Other Factors To Consider:
- The insulin pump doesnt take away the need to check blood sugar.
- There are technical aspects to using a pumpsetting it up, putting it in, interacting with itthat are more complicated in some ways than using injections.
- If it breaks or falls off, the person wearing it needs to be ready to give insulin by injection any time it is needed.
- It can be expensive, so find out which pumps are covered by your insurance and if those pumps meet your needs.
- All pumps are an extra piece of hardware attached to your body, either with tubing or attached to your skin. There are many clever ways to wear pumps and hide them from view, but they do take a bit of getting used to at first.
Recommended Reading: How To Test For Diabetes Insipidus
Insulin As Treatment For Diabetes
Injections of insulin can help treat both types of diabetes. The injected insulin acts as a replacement for or supplement to your bodys insulin. People with type 1 diabetes cant make insulin, so they must inject insulin to control their blood glucose levels.
Many people with type 2 diabetes can manage their blood glucose levels with lifestyle changes and oral medication. However, if these treatments dont help to control glucose levels, people with the condition may also need insulin to help control their blood glucose levels.
What It The Insulin Pump Function
Insulin pump is a treatment method used instead of needle therapy in diabetes mellitus. Insulin pump is an ideal method for pediatric use, provided that blood sugar measurement is guaranteed much more than needle treatment and a great responsibility is given to how the pump should be used. Individuals using insulin pumps should be under the control of a physician who can transfer the requirements of diabetic care to the patient and know how to use the insulin pump, according to needle therapy.
The insulin pump performs an insulin release called the basal dose, which periodically provides insulin to meet metabolic needs and body functions. Patients send a meal before the meal before they eat. As long as mid-range insulin is used, as in the case of needle therapy in the treatment of insulin pump, the patient will not have to feed on meal times based on the insulin injection schedule, which he must apply in pencil therapy.
The insulin pump is an alachronic device that releases body insulin by means of a tube connected to a catheter placed in the hip, belly, upper arm or leg region. The catheter is replaced every three days.
Many insulin pumps can calculate the meal or correction bolus.
Recommended Reading: What Cells Produce Glucagon
Insulin Levels Hunger And Food Intake: An Example Of Feedback Loops In Body Weight Regulation
Abstract The paper reviews studies considering whether hyperinsulinemia, and its resultant effects on adipose tissue mass, can alter perceived hunger, taste, and food consumption. It also describes work addressing the reciprocal question of whether cues associated with food can affect insulin response. Specifically, four general categories of studies are presented. First, studies considering the causes and physiological consequences of chronic hyperinsulinemia are reviewed. Second, work investigating environmental and cognitive influences on insulin secretion are described. These show that high acute levels of insulin can be produced by simply seeing and thinking about food and that individuals showing this response show a greater tendency toward weight gain in a food-abundant environment. Third, studies are covered in which direct manipulations of insulin level, controlling for blood glucose, are performed. These experiments show that elevations in insulin produce increased hunger, heightened perceived pleasantness of sweet taste, and increased food intake. Finally, a study is described that considers how different insulin levels, produced by the type of food ingested, may affect subsequent food intake. Together, these studies show that “overeating” is caused by a complex feedback system of environmental, behavioral, and biological factors.Continue reading > >
When Should I Take Insulin
You and your doctor should discuss when and how you will take your insulin. Each persons treatment is different. Some people who use regular insulin take it 30 to 60 minutes before a meal. Some people who use rapid-acting insulin take it just before they eat.
Types of insulin:
- Rapid-acting insulin starts working in about 15 minutes. It lasts for 3 to 5 hours.
- Short-acting insulin starts working in 30 to 60 minutes and lasts 5 to 8 hours.
- Intermediate-acting insulin starts working in 1 to 3 hours and lasts 12 to 16 hours.
- Long-acting insulin starts working in about 1 hour and lasts 20 to 26 hours.
- Premixed insulin is a combination of 2 types of insulin .
Also Check: What Happens If A Diabetic Eats Too Much Sugar
What Happens If You Avoid Taking Your Insulin
If you have type 1 diabetes, taking insulin is essential and you cannot live without it. If you avoid taking it, your blood sugar levels can become too high and you risk developing diabetic ketoacidosis . If left untreated, DKA could be life-threatening. Thats why its important to make sure you take your insulin.
If you have type 2 diabetes and use insulin to treat your condition, you should continue to take it as prescribed. If you avoid taking it, your blood sugar levels could become too high and you may become ill. Please speak to your healthcare professional if you have any questions or concerns about taking your insulin.
Insulin is a treatment that helps manage blood sugars, so this also reduces the risk of serious long-term complications as well a shorter-term consequences. Its still important to keep going to your appointments and manage your condition with healthy lifestyle choices. Staying active and eating a healthy diet will reduce the risk of complications from your diabetes, but insulin is also an important part of your treatment.
How Is Insulin Resistance Diagnosed
Although insulin resistance doesnt usually have symptoms, your doctor may recommend testing your blood sugar if you have risk factors for this condition, such as obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, or high blood pressure.
Test
Also Check: What Is A High Blood Sugar Reading
Where Do I Inject The Insulin
Insulin is injected just under the skin. Your doctor or his or her office staff will show you how and where to give an insulin injection. The usual places to inject insulin are the upper arm, the front and side parts of the thighs, and the abdomen. Dont inject insulin closer than 2 inches from your belly button.
To keep your skin from thickening, try not to inject the insulin in the same place over and over. Instead, rotate injection places.
How Is Insulin Controlled
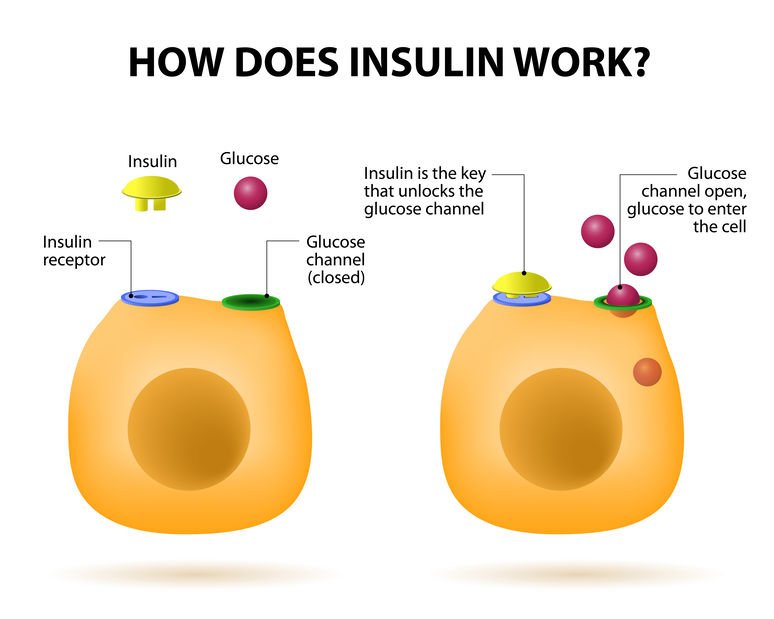
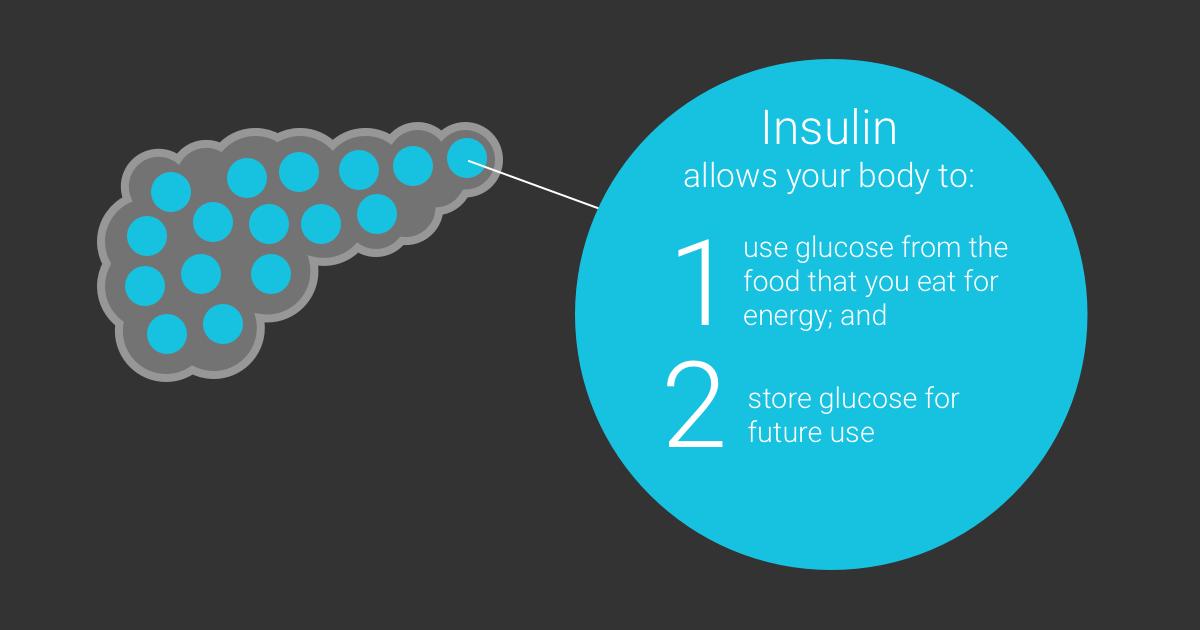
The main actions that insulin has are to allow glucose to enter cells to be used as energy and to maintain the amount of glucose found in the bloodstream within normal levels. The release of insulin is tightly regulated in healthy people in order to balance food intake and the metabolic needs of the body. This is a complex process and other hormones found in the gut and pancreas also contribute to this blood glucose regulation. When we eat food, glucose is absorbed from our gut into the bloodstream, raising blood glucose levels. This rise in blood glucose causes insulin to be released from the pancreas so glucose can move inside the cells and be used. As glucose moves inside the cells, the amount of glucose in the bloodstream returns to normal and insulin release slows down. Proteins in food and other hormones produced by the gut in response to food also stimulate insulin release. Hormones released in times of acute stress, such as adrenaline, stop the release of insulin, leading to higher blood glucose levels to help cope with the stressful event.
Insulin works in tandem with glucagon, another hormone produced by the pancreas. While insulin’s role is to lower blood sugar levels if needed, glucagon’s role is to raise blood sugar levels if they fall too low. Using this system, the body ensures that the blood glucose levels remain within set limits, which allows the body to function properly.
You May Like: Insulin Promotes Glycolysis
How Are Doses Scheduled
Follow your doctor’s guidelines on when to take your insulin. The time span between your shot and meals may vary depending on the type you use.
In general, though, you should coordinate your injection with a meal. You want to time your shot so that the glucose from your food gets into your system at about the same time that the insulin starts to work. This will help your body use the glucose and avoid low blood sugar reactions. From the chart on page 1, the “onset” column shows when the insulin will begin to work in your body. You want that to happen at the same time you’re absorbing food. Good timing will help you avoid low blood sugar levels.
- Rapid acting insulins: About 15 minutes before mealtime
- Short-acting insulins: 30 to 60 minutes before a meal
- Intermediate-acting insulins: Up to 1 hour prior to a meal
- Pre-mixed insulins: Depending on the product, between 10 minutes or 30 to 45 minutes before mealtime
Causes And Risk Factors Of Insulin Resistance
- Having polycystic ovary syndrome or Cushings disease
- With a family history of type 2 diabetes
- With a personal history of gestational diabetes
- Over the age of 45
- Who are Hispanic, African American, Native American, or Asian American
- With a waist circumference larger than 40 inches or larger than 35 inches
- With a history of high blood pressure or high triglycerides
The risk factors for insulin resistance are similar to the risk factors for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. But lifestyle changes can help your body use insulin properly, which can reduce your risk of diabetes.
Also Check: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Prevention Of Insulin Resistance
Making lifestyle changes can help reverse insulin resistance so that your body can respond properly to insulin.
Lose weight.Eat a .
Physiological Role Of Insulin
Insulin is the pivotal hormone regulating cellular energy supply and macronutrient balance, directing anabolic processes of the fed state. Insulin is essential for the intra-cellular transport of glucose into insulin-dependent tissues such as muscle and adipose tissue. Signalling abundance of exogenous energy, adipose tissue fat breakdown is suppressed and its synthesis promoted. In muscle cells, glucose entry enables glycogen to be synthesised and stored, and for carbohydrates, rather than fatty acids to be utilised as the immediately available energy source for muscle contraction. Insulin therefore promotes glycogen and lipid synthesis in muscle cells, while suppressing lipolysis and gluconeogenesis from muscle amino acids. In the presence of an adequate supply of amino acids, insulin is anabolic in muscle.
Read Also: Banana Diabetes Type 2
Pharmacological Influences On Insulin Action And Insulin Resistance
A wide range of pharmacological agents have been associated with impaired glucose tolerance. Antihypertensive agents such as diuretics and -blockers, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives, nicotinic acid and antipsychotic agents have been reported to impair glucose tolerance, as have the anti-retroviral protease inhibitors used to treat human immunodeficiency virus infection. The mechanisms vary -blockers impair insulin secretion from the pancreas by blockade of -adrenoceptors, thiazide diuretics are thought to act by depleting potassium levels, corticosteroids and oral contraceptives have counter-regulatory hormonal activity, and the HIV-1 protease inhibitors result in partial lipodystrophy with loss of peripheral subcutaneous fat and accumulation of truncal adipose tissue leading to insulin resistance.
What Will Insulin Be Like In The Future
Pharmaceutical companies are working on very long-acting versions of insulin that could last for a week. There is also an ultra-fast version of insulin under development that will act in less than 15 minutes.
Another group of researchers is looking at glucose responsive insulin , which would react to the needs of your body in real time. It would have nanosensors bound to the insulin so that when insulin is needed, it releases, and when it isnt, it stops, according to Dr. Hirsch.
Don’t Miss: Type 2 Diabetes Dizziness
What Else Can I Do To Control My Blood Glucose Levels
Food, sleep, and exercise are all of vital importance for regulating your blood sugar when you have diabetes.
The Pancreas And Insulin
The pancreas is responsible for producing insulin. The cells which produce insulin are beta cells. These cells are distributed in a cluster of cells in the pancreas called the Islets of Langerhans, named after the anatomist who discovered them
Insulin is a hormone that helps to regulate blood sugar levels by assisting the transport of glucose from the blood into neighbouring cells.
Also Check: Do Type 1 Diabetics Take Insulin
Do I Need To Monitor My Blood Sugar Level
Yes. Monitoring and controlling your blood sugar is key to preventing the complications of diabetes. If you dont already monitor your blood sugar level, you will need to learn how. Checking your blood sugar involves pricking your finger to get a small drop of blood that you put on a test strip. You can read the results yourself or insert the strip into a machine called an electronic glucose meter. The results will tell you whether your blood sugar is in a healthy range. Your doctor will give you additional information about monitoring your blood sugar.
Types Of Insulin Where To Inject It And The Best Methods For Insulin Delivery
role of insulinshort- and long-term complicationsYour diabetes treatment team is there to help you. Patients’ Guide to Managing Your Child’s Type 1 Diabetes
This article will provide a basic overview of insulin. You can also visit our Patients’ Guide to Insulin for more information as well as read more in the section on Type 1 Diabetes Treatments, which has a chart providing more detail about the types of insulin that your doctor may prescribe.
Also Check: Can Diabetics Eat Macaroni And Cheese
How Do Insulin Pumps Work
Insulin pumps deliver insulin by continuous infusion through a single subcutaneous site which is replaced, on average, every three days. Only rapid-acting insulin is used, and the analogue insulins have gained popularity over regular insulin for this purpose . A pump delivers programmable basal insulin around the clock which is tailored to the patients 24-h glucose profile. The insulin requirements may be affected by the individuals physiology, the type and duration of daily activity, work schedule, exercise, illness, concomitant medications, etc. Most patients utilize multiple basal rates over a 24-h period, but some may use a single rate. Almost all pumps have the capability of programming basal rates that are modifiable every hour and also have a temporary basal rate feature for special situations. Patients can also deliver bolus insulin which infuses over a few minutes to a few hours. Insulin boluses cover meals and correct for high blood glucose levels. For the pump to accurately calculate bolus insulin amounts, the carbohydrate content of food and the blood glucose level are required. Insulin delivery via the pump can be suspended by the patient if necessary.
How Are These Insulins Used

Some people with diabetes may only need 1 type of insulin, while others may need multiple types to manage their blood sugar. Your doctor will help choose an insulin regimen thats right for you.
Here are a few examples of insulin regimens your doctor may prescribe:
- Once-daily or twice-daily insulin. If you have type 2 diabetes that is somewhat managed with oral medication but you need injectable insulin to get a better handle on your blood sugar levels, your doctor may suggest once- or twice-daily dosing with intermediate- or long-acting insulin.
- Basal-bolus regimen. This regimen mimics the way the human body naturally releases insulin. Basal insulin release helps manage blood sugar throughout the day, so you may use a long-acting or ultra-long-acting insulin for basal control. Bolus insulin release helps manage blood sugar at mealtimes, so you may use rapid- or short-acting insulin injections for mealtime control. With a basal-bolus regimen, you could inject insulin up to 4 times a day. People with type 1 or type 2 diabetes may use a basal-bolus insulin regimen.
- Sliding scale insulin. A sliding scale is when you inject a certain amount of insulin depending on your current blood sugar level. This means your insulin dose may vary throughout the day. Sliding scale insulin regimens require you to eat the same number of carbohydrates at each meal in order to be effective.
Read Also: The Hormone Insulin Stimulates
Conventional Insulin Pump Therapy
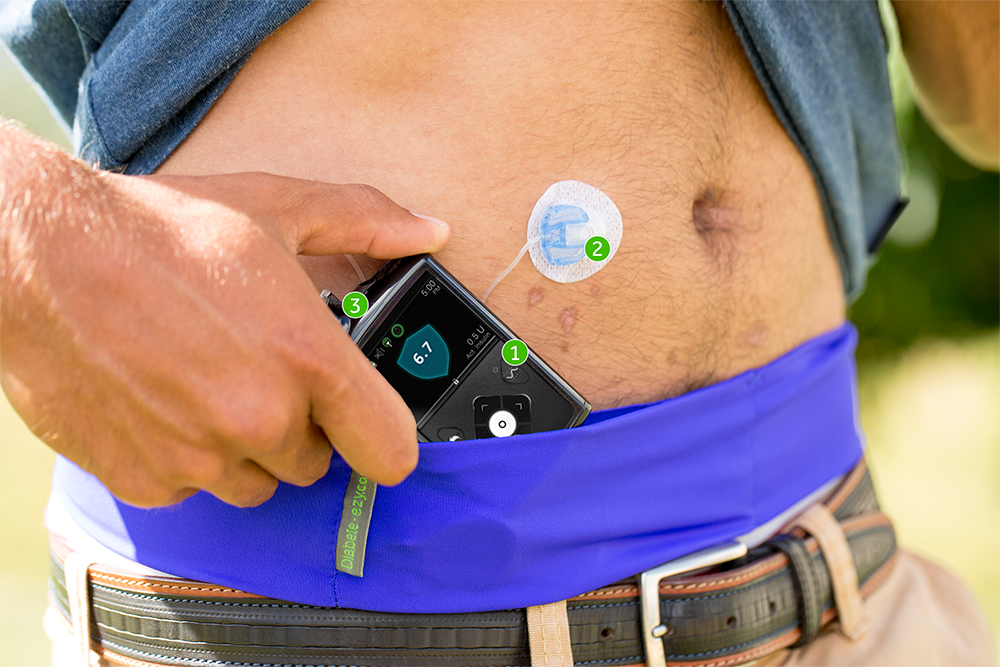
An insulin pump is a small, digital device that continuously delivers rapid-acting insulin through a small catheter inserted into the subcutaneous tissue and secured in place on the skin with adhesive . In most insulin pumps, the infusion set connects to the pump by plastic tubing, and insulin infuses from the pump through the tubing to the infusion set cannula and into the subcutaneous tissue . Some pumps, referred to as patch pumps, do not use tubing and instead adhere directly to the skin. Patch pumps deliver insulin through the infusion cannula and are programmed from a remote device using wireless technology .
Insulin pump with tubing. The tubing connects the insulin pump, which contains the reservoir where the insulin is held, to the infusion cannula inserted in the subcutaneous tissue.
Insulin pump without tubing . Tubeless patch pumps contain the insulin reservoir and the infusion cannula and adhere directly to the skin. A handheld device is used to program insulin delivery and insert the infusion cannula.
Commercially Available Insulin Pumps, United States, as of March 2019
Dont Miss: What Pasta Can Diabetics Eat

