for MODY from them.
If a child inherits the MODY gene, they are likely to develop this form of diabetes before they turn 25, despite any lifestyle changes they may make.
MODY is often treated with oral diabetes medications or insulin, and some forms may not require any treatment at all. There are four types of MODY:
Also Check: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
How Do Different Types Of Insulin Work
Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that allows your body to use sugar from carbohydrates in the food that you eat for energy or to store glucose for future use. Diabetes is a health condition in which the body is unable to regulate blood sugar on its own through insulin. There are two distinct types of diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes :T1D, once known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Different factors, including genetics and some viruses, may contribute to T1D.
Type 2 Diabetes :T2D is a chronic condition that affects the way your body metabolizes sugar. In T2D, the body either resists the effects of insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. Genetics and environmental factors, such as being overweight and inactive, have been established as contributing factors.
All patients with T1D and patients with more serious forms of T2D need to take insulin medications to help their body regulate blood sugar.
There are many types of insulin medications available. Each kind has its own unique action and they are not interchangeable. The chart below will help you understand how the various insulin medications work and why your healthcare provider has prescribed them for you.
How To Take Long
Usually, you inject long-acting insulin once a day to keep your blood sugar levels steady. You use a needle or pen device to give yourself the injection. Be sure to inject your long-acting insulin at the same time every day to avoid lags in insulin coverage or stacking your insulin doses. Stacking means taking your doses too close together, causing their activity to overlap.
Your doctor might recommend adding short-acting insulin before a meal to prevent a blood sugar spike after you eat.
If you change brands of long-acting insulin, you may need a different dose. Talk to your doctor for advice if you change brands of any insulin.
As with any medicine you take, insulin injections can cause side effects.
One possible side effect is low blood sugar . Symptoms of low blood sugar include:
- dizziness
- headache
- fainting
Other possible side effects of insulin injections include pain, redness, or swelling of the skin at the injection site.
Sometimes insulin is given in combination with thiazolidinediones. This drug group includes oral diabetic drugs like Actos and Avandia. Taking insulin with thiazolidinediones increases the risk of fluid retention and heart failure.
For those taking degludec, precautions may be necessary because of its long effect in the body. You doctor may need to increase your dose at a very gradual rate, at least three to four days apart. It will also take longer to clear the drug from your body.
Don’t Miss: How Long Do Type 1 Diabetics Live
How Are Doses Scheduled
Follow your doctor’s guidelines on when to take your insulin. The time span between your shot and meals may vary depending on the type you use.
In general, though, you should coordinate your injection with a meal. You want to time your shot so that the glucose from your food gets into your system at about the same time that the insulin starts to work. This will help your body use the glucose and avoid low blood sugar reactions. From the chart on page 1, the “onset” column shows when the insulin will begin to work in your body. You want that to happen at the same time you’re absorbing food. Good timing will help you avoid low blood sugar levels.
- Rapid acting insulins: About 15 minutes before mealtime
- Short-acting insulins: 30 to 60 minutes before a meal
- Intermediate-acting insulins: Up to 1 hour prior to a meal
- Pre-mixed insulins: Depending on the product, between 10 minutes or 30 to 45 minutes before mealtime
Insulin Syringe Types And How To Choose The Right One
Curious about insulin syringe types? The fact is, not all insulin syringe types are the same. They come in many different types, and each type has a specific purpose.
When shopping for insulin syringes, youll need to know about the purpose behind each design. Some may work for you, and other designs might meet your needs a little better.
If youve been looking for new insulin syringes, keep scrolling. In this article, we are going over the different syringe types and how to choose the right one.
Read Also: Does Metformin Lower A1c
Factors That Speed Insulin Absorption
Variation in insulin absorption can cause changes in blood glucose levels. Insulin absorption is increased by:
- injecting into an exercised area such as the thighs or arms
- high temperatures due to a hot shower, bath, hot water bottle, spa or sauna
- massaging the area around the injection site
- injecting into muscle this causes the insulin to be absorbed more quickly and could cause blood glucose levels to drop too low.
People With Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is typically a progressive disease and most do not require insulin when first diagnosed. Blood glucose levels are often manageable with lifestyle changes such as more careful meal planning and exercise. Antidiabetic drugs, such as oral medications like metformin or non-insulin injectables, may be added if blood glucose level goals are not being met. Because Type 2 diabetes is a progressive disease, at some point the production of insulin in the pancreas may not be sufficient and insulin injections may be necessary.
RELATED: Can you reverse diabetes?
You May Like: Max Dosage Metformin
What Causes Someone To Be Prescribed Insulin
If your body doesnt make insulin or doesnt make enough, you are eventually diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. It used to be called juvenile diabetes, but new estimates show that as many as half of people with type 1 diabetes are not diagnosed until adulthood. On the other hand, if your body doesnt use insulin properly, you have type 2 diabetes.
While people with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin to survive, many people with type 2 are able to stave off insulin use or even avoid it altogether by exercising, losing weight, adapting healthier eating habits, or using other prescription medications.
Insulin Types And Actions Chart
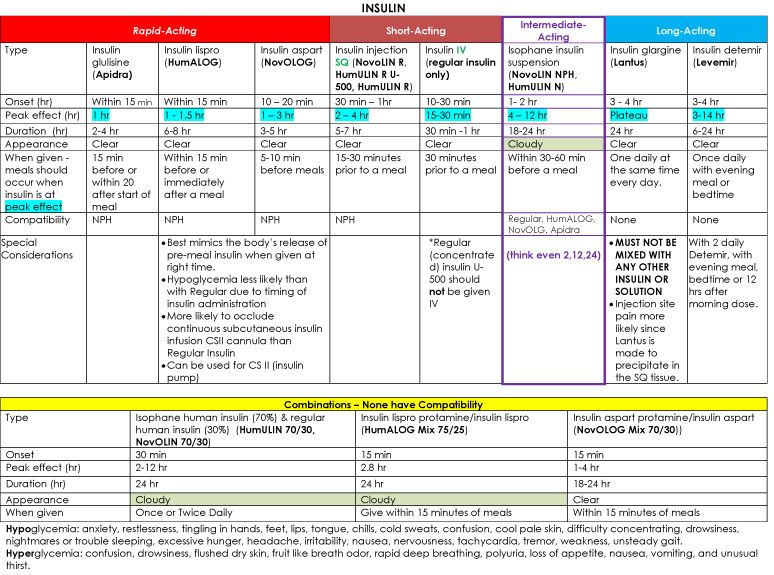
This chart covers the different brands of insulin, how long it takes for each to start lowering blood sugar, when the peak of action will occur, and how long it will continue to work. Read the product information provided with your medication and follow the instructions from your healthcare provider and pharmacist for using insulin.
| Brand Name |
Don’t Miss: Type 1 Diabetes Age Of Onset

