Prevention Is Still The Best Cure
Because there is no cure for diabetes or diabetic retinopathy, the best way to treat these conditions is to stay on top of your health. Taking care of yourself and following your doctors instructions can help you prevent comorbid conditions from developing.
High blood glucose, hypertension, and high ketone levels can increase your risk of retinopathy. As such, managing them is the first step in prevention.
Even though its difficult, eating a healthy diet and exercising will go a long way toward keeping your eyes healthy in the long run. Along with diet and exercise, monitoring your blood sugar levels and taking your medication as prescribed can help as well.
Finally, the importance of frequent eye exams cant be stressed enough.
If you have diabetes, seeing an eye doctor every few months can help you stop retinopathy in its tracks. You should also get a thorough exam with dilation every year. Your doctor may then be able to notice and treat the damage before you experience any symptoms.
Stage 4: Proliferative Retinopathy Blood Vessels Grow On The Retina
Stage four diabetic retinopathy is the most advanced stage of diabetic retinopathy, during which new blood vessels begin to grow on the retina. Unfortunately, these blood vessels are typically both weak and abnormal, which can lead to blood leaking into the eye, vision problems, and potentially blindness.
What Are The Four Stages Of Diabetic Retinopathy
The one on the left has no signs of diabetic retinopathy, while the other one has severe signs of it. If you are not a trained clinician, the chances are, you will find it quite hard to correctly identify the signs of this disease. So, how well can a computer program do it Background retinopathy is the earliest stage of changes to your retina caused by diabetes. Background retinopathy is common. At this stage, diabetes has started to affect the small blood vessels in.. Drugs used to treat Diabetic Retinopathy The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition. Select drug class All drug classes anti-angiogenic ophthalmic agents (4
Warning Signs & Symptoms
Many people with early diabetic retinopathy have no symptoms. As diabetic retinopathy progresses, symptoms include blurred vision, blindness, floaters or shadows and missing areas of vision. There are two kinds of diabetic retinopathy. The early stage is nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy, where blood vessels in the retina begin to leak. If the leakage results in accumulation of fluid in the retina, blurring of the vision can occur.
In the later stage, proliferative diabetic retinopathy, the blood vessels in the retina close, and abnormal blood vessels grow in their place. This can lead to vision loss, as well as detachment of the retina and even .
Get A Diabetic Eye Exam Once A Year
An eye exam can help diagnose eye problems for treatment and can alert you and your health care provider if your diabetes needs to be better controlled. Women with diabetes should have an eye exam before pregnancy or in the first trimester. Continue to be monitored every trimester and for one year after birth depending on the severity of the retinopathy.
Am I At Risk From Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy risk factors include the following.
If any of the below affect you its worth having an retinopathy screening examination as quickly as possible.
- Poor blood glucose control
- Raised fats in the blood
Anyone suffering from diabetes faces the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy and other diabetes complications
The longer a person has diabetes, the greater the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy becomes. However, keeping blood glucose levels well controlled can help to significantly slow down the development of retinopathy.
People with diabetes should, however, be aware that a rapid improvement in blood glucose levels can lead to a worsening of retinopathy. A rapid improvement in blood glucose levels in this case is defined as a drop in HbA1c of 30 mmol/mol or 3%.
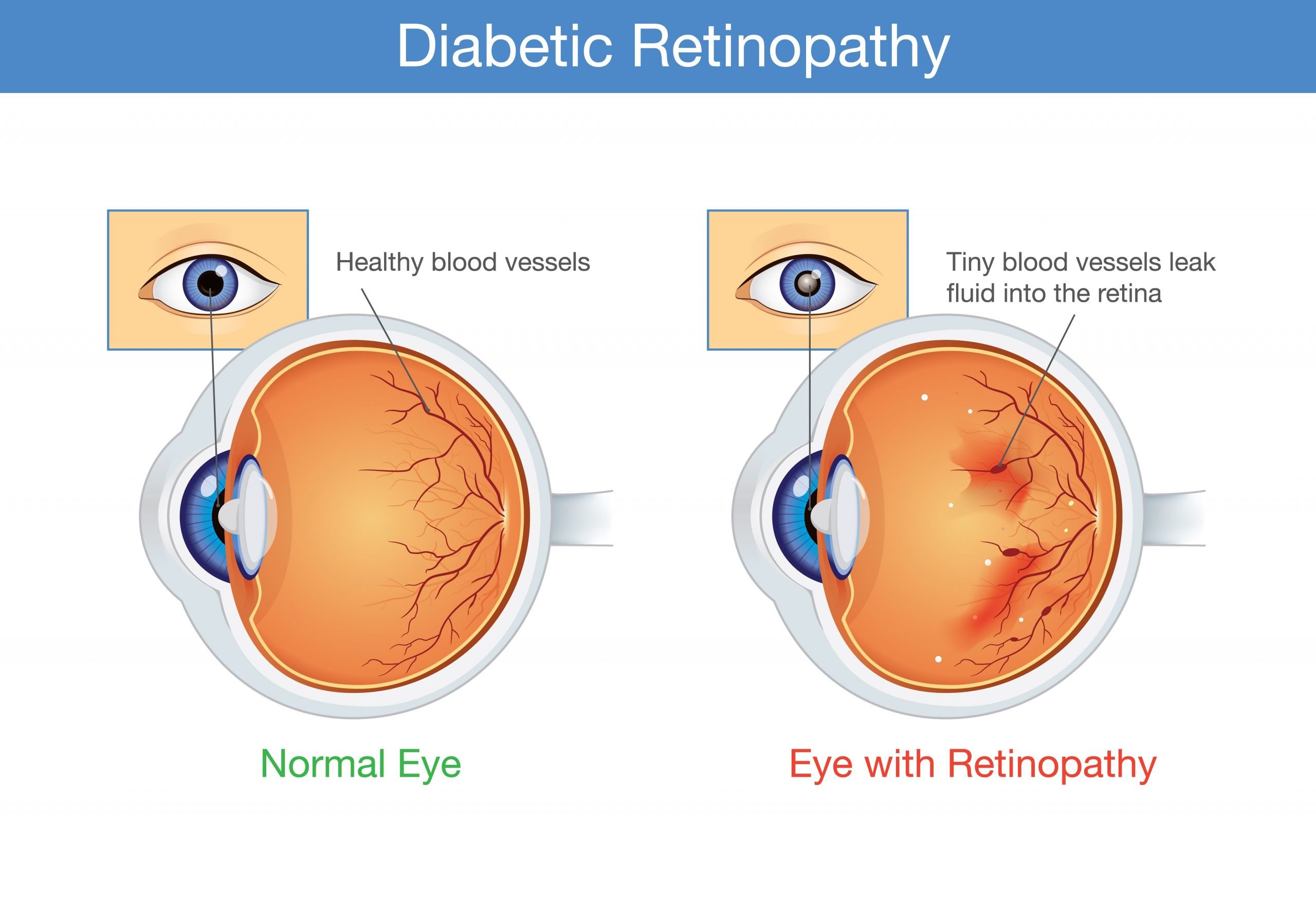
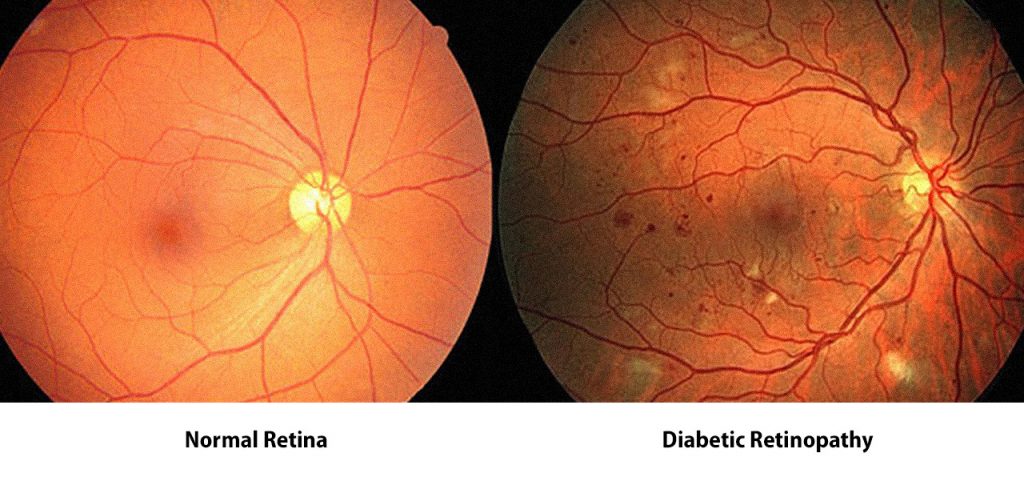
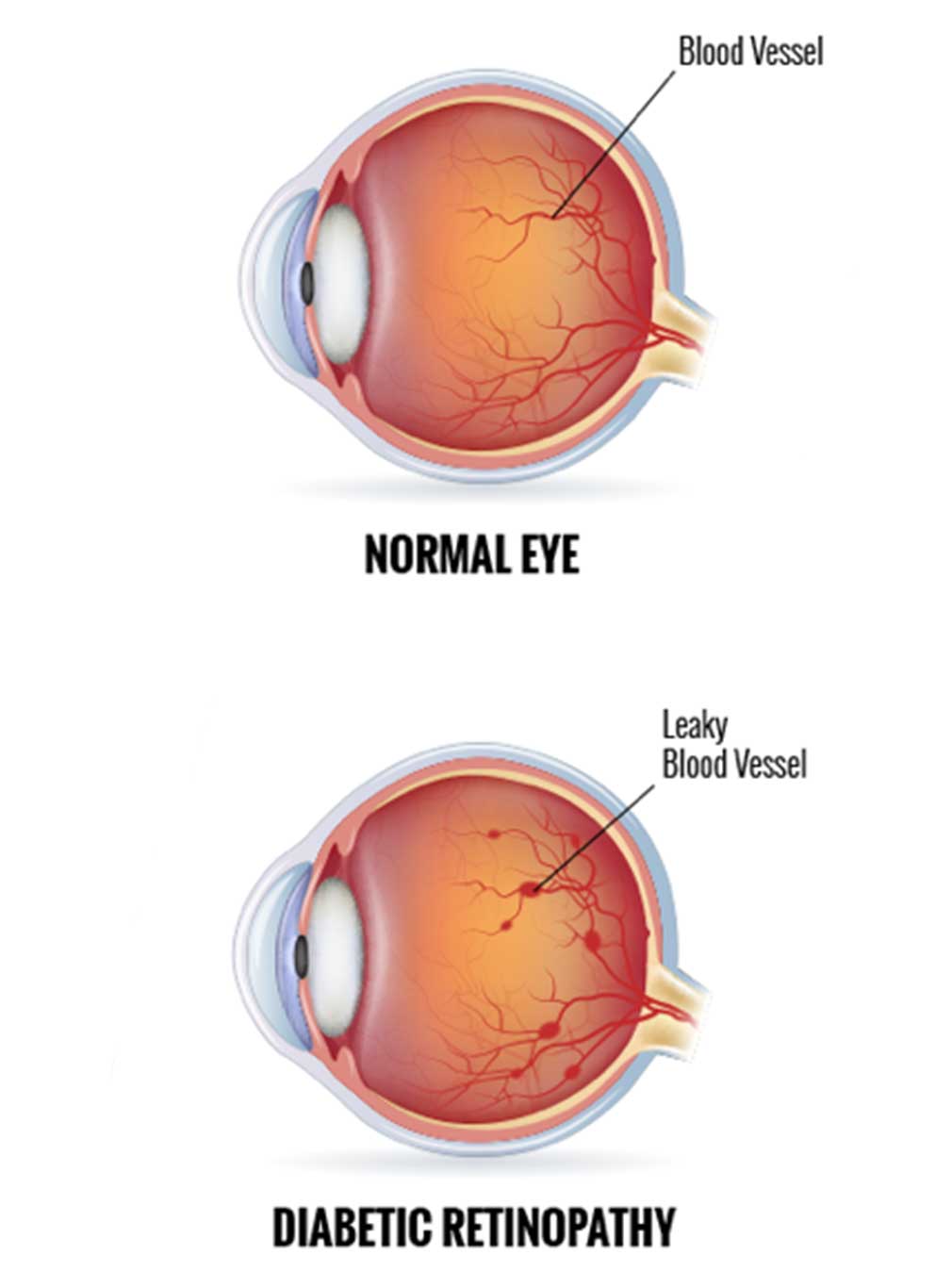
Retinopathy occurs when blood vessels in the back of the eye, the retina, become damaged. When the blood vessels become damaged they can leak and these leaks can cause dark spots on our vision.
The main causes of retinopathy tend to be sustained high blood glucose levels and high blood pressure as well. Retinopathy can progress over years or decades depending on how good your blood glucose control is.
The good news is that because it takes a long time to develop, it can be spotted before it becomes too serious.
Its important therefore that you attend your retinopathy screening each year.
FREE eye health guide
Signs Causes And Treatments Of Diabetic Retinopathy
Patricia, Facty Staff
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that causes damage to the eyes. Over time, the blood vessels in the back of the eye become damaged and very sensitive to light. Most people notice only mild vision problems at first, but if left untreated, diabetic retinopathy can lead to blindness. This condition can be a symptom of type 1 and type 2 diabetes and is something that should be monitored in people with diabetes. The following is a brief look at diabetic retinopathy, including common signs, causes, risk factors, and treatments.
What Will Your Eye Doctor Look Out For During An Eye Examination
Your doctor will perform a comprehensive dilated eye examination to assess the health of the eyes and your vision.
The exam should be simple and painless. Before the examination, an eye drop will be placed into your eyes to dilate or widen the pupils. This will allow the doctor to view the inside of the eyes more clearly. The drops can cause your near vision to blur for a few minutes. However, the effect would wear off after a few hours restoring your vision.
During the comprehensive eye examination, your ophthalmologist will look for the following :
Treatments For Diabetic Retinopathy
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy is only necessary if screening detects significant problems that mean your vision is at risk.
If the condition hasn’t reached this stage, the above advice on managing your diabetes is recommended.
The main treatments for more advanced diabetic retinopathy are:
- laser treatment
- injections of medication into your eyes
- an operation to remove blood or scar tissue from your eyes
What Other Problems Can Diabetic Retinopathy Cause
Diabetic retinopathy can lead to other serious eye conditions:
- Diabetic macular edema . Over time, about 1 in 15 people with diabetes will develop DME. DME happens when blood vessels in the retina leak fluid into the macula . This causes blurry vision.
- Neovascular glaucoma. Diabetic retinopathy can cause abnormal blood vessels to grow out of the retina and block fluid from draining out of the eye. This causes a type of glaucoma .
Learn more about types of retinal detachment
Whats The Treatment For Diabetic Retinopathy And Dme
In the early stages of diabetic retinopathy, your eye doctor will probably just keep track of how your eyes are doing. Some people with diabetic retinopathy may need a comprehensive dilated eye exam as often as every 2 to 4 months.
In later stages, its important to start treatment right away especially if you have changes in your vision. While it wont undo any damage to your vision, treatment can stop your vision from getting worse. Its also important to take steps to control your diabetes, blood pressure, and cholesterol.
Injections. Medicines called anti-VEGF drugs can slow down or reverse diabetic retinopathy. Other medicines, called corticosteroids, can also help.
Stage 4: Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
This is an advanced stage of the disease, in which new blood vessels form in the retina. Since these blood vessels are often fragile, theres a higher risk of fluid leakage. This triggers different vision problems such as blurriness, reduced field of vision, and even blindness.
Diabetic retinopathy doesnt usually cause symptoms during the nonproliferative stages, so its possible to have it and not know it. This is because blood vessels dont always leak in these stages.
Many people dont have symptoms until the disease progresses to proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
However, an eye examination by an eye care specialist or ophthalmologist can detect diabetic retinopathy in its earlier stages, before symptoms become apparent.
Symptoms of proliferative diabetic retinopathy include:
- depth perception
- curvature of the cornea
Your doctor will likely also dilate your eye to examine your optic nerve and retina using special eye drops.
Doctors can also diagnose diabetic retinopathy with fluorescein angiography, which checks for abnormal blood vessel growth or leakage.
Theyll inject a yellow dye into a vein in your arm, allowing the dye to travel through your blood vessels. A special camera takes images of the dye as it travels through the blood vessels in your retina.
Keeping blood sugar within a healthy range can slow the progression of vision loss.
If youre in a nonproliferative stage but experience some eye damage, treatment options might include:
Mild Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
This is the first stage of diabetic retinopathy. In this stage, a person may experience no symptoms at all. During this time, small areas of balloon-like swelling develop on the tiny vessels in the retina. The microaneurysms may leak fluid into the retina. In addition, hard exudates are often noted.
While you may not have any symptoms, eye disease can begin before symptoms do. The American Diabetes Association recommends:
- All people newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes should receive an eye exam shortly after diagnosis and every year thereafter.
- People with type 1 diabetes should receive a dilated eye exam within five years of diagnosis and every year after that.
Four Stages Of Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is classified into four stages; they are:
- Mild Nonproliferative Retinopathy
This is the initial stage where the tiny parts of the vessels may leak, and these leakages are called microaneurysms. In this stage, patients are unlikely to experience symptoms.
- Moderate Nonproliferative Retinopathy
Moderate Nonproliferative Retinopathy stage shows the blocking of the blood vessels that nourish the retina. At this stage, the patients are unlikely to experience any major symptoms.
- Severe Nonproliferative Retinopathy
During this Severe Nonproliferative Retinopathy stage, a greater number of blood vessels become blocked, depriving the retina of blood supply and, therefore, oxygen. And for the growth of new blood vessels, the blocked areas of the retina send messages to the body.
- Proliferative Retinopathy
At this Proliferative Retinopathy stage, the messages sent by the retina for new blood vessels are responded to, and new blood vessels grow. But these vessels are abnormal and fragile to grow along the retina. And due to their fragility, they are likely to leak blood, and these causes noticeable symptoms such as loss of vision and if untreated, possible blindness.
Know Your Blood Sugar Blood Pressure And Cholesterol Levels
It can be easier to keep your blood sugar levels, blood pressure and cholesterol levels under control if you know what level they are and monitor them regularly.
The lower you can keep them, the lower your chances of developing retinopathy are. Your diabetes care team can let you know what your target levels should be.
The First Signs Of Diabetic Retinopathy
According to the NIH , this is the leading cause of blindness among working-age Americans. But may not realize is that one of the conditions associated with diabetes is a type of vision loss called diabetic retinopathy. This condition is caused when high blood sugar levels cause damage to blood vessels in the retina. It does not show any symptoms, and its difficult to sense its presence in its initial stages.
Continue reading the full article and find out more about, including common signs, causes, risk factors, and treatments. A glucometer is essentially another term for Blood Glucose Meter. To accurately test your blood sugar levels, you can use one of the best blood sugar monitors at your home itself. You may be able to tell if you are hypoglycemic or hyper with symptoms related to each, however, one can never be certain about their blood levels without testing them with the best blood glucose meter.
Risk Factors For Diabetic Retinopathy
The largest risk factor for diabetic retinopathy is diabetes, but other conditions can increase your risk, as well. High blood sugar, high cholesterol, and tobacco use can increase the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy, sometimes at a younger age. Additionally, not controlling your blood sugar levels can increase your risk. Other risk factors are outside of human control, such as ethnicity: people who are African-American, Native American, or Hispanic are at greater risk.
How Does Diabetes Affect My Eyes
Diabetes affects your eyes when your blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high.
In the short term, you are not likely to have vision loss from high blood glucose. People sometimes have blurry vision for a few days or weeks when theyre changing their diabetes care plan or medicines. High glucose can change fluid levels or cause swelling in the tissues of your eyes that help you to focus, causing blurred vision. This type of blurry vision is temporary and goes away when your glucose level gets closer to normal.
If your blood glucose stays high over time, it can damage the tiny blood vessels in the back of your eyes. This damage can begin during , when blood glucose is higher than normal, but not high enough for you to be diagnosed with diabetes. Damaged blood vessels may leak fluid and cause swelling. New, weak blood vessels may also begin to grow. These blood vessels can bleed into the middle part of the eye, lead to scarring, or cause dangerously high pressure inside your eye.
Most serious diabetic eye diseases begin with blood vessel problems. The four eye diseases that can threaten your sight are
Modern Ways Of Detecting Diabetic Retinopathy
New systems consisting of fundus imaging cameras and artificially intelligent software offer the promise of faster, earlier, more accurate, and immediate detection of diabetic retinopathy, including in the PCPs office. Machine learning may be the key to reduced instances of diabetic retinopathy. It uses data analysis to spot patterns that can suggest an onset of the disease. The theory is that machines can analyze fundus camera scans at a level and accuracy that humans cannot, according to Modern Retina .
Modern Retina also cited a study of 3,000 patients in India and looked at the performance of the artificially intelligent system against human readers of fundus scans. The result: the machines performed as good, if not better, than humans. eep-learning technology could make screening for retinal diseases more cost-effective and efficient, the researchers concluded.
Using machine learning may help address one of the challenges in the prevention of retinopathy: a shortage of trained eye technicians with the skills to read and interpret retinal scans. The problem is significant both in the United States and in locations around the world, according to the Review of Ophthalmology. Retinal specialists practice in an estimated 12-20% of US counties, according to a 2019 paper presented at the American Society of Retinal Specialists conference.
How Is Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosed And Treated
Early diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy is key to prevent vision loss.
Diabetic retinopathy refers to a condition caused due to the damage to the retina in patients with diabetes. Uncontrolled diabetes can result in the persistently elevated levels of sugar in the blood due to which the light-sensitive part of the eye called the retina is damaged.
If you are suffering from diabetes, read on to learn how diabetic retinopathy is detected and treated.
What Are The Signs Of Diabetic Retinopathy
What Stage Do I Have
To diagnose diabetic retinopathy, your doctor will give you a diabetic eye screening. They may test your ability to see at different distances. They may test the pressure inside your eye. They may put drops in your eyes to make your pupils bigger, which lets the doctor see inside your eye.
The doctor may do an optical coherence tomography scan. It uses light waves to take pictures inside your eyes.
One final test the doctor may use is a fluorescein angiogram. This is when they inject dye into your vein, often in the arm. The dye travels to your eyes. Then the doctor will take photos of the dye in your eyes blood vessels to look for leaks and damage.
All of these tests will help your doctor diagnose the stage of your diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetic Retinopathy In The United States
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention describes diabetic retinopathy as the most common cause of vision impairment and blindness among working-age adults in the United States. The CDC has forecast that the number of Americans with diabetic retinopathy will reach almost 15 million by 2050, nearly doubling in forty years.
Human behavior is one of the drivers in the increase of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetic patients are frequently encouraged to pursue follow-up eye exams, but many do not. A 2017 study published in BMJ Open Diabetes Research and Care found that only four out of ten diabetes patients adhered to recommendations for follow-up care.
In a general sense, many PCPs have not been in a position to help beyond a specialist referral. They lack the time, equipment, expertise, and resources to integrate eye exams into regular visits. New technology is poised to change this by enabling the provider to spot problems sooner for referral to specialist care.
Diabetic Retinopathy: Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Stage One: Background Retinopathy
This means that tiny bulges have appeared in the blood vessels in the back of your eyes , which may leak small amounts of blood. This is very common in people with .
At this stage:
- your sight isn’t affected, although you’re at a higher risk of developing vision problems in the future
- you don’t need treatment, but you’ll need to take care to prevent the problem getting worse read more about preventing diabetic retinopathy
- the chances of it progressing to the stages below within three years is over 25% if both of your eyes are affected
What Is Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy is known as the most common form of diabetic eye disease, and it usually affects people who have had diabetes for a significant number of years. It mainly occurs when changes in blood glucose levels cause changes in retinal blood vessels, and in some cases, these vessels will swell up and leak fluid into the rear of the eye. Also, this condition can particularly become dangerous by increasing the risk of blindness if it is left untreated. There are three different types of Diabetic Retinopathy disease they are:
- Background Retinopathy:
This is an early stage of retinal damage when small blood vessels in the retina show signs of damage that can result from diabetes. Background retinopathy is also known as simple retinopathy, which involves tiny swellings in the walls of the blood vessels.
- Diabetic maculopathy
Diabetic maculopathy can result from retinopathy Maculopathy is damage to the macula. The macula is the part of the eye that helps to provide us with our central vision, and Diabetic maculopathy is when the macula sustains some form of damage. This can cause vision problems such as difficulty with reading and or seeing faces in the center of your vision.
- Proliferative retinopathy
Why Is Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Classified As High Risk
PDR is classified as a high-risk form of retinopathy as the development of this condition is marked by a significant loss of vision.
In some cases, a combination of two mechanisms including traction and rhegmatogenous retinal detachments may occur in patients with PDR putting them at a much greater risk of vision loss.
Macular edema caused due to these abnormal changes in the retina is one of the leading causes of visual impairment, especially in patients with uncontrolled diabetes. It may occur due to functional damage or necrosis of the small capillaries in the retina.
In patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy, edema may also be caused due to retinal traction when the retina has been elevated away from the epithelial tissues.
These are some reasons why proliferative diabetic retinopathy is classified as high risk. This also emphasizes the need to be watchful about the early signs of this condition in order to protect your eyesight.
Read on to learn more about the key characteristics of proliferative diabetic retinopathy that could help in the early diagnosis of this condition.
Who Is At Risk
Anyone who has type I or II diabetes is at risk of diabetic retinopathy.
However, if youve had diabetes for a long time or dont manage and control your blood sugar well, youre more likely to experience complications. Pregnancy, tobacco use, and high blood pressure or cholesterol also increase your risk.
What To Think About
Pan-retinal laser treatment is used to treat several spots on the retina during one or, most often, two sessions. It reduces the risk of serious bleeding and the progression of severe proliferative retinopathy.
Laser photocoagulation can result in some loss of vision, because it destroys some of the nerve cells in the retina and can cause the abnormal blood vessels to go away. With pan-retinal photocoagulation, this most often affects the outside vision, because the laser is directed at that area. Your vision may be worse right after treatment. But vision loss caused by laser treatment is mild compared with the vision loss that may be caused by untreated retinopathy.
Can Diabetic Retinopathy Be Treated
Laser surgery is often used in the treatment of diabetic eye disease, but each stage of diabetic retinopathy can be treated in a different way.
Background retinopathy has no treatment but patients will need regular eye examinations. Maculopathy is usually treated with laser treatment .
This is usually painless and has no side effects, but can influence night driving and peripheral vision.
This type of laser treatment for diabetic retinopathy will not improve vision, but it can prevent deterioration. Proliferative retinopathy is also treated with lasers, with a scattering over the whole retina. This destroys the starved area of the retina. Serious diabetes retinopathy cases may require eye surgery.
This is usually diagnosed due to bleeding in the eye, late-stage proliferative retinopathy or ineffective laser treatment. This type of diabetic retinopathy eye surgery is called vitrectomy.
- Read more on treating retinopathy

