% Of Your Donation For Research Goes Directly To The Scientists
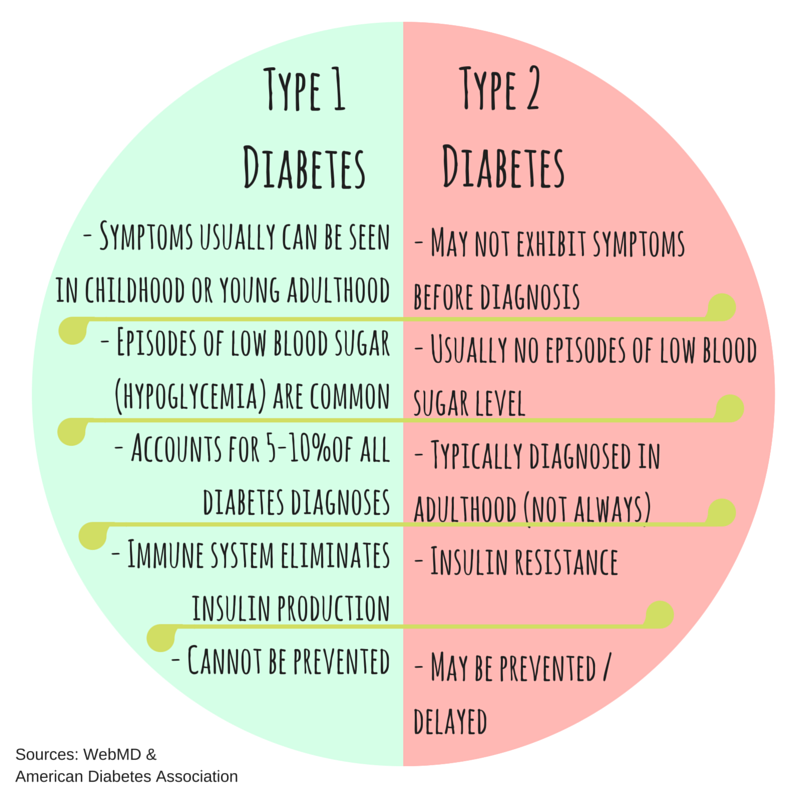
Currently 1.25 million Americans live with type 1 diabetes , including 200,000 children. Approximately 40,000 new patients are diagnosed yearly. Despite this, diabetes research funding has decreased for research to prevent, cure, and better manage the disease. What diabetes funding is available generally goes to established scientists.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms, treatment, and complications from type 2 diabetes may vary from person to person. The following information will help you learn more about this disease and provide you with helpful tools, assessments and resources.
-
If left untreated or improperly managed, diabetes can lead to a variety of life-threatening complications.
Is Diagnosing Diabetes Types 1 And 2 Similar
Blood tests used to diagnose type 1 and type 2 diabetes include fasting blood sugar, a hemoglobin A1C test, and a glucose tolerance test. The A1C test measures the average blood sugar level over the past few months. The glucose tolerance test measures blood sugar after a sugary drink is given.
“The blood sugar testing we do to diagnose and manage type 1 diabetes is very similar to the testing we do for type 2 diabetes,” says Drincic. “We can do a blood test that looks for antibodies. That tells us if it is type 1 or 2.” In type 1 diabetes, the immune system makes antibodies that act against the cells in the pancreas that make insulin, and these antibodies can be detected in a blood test. Your doctor may suspect type 2 diabetes based on your symptoms and risk factors, such as obesity and family history.
Read Also: Blood Sugar 112
What Is The Prognosis Of Diabetes
Diabetes is a leading cause of death in all industrialized nations. Overall, the risk of premature death of people with diabetes is twice that of people without diabetes. Prognosis depends on the duration of diabetes, degree of blood sugar control, and development of complications.
Type 1 diabetes
About 15% of people with T1D die before age 40 years, which is about 20 times the rate of this age group in the general population.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis , kidney failure, and heart disease compose the most common causes of death related to T1D.
- The good news is prognosis improves with good sugar control. Maintaining tight blood sugar control prevents, slows the progression of, and can improve established complications of T1D.
Type 2 diabetes
The life expectancy of people who are diagnosed with T2D during their 40s decreases by five to 10 years because of the disease.
- Heart disease leads the causes of death related to T2D.
- Aim for excellent glycemic control, tight blood pressure control, keeping the “bad”cholesterol level at the recommended level below 100 mg/dL , and keeping the “good” cholesterol as high as possible. When indicated, aspirin can prevent, slow the progression of, and improve established complications related to diabetes.
The Difference Between Type1 And Type2 Diabetes Mellitus
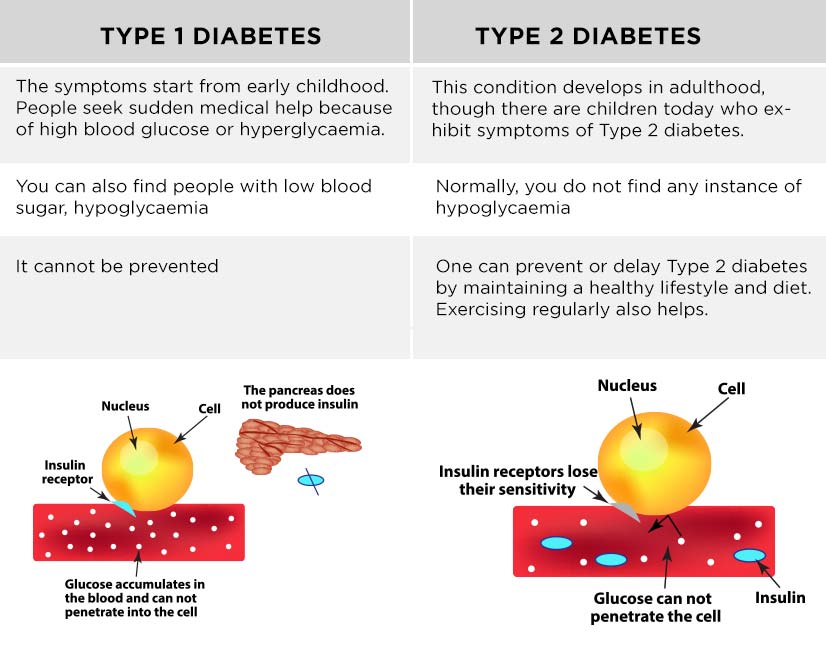
There are several differences between type1 and type2 diabetes mellitus. First, type 1 diabetes most often develops in young children while type2 diabetes can occur at any age. Additionally, type1 patients are dependent on insulin because their pancreas does not produce any. Those with type2 may produce some insulin in their pancreas, but they do not produce enough, or it is not used efficiently in their bodies.
Another difference between the two types is that those with type one can experience episodes of low blood sugar as well as high levels while those with type2 rarely do. Moreover, type1 diabetes cannot be prevented, but, in many cases, type2 can be avoided. Finally, there are many more cases of type2 diabetes are documented.
Recommended Reading: What Happens When Diabetics Don’t Eat
What Is Type 2 Diabetes
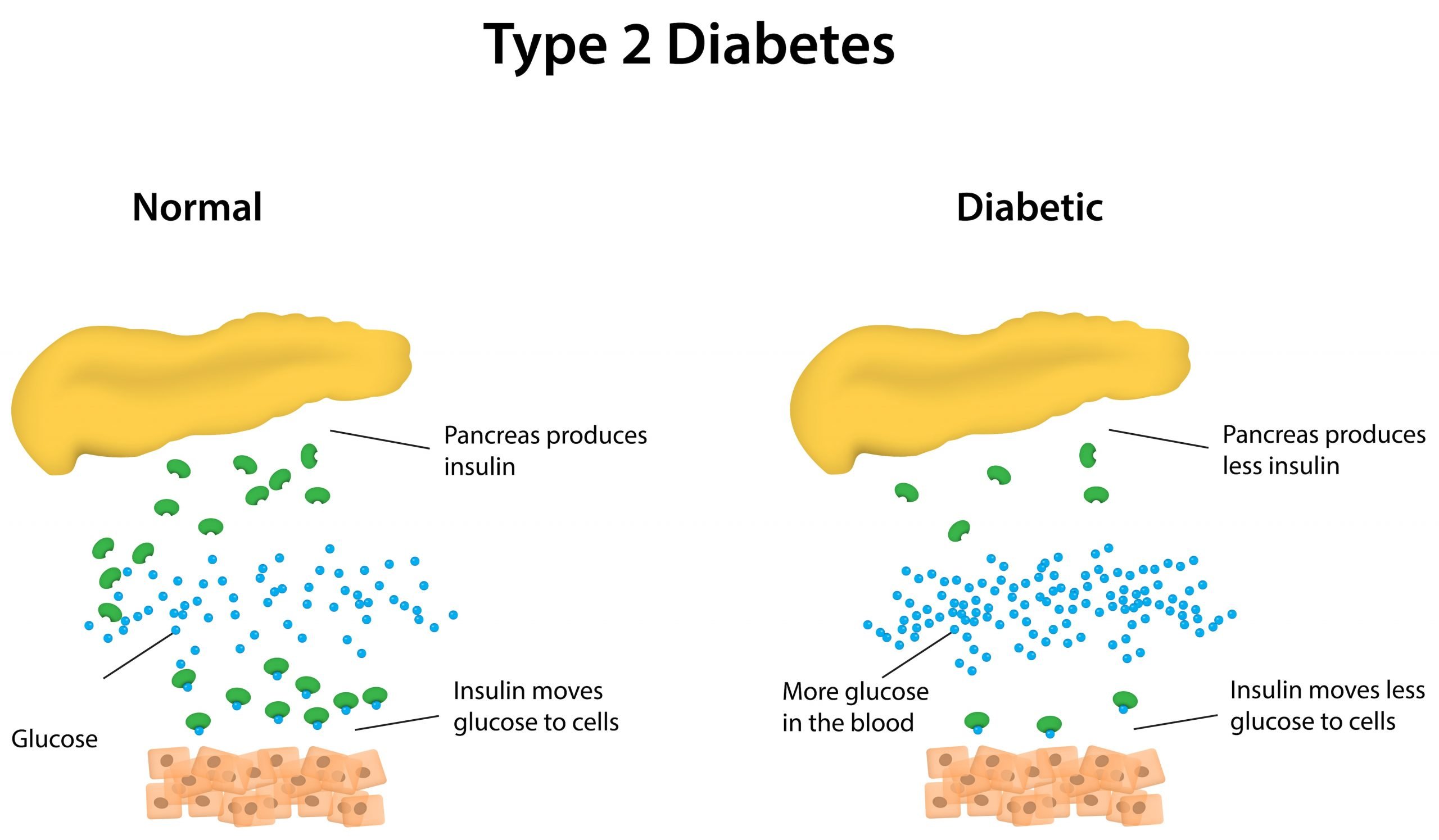
Type 2 diabetes is a disease where your body cant use energy from food properly. Your pancreas produces insulin to help your cells use glucose . But over time your pancreas makes less insulin and the cells resist the insulin. This causes too much sugar to build up in your blood. High blood sugar levels from Type 2 diabetes can lead to serious health problems including heart disease, stroke or death.
Type 2 Diabetes And Insulin Injections
People with type 2 diabetes may need to take insulin injections, usually for one of two main reasons:
- Low sensitivity to insulin: The more excess body weight we carry, the less sensitive we are to insulin Being insensitive to insulin means insulin doesnt reduce blood glucose levels as much as it should. People with low insulin sensitivity often need to be injected with insulin to avoid hyperglycemia
- Beta cell failure: If you develop insulin resistance, you need more of it to keep your blood glucose levels stable. More insulin production means more work for the pancreas. Over time, the beta cells can become burnt out by the constant strain, and stop producing insulin altogether. Eventually, you can get to a similar situation as someone with type 1 diabetes, in which your body is incapable of producing the amount of insulin you need to keep blood glucose levels under control. Insulin injections are necessary in these situations
Don’t Miss: Does Metformin Lower Cholesterol
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Managed
Theres no cure for Type 2 diabetes. But you can manage the condition by maintaining a healthy lifestyle and taking medication if needed. Work with your healthcare provider to manage your:
- Blood sugar: A blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring can help you meet your blood sugar target. Your healthcare provider may also recommend regular A1c tests, oral medications , insulin therapy or injectable non-insulin diabetes medications.
- Blood pressure: Lower your blood pressure by not smoking, exercising regularly and eating a healthy diet. Your healthcare provider may recommend blood pressure medication such as beta blockers or ACE inhibitors.
- Cholesterol: Follow a meal plan low in saturated fats, trans fat, salt and sugar. Your healthcare provider may recommend statins, which are a type of drug to lower cholesterol.
Is It Possible To Prevent Diabetes
No approach has yet been approved by the FDA to prevent T1D, though recent research showed promising results for teplizumab for some at highest risk of developing T1D.
T2D can be prevented in some cases.
- Control weight to normal or near-normal levels by eating a healthy low-fat, high-fiber diet with appropriate content of calories.
- Regular physical activity is essential to prevent T2D.
- Keep alcohol consumption low.
- Quit smoking and other tobacco products.
- To control high blood fat levels or high blood pressure, take medications as directed.
- Lifestyle modifications and/or certain medications can sometimes prevent progression of prediabetes to T2D. Prediabetes can be diagnosed by checking fasting glucose or two hours after ingesting up to 75 grams of glucose .
If you or someone you know has any type of diabetes, focus on preventing diabetes-related complications. Complications can cause serious disabilities, such as blindness, kidney failure requiring dialysis, amputation, or even death.
Also Check: Metformin Common Dosage
Differentiating Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
For people who fit the classic pattern of type 2 diabetes , and where two glucose test results are in the diabetic range , no further testing is required for diagnosis, and management should follow current guidelines.1 Follow-up testing of glycated haemoglobin is useful to assess glycaemia over time and to tailor treatment.1
Clinical features at presentation that help to distinguish type 1 and type 2 diabetes
When It Becomes An Emergency:
Theres a complication of type 1 diabetes called diabetic ketoacidosis , which results from very high blood sugar and is serious and life-threatening. With DKA, the cells in the body are starved for energy, so they start breaking down fat, producing toxic acids known as ketones. So if you or someone you love experiences these symptoms on top of diabetes symptoms, its time to go to the ER:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Tingling or numbness of the lips, tongue or cheek
Don’t Miss: Glucose Definition Medical
Understanding Diabetes From Other Causes
In addition to type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes, a small minority of people develop specific types of diabetes due to other causes. This includes:
- Monogenic diabetes syndromes, such as neonatal diabetes and maturity-onset diabetes of the young
- Diseases of the exocrine pancreas, such as cystic fibrosis and pancreatitis
- Drug or chemical-induced diabetes, such as with glucocorticoid use, in the treatment of HIV/AIDS or after organ transplantation
Because these types of diabetes are rare, they are often misdiagnosed as other types of diabetes. You can learn more about these types of diabetes in the Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes section in the Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. If you think you might have one of these types, be sure to talk with your doctor.
How Are The Signs And Symptoms Similar
There isn’t a difference between the symptoms of either disease. The “classic” symptoms are the same for both diabetes type 1 and type 2:
- Increased urine output
- Unexplained weight loss
For both type 1 and type 2, early symptoms of untreated diabetes arise due to elevated blood sugar levels and the presence of glucose in the urine. High amounts of glucose in the urine can cause increased urine output and dehydration. Dehydration, in turn, causes increased thirst.
A lack of insulin or an inability of insulin to work properly affects protein, fat, and carbohydrate metabolism. Insulin normally encourages the storage of fat and protein, so when there is inadequate insulin or poorly functioning insulin, this eventually leads to weight loss despite an increase in appetite.
Some untreated diabetes patients also experience generalized symptoms like fatigue, nausea, and vomiting. People with diabetes are also at risk for infections of the bladder, skin, and vaginal areas. Changes in blood glucose levels can lead to blurred vision. When blood sugar levels are extremely high, lethargy and coma can result.
You May Like: Glucotrol Vs Metformin
Are There Home Remedies For Diabetes
If a person has diabetes, healthful lifestyle choices in diet, exercise, sleep, and other habits will help improve glycemic control and prevent or minimize complications from diabetes.
Diabetes diet
A healthy diet is key to controlling blood sugar levels and preventing diabetes complications.
- Patients who are obese and have had difficulty losing weight on their own should talk to a health care professional. He or she can recommend a dietitian, help set feasible goals, or supervise a weight-modification program.
- Eat a consistent, well-balanced diet high in fiber, low in saturated fat, low in concentrated sweets, and eliminate excess calories.
- A consistent diet includes roughly the same number of calories at predictably similar times of day. Such a disciplined diet helps match the correct dose of insulin or other medications.
- A healthy diet helps keep the blood sugar level relatively even. A healthy, predictable diet avoids excessively low or high blood sugar levels, which can be dangerous and even life-threatening.
Exercise
In any form, regular exercise helps reduce the risk of developing diabetes. Activity can reduce the risk of developing diabetes-related complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, blindness, and leg ulcers.
Alcohol use
Smoking
Self-monitored blood glucose
Check blood sugar levels frequently, then record the results in a logbook or digital record. At a minimum, check blood sugar before meals and at bedtime.
How Else Can I Manage Type 1 Diabetes
Along with insulin and any other medicines you use, you can manage your diabetes by taking care of yourself each day. Following your diabetes meal plan, being physically active, and checking your blood glucose often are some of the ways you can take care of yourself. Work with your health care team to come up with a diabetes care plan that works for you. If you are planning a pregnancy with diabetes, try to get your blood glucose levels in your target range before you get pregnant.
You May Like: Reduce Blood Sugar Fast
What You Need To Know
-
In patients with new onset hyperglycaemia where the type of diabetes is ambiguous, diabetes specific autoantibodies are the diagnostic test of choice to distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes
-
Patients with newly diagnosed diabetes who are over 40 and respond well to oral anti-hyperglycaemic therapy do not need to undergo testing to distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes
-
Glycated haemoglobin is not recommended as a diagnostic test for patients with possible or suspected type 1 diabetes because it may not reflect a recent rapid rise in blood glucose and results take longer than with serum glucose testing
A 33 year old man with no notable medical history attends his general practitioner reporting two months of fatigue, with no other symptoms. His mother has hypothyroidism. His body mass index is 25 kg/m2 and he has a pulse rate of 72 beats/min and blood pressure 135/88 mmHg with no postural drop. Examination is unremarkable. A random blood glucose test shows 14 mmol/L . Urinalysis is normal. The next day the patient returns, and a repeat fasting glucose test finds 14 mmol/L.
This article is intended to help primary care doctors to differentiate between type 1 and type 2 diabetes when first diagnosing diabetes in a patient where the distinction is unclear.
Type 1 Diabetes Diagnosis
- A c-peptide value lower than 0.2ng/mL
- The presence of one or more diabetes autoantibodies
- A fasting blood glucose greater than 125 mg/dL
- A random finger stick blood glucose greater than 200 mg/dL
- An A1c greater than or equal to 6.5%
- An Oral Glucose Tolerance Test with a blood glucose value exceeding 200 mg/dL at any time
Don’t Miss: Do Skinny People Get Diabetes
What Is Type 1 Diabetes
People of all ages can develop type 1 diabetes.
If you have type 1 diabetes, your pancreas doesnt make insulin or makes very little insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps blood sugar enter the cells in your body where it can be used for energy. Without insulin, blood sugar cant get into cells and builds up in the bloodstream. High blood sugar is damaging to the body and causes many of the symptoms and complications of diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children, teens, and young adults, but it can develop at any age.
Type 1 diabetes is less common than type 2approximately 5-10% of people with diabetes have type 1. Currently, no one knows how to prevent type 1 diabetes, but it can be managed by following your doctors recommendations for living a healthy lifestyle, managing your blood sugar, getting regular health checkups, and getting diabetes self-management education and support.
Who Is At Risk For Type 2 Diabetes
You are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes if you:
- Are over age 45. Children, teenagers, and younger adults can get type 2 diabetes, but it is more common in middle-aged and older people.
- Have prediabetes, which means that your blood sugar is higher than normal but not high enough to be called diabetes
- Had diabetes in pregnancy or gave birth to a baby weighing 9 pounds or more.
- Have a family history of diabetes
- Are overweight or have obesity
- Are Black or African American, Hispanic/Latino, American Indian, Asian American, or Pacific Islander
- Are not physically active
- Have low HDL cholesterol and high triglycerides
- Have acanthosis nigricans dark, thick, and velvety skin around your neck or armpits
Also Check: Does Metformin Give You Gas
Heres How You Can Get Started:
- Work with your doctor to determine what level of physical activity you should engage in
- Figure out how much time per day you can devote to exercise
- Set fitness goalshaving clear goals can help you stay motivated
- Consider where youll start working outthe gym, in your neighborhood, in a park?
- Build different activities into your daily routine
- Start slowly and allow for recovery time
- Keep track of what you do and stay focused on your goals
- Listen to your body
The Emotional Impact Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Living with type 1 or type 2 diabetes can sometimes feel overwhelming.
Both types are different but feeling down or anxious because of your diabetes can affect anyone. It is important to understand that a long-term condition can come with an emotional impact, no matter how it has been caused or how you treat it.
If youre struggling with your diabetes, remember that youre not alone.
There is lots of support available to you, like our helpline. There you can speak to our highly trained advisors about how you’re feeling. And you can also speak to people who are going through similar experiences on our forum. There are lots of things you can do to help yourself and its just about finding what works for you.
It can be frustrating to explain the differences between type 1 and type 2.
Both types face confusion over what causes the condition and how it can be treated. This will be slightly different whether you’re type 1 or the more common type 2. Just because something is more common, doesn’t mean it is understood.
And while it is emotionally draining to constantly correct people, you should also know that you’re not alone. There are many people living with diabetes facing similar questions and struggles, regardless of type. You can reach out to them to give or receive support in the forum and at local groups.
Read Also: Insulin Is Secreted By Alpha Cells

