What Is A Normal Blood Sugar
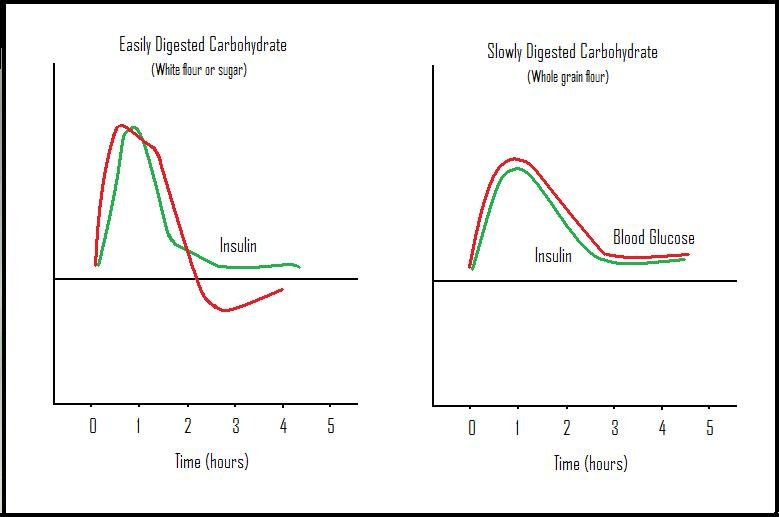
Ideas about normal blood sugar levels are based on individuals eating a standard American diet. This type of diet usually contains about 50% of calories from carbohydrate, the nutrient that tends to raise blood sugar the most.2
If your own carbohydrate intake is much lower than this, you may have a different normal. You can jump to How a low-carb diet affects blood sugar measurements for more information.
Fasting blood sugar levels
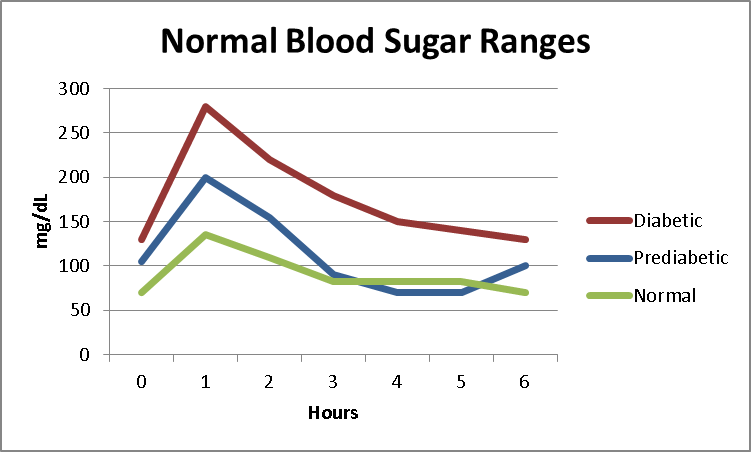
A normal fasting blood sugar level in someone who does not have diabetes is generally between 70 and 100 mg/dL .
Fasting blood sugar that consistently falls in the range of 100 to 125 mg/dL is considered prediabetes, which is also referred to as impaired fasting glucose.
If your fasting blood sugar is above 126 mg/dL on two separate occasions, then you may have diabetes.
If you are concerned about the measurements youre getting, especially if you are already on a low-carbohydrate diet, see How a low-carb diet affects blood sugar measurements. A few blood sugar measurements may not always provide an accurate picture of your health.
Post-meal blood sugar levels
If your healthcare provider has not given you specific instructions regarding when to test post-meal blood sugar, you may want to try measuring it one to two hours after you begin eating. Whichever reading is the highest is the one that you should pay attention to, because blood sugar levels may peak at different times.
Blood glucose chart
Take Extra Precautions With Evening Exercise
Exercise does two things for those who have type 2 diabetes, says Dr. Hatipoglu.
First, your muscles need energy to work. To feed them, your body burns sugar as an energy source, lowering the glucose levels in your blood.
Second, when you exercise regularly, it helps your body use insulin more efficiently. This can lower your blood sugar levels for up to 12 hours after you exercise.
Also, keeping blood sugar low on a regular basis can dramatically reduce your risk of heart disease, Dr. Hatipoglu says.
Every person reacts a little differently to exercise, so she recommends tracking your blood sugar levels for four to five hours after post-meal exercise to see what your trend is. This can help you determine if your levels are healthy or drop too much.
This is particularly important if you exercise in the evening.
Especially after dinner, you need to know what your body will do when you exercise, she says. If you go to bed and glucose drops it can create a dangerous clinical situation.
Exercising after a meal is a good way to reduce blood glucose levels and lower your risk of complications from diabetes, including heart disease.
But, before starting or changing your exercise regimen, talk with your doctor to determine what is best for you.
How To Deal With High Postprandial Blood Sugar Levels
Obviously, check your levels first meaning at least 90 minutes after a meal. Why? By that time rapid-acting analog insulin has reached its maximum effect By the way, the blood sugar reminder in the mySugr app is a great way to check your glucose after a meal. After all, no one can be expected to remember everything! Just set the reminder for a specific time and youll automatically be reminded. If you have type 1 diabetes, your blood sugar should be between 5 and 9 mmol/liter at least 90 minutes after eating . Of course, your doctor may recommend another postprandial level according to your personal needs and state of health
Also Check: Why Does Blood Sugar Go Up At Night
Checking For Low Blood Sugar Levels
The warning signs of hypoglycemia are the body’s natural response to low blood sugar levels. When blood sugar levels fall too low, the body releases the hormone adrenaline, which helps get stored glucose into the bloodstream quickly. This can make someone:
- pale
- start shaking
- have an increased heart rate
If the hypoglycemia isn’t treated, more serious symptoms may happen, such as drowsiness, confusion, seizures, and loss of consciousness.
The only way to know for sure if you’re having a low blood sugar level is to test. Blood sugar levels can be tested with a . This computerized device measures and displays the amount of glucose in a blood sample. But if you can’t quickly check your blood sugar level, it’s important to treat yourself for hypoglycemia immediately to prevent symptoms from getting worse.
Sometimes a person with diabetes may have symptoms of low blood sugar levels, but blood sugar levels are not actually low. This is a called a false reaction. The hormone adrenaline is not just released when blood sugar drops too low it’s also released when blood sugar levels fall quickly when they’re too high. If you’re having a false reaction, you might actually have blood sugar levels in a healthy range but feel as if you have low blood sugar. Testing blood sugar levels before treating yourself for hypoglycemia can help you figure out if you’re having a false reaction.
page 3
Can You Raise Blood Sugar Without Food
Two products glucose gel and chewable glucose tablets are also effective at quickly raising blood sugar. Theyre available without a prescription and are recommended for people who experience frequent episodes of low blood sugar.
If youve had severe low blood sugar symptoms in the past, speak with your doctor about whether a glucagon kit is right for you. Glucagon is a hormone that triggers your liver to release glucose into the bloodstream.
These kits are only available by prescription. Theyre used to raise your blood sugar when youre not able to eat or drink, such as in a state of unconsciousness. Therefore, someone else, like a friend or family member, typically administers this medication for you.
An episode of low blood sugar that necessitates assistance from another person is by definition severe hypoglycemia. The kits come with a syringe and needle that can be used to inject glucagon into your arm, thigh, or buttocks.
Be sure to ask your doctor when and how to use a glucagon kit. Also, let your family and friends know how to use it and how to recognize a hypoglycemic emergency.
There are many different factors that can cause a dip in your blood sugar levels. Here are some of the most common causes.
Don’t Miss: Does Blood Sugar Rise At Night
How Can I Pay For Tests And Diabetes Supplies
Medicareexternal icon, Medicaid, and most private insurance plans pay for the A1C test and fasting blood sugar test as well as some diabetes supplies. Check your plan or ask your health care team for help finding low-cost or free supplies, and see How to Save Money on Diabetes Care for more resources.
What Should My Blood Sugar Level Be
When you’re first diagnosed with diabetes, your diabetes care team will usually tell you what your blood sugar level is and what you should aim to get it down to.
You may be advised to use a testing device to monitor your blood sugar level regularly at home.
Or you may have an appointment with a nurse or doctor every few months to see what your average blood sugar level is. This is known as your HbA1c level.
Target blood sugar levels differ for everyone, but generally speaking:
- if you monitor yourself at home with a self-testing kit a normal target is 4 to 7mmol/l before eating and under 8.5 to 9mmol/l 2 hours after a meal
- if your HbA1c level is tested every few months a normal HbA1c target is below 48mmol/mol
The Diabetes UK website has more about blood sugar levels and testing.
Don’t Miss: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
How Long After Eating Does Blood Sugar Peak
blood sugaraftermealpeak after
Questions and Answers – blood sugar
| Fasting Blood Glucose | |
|---|---|
| Less than 140 | |
| Pre-diabetes | |
| 126mg/dl and greater | 200 or greater |
Furthermore, what should blood sugar be 3 hours after eating? They’re less than 100 mg/dL after not eating for at least 8 hours. And they’re less than 140 mg/dL 2 hours after eating. During the day, levels tend to be at their lowest just before meals. For most people without diabetes, blood sugar levels before meals hover around 70 to 80 mg/dL.
One may also ask, what should my blood sugar be 2 hours after eating?
Blood sugar chart
| Target blood sugar levels for people without diabetes | |
|---|---|
| Before meals | |
| 12 hours after the start of a meal | less than 140 mg/dl |
| Over a 3-month period, which an A1C test can measure | less than 5.7% |
How does squeezing finger affect blood sugar?
Overall, the study found, clean hands are still key. Based on that, the researchers recommend that people wash and dry their hands before testing, then use the first blood drop.
Blood Sugar Level After 2 Hours:
Another crucial time to check blood glucose level is about an hour and a half after a meal. Generally, around this time the process of digestion and absorption is near its end. So, high blood sugar during this time generally means that the body cant process sugar properly.
In case of a normal individual, blood glucose level at this time is below 7.8 mmol/L. If the sugar level is 11.1 mmol/L or more, then the individual is considered to be diabetic.
Read Also: Non Diabetic A1c Numbers
Why Are Blood Sugar Spikes A Problem
Even though the spike is temporary, all of those spikes throughout the day can raise your HbA1c. Research has shown that for those with an A1c below 7.5%, post-meal readings actually have a greater influence on A1c than fasting blood sugars. In other words, managing pre-meal readings will only get you so far. If you want tight control, you need to pay attention to the after-meal glucose as well.
The long-term effects of postprandial hyperglycemia have been studied extensively. For those with type 1 diabetes, significant post-meal rises have been shown to produce earlier onset of kidney disease and accelerate the progression of existing eye problems . And like a dagger through the heart, post-meal hyperglycemia is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular problems. Recently, post-meal spikes and glucose variability have been associated with diminished brain function and an increased risk of dementia.
But the problems are not limited to long-term health issues. Any time blood sugars rise particularly high, even temporarily, our quality of life suffers. Energy decreases, cognitive ability falters, physical/athletic abilities become diminished, and moods become altered. And dont forget: What goes up must come down. The rapid blood sugar decline that usually follows a post-meal spike can cause false hypoglycemic symptoms.
The Fattest People On Earth
The Pimas of Arizona are among the fattest groups of people in the world. The only populations more obese are people living on some isolated Pacific Islands. On the Gila River reservation in Arizona, children as young as six and seven are so obese they cannot run. They lumber across baseball fields, out of breath before they get to first base.
You May Like: Blood Sugar Medical Term
What Is Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Eating For Non
It would be remiss of me, if I left you hanging without letting you in on what normal blood sugars should be after eating if you are non-diabetic.
Whats the point of telling about blood sugar spikes in non-diabetics if I dont reveal what normal blood sugars should be after eating.
The essential point here though is the importance of non-diabetics having a control on their diet. What you eat has either a positive effect on your health or a negative one.
Let me repeat that.
Non-diabetics are obliged to take control of their food choices, if they are to avoid the health implications of blood sugar highs. This is the whole point of this exercise.
You may want to use the figures below as your non-diabetic blood sugar chart if you like. It works just the same way.
So, below is your non-diabetic blood sugar or glucose chart and this is what is recommended by the American College of Clinical Endocrinologists.
Of particular interes,t are the values there that represent what you, as a non-diabetic should be aiming for at 1 hour after eating and 2 hours post meal. They represent what should be normal blood sugar levels after eating your meal.
As you can see it is anticipated that your blood sugar should peak 1 hour after you have eaten but some foods may swing either way.
For instance, an oatmeal may peak just beyond the 1-hour mark compared to a bagel, doughnut or potato fries which might peak much earlier.
Who Should Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
If you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes, monitoring your blood sugar regularly will help you understand how medication like insulin, food, and physical activity affect your blood glucose. It also allows you to catch rising blood sugar levels early. It is the most important thing you can do to prevent complications from diabetes such as heart attack, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, and amputation.
Other people who may benefit from checking their blood glucose regularly include those:
- Taking insulin
Recommended Reading: What Happens In Type 1 Diabetes
Why Is It Important To Reduce The Size And Duration Of These Spikes
Reducing these spikes may help you to increase the amount of time you spend in your target blood sugar range , which will have a positive impact on your future health. You should consult your healthcare team to understand the best target range for you, as this will differ from person to person. However, the International Society for Paediatric and Adolescent Diabetes recommends a target of 5.0-10.0 mmol/L .
Symptoms of a high blood sugar level also vary in individuals, but they may cause you to feel thirsty, tired, stressed and need to go to the toilet a lot. In the short term, by avoiding prolonged high blood sugar readings after eating, you should also reduce the occurrence of these symptoms and improve your energy, cognitive and athletic ability and overall mood.
Carbohydrates And Blood Sugar
When people eat a food containing carbohydrates, the digestive system breaks down the digestible ones into sugar, which enters the blood.
- As blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that prompts cells to absorb blood sugar for energy or storage.
- As cells absorb blood sugar, levels in the bloodstream begin to fall.
- When this happens, the pancreas start making glucagon, a hormone that signals the liver to start releasing stored sugar.
- This interplay of insulin and glucagon ensure that cells throughout the body, and especially in the brain, have a steady supply of blood sugar.
Carbohydrate metabolism is important in the development of type 2 diabetes, which occurs when the body cant make enough insulin or cant properly use the insulin it makes.
- Type 2 diabetes usually develops gradually over a number of years, beginning when muscle and other cells stop responding to insulin. This condition, known as insulin resistance, causes blood sugar and insulin levels to stay high long after eating. Over time, the heavy demands made on the insulin-making cells wears them out, and insulin production eventually stops.
Also Check: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
Choose The Right Medication
Two classes of injectable hormones, GLP-1 agonists , semaglutide ) and amylin mimetics , have powerful effects on post-meal blood sugar. Both GLP-1s and Symlin slow gastric emptying and keep carbohydrates from raising the blood sugar too quickly after meals. Symlin, which is a replacement for the amylin hormone , also helps to diminish appetite and blunt post-meal glucagon secretion. GLP-1s blunt appetite and promote the growth of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas of those with type 2 diabetes. So both can contribute to better post-meal high blood glucose control.
Your choice of oral medication can also impact your after-meal control. Sulfonylureas stimulate the pancreas to secrete a little extra insulin throughout the day, without regard to meal timing. Because these medications fail to concentrate the insulin secretion at times when it is needed most, after-meal blood sugars can run very high. There are alternative medications called meglitinides which also stimulate the pancreas but do so in a much faster and shorter manner. When taken at mealtimes, meglitinides produce better after-meal high blood glucose control than sulfonylureas.
Another class of oral diabetes medications improve after-meal control by partially blocking the transport of sugars across the intestines and into the bloodstream. However, these medications can sometimes cause gas, bloating and stomach upset, so the pros dont always outweigh the cons.
What Causes High Blood Sugar
A variety of things can trigger an increase in blood sugar level in people with diabetes, including:
- stress
- missing a dose of your diabetes medicine or taking an incorrect dose
- overtreating an episode of low blood sugar
- taking certain medicines, such as steroids
Occasional episodes of hyperglycaemia can also occur in children and young adults during growth spurts.
Also Check: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
How Do I Check Blood Sugar Level
Checking blood sugar level is very simple thanks to the availability of easy-to-use handheld glucometers. These consumer glucometers have made it very easy to always keep an eye on your blood sugar level. They are an absolute essential for diabetics and also for people trying to maintain their blood glucose level.
- Check out Here how to choose the best diabetic blood sugar meter.
They operate by taking pin-pricks of blood onto a small electrode slip, which when inserted into the device gives a digital readout of the amount of glucose content in the blood. These devices have become extremely popular for their convenience, reliability and accuracy.
An essential laboratory test of blood glucose level is the Oral Glucose Tolerance Test or OGTT. It is a diagnostic test for DM or any glucose intolerance. Here, a blood sugar reading is taken after a 10-12 hour fast. Then another reading is taken after 2 hours after ingesting a measured amount of glucose. This test shows the bodys ability to absorb glucose, thus is a confirmatory test for DM.

