What Is A Dangerous Blood Sugar Reading And What Should You Do About It
How high is high and how low is low find out so that next time you know how to handle an emergency.
Your blood sugar levels dont stay constant throughout the day. They vary, rising and falling before and after you have a meal, exercise, or take your medication. People who do not have diabetes dont feel the difference very much, as their variations remain within a certain range. But if you have diabetes, you may unexpectedly experience blood glucose levels that are acutely higher or lower than usual, which can be dangerous.It is important for you to be able to recognise the symptoms of high blood sugar hyperglycaemia, and low blood sugar hypoglycaemia, and know how to treat them quickly before they can lead to disastrous complications. The best way to do this is to frequently self-monitor blood glucose levels with a glucometer.
According to Dr Ketan K Mehta, Consulting Physician, CardioPulmonologist &;Diabetologist at Health Harmony, Mumbai, Blood sugar levels are a marker of diabetes;complications. Too high or too low levels of blood sugar values are detrimental. An important aspect of managing diabetes is self-monitoring of blood sugar levels. But do more than only monitoring blood sugar levels. Go the extra mile and use smartphone;app-based programmes to keep track of your blood sugar levels and learn to get them under control by managing your diet, activity levels and weight.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels For Adults With Diabetes
Normally, your pancreas releases insulin when your blood sugar, or âblood glucose,â gets high — after a meal, for example. That signals your body to absorb glucose until levels get back to normal.
But if you have diabetes, your body doesnât make insulin or doesnât respond to it normally . That can leave your blood sugar too high for too long. Over time, that can damage nerves and blood vessels and lead to heart disease and other problems.
If you have diabetes, your doctor may ask you to keep track of your blood sugar by testing it at home with a special device called a blood glucose monitor or home blood sugar meter. It takes a small sample of blood, usually from the tip of your finger, and measures the amount of glucose in it.
Follow your doctorâs instructions about the best way to use your device.
Your doctor will tell you when and how to test your blood sugar. Each time you do it, log it in a notebook or online tool or in an app. The time of day, recent activity, your last meal, and other things can all affect whether a reading will be of concern to your doctor. So try to log relevant information like:
- What medication and dosage you took
- What you ate, when you ate, or whether you were fasting
- How much, how intense, and what kind of exercise you were doing, if any
That will help you and your doctor see how your treatment is working.
When To See A Healthcare Provider
Getting professional medical advice from a healthcare provider like an endocrinologist is the best way to learn more about whether your blood sugar levels are where they should be. Not getting proper treatment for low or high blood sugar levels can be serious and lead to health complications, especially for those with diabetes. Diabetes complications include nerve damage, kidney disease, heart disease, or heart attacks.;;
If you see a healthcare provider about your blood sugar levels, be prepared to answer questions about risk factors like what you eat, how much you exercise, and about your family history. Some healthcare providers may want to take a blood sample to test your blood sugar levels. They may also order an A1C test, which is a blood test that measures blood sugar levels over several months. You may have to fast eight hours beforehand to get accurate test results, so its always a good idea to check before your appointment.;;;;;;;;
If your blood sugar level goes above 250 mg/dL, you should go to the ER for immediate medical attention, says Dr. Tarugu. Emergency rooms are equipped to handle high blood sugar levels and can administer treatments like insulin therapy and fluid or electrolyte replacement.;;;;;;;;;
Don’t Miss: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
What Blood Sugar Levels Are Healthy
Weve established what normal blood sugar looks like, more or less. But normal levels can be challenging for people with diabetes to achieve. At what point does high blood sugar get dangerous?
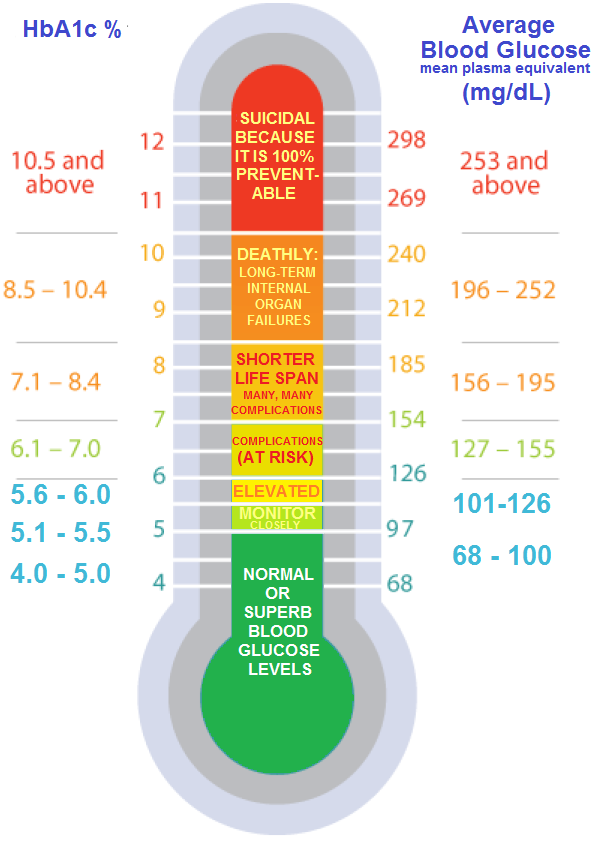
This is an area of some debate. The long-term studies show that the risk of complications drop off dramatically when an HbA1c is lower than 7%, which is an estimated average blood glucose of 154 mg/dL or 8.6 mmol/L. The risks continue to drop until its below 6%, an average blood sugar of 126 mg/dL or 7 mmol/L. There are many people with diabetes who strive for even lower targets, but there is not much research outlining the benefits of that approach yet.
Its important to note that studies of A1c and the rate of complications are only looking at averages. In reality, there seems to be a huge difference in the risk of complications based on genetics and perhaps other unknown factors. There are many people who have lived for many decades with type 1 diabetes, running high blood sugars almost continuously, and have no complications. There are others who have had well-controlled blood sugars that still get complications.
For most people, its safe to say that striving for an HbA1c of below 7% and probably below 6.5% is a realistic goal for staying healthy.
This chart from the American Diabetes Association lists some of the other factors that may indicate when a patient should target a lower or higher blood sugar level:
At What Number Range Are You Considered Diabetic
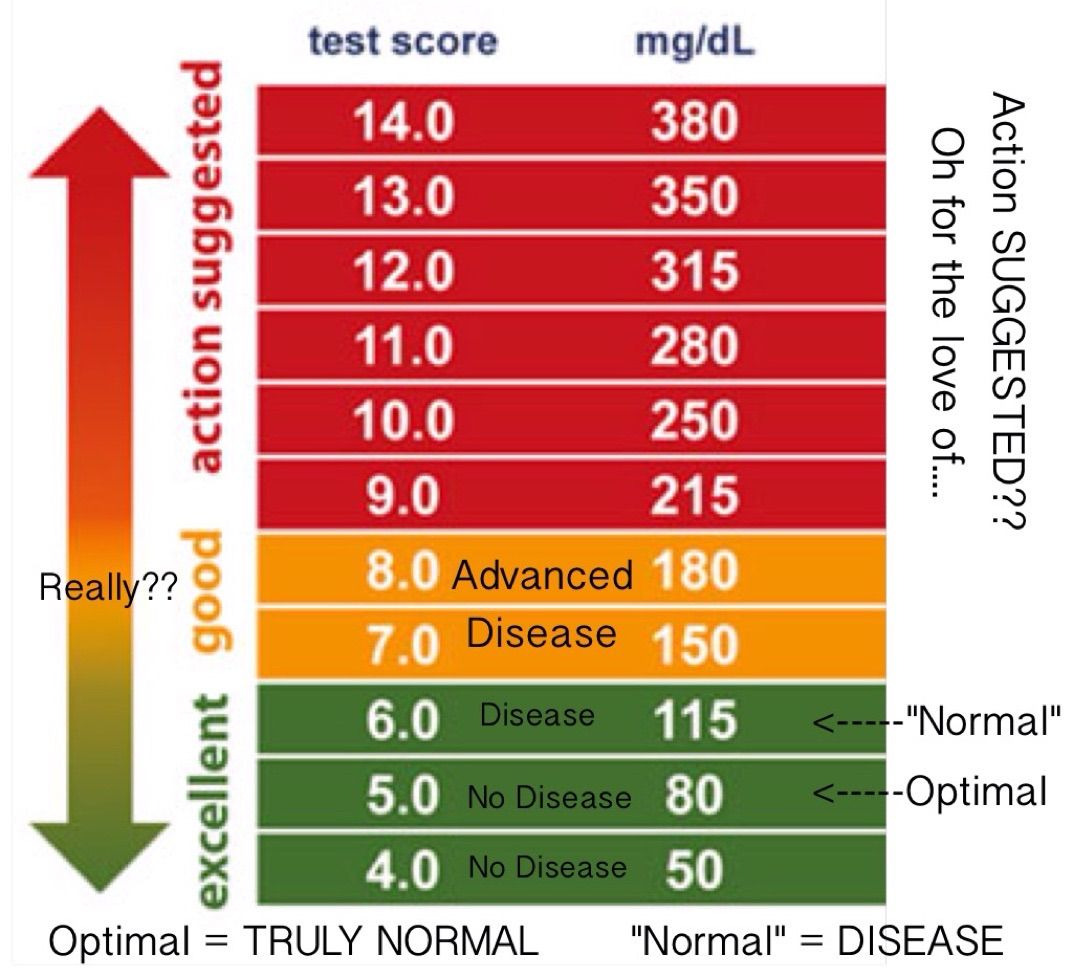
Question Originally asked by Community Member teresa At What Number Range Are You Considered Diabetic what numbers must you have to be consider borderline and what number range to be considered to be diabetic such as type 2 diabectic and type 1 Answer Hello teresa, Diagnosis of diabetes is based on blood sugar measurements. The difference between type 1 and type 2 is not based on blood sugar levels, but in the mechanisms that raise blood sugar. Fasting glucose levels above 140 mg/dl on at least two occations are diagnosic for diabetes. Anything above 110mg/dl but less than 140mg/dl after fasting is considered impaired impaired glocose tolerence. There is a formal test, called a glucose tolerance test, that involves ingesting a specified amount of glucose and lthen measuring how the blood sugar levels increase and fall. Likely, anybody with a blood sugar level about 200 mg/dl on at least 2 occasions without fasting is likely diabetic and needs to be treated. To your health, Neil MD You should know Answers to your question are meant to provide general health information but should not replace medical advice you receive from a doctor. No answers should be viewed as a diagnosis or recommended treatment for a condition. Answered By: Neil MDContinue reading >>
Read Also: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
How Food Affects Blood Sugar
When you eat food, your body breaks it down into essential parts:
- Carbohydrates
- Fats
- Vitamins and minerals
All parts are necessary in a healthy diet, but the three types of carbohydrates are particularly important when it comes to your blood glucose level. While the general rule is that the more carbohydrates you eat, the higher your blood sugar level, not all three types of carbohydrates convert to blood sugar at the same rate.;
The foods that fit into each carb category include:
- Starches, or complex carbohydrates: Starchy vegetables, dried beans, and grains
- Sugars: Fruits, baked goods, beverages, and processed food items like cereals or granola bars
- Fiber: Whole wheat products, chickpeas, lentils, berries, pears, and brussels sprouts
The glycemic index helps you find out which foods can increase or help decrease blood sugar levels. Based on a scale ranging from 0 to 100, high-indexed foods are rapidly digested, absorbed, and metabolized, resulting in marked fluctuations in blood sugar levels, while low-indexed foods produce smaller fluctuations in your blood glucose.;
The American Diabetes Association advises adding lean sources of protein and heart-healthy fats to help reduce the overall glycemic impact of a meal or snack.
Know Your Body Mass Index
Being overweight or obese puts you at risk for developing type 2 diabetes. BMI is an easy way to estimate excess fat. Even a small change in body weight can reduce your risk of diabetes.
If your score is:
25.029.9 = Overweight/Pre-obese 30.0 and over = Obese
To calculate your BMI, you can use the BMI chart or the formulas at the bottom of this page or complete the Canadian diabetes risk questionnaire.
You May Like: Bananas Raise Blood Sugar
Now That Youre Checking Your Blood Glucose What Do The Numbers Mean
Depending on your diabetes treatment plan, your doctor or diabetes educator may advise you to check once a week, once a day or up to 10 times a day . But what does it mean when you see a 67, 101 or 350 on your meter? And what is a normal blood sugar, anyway? Great questions! After all, if you dont know what the numbers on your meter mean, its hard to know how youre doing.
The American Diabetes Association provides guidelines for blood glucose goals for people with diabetes, and the goals vary depending on when youre checking your glucose:
Fasting and before meals: 80130 mg/dl
Postprandial : Less than 180 mg/dl
By the way, these guidelines are for non-pregnant adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Children, adolescents and pregnant women may have different goals.
Your blood glucose goals may be different, however. If youre younger, have had diabetes for a shorter amount of time or are not taking any medicine for your diabetes, your glucose goals might be a little tighter, or lower. Likewise, your blood glucose goals may be higher than what ADA recommends if youre older, have diabetes complications, or dont get symptoms when your blood glucose is low.
Bottom line: talk with your health-care provider about the following:
When to check your blood glucose How often to check your blood glucose What your blood glucose goals are
Recommended Reading: Dosages Of Metformin
Blood Sugar Level Chart
- Normal reading for nondiabetic person = 7099 mg/dl
- The recommendation for someone who is diabetic = 80130 mg/dl
Two hours after a meal
- Normal reading for nondiabetic person = Below 140 mg/dl
- The recommendation for someone who is diabetic = Below 180 mg/dl
HbA1c
- Normal reading for nondiabetic person = Below 5.7%
- The recommendation for someone who is diabetic = 7% or less
**My Med Memo The measurement mmol is the abbreviation for millimole.
Recommended Reading: A1c Cutoff
What Is Blood Sugar
Blood sugar is sugar that is in your bloodstream. The specific type of sugar in your blood is called glucose, and blood sugar is the same as blood glucose. You need sugar in your blood because many of the cells in your body use it for fuel, or energy. It is normal and healthy to have some blood sugar, but too much is considered prediabetic.
So how does sugar get into your bloodstream? One way is after you eat a meal with carbohydrates. Another way is from your liver: if your blood sugar dips too low because you have not eaten for a while or for another reason, such as exercising, your liver will sense the lower levels and release stored sugar into your bloodstream. The goal is to keep your levels neither too high, nor too low, at all times.
Different Levels And What They Mean
The ranges of safe levels of blood glucose depend on factors such as what time of day it is and when you last ate. Safe levels of blood sugar are high enough to supply your organs with the sugar they need, but low enough to prevent symptoms of hyperglycemia or complications of diabetes which follow the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases guides. Dangerous levels of blood glucose are outside of this range.
The target levels can also vary if you have diabetes. For example, if you are diabetic and are monitoring your blood sugar, you might get a reading of 65 mg/dl. That is considered to be mild hypoglycemia, and you would be wise to eat 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates and retest your blood sugar in 15 minutes.;
If you were not diabetic, you probably would not know that your sugar was low because you would not test and because you would not symptoms, and you would not act.
That is fine because your body is capable, under normal circumstances, of raising your blood glucose to healthy levels when needed, even if you have not eaten. It is important to keep them in control to help prevent issues like heart disease or nerve damage.
Looking for the best prediabetes diet? Learn what foods are best to help you manage your prediabetes.
Read Also: Can You Donate Blood If Your Diabetic
Official Hba1c Ada Recommendation For Someone With Diabetes
The American Diabetes Association recommends an HbA1C of less than 7% for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. A lower goal, such as less than 6.5%, may be appropriate for some people who have had diabetes for a shorter amount of time, for younger people, for those without heart disease, and/or for those with type 2 diabetes treated with lifestyle or metformin only. A higher HbA1C goal, such as less than 8%, may be appropriate for people with a history of severe hypoglycemia, a limited life expectancy, advanced diabetes complications, other illnesses, or for whom a lower HbA1C goal is difficult to achieve. Its important that people with diabetes discuss their target blood sugar goals with their healthcare provider.
HbA1C levels should be checked between two to four times per year in people who have diabetes.
What Causes Low Blood Sugar
Low blood sugar has many causes, including missing a meal, taking too much insulin, taking other diabetes medicines, exercising more than normal, and drinking alcohol. Blood sugar below 70 mg/dL is considered low.
Signs of low blood sugar are different for everyone. Common symptoms include:
- Shaking.
- Dizziness.
- Hunger.
Know what your individual symptoms are so you can catch low blood sugar early and treat it. If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms.;Low blood sugar can be dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible.
Recommended Reading: Can People With Diabetes Donate Blood
How Is Gestational Diabetes Diagnosed
Gestational diabetes is regularly diagnosed by measuring blood glucose levels. There are different ways to test for diabetes. Your healthcare provider can identify which test is best for you.
Did You Know?
Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy, affecting four per cent of all pregnant women.You can help manage gestational diabetes by eating well and exercising regularly.
What Blood Sugar Level Is Prediabetic
Prediabetes is a condition with increased blood sugar, but how is it measured? Exactly what sugar level range is considered prediabetic, and how is that different from diabetes? Here is what you need to know about blood sugar levels in prediabetes, and what you can do about yours.
If you have been told that you have prediabetes, or you think that you might have it or be at risk for it, you can take your awareness in a positive way. While nobody actually wants to think about having a chronic health condition, being aware of prediabetes can be seen as a fork in the road of life.
On one branch of the fork in the road, prediabetes can lead to type 2 diabetes. Most people who get prediabetes take this branch, and end up with diabetes. However, you can choose to take the other branch in the road because in most cases, prediabetes is reversible.;
Are you at risk for type 2 diabetes? Lark Diabetes Prevention Program is a personalized program to help you lower your risk by making healthy lifestyle changes, such as losing weight and increasing physical activity. Your personal Lark coach is available to support you 24/7 on your smartphone. Lark can help you make small changes that fit into your lifestyle and have big results for your health!
You May Like: Is Vitamin B12 Good For Diabetics
Normal Waking Blood Sugar
After a night of sleep, and without any recently digested food in the system, the bodys glucose level tends to settle down to a healthy, normal level.
In the context of diabetes, this doesnt happen naturally, but it can be achieved with the proper use of insulin and other glucose-lowering medications. Ideally, everyone with diabetes will wake up with blood sugars in the normal range.
However, many people experience what is called the dawn phenomenon. As the body prepares to wake and start moving, it releases stored sugar from the liver into the blood. This can cause a moderate spike in blood sugar. You can read How to Fix High Morning Blood Sugars;for tips on how to improve these numbers.
To confirm if this is happening to you, you can wake up in the middle of the night and check your blood sugar. If its in the normal range then, but higher after waking, this is probably the cause. If the spike is small and goes away quickly, then its likely nothing to worry about . The spike from dawn phenomenon is often less pronounced than one you would get from eating a typical meal.

