Is Blood Sugar Regulated By Negative Or Positive Feedback
DIGITAL HEALTH BRIEFING: ASCOs new partnerships aim to improve oncology care MedStar Health provides digital tools for prenatal care DarioHealth awarded new patent to improve its offerings DIGITAL HEALTH BRIEFING: ASCOs new partnerships aim to improve oncology care MedStar Health provides digital tools for prenatal care DarioHealth awarded new patent to improve its offeringsContinue reading >>
Comparing Positive And Positive Feedback
contrast negative and positive feedback, giving examples of each. Explain why negative rather than positive feedback is required for maintenance of homeostasis.In order to maintain a constant internal environment, organisms require mechanisms for maintaining internal stability in spite of intrinsic or extrinsic changes. Negative feedback is a corrective mechanism that opposes a variation from normal limits. It is required for the maintenance of homeostasis in the body. However, positive feedback is
What Kind Of Feedback Loop Prevents Sudden Changes In Body Temperature
Homeostasis is generally maintained by a negative feedback loop that includes a stimulus , sensor , control centre , and effector . Negative feedback serves to reduce an excessive response and to keep a variable within the normal range. Negative feedback loops control body temperature and the blood glucose level.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Positive And Negative Feedback Homeostasis
Homeostasis refers to the steady state of internal conditions maintained by living organisms. Humans have control centers in the brain and other parts of the body that constantly monitor conditions like temperature, pressure, and blood and tissue chemistry. When any condition gets out of balance, feedback loops return the body to homeostasis. This is a natural response to changes in the optimal conditions for the body to function.
To sense when things are out of balance, bodily functions have set points around which normal values fluctuate within a range. For example, normal human body temperature set point is 98.6°F, and the range varies a few degrees above and below that. There are positive and negative feedback loops in physiological processes that react when conditions venture outside the range.
Feedback loops have three componentsthe sensors, the control, and the effector. Sensors are also called receptors and they monitor conditions inside and outside the body. Some examples are thermoreceptors and mechanoreceptors. The control center, often in the brain, compares the value the sensor receives to the values in the range. Finally, the effector is what the feedback loop acts on.
The Effect Of Blood Glucose Regulation On The Body
Glucose is the primary energy source for the brain and it also serves as a source of energy for cells throughout the body. The energy provided by glucose helps the cells to carry out nerve cell conduction, muscle cell contraction, active transport and the production of chemical and metabolic reactions. These processes are all essential for the bodies survival and all require glucose to carry out their actions. Blood glucose regulation is the process by which the levels of blood glucose, are maintained
Also Check: Diabetes Type 2 Life Expectancy
Diseases And Blood Sugar Regulation
Glucose levels above or below the normal range are indicative of the presence of disease states. For example, elevated glucose levels are present in diabetes mellitus, Cushing’s syndrome, liver disease, and hyperthyroidism, while decreased glucose levels are present in Addison’s disease, hyperinsulinism, and hypothyroidism.
The most prevalent of these diseases is diabetes mellitus. There are two types of this disease: Type I diabetes mellitus, and Type II diabetes mellitus. In Type I diabetes, pancreatic beta cells are destroyed by an erroneous attack by the body’s own immune system, and thus insulin secretion is reduced to negligible levels. In Type II diabetes, insulin secretion is not reduced; however, there is a reduced sensitivity of target cells to insulin, a phenomenon known as insulin resistance.
SEE ALSO
Heat Conservation And Dissipation
Animals conserve or dissipate heat in a variety of ways. In certain climates, endothermic animals have some form of insulation, such as fur, fat, feathers, or some combination thereof. Animals with thick fur or feathers create an insulating layer of air between their skin and internal organs. Polar bears and seals live and swim in a subfreezing environment and yet maintain a constant, warm, body temperature. The arctic fox, for example, uses its fluffy tail as extra insulation when it curls up to sleep in cold weather. Mammals have a residual effect from shivering and increased muscle activity: arrector pili muscles cause goose bumps, causing small hairs to stand up when the individual is cold; this has the intended effect of increasing body temperature. Mammals use layers of fat to achieve the same end. Loss of significant amounts of body fat will compromise an individuals ability to conserve heat.
Some ectothermic animals use changes in their behavior to help regulate body temperature. For example, a desert ectothermic animal may simply seek cooler areas during the hottest part of the day in the desert to keep from getting too warm. The same animals may climb onto rocks to capture heat during a cold desert night. Some animals seek water to aid evaporation in cooling them, as seen with reptiles. Other ectotherms use group activity such as the activity of bees to warm a hive to survive winter.
Don’t Miss: What Happens If You Stop Taking Diabetes Medication
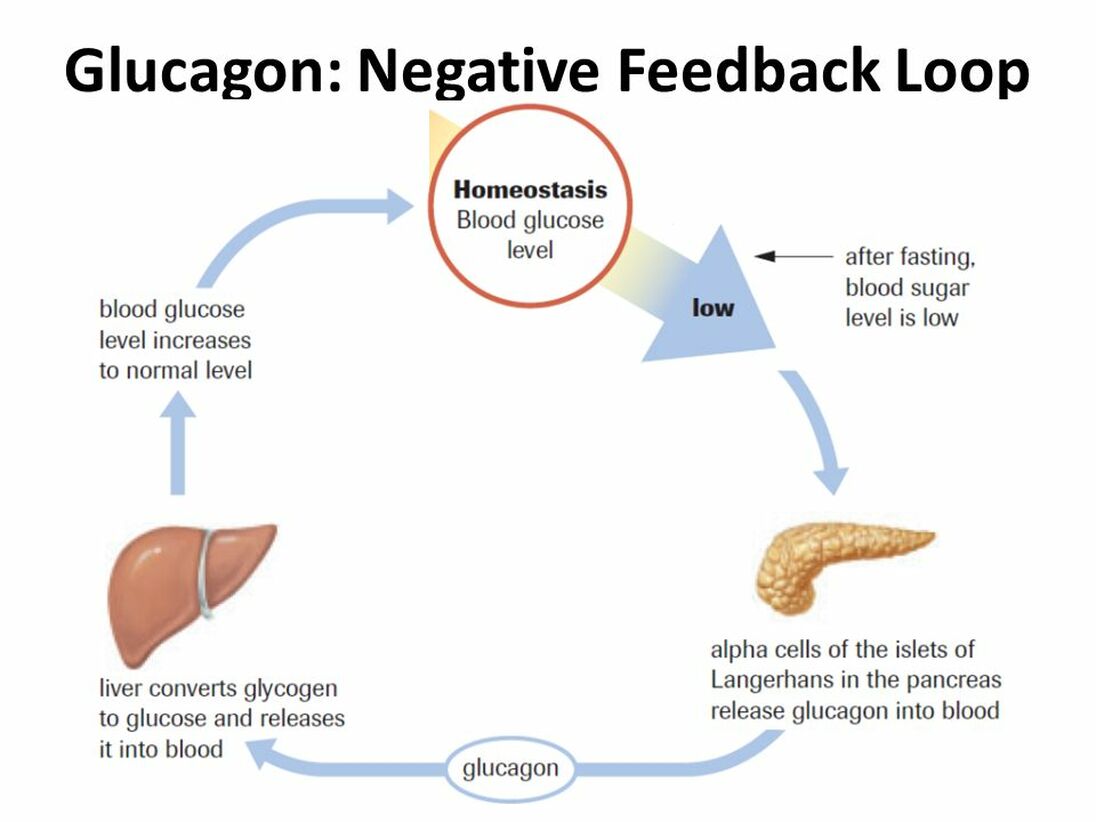
How Does Negative Feedback Control Blood Glucose Concentration After A Meal
Negative feedback If the blood glucose level is too low, the pancreas releases the hormone glucagon. This travels to the liver in the blood and causes the break-down of glycogen into glucose. The glucose enters the blood stream and glucose levels increase back to normal. This is an example of negative feedback.
Blood Sugar Levels Are Regulated By Negative Feedback In Order To Keep The Body In Homeostasis
which assists the glucose in the blood to enter in the cells. When blood glucose levels rise, cells namedbody goes for the alternative way to fulfill the deficit. When blood glucose levels fall, cells namedalpha cells. Glucagon has the greatest effect on the liver although it affects many different cells in thebody. When glucose levels are low our liver releases the stored glucose into the bloodstream to keepContinue reading >>
You May Like: Can People With Diabetes Donate Blood
Set Point And Normal Range
For any given variable, such as body;temperature;or;blood;glucose level, there is a particular;set point;that is the physiological optimum value.;The set point for;human body;temperature, for example, is about 37 degrees C . As the body works to maintain homeostasis for temperature or any other internal variable, the value typically fluctuates around the set point. Such fluctuations are normal, as long as they do not become too extreme. The spread of values within which such fluctuations are considered insignificant is called the;normal range. In the case of body temperature, for example, the normal range for an adult is about 36.5 to 37.5 degrees C .
A good analogy for set point, normal range, and maintenance of homeostasis is driving.; When you are driving a vehicle on the road, you are supposed to drive in the centre of your lane this is analogous to the set point.; Sometimes, you are not driving in the exact centre of the lane, but you are still within your lines, so you are in the equivalent of the normal range.; However, if you were to get too close to the centre line or the shoulder of the road, you would take action to correct your position.; Youd move left if you were too close to the shoulder, or right if too close to the centre line which is analogous to our next concept, negative feedback
Example : Fruit Ripening
There is a surprising effect in nature where a tree or bush will suddenly ripen all of its fruit or vegetables, without any visible signal. This is our first example of a positive biological feedback loop. If we look at an apple tree, with many apples, seemingly overnight they all go from unripe to ripe to overripe. This will begin with the first apple to ripen. Once ripe, it gives off a gas known as ethylene through its skin. When exposed to this gas, the apples near to it also ripen. Once ripe, they too produce ethylene, which continues to ripen the rest of the tree in an effect much like a wave. This feedback loop is often used in fruit production, with apples being exposed to manufactured ethylene gas to make them ripen faster.
Figure 2: The process of apples ripening is a positive feedback loop.
Read Also: Life Expectancy For Type 2 Diabetes
Means Of Heat Transfer
Heat can be exchanged between an animal and its environment through four mechanisms: radiation, evaporation, convection, and conduction. Radiation is the emission of electromagnetic heat waves. Heat radiates from the sun and from dry skin the same manner. When a mammal sweats, evaporation removes heat from a surface with a liquid. Convection currents of air remove heat from the surface of dry skin as the air passes over it. Heat can be conducted from one surface to another during direct contact with the surfaces, such as an animal resting on a warm rock.
Mechanisms for heat exchange: Heat can be exchanged by four mechanisms: radiation, evaporation, convection, or conduction.
What Is A Negative Feedback Mechanism In The Endocrine System
Endocrine System Feedbacknegative feedbackNegative feedback
Most hormones are regulated by feedback mechanisms. A feedback mechanism is a loop in which a product feeds back to control its own production. Most hormone feedback mechanisms involve negative feedback loops. Negative feedback keeps the concentration of a hormone within a narrow range.
what is positive and negative feedback in the endocrine system? Positive and Negative Feedback. Negative and Positive Feedback Mechanisms. <_o3a_p> The endocrine system helps regulate and maintain various body functions by synthesizing and releasing hormones. It is composed of glands located through out the body that secrete chemicals called hormones directly into the blood.
Secondly, what is the negative feedback mechanism of the body?
Negative feedback is a reaction that causes a decrease in function. It occurs in response to some kind of stimulus. Often it causes the output of a system to be lessened; so, the feedback tends to stabilize the system. This can be referred to as homeostatis, as in biology, or equilibrium, as in mechanics.
What is a positive and a negative feedback mechanism?
Positive vs. Negative Feedback. The key difference between positive and negative feedback is their response to change: positive feedback amplifies change while negative feedback reduces change. This means that positive feedback will result in more of a product: more apples, more contractions, or more clotting platelets
Recommended Reading: How Long Can You Live With Type 1 Diabetes
With Reference To Acid
School of Nursing, Midwifery and Interprofessional Studies.With reference to acid-base balance explore the role of the respiratory system in maintaining blood pH?We live and die at the cellular level . Homeostasis is crucial for normal cellular function. Acid-base homeostasis is the part of human homeostasis and refers to the balance between the production and elimination of H+ hydrogen ions within the body fluids . Metabolic reactions
Positive Vs Negative Feedback
The key difference between positive and negative feedback is their response to change: positive feedback amplifies change while negative feedback reduces change. This means that positive feedback will result in more of a product: more apples, more contractions, or more clotting platelets. Negative feedback will result in less of a product: less heat, less pressure, or less salt. Positive feedback moves away from a target point while negative feedback moves towards a target.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If You Stop Taking Diabetes Medication
Maintaining The Blood Glucose Level
control in order for this to happen and one of these is maintaining the blood glucose level .Glucose is the preferred fuel source used in the human body.There are several important cells and organs in the body that require a constant supply of glucose to properly function, these include red blood cells and immune cells. The purpose of blood glucose regulation is to keep the body in homeostasis because abnormal levels of glucose can manifest in pathological conditions such as seizures, hypoglycaemic
Connection For Ap Courses
Animals must be able to maintain homeostasisthe ability to maintain dynamic equilibrium around a set pointwhile also being able to respond to changing conditions. For example, as an endotherm, your body temperature remains fairly constant around 37 °C or 98.6 °F. If your temperature climbs above the set point, you sweat to cool off; if your temperature drops below the set point, you shiver to warm up. Your blood glucose levels also remain fairly constant because the liver removes glucose from the blood and converts it to glycogen; when the body cells require glucose, glycogen is broken down. You can probably hypothesize how your liver will respond if you eat a dozen jelly donuts! The failure to maintain homeostasis can be detrimental and can even cause death. Consequently, negative– and/or positive-feedback loops regulate homeostasis.
Information presented and the examples highlighted in the section support concepts outlined in Big Idea 2 of the AP Biology® Curriculum Framework. The AP® Learning Objectives listed in the Curriculum Framework provide a transparent foundation for the AP® Biology course, an inquiry-based laboratory experience, instructional activities, and AP® exam questions. A learning objective merges required content with one or more of the seven Science Practices.
Don’t Miss: Bananas Raise Blood Sugar
Exploring The Role Of Homeostasis In The Human Body
functions and chemicals, such as glucose, are kept in stasis to allow the human body to function properly. There are various systems in the human body that must be maintained through procedures of biological and chemical balances and checks so the human body may function at its optimum. Blood glucose regulation is an example of homeostasis in humans as the concentration of glucose in the blood has to be homeostatically regulated. To achieve homeostasis blood glucose concentration in a healthy individual
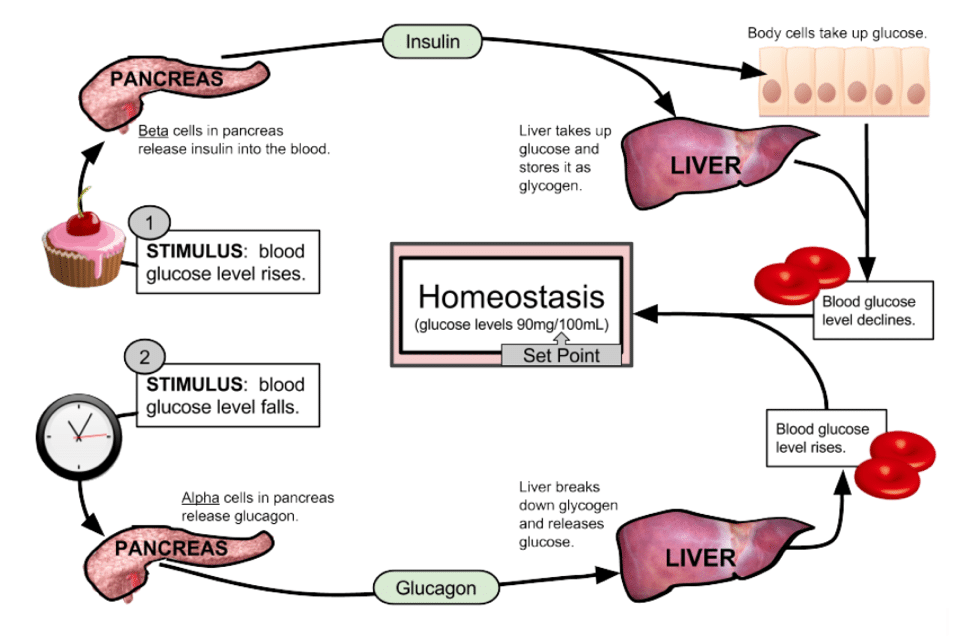
Negative Feedback And Blood Glucose Regulation
I did not believe is possible that HIV can be cured because i have been scammed so many times not until i came across this great man dr agbebaku who helped me at first I never believe all this comment and post about him and I was very sick because i have been infected with HIV for the past seven years,just last year I keep reading the testimony about this man named dr agbebaku they said that the man is so powerful he have cured different type of diseases, I keep monitor the post of some people about this man and I found out that he was real so i decided to give him a try I contacted him for help and he said he was going to help me get my cure that all i needed to do was to send him money to prepare the medication after which it will be sent to me via dhl service which i did to my greatest suprise the medication was sent to me he gave me instructions on how to use it that after three weeks i should go for check up at first i was shocked when the doctor told me that i was hiv negative i ask the doctor to check again and the result was the same that i was now free from hiv at of the shock i decided to come and share my testimony with you for those who think there is no cure for hiv the cure as finally come stop doubting and contact dr agbebaku via email he will help you out you can also wattssap him via +2349053099479 he said he also as cure for DIABETICS,HERPES,INFERTILITY;ALS,ANCE PIMPUS,LUPUS VIRUS AND PENIS AND BREAST ENLARGEMENT ReplyContinue reading >>
You May Like: Life Expectancy For Type 1 Diabetic
Why Does Negative Feedback Regulate Blood Sugar
4.3/5blood glucose levelswouldnegative feedbackNegative feedbackare
The control of blood sugar by insulin is a good example of a negative feedback mechanism. When blood sugar rises, receptors in the body sense a change. In turn, the control center secretes insulin into the blood effectively lowering blood sugar levels.
Likewise, is glucagon a negative feedback? Glucagon primarily affects the liver and causes it to break down glycogen into glucose and convert other nutrients into glucose. Both hormones are regulated in a negative feedback loop which shuts off production of the hormone when blood-glucose levels reach homeostasis.
Accordingly, how does negative feedback maintain homeostasis?
Negative feedback occurs when a system’s output acts to reduce or dampen the processes that lead to the output of that system, resulting in less output. In general, negative feedback loops allow systems to self-stabilize. Negative feedback is a vital control mechanism for the body’s homeostasis.
Why is insulin a negative feedback?
A good example of negative feedback is with the hormone insulin. Insulin is produced by the pancreas. As insulin levels in the blood decrease, so does glucose uptake by cells. This negative feedback therefore helps to maintain normal blood glucose levels and prevents extreme changes.
What Is The Purpose Of Negative Feedback
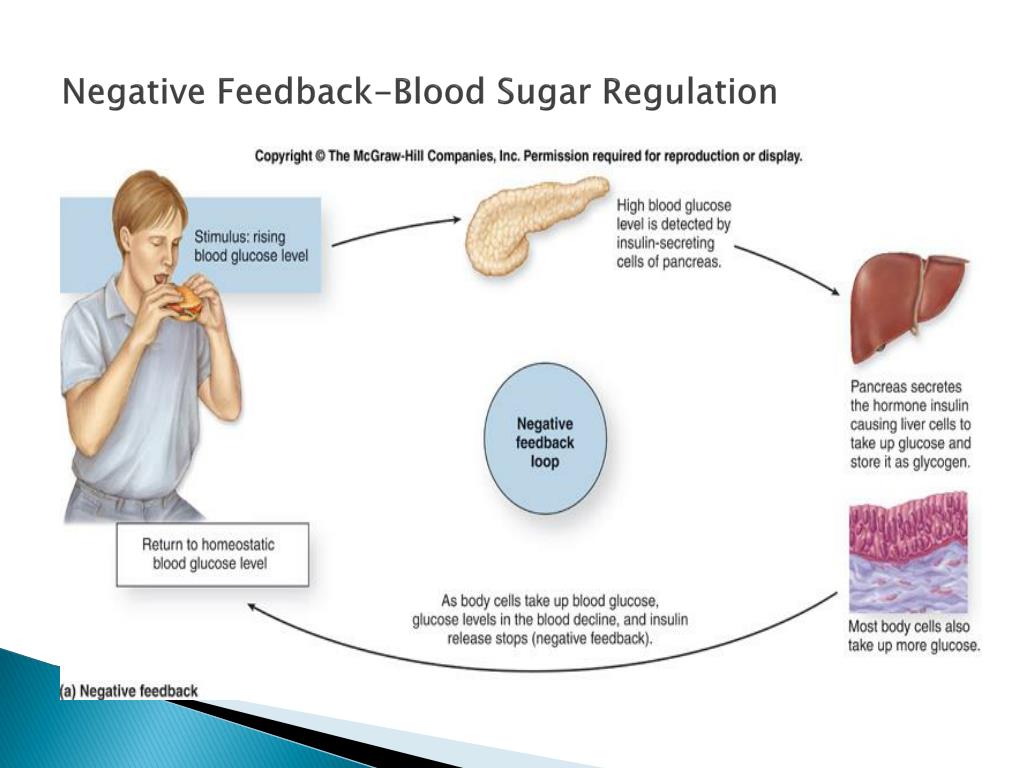
A negative feedback loop is a reaction that causes a decrease in function. It occurs in response to some kind of stimulus. Often, it causes the output of a system to be lessened; so, the feedback tends to stabilize the system. This can be referred to as homeostasis, as in biology, or equilibrium, as in mechanics.
Recommended Reading: Average A1c Non Diabetic
Example : Temperature Regulation
Temperature regulation in humans occurs constantly. Normal human body temperature is approximately 98.6°F. When body temperature rises above this, two mechanisms kick in the body begins to sweat, and vasodilation occurs to allow more of the blood surface area to be exposed to the cooler external environment. As the sweat cools, it causes evaporative cooling, while the blood vessels cause convective cooling. Normal temperature is regained. Should these cooling mechanisms continue, the body will become cold. The mechanisms which then kick in are the formation of goose bumps, and vasoconstriction. Goosebumps in other mammals raise the hair or fur, allowing more heat to be retained. In humans, they tighten the surrounding skin, reducing the surface area from which to lose heat. Vasoconstriction ensures that only a small surface area of the veins is exposed to the cooler outside temperature, retaining heat. Normal temperature is regained.
Figure 5: The process of temperature regulation in humans is a negative feedback loop.

