When The Blood Glucose Level Goes Down
- Blood sugar drops
- The pancreas detects the drop in blood sugar
- The pancreas switches on the output of glucagon into the blood
- Glucagon signals the liver to break down glycogen into glucose
- The liver releases glucose into the bloodstream
- Blood glucose goes up to its normal set point and
- The pancreas detects the rise in blood sugar and switches off glucagon release.
Problems With The Pancreas
If there is a problem with the pancreas, it can affect the entire body. This can affect the amount of digestive enzymes that are produced by the pancreas. In case there is not enough digestive enzymes being produced, food will not be properly absorbed. This may lead to health complications such as diarrhea and weight loss. The pancreatic islets are responsible for producing the hormone insulin. People with type 1 diabetes do not produce any insulin. This is because the insulin producing beta cells are mistakenly attacked by the immune system. When we eat carbohydrates, the amount of glucose in the bloodstream tends to rise. Glucose is a form of sugar which is one of the biggest sources of fuel for the body.
An increase in blood sugar will stimulate the pancreas to release the hormone insulin, which helps to regulate blood sugar levels. As a result of beta cells dying, the pancreas in people with type 1 diabetes will struggle to secrete enough insulin. This leads to a build up of blood sugar levels which, if not treated, can lead to serious health problems like nerve and kidney damage. To prevent this risk, people with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections to keep their blood sugar levels normal.
How Is Insulin Controlled
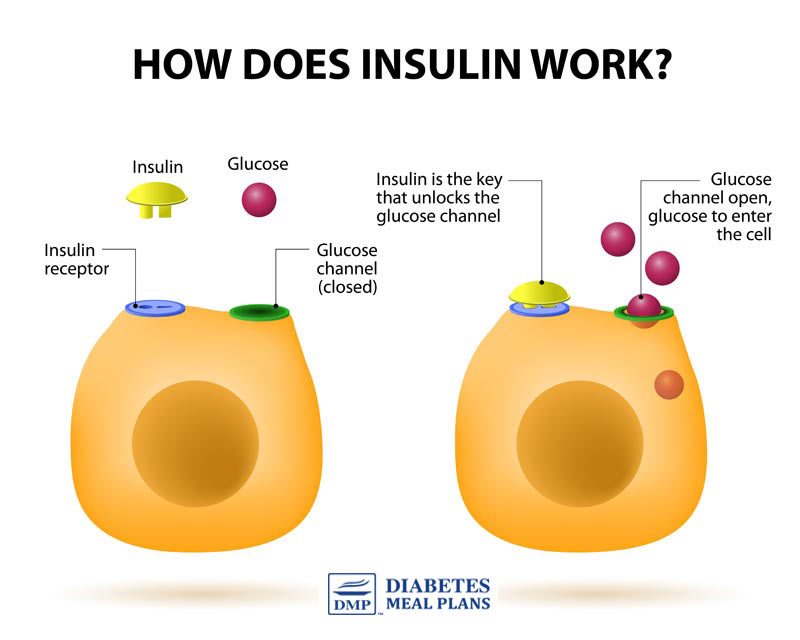
The main actions that insulin has are to allow glucose to enter cells to be used as energy and to maintain the amount of glucose found in the bloodstream within normal levels. The release of insulin is tightly regulated in healthy people in order to balance food intake and the metabolic needs of the body. This is a complex process and other hormones found in the gut and pancreas also contribute to this blood glucose regulation. When we eat food, glucose is absorbed from our gut into the bloodstream, raising blood glucose levels. This rise in blood glucose causes insulin to be released from the pancreas so glucose can move inside the cells and be used. As glucose moves inside the cells, the amount of glucose in the bloodstream returns to normal and insulin release slows down. Proteins in food and other hormones produced by the gut in response to food also stimulate insulin release. Hormones released in times of acute stress, such as adrenaline, stop the release of insulin, leading to higher blood glucose levels to help cope with the stressful event.
Insulin works in tandem with glucagon, another hormone produced by the pancreas. While insulin’s role is to lower blood sugar levels if needed, glucagon’s role is to raise blood sugar levels if they fall too low. Using this system, the body ensures that the blood glucose levels remain within set limits, which allows the body to function properly.
Read Also: What Helps Bring Blood Sugar Down
Faq: Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is insulin so expensive?
Though reforms are underway in many parts of the US, insulin costs are still prohibitively expensive for many people with diabetes. Reasons include the complexity of the pharmaceutical supply chain and lack of generic substitutes.
2. What is sliding scale insulin?
Sliding scale therapy is a regimen that prescribes a progressive increase in insulin doses before meals and at bedtime, based on your blood sugar levels.
3. What is an insulin index?
The insulin index gives foods a rating based on how much your blood insulin concentration rises in the two hours after consumption.
4. What is an insulin resistance diet?
An insulin resistance diet incorporates foods that will help maintain your bodys balance of insulin and blood sugar. Think nourishing calories from veggies, fruit, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Regulator Of Endocannabinoid Metabolism
Insulin is a major regulator of endocannabinoid metabolism and insulin treatment has been shown to reduce intracellular ECs, the 2-arachidonoylglycerol and anandamide , which correspond with insulin-sensitive expression changes in enzymes of EC metabolism. In insulin-resistant adipocytes, patterns of insulin-induced enzyme expression is disturbed in a manner consistent with elevated EC synthesis and reduced EC degradation. Findings suggest that insulin-resistant adipocytes fail to regulate EC metabolism and decrease intracellular EC levels in response to insulin stimulation, whereby obese insulin-resistant individuals exhibit increased concentrations of ECs. This dysregulation contributes to excessive visceral fat accumulation and reduced adiponectin release from abdominal adipose tissue, and further to the onset of several cardiometabolic risk factors that are associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Hypoglycemia, also known as “low blood sugar”, is when blood sugar decreases to below normal levels. This may result in a variety of symptoms including clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, loss of consciousness, seizures or death. A feeling of hunger, sweating, shakiness and weakness may also be present. Symptoms typically come on quickly.
Don’t Miss: What Meats Are Good For Diabetics
Signs And Symptoms Of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance may not cause any noticeable symptoms, so you can have insulin resistance and not know it. Symptoms dont usually occur until you develop prediabetes or type 2 diabetes.
Key Protein In The Production Of Insulin Discovered
- Date:
- University of Copenhagen The Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences
- Summary:
- The crucial hormone insulin needs help acquiring the right structure. A protein that assists in the process of insulin folding has just been discovered in a new study. They hope the new research results can be used to develop treatments for conditions such as increased level of insulin in the blood known as hyperinsulinemia.
The crucial hormone insulin needs help acquiring the right structure. A protein that assists in the process of insulin folding has just been discovered in a new study conducted by researchers at the Department of Biomedical Sciences, University of Copenhagen. They hope the new research results can be used to develop treatments for conditions such as increased level of insulin in the blood known as hyperinsulinemia.
Even though researchers have been familiar with and studied the hormone insulin for more than a hundred years, especially in connection with diabetes, they still make new discoveries concerning the hormone. Now researchers from the Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences at the University of Copenhagen have uncovered a hitherto unknown process in the production of insulin. The new research results have just been published in the scientific journal Diabetes.
Impaired Insulin Production and Secretion
Story Source:
Read Also: How Do Carbs Affect Blood Sugar
Recover The Ability To Produce Insulin
Lars Krogvold explains:
We found that the insulin-producing cells still have the ability to produce insulin when they are stimulated in the lab.
But whats new is our additional discovery that the cells increased their ability to produce insulin after a few days outside the body.
Indeed, some became roughly as good at making insulin as cells from people without diabetes.
Some of the hormone-producing cells in the pancreas, the beta cells, produce insulin when they are stimulated by sugar.
Previous work has shown that you do not immediately lose your ability to produce insulin when you are first diagnosed with type 1 diabetes.
Causes And Risk Factors Of Insulin Resistance
- Having polycystic ovary syndrome or Cushings disease
- With a family history of type 2 diabetes
- With a personal history of gestational diabetes
- Over the age of 45
- Who are Hispanic, African American, Native American, or Asian American
- With a waist circumference larger than 40 inches or larger than 35 inches
- With a history of high blood pressure or high triglycerides
The risk factors for insulin resistance are similar to the risk factors for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. But lifestyle changes can help your body use insulin properly, which can reduce your risk of diabetes.
Also Check: What Does Insulin Do For Diabetics
How Do You Take Insulin Without A Syringe
- Insulin pens look like large writing pens and can help prevent under- and overdosing. They also dont require refrigeration, are conveniently prefilled, and are more durable than syringes.
- Insulin pumps are attached to a thin tube thats implanted under your skin. Pumps are computerized or motorized, and some models also act as glucose monitors. They deliver insulin before each meal along with small amounts through the course of the day. In the US, about 60% of people with diabetes use some form of insulin pump.
- Jet injection devices are a good option if you hate needles. A jet injector holds several doses of insulin. After placing it against your skin, you press a button, and the insulin is pushed through.
- Inhalable insulin comes in a premeasured inhaler and was first approved in 2014. Its short-acting and usually not covered by insurance, which makes it more cost prohibitive than other types of insulin for most people with diabetes.
Unless you have an insulin pump that also works as a glucose monitor, insulin dosing is based on self-monitoring your blood glucose levels. You can check them by doing finger pricks or wearing a device that continuously monitors them for you.
What Happens If I Have Too Little Insulin
People with diabetes have problems either making insulin, how that insulin works or both. The main two types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2 diabetes, although there are other more uncommon types.
People with type 1 diabetes produce very little or no insulin at all. This condition is caused when the beta cells that make insulin have been destroyed by antibodies , hence they are unable to produce insulin. With too little insulin, the body can no longer move glucose from the blood into the cells, causing high blood glucose levels. If the glucose level is high enough, excess glucose spills into the urine. This drags extra water into the urine causing more frequent urination and thirst. This leads to dehydration, which can cause confusion. In addition, with too little insulin, the cells cannot take in glucose for energy and other sources of energy are needed to provide this energy. This makes the body tired and can cause weight loss. If this continues, patients can become very ill. This is because the body attempts to make new energy from fat and causes acids to be produced as waste products. Ultimately, this can lead to coma and death if medical attention is not sought. People with type 1 diabetes will need to inject insulin in order to survive.
Read Also: What Is The Difference Between Diabetes 1 And 2
Insulin And Fatty Acids
Insulin helps synthesize fatty acids in the liver cells. If the glycogen levels make up at least 5 percent of the mass of the liver, the glycogen synthesis is suppressed and fatty acids are instead made by the liver to be used to make the lipid layer of the cells of the body. The fatty acids are then taken out of the liver and are transferred to lipoproteins, which allow for the transportation of the fatty acids to make cells or to be stored inside fat cells as fat.
What Else Can I Do To Control My Blood Glucose Levels
Food, sleep, and exercise are all of vital importance for regulating your blood sugar when you have diabetes.
You May Like: Does Type 2 Diabetes Require Insulin
What Are The Signs Of High And Low Blood Sugar
Change your medication with doctor supervision. according to the British Diabetes AssociationGet plenty of sleep.According to recommendations published March 2015 in Sleep Health, according to the Sleep FoundationManage stress well.cortisolstress hormoneaccording to Harvard Health Publishingaccording to the ADA
What Are Alternative Medications For People With Diabetes That Arent Insulin
- Metformin a pill that stops sugar production in the liver
- Glitazones pills that remove sugar from the bloodstream
- Sufonylureas and glinides pills that increase the release of insulin from your pancreas
- Starch blockers pills that slow starch absorption
- Incretin therapies and amvlin analogs pills and injections that reduce sugar production in the liver and slow food absorption. Types of the former include DPP4 inhibitors and GLP1 analogs .
- SGLT2 inhibitors pills that are taken before meals that prevent the reabsorption of glucose
Recommended Reading: How Many People Have Diabetes In The World
What Is Human Insulin
Insulin is a hormone produced by beta cells in your pancreas. The purpose of this hormone is to help regulate your blood sugar levels by moving sugar from your blood into the cells of your body.
When you eat carbohydrates, your digestive system breaks it down and turns it into glucose. Glucose enters your blood through your small intestines.
The cells in your body need glucose for energy. To get glucose from your blood into your cells, your pancreas produces insulin, which sends signals to the cells in your body to absorb the sugar in your blood.
People with type 1 diabetes dont produce enough insulin and, as a result, need to administer insulin medications to help regulate their blood sugar.
In type 2 diabetes, the cells in your body dont respond well to insulin and, in later stages, the pancreas may not produce enough insulin. People with advanced type 2 diabetes may also need to take insulin medication to control their blood sugar.
High levels of glucose in your blood can damage your blood vessels and organs.
Combination With Other Antidiabetic Drugs
A combination therapy of insulin and other antidiabetic drugs appears to be most beneficial in people who are diabetic, who still have residual insulin secretory capacity. A combination of insulin therapy and sulfonylurea is more effective than insulin alone in treating people with type 2 diabetes after secondary failure to oral drugs, leading to better glucose profiles and/or decreased insulin needs.
Don’t Miss: How Fast Does Blood Sugar Rise After Eating
Is Insulin Required To Digest Proteins & Fats
Insulin is a peptide harmone, which does not directly involve in digestion of any macromolecules. insteed it act indirectly as peptide signalling harmone, what it does is it goes and binds the receptors on the cell surface and stimulates them to uptake glucose from the bloodstream into the inside of cell to undergo oxidative brakdown of glucose in to carbon dioxide and water and energy. apart from this it doesn’t stimulate uptake of any other biomolecules from blood stream except glucose. in diabetic absence of insulin, results in not activation of cells to uptake glucose from blood, hence glucose remains more and undigested in blood itself, hence this condition is called glucosemia above the normal, which is detrimental. Insulin is an anabolic hormone mainly affecting the carbohydrate metabolism. As such insulin is not involved in digestion process but yes it is involved in the metabolism of fat and proteins also. Insulin has several actions: 1. It causes the cells in the liver, muscle, and fat tissue to take up glucose from blood and convert it to glycogen that can be stored in the liver and muscles 2. Insulin also prevents the utilization of fat as an energy source. In absence of insulin or in conditions where insulin is low glucose is not taken up by body cells, and the body begins to use fat as an energy source 3. Insulin regulates the amino acid uptake by body cells.Continue reading > >
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
People who have type 2 diabetes may not know it because the symptoms aren’t always obvious and they can take a long time to develop. Some people don’t have any symptoms at all.
But when a person gets type 2 diabetes, he or she may:
- pee a lot because the body tries to get rid of the extra blood sugar by passing it out of the body in the urine
- drink a lot to make up for all that peeing
- feel tired all the time because the body can’t use sugar for energy properly
Also, people whose bodies are having problems using insulin or who are overweight may notice something called acanthosis nigricans. This can cause a dark ring around the neck that doesn’t wash off, as well as thick, dark, velvety skin under the arms, in between fingers and toes, between the legs, or on elbows and knees. This skin darkening can lighten over time with improvement in insulin resistance.
In addition, girls with insulin resistance may have polycystic ovary syndrome . In PCOS, the ovaries get bigger and develop fluid-filled sacs called cysts. Girls with this condition often have irregular periods or may stop having periods, and they might have excess facial and body hair.
You May Like: Can Children Get Type 2 Diabetes

