How Can Diet Affect Insulin Resistance
Your diet has a big impact on your blood sugar and insulin levels. Highly processed, high-carbohydrate and high-fat foods require more insulin.
In general, eating foods that have a low to medium glycemic index and limiting foods that have a high glycemic index can help you reverse and/or manage insulin resistance. Eating foods with fiber also helps regulate blood sugar levels because it takes your body longer to digest fiber, meaning your blood sugar levels dont spike as much.
The glycemic index is a measurement that ranks foods containing carbohydrates according to how much they affect your blood sugar levels. The Glycemic Index Foundation classifies the GI of foods as either low, medium or high, with pure glucose generally as a reference at 100:
- Low GI: 55 or less.
- Medium GI: 5669.
- High GI: 70 or greater
High-GI foods generally have a lot of carbohydrates and/or sugar and low to no fiber content. Low-GI foods generally have low amounts of carbohydrates and higher amounts of fiber.
Examples of foods with a high GI include:
- White bread.
- Indigenous people from the continental United States.
- Indigenous people from the Pacific Islands.
Although you cant change certain risk factors for insulin resistance, such as family history or age, you can try lowering your chances of developing it by maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly.
How Does Insulin Work In Our Bodies
What is insulin and how do our bodies use it?
The prevalence of diabetes, a condition related to the bodys inability to appropriately produce a hormone called insulin, has been steadily increasing worldwide over the last 30 years. According to the World Health Organization, over 422 million people worldwide are currently living with diabetes. An estimated 30.3 million of those people, or 9.4% of the population, are in the US. Also in the US, as many as one in four adults with diabetes dont even know that they have it, and another 84 million people are pre-diabetic which often means they will be diabetic within five years without treatment. These numbers are higher in the American Indian, black, and Hispanic communities.
What is insulin and how do our bodies use it? What progress are scientists making toward regulating the hormone without insulin pumps or injections?
The Basics Of High Blood Sugar
Diabetes is a problem with your body that causes blood sugar levels to rise higher than normal. This is also called hyperglycemia.
When you eat, your body breaks food down into sugar and sends it into the blood. Insulin then helps move the sugar from the blood into your cells. When sugar enters your cells, it is either used as fuel for energy right away or stored for later use. In a person with diabetes, there is a problem with insulin. But, not everyone with diabetes has the same problem.
There are different types of diabetestype 1, type 2 and gestational diabetes. If you have diabetestype 1, type 2 or gestationalyour body either doesn’t make enough insulin, can’t use the insulin well, or both.
Learn more about blood sugar Learn more about insulin
Recommended Reading: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Types Of Insulin Where To Inject It And The Best Methods For Insulin Delivery
role of insulinshort- and long-term complicationsYour diabetes treatment team is there to help you. Patients’ Guide to Managing Your Child’s Type 1 Diabetes
This article will provide a basic overview of insulin. You can also visit our Patients’ Guide to Insulin for more information as well as read more in the section on Type 1 Diabetes Treatments, which has a chart providing more detail about the types of insulin that your doctor may prescribe.
Ideal Blood Sugar Levels
A range of factors, including insulin resistance, diabetes, and an unbalanced diet, can cause blood sugar levels to spike or plummet.
The standard measurement units for blood sugar levels are milligrams per deciliter . Ideal blood sugar ranges are as follows:
| Timing |
Insulin and glucagon do not take immediate effect, particularly in people whose blood sugar levels are extremely high or low.
Read Also: Hypoglycemia And Prediabetes
What Are The Drawbacks To Insulin Treatment For Diabetes
The biggest issue with insulin right now is unaffordability. A box of rapid-acting insulin can cost $400 without insurance. As so many people continue to lose their health coverage, its becoming an enormous problem, Dr. Zilbermint says.
Consistently rising costs have led some patients to ration their insulin, which can be dangerous and even deadly. The cost of testing strips is also an issue, and both have led to a black market in testing strips and insulin. Its illegal, says Dr. Zilbermint, but its happening.
Insulin And The Liver
A great deal of glucose absorbed into the bloodstream is put into liver cells, also known as hepatocytes. The hepatocytes have the primary responsibility of turning the glucose into its storage form, a long polymer known as glycogen.
Insulin affects the liver in several ways. It causes the activation of hexokinase, which is an enzyme that phosphorylates glucose so that it becomes unable to leave the cells. Insulin also activates other enzymes necessary for the storage of glycogen in the liver. Two of these enzymes are called glycogen synthase and phosphofructokinase. In its general role on the liver, insulin is responsible for the storage of glucose within the liver.
You May Like: Symptoms Of High Glucose Levels
The Primary Role Of Insulin: To Hold Your Fat And Glucose In Storage
Rather than seeing insulin as a pusher, its much more helpful to see insulin as an anti-catabolic hormone that stops your body from breaking itself down .
Without insulin, the fat and glycogen in your liver and muscles would flow freely into your bloodstream. Once your stored glucose was used up, your body would then resort to using other more valuable tissues for fuel, like your muscles and organs!
Insulin is the signal sent from your pancreas to your liver to regulate the flow of just enough energy into your bloodstream to meet your current energy needs.
You can think of the stored fuel in your body like a water tank: the more fat and glucose you have in storage, the higher the pressure is to push the stored energy out of the liver. You can think of insulin as the signal that regulates the tap. With no insulin to turn off the tap, all your stored energy would gush out. Conversely, if you have a LOT of energy in storage, you need to go to greater lengths to turn off the tap to make sure it doesnt leak.
When Insulin Production Goes Awry
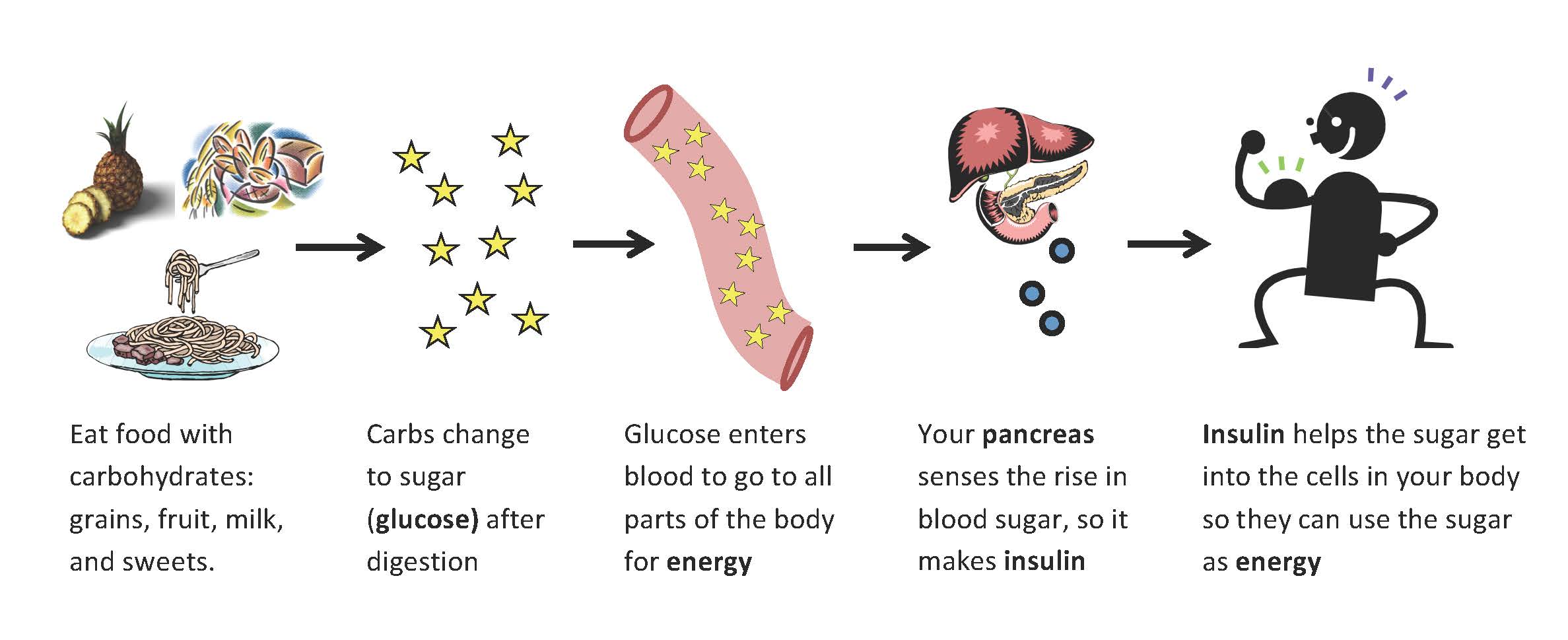
Insulin, along with another hormone glucagon balance your blood glucose levels . The food you eat is the source of glucose, which is your body’s fuel. Insulin and glucagon partner to ensure that your blood sugar levels are properly regulated.
When you digest your food, carbohydrates convert to glucose. The glucose is directed into your bloodstream, which causes your blood glucose levels to rise. This is what sends the message to your pancreas to produce insulin, which instructs your cells to absorb the glucose traveling through your bloodstream.
Certain cells use glucose as energy, while others, like those within your muscles and liver, put away surplus glucose after it becomes glycogen, a substance that serves as your bodys fuel in between meals.
Yet another player, glucagon, offsets the effects of insulin. Between four and six hours after a meal, your blood glucose levels go down, and this signals to your pancreas to manufacture glucagon.
The hormone glucagon instructs your liver and muscle cells to convert the glycogen your body has stored back into glucose. The cells send the glucose into your bloodstream, furnishing your other cells with energy.
This exquisitely balanced dynamic between insulin and glucagon is never-ending, ensuring that your blood sugar never gets dangerously low and that you have the energy you need to live.
You May Like: Is Old Fashioned Oatmeal Good For Diabetics
Structure And Chemical Properties Of Insulin
Insulin was found to be a polypeptide in 1928 with its amino acid sequence identified in 1952. It is in fact a dipeptide, containing A and B chains respectively, linked by disulphide bridges, and containing 51 amino acids, with a molecular weight of 5802. Its iso-electric point is pH 5.5. The A chain comprises 21 amino acids and the B chain 30 amino acids. The A chain has an N-terminal helix linked to an anti-parallel C-terminal helix the B chain has a central helical segment. The two chains are joined by 2 disulphide bonds, which join the N- and C-terminal helices of the A chain to the central helix of the B chain. In pro-insulin, a connecting peptide links the N-terminus of the A chain to the C-terminus of the B chain.
Energy Flux And Your Fat And Glucose Fuel Tanks
Your body is a dynamic system similar to a dual-fuelled engine that runs predominantly on glucose and fat.
In an emergency, you can use alcohol, ketones, and protein. However, your body uses the fat and glucose from your food most of the time.
Most of the time, your body is extremely capable of regulating just enough fuel in your bloodstream. Your body also likes to maintain a healthy reserve of energy in its two fuel tanks:
- your adipose tissue , and
- liver for reserving glycogen .
These fuel tanks are depicted diagrammatically in the image below.
Energy in the form of glucose and fat is constantly flowing into your bloodstream and being utilised as energy by your body.
You only have about five grams of glucose in your bloodstream at any time, equating to roughly 20 calories. This would only last you about 15 minutes if your liver didnt manage the constant flow of fuel into your bloodstream so precisely!
But, your body only wants to have just enough glucose and fat in your blood at any one time to fuel your immediate activities like thinking, breathing, walking, running or exercise. Too much glucose in your bloodstream leads to a range of complications, so its tightly regulated.
You May Like: Can A Type 2 Diabetic Eat Bananas
What Are The Symptoms Of Insulin Resistance
If you have insulin resistance, but your pancreas can increase insulin production to keep your blood sugar levels in range, you wont have any symptoms.
However, over time, insulin resistance can get worse, and the cells in your pancreas that make insulin can wear out. Eventually, your pancreas is no longer able to produce enough insulin to overcome the resistance, leading to elevated blood sugar , which does cause symptoms.
Symptoms of high blood sugar include:
- Increased thirst.
- Vaginal and skin infections.
- Slow-healing cuts and sores.
Many people have no symptoms of prediabetes, often for years. Prediabetes may be invisible until it develops into Type 2 diabetes. Some people with prediabetes may experience the following symptoms:
- Darkened skin in your armpit or back and sides of your neck, called acanthosis nigricans.
- Skin tags .
- Eye changes that can lead to diabetic retinopathy.
If youre experiencing any of these symptoms, its important to see your healthcare provider.
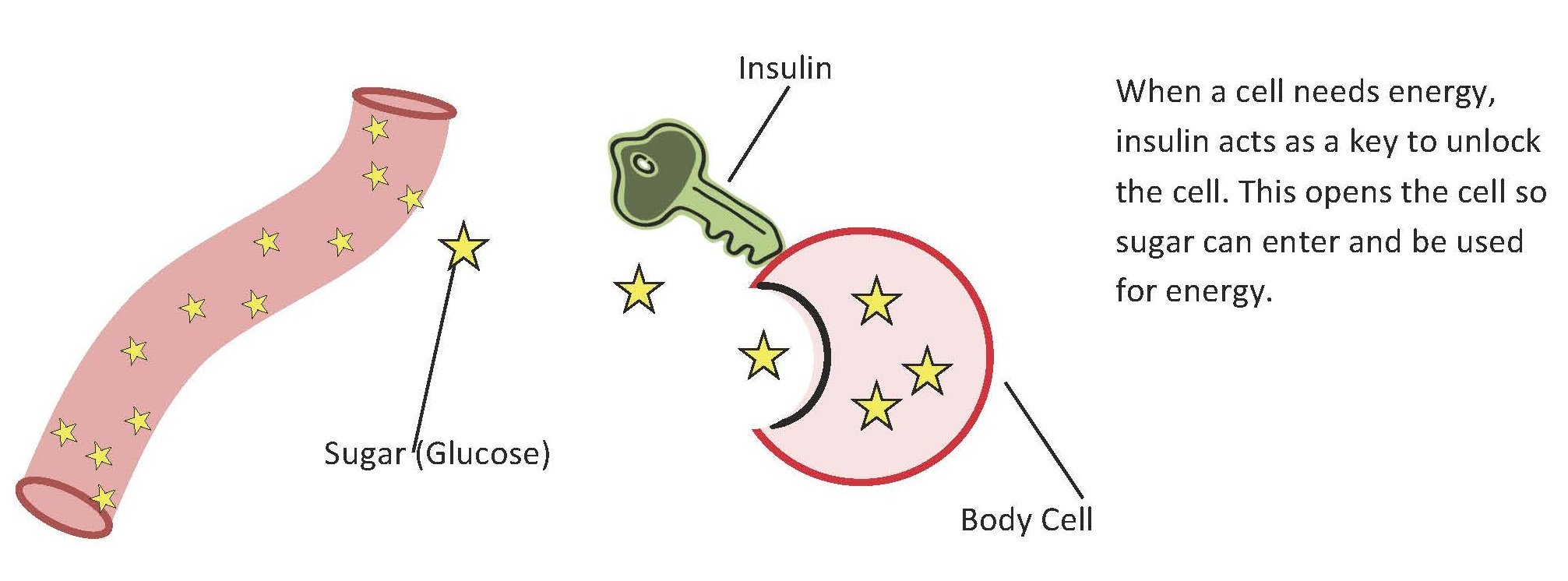
Insulins Action On The Digestive System
When a person eats a meal, food is allowed to travel to the stomach and the small intestines. There the food undergoes a breakdown into small nutrient particles that are then absorbed into the blood. In response to this absorption of carbohydrate nutrients, the pancreas secretes insulin in order to make use of the glucose for cellular metabolism. The pancreas is considered part of the digestive system as well as the endocrine system.
Insulin allows the fat cells, muscle cells, and liver cells to keep glucose in storage until it is later needed for cellular fuel. At the same time, the liver makes less glucose and instead stores it as glycogen. This allows the blood sugars to remain stable. Between meals, the liver breaks down its glycogen stores so that there will always be enough glucose in the bloodstream.
You May Like: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Where Does Insulin Come From
Insulin is produced in the pancreas, a gland located in the abdomen. It produces enzymes that aid in digestion, along with hormones that help to regulate glucose levels.
The pancreas is very efficient at delivering insulin when needed. In someone with normal insulin function, the pancreas is constantly delivering insulin to all different parts of the body.
When youre running and exercising, your muscles need glucose, and insulin lets those muscle cells absorb glucose, Dr. Pinsker explained. When youre thinking, your brain needs glucose. Your brain is actually the biggest user of glucose. Insulin allows that glucose to go into your brain.
For someone living with type 1 diabetes, glucose is unable to enter those cells because they lack the key i.e., insulin. Thus, there is a buildup of blood sugars, which are eventually let out of the body through urine.
Types Of Insulin Treatments
All types of insulin produce the same effect. They are used to mimic the natural increases and decreases of insulin levels in the body during the day. The makeup of different types of insulin affects how fast and how long they work.
The type of insulin youll be prescribed will vary depending on things like:
- your age
- how long it takes your body to absorb insulin
- how long insulin stays active in your system
| Insulin type | ||
|---|---|---|
| varied peaks | 10 to 16 hours | Taken twice a day, commonly 10 to 30 minutes before breakfast and dinner. This type is a combination of intermediate- and short-acting insulin. |
Talk with a doctor about the right insulin for you and your lifestyle.
Read Also: Metformin Er Dose
Evolution And Species Distribution
Insulin may have originated more than a billion years ago. The molecular origins of insulin go at least as far back as the simplest unicellular eukaryotes. Apart from animals, insulin-like proteins are also known to exist in the Fungi and Protista kingdoms.
Insulin is produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets in most vertebrates and by the Brockmann body in some teleost fish.Cone snailsConus geographus and Conus tulipa, venomous sea snails that hunt small fish, use modified forms of insulin in their venom cocktails. The insulin toxin, closer in structure to fishes’ than to snails’ native insulin, slows down the prey fishes by lowering their blood glucose levels.
Who Gets Type 2 Diabetes
What makes people more likely to develop type 2 diabetes? No one knows for sure. But experts have a few ideas about what puts a person at greater risk:
- Most people who have type 2 diabetes are overweight.
- People with family members who have diabetes get diabetes more often.
- People who are older than 10 are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than younger kids.
Don’t Miss: D50 And Insulin For Hyperkalemia
Insulin Secretion In Response To Stimuli
Response to Glucose
In healthy individuals glucose stimulated pancreatic secretion is biphasic. Intravenous administration of glucose is associated with a rapid first phase of insulin release within 1 minute, peaking at 35 minutes, and lasting about 10 minutes the slower onset second phase of insulin secretion begins shortly after the glucose bolus but is not apparent until 10 minutes later, lasts the duration of the hyperglycaemia and is proportional to the glucose concentration immediately prior to the glucose administration. The first phase of insulin secretion represents release of insulin already synthesised and stored in secretory granules the second phase represents secretion of both stored and newly synthesised insulin. Overall insulin secretion relates to the total dose of glucose and its rate of administration maximal pancreatic response occurs with 20 g of glucose given intravenously over 3 minutes in humans.
In contrast to the reproducible pattern of insulin secretion in response to intravenous glucose, insulin secretion following oral glucose is much more variable. With an oral glucose load, gastric emptying and gastrointestinal motility affect glucose absorption, gastro-intestinal hormones and neural input associated with glucose ingestion modify the insulin response, and insulin secretion continues some time after glucose ingestion.
Response to Arginine
Effects of Lipids
Response to Mixed Meal
Incretin Hormones
Effects of Neural and Hormonal Stimuli
How Do You Know If The Insulin In Your Body Isnt Working Properly
People with type 1 diabetes are generally diagnosed when symptoms cause them to seek medical care.
Type 2 diabetes is often diagnosed with a simple blood test during a routine physical exam or annual checkup.
A lab test of your fasting blood sugar levels or an A1C test can indicate if your blood sugar is within a healthy range. This can signal whether the insulin in your body is working correctly.
Read Also: Ripe Banana And Diabetes
Insulin Treatment In Type 2 Diabetes
The decision to take insulin is never an easy one. For many patients, it comes after years of having type 2 diabetes and trying multiple weight-loss regimens, diets, and oral medications. For other patients, the decision to take insulin is made when blood glucose levels are simply too high to control with other drugs.
The good news is that insulin almost always works. Daily injections, however inconvenient or painful at first, can be very effective at controlling blood glucose. Anxious about giving injections? Help is available. If your health care provider prescribes insulin, a trained diabetes educator or pharmacist can teach you how to measure out the proper dose and administer your daily injections.
Why should I use insulin?
With type 2 diabetes, over time, the pancreas is often unable to produce insulin on its own. When that happens, your blood glucose levels will become very difficult to control without daily injections of insulin. Injectable insulin is identical to the insulin made by the body, but can be categorized into two main types: basal insulin keeps your blood glucose stable all day long, even when not eating, while bolus insulin helps your body respond to the quick rise in blood glucose after meals.

