Southern Cross Medical Library
The purpose of the Southern Cross Medical Library is to provide information of a general nature to help you better understand certain medical conditions. Always seek specific medical advice for treatment appropriate to you. This information is not intended to relate specifically to insurance or healthcare services provided by Southern Cross. For more articles go to the Medical Library index page.
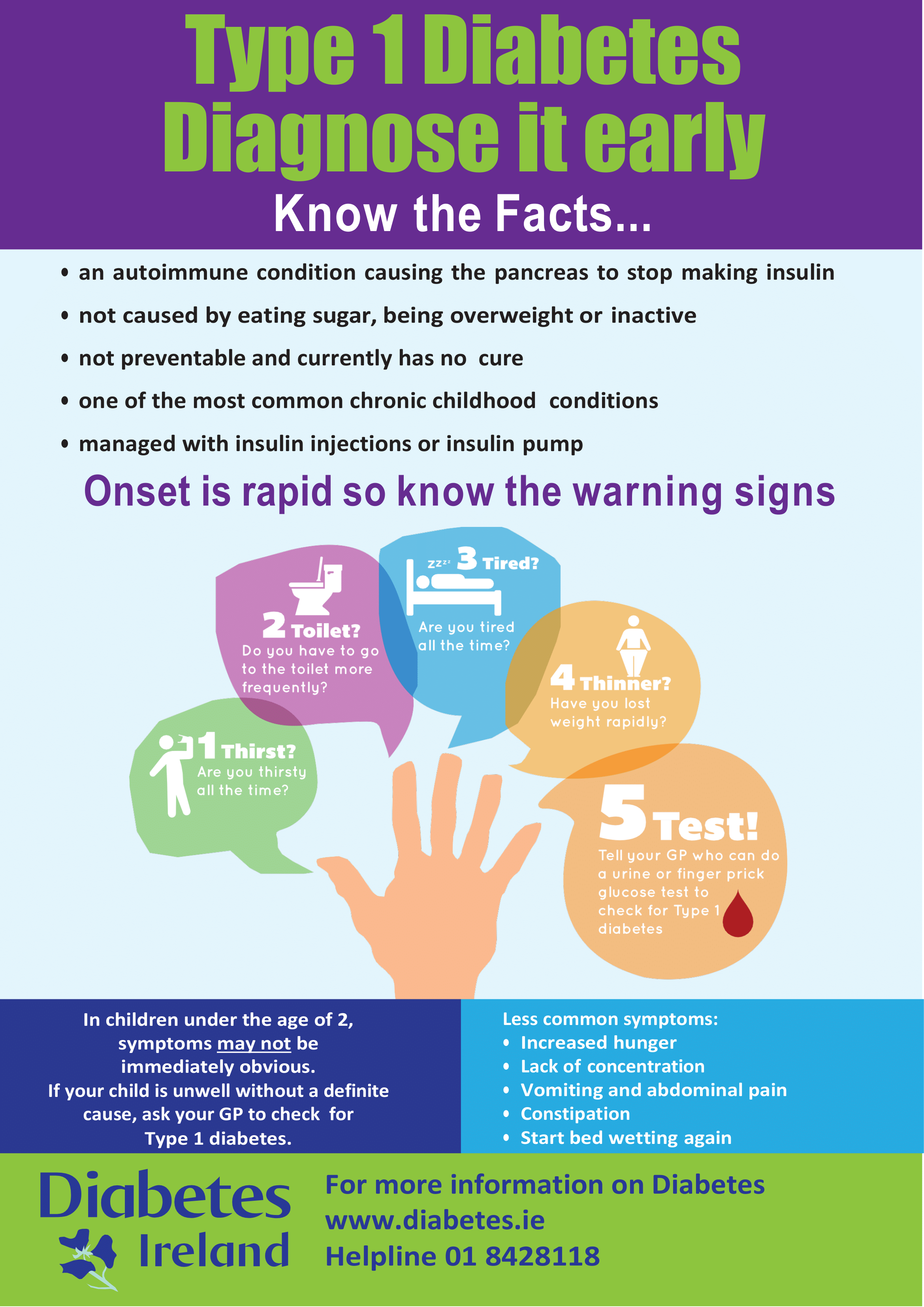
What Are The Risk Factors For Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Risk factors for type 1 diabetes include:
- Family history: People with a parent or sibling with type 1 diabetes have a higher risk of developing it themselves.
- Age: Type 1 diabetes can appear at any age, but its most common among children and adolescents.
- Geography: The prevalence of type 1 diabetes increases the farther away you are from the equator.
- Genetics: The presence of certain genes points to an increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
Youre at risk of developing type 2 diabetes if you:
- have prediabetes, or slightly elevated blood sugar levels
- are carrying excess weight or have obesity
- are Black, Hispanic, American Indian, or Alaska Native
- have an immediate family member with type 2 diabetes
How Does My Diet Affect Diabetes
A healthy diet is an important part of managing Type 1 diabetes. The right foods can help keep your blood pressure and blood glucose in check. Healthy meal planning for people without Type 1 diabetes is similar to healthy meal planning for people with Type 1 diabetes:
- Avoid foods with added sugar, sodium and trans fats.
- Eat a balance of proteins, carbohydrates and healthy fats.
- Read nutrition labels to select foods with more fiber and less sugar.
- Skip the highly processed foods found in cans or packages.
In addition, it’s important for people with Type 1 diabetes to understand how foods with carbohydrates impact their blood sugar levels and how much insulin to take for various amounts of carbs. Work with your healthcare team to figure out the best plan for you.
Read Also: What Foods Should Not Be Taken With Metformin
Causes Of Type 1 Diabetes
The bodys immune system is responsible for fighting off foreign invaders, such as harmful viruses and bacteria.
In people with type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakes the bodys own healthy cells for foreign invaders. The immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. After these beta cells are destroyed, the body is unable to produce insulin.
Researchers dont know why the immune system sometimes attacks the bodys own cells. It may have something to do with genetic and environmental factors, such as exposure to viruses. Research into autoimmune diseases is ongoing.
What Are The Possible Complications Of Type 1 Diabetes
Even with careful management, type 1 diabetes can put your child at risk of some serious complications that require prompt medical attention. These include hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia and diabetic ketoacidosis.
Hypoglycemia, also known as low blood sugar or insulin reaction, can happen when your childs blood sugar drops too low and their body doesnt have enough energy to function properly. Hypoglycemia can result from too high an insulin dose, a missed meal or snack, more physical activity than usual, or illness that causes vomiting and/or diarrhea.
- Symptoms of hypoglycemia include shakiness, sweating, weakness, blurry vision, and rapid heartbeat.
- If your child has any of these symptoms, measure their blood glucose level and give them a fast-acting carbohydrate, such as fruit juice, hard candy, or raisins. Seek medical attention right away.
- If left unchecked, hypoglycemia can result in a medical emergency. Your child could lose consciousness or go into seizure.
Hyperglycemia, also known as high blood sugar, happens when blood sugar is too high and builds up in the blood stream. It can be caused by not having enough insulin, eating too much food or the wrong kinds of food, getting too little physical activity, or illness.
Diabetes ketoacidosis can cause fluid to build up in the brain and lead to a loss of consciousness, cardiac arrest, or kidney failure.
Your child should receive medical attention right away if they have any of these symptoms:
Also Check: What Is A Normal A1c Level Non Diabetic
Anyone Can Get Type 1 Diabetes
It isnt completely clear what causes type 1 diabetes, but we know that diet and lifestyle habits dont. Type 1 is thought to be the result of an autoimmune response, where your body attacks the cells in your pancreas that make insulin. Insulin is a hormone that acts like a key to let blood sugar into your bodys cells for use as energy. Sometimes infection with a virus seems to trigger the autoimmune response. Many people with type 1 diabetes have family members with type 1, but most dont.
The peak age for being diagnosed with type 1 diabetes is around 13 or 14 years, but people can be diagnosed when theyre much younger and older .
Type 1 Diabetes Treatment
People who have type 1 diabetes can live long, healthy lives. Youâll need to keep a close eye on your blood sugar levels. Your doctor will give you a range that the numbers should stay within. Adjust your insulin, food, and activities as necessary.
Everyone with type 1 diabetes needs to use insulin shots to control their blood sugar.
When your doctor talks about insulin, theyâll mention three main things:
- “Onset” is how long it takes to reach your bloodstream and begin lowering your blood sugar.
- “Peak time” is when insulin is doing the most work in terms of lowering your blood sugar.
- “Duration” is how long it keeps working after onset.
Several types of insulin are available.
- Rapid-acting starts to work in about 15 minutes. It peaks about 1 hour after you take it and continues to work for 2 to 4 hours.
- Regular or short-acting gets to work in about 30 minutes. It peaks between 2 and 3 hours and keeps working for 3 to 6 hours.
- Intermediate-acting wonât get into your bloodstream for 2 to 4 hours after your shot. It peaks from 4 to 12 hours and works for 12 to 18 hours.
- Long-acting takes several hours to get into your system and lasts about 24 hours.
Your doctor may start you out with two injections a day of two types of insulin. Later, you might need more shots.
Don’t Miss: When To Take Glipizide And Metformin
Who Should Be Tested For Diabetes
Anyone who has symptoms of diabetes should be tested for the disease. Some people will not have any symptoms but may have risk factors for diabetes and need to be tested. Testing allows health care professionals to find diabetes sooner and work with their patients to manage diabetes and prevent complications.
Testing also allows health care professionals to find prediabetes. Making lifestyle changes to lose a modest amount of weight if you are overweight may help you delay or prevent type 2 diabetes.
Further Information And Support
For further information and support contact your doctor, practice nurse, or: Diabetes New Zealand Freephone: 0800 DIABETES Email: admin@diabetes.org.nz Website: www.diabetes.org.nz Diabetes New Zealand provides education and support resources specifically for young New Zealanders with type 1 diabetes and many of its branches around the country host Type 1 youth support groups.
Kids Health Website: www.kidsheatlh.org.nz
Also Check: How Many Carbs Per Day For Diabetics
Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
There are important differences between type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes . Other types, such as unusual genetic forms of diabetes, also exist. Diagnosing the type of diabetes is important for appropriate medical treatment.
| âJuvenile Onsetâ or âInsulin DependentâDiabetes | âAdult Onsetâ or âNoninsulin Dependentâ Diabetes | |
| Who is diagnosed? |
Children and teens, usually with healthy body weight, but also diagnosed in adults. These individuals may be the only ones in their family with the disease. |
Usually diagnosed in adults who are overweight or obese but also diagnosed in children. These individuals often have relatives with diabetes. |
| What causes it? | The individualâs immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the pancreas. The pancreas can no longer produce insulin, a hormone needed for controlling blood glucose. | These individuals can still produce insulin but the body becomes resistant to its effects. Over time, the pancreas eventually stops producing insulin. |
| How is it detected? |
The same diagnostic criteria are used for both types of diabetes. However, blood tests may help clarify whether a patient has type 1 versus type 2 diabetes. |
|
| How is it treated? | Patients with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin. | Some patients with type 2 diabetes can control their blood glucose by reducing their weight and changing their diet. Most others are treated with pills, injectable medicines, or insulin. |
Explore more articles:
Why Do Some People Get Type 1 Diabetes
No one knows for sure why some people get type 1 diabetes. Doctors and scientists think a persons genes make them more likely to get it. But just having the genes for diabetes probably isn’t enough. Its likely that something else needs to happen. Scientists are studying if other things like some viral infections, a persons birth weight, or their diet might make someone who already has the genes for type 1 diabetes more likely to get it.
Type 1 diabetes cant be prevented, and can happen in people of any age.
Recommended Reading: Is Metformin A Diuretic
Whats The Purpose Of A Gad Antibodies Test
Your doctor will use diagnostic tools to diagnose diabetes, such as checking for high glucose and a high HbA1c. Once they can diagnose diabetes, theyll take steps to determine if its type 1 or 2.
Type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes are two distinct conditions. Each requires a specific approach to management and treatment.
Your doctor may order a GAD test to find out more about your condition. You might also hear this test referred to as GADA or anti-GAD. Or your doctor may recommend an autoantibody panel to test for GAD and other antibodies.
Other antibodies associated with type 1 diabetes include:
- islet cell cytoplasmic autoantibodies
- insulinoma-associated-2 autoantibodies
- insulin autoantibodies , which are more common in children than adults
All these tests are done through a simple blood test. You wont need to do anything to prepare, such as fasting. A healthcare provider will take blood from a vein in your arm and send it to a laboratory for analysis.
If GAD or any of the other autoantibodies are found, it means you most likely have type 1 diabetes. If no GAD or other autoantibodies are found, you probably have type 2.
Having Your Blood Glucose Levels Checked
You’ll be measuring your blood glucose yourself every day, to check your levels.
Your GP or diabetes care team will also carry out a different blood test every two to six months, called the HbA1c test.
This gives a clearer idea of how well your treatment plan is working, by measuring how stable your glucose levels have been over the past 6-12 weeks.
It measures the amount of haemoglobin, which is the oxygen-carrying substance in red blood cells that has glucose attached to it. A high HbA1c level may indicate that your blood glucose level is consistently high and that your diabetes treatment plan needs to be altered.
The ideal HbA1c target for people with diabetes is below 53 mmol/mol.
Don’t Miss: Glucose Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide
Which Diets Are Recommended For Diabetes
Nutritional management is an important part of life for people with diabetes.
If you have type 1 diabetes, work with your doctor to identify how much insulin you may need to inject after eating certain types of food.
For example, carbohydrates can cause blood sugar levels to quickly increase in people with type 1 diabetes. Youll need to counteract this by taking insulin, but youll need to know how much insulin to take. Learn more about type 1 diabetes and diet.
People with type 2 diabetes need to focus on healthy eating. Weight loss is often a part of type 2 diabetes treatment plans, so your doctor may recommend a low-calorie meal plan. This could mean reducing your consumption of animal fats and junk food.
Complications Of Untreated Type 1 Diabetes
- kidney damage
- increased likelihood of infections such as thrush and also more serious infections
- damage to the eyes
- poor blood circulation in the legs and feet, potentially leading to lower limb amputation
- damage to the nerves of the feet
- much higher risk of heart disease and stroke
- sexual impotence.
Read Also: Oatmeal Ok For Diabetics
How Is Type 1 Diabetes Treated
People with Type 1 diabetes need to replenish their insulin each day. There are different types of insulin. Some insulin starts acting as soon as you take the medicine other insulins take several hours to work. The various types of insulin also last in your body for different lengths of time. Some are more expensive than others. Work with your doctor to find the right type of insulin for your needs.
Whats The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes occurs when your pancreas is unable to produce enough insulin to effectively process your blood glucose. This can be solved by exogenous insulin through a pump, syringe, or pen.
Meanwhile, type 2 diabetes occurs as a result of an underlying condition called insulin resistance, which is the buildup of excess dietary fat in cells that are not meant to store fat.
Your body is still producing enough insulin, but because of insulin resistance, your blood glucose spikes. This condition can be reversed by lifestyle changes.
Recommended Reading: Drug Class Metformin
Just Diagnosed With Type 1 Diabetes
There isnt a cure yet for type 1 diabetes, but its very treatable.
You may have found out you have type 1 diabetes from a routine blood test. Or you may have had sudden and severe symptoms that led to a trip to the doctor or even the emergency room.
Either way, getting the diagnosis can be overwhelming, and youre likely to have lots of questions. Did you somehow cause type 1 diabetes? What will life be like now? Is there a cure, or is type 1 forever?
Managing a chronic health condition like diabetes takes work, but you wont have to do it alone. Your health care team will help you learn about day-to-day care and let you know about all the tools available to make it easier. Type 1 diabetes is very treatable. Lets take it one step at a time.
What Causes Type 1 Diabetes In Children
Type 1 diabetes occurs when your immune system mistakenly targets the insulin-producing beta cells in your pancreas as foreign, and creates antibodies to attack them. This is why type 1 diabetes is classified as an autoimmune condition.
Type 1 diabetes occurs differently worldwide but there are currently no clear results about what causes this initial form of biological friendly fire.
For example, there is extensive research being done on certain risk factors ranging from the consumption of cows milk protein to distance from the equator, but these studies have been inconclusive.
However, there is one clear indicator of increased risk of type 1 diabetes, which is a family history of the disease.
You May Like: What To Eat To Lower Blood Sugar Quickly
What Medications And Other Treatments Can Help Gastroparesis
Your doctor may recommend medication to improve gastric emptying or reduce nausea, such as the following:
- Metoclopramide. This is a commonly used gastroparesis drug approved by the Food and Drug Administration . It stimulates movement in your stomach and gut while relieving symptoms like nausea and vomiting. It belongs to a category of drugs called prokinetics, several of which have been used to successfully manage gastroparesis.
- Antiemetics. This type of medication may also help reduce nausea and vomiting.
Your doctor may also review any medications that youre taking that could be contributing to the problem. For example, can slow down the process, including:
- opioid painkillers
gastric neuromodulation , which stimulate your GI system and improve symptoms.
In severe cases, some people may need to turn to enteral nutrition. This essentially means liquid nutrition but it can also mean feeding through a tube thats inserted in your stomach or small intestine. A surgeon can perform a gastrostomy, which is a procedure that creates an opening for the placement of a feeding tube.
Diabetes And Your Child
For a parent whose child is diagnosed with a life-long condition, the job of parenting becomes even tougher.
Although being diagnosed with type 1 diabetes will involve coming to terms with the diagnosis, getting used to treatment and making changes to everyday life, your child can still lead a normal and healthy life.
The Diabetes UK website has information and advice about your child and diabetes.
Also Check: Is Greek Yogurt Good For Diabetes
Ketone Monitoring And Managing Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Ketone self-monitoring to prevent diabetic ketoacidosis
- 1.11.1.
-
Consider ketone monitoring as part of sick-day rules for adults with type 1 diabetes, to help with self-management of hyperglycaemia.
Ketone monitoring in hospital
- 1.11.2.
-
In adults with type 1 diabetes presenting to emergency services, consider capillary blood ketone testing if:
- diabetic ketoacidosis is suspected or
- the person has uncontrolled diabetes during an illness, and urine ketone testing is positive.
- 1.11.3.
-
Consider capillary blood ketone testing for inpatient management of DKA in adults with type 1 diabetes.
Management of DKA
Young People And Diabetes
Although it can be diagnosed later in life too, type 1 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes found in children. We know that this can mean you have to make changes to how you and your family live your life, but were here to help.
Whether youre a parent in need of advice about schools and caring for a child with type 1, or a young adult looking for information about going to university and becoming more independent, weve got a range of resources to help you understand more about diabetes and how to manage it.
You May Like: Management Of High Blood Sugar

