Risk Factors For Diabetic Coma
A diabetic coma can happen in anyone who is diabetic. Type 1 diabetics have a greater risk of having a diabetic coma because they often use insulin and have wider fluctuations in their blood glucose numbers when compared to type 2 diabetics. Any diabetic with high levels of glucose or low levels of glucose are at risk for developing a diabetic coma. Type 2 diabetics are at a greater risk of having a diabetic coma from diabetic hyperosmolar syndrome rather than diabetic ketoacidosis or hypoglycemia.
Problems that contribute to developing a diabetic coma include the following:
Emergencies At School College Or Work
To minimise the chance of a serious emergency at work, school or university, its best to ensure the people around you are aware you have diabetes, what dangers could potential happen and how to deal with any such situation should it develop.
Particularly at work, some people may be worried about disclosing their diabetes to their employer In terms of health, its best to do so.
You Feel Shakyor Tired
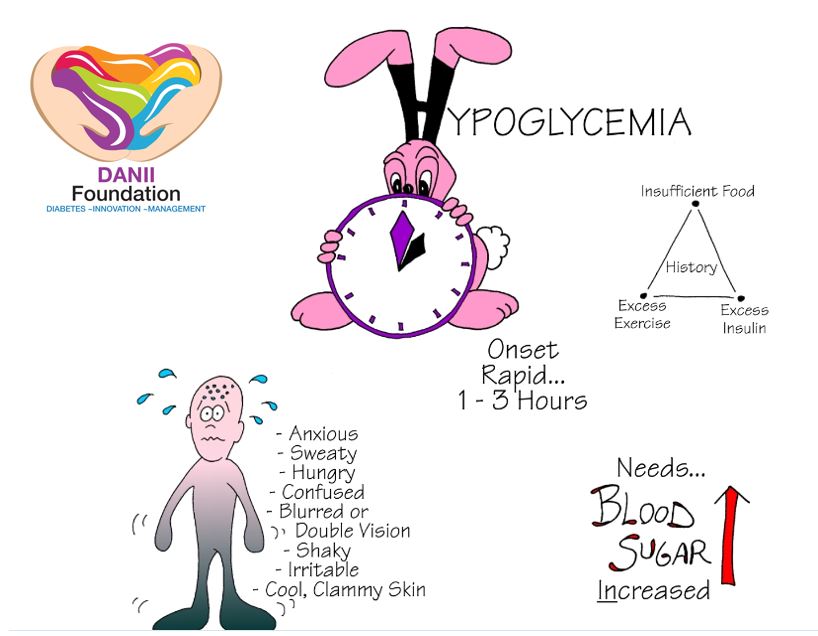
Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia each have different warning signs, but can lead to the same resultdiabetic coma. Warning signs that you are in danger because the blood sugar is dropping or is too low include feeling shaky, says Gillian Goddard, MD, board certified in internal medicine and endocrinology, diabetes and metabolism, from Park Avenue Endocrinology & Nutrition. Learn about silent diabetes symptoms you might miss. On the other hand, you could notice high blood sugar leaving you fatigued, according to the Mayo Clinic.
Also Check: Diabetic Coma How Long Before Death
How Is Alcoholic Ketoacidosis Treated
Treatment for alcoholic ketoacidosis is typically administered in the emergency room. Your doctor will monitor your vital signs, including your heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing. They will also give you fluids intravenously. You may receive vitamins and nutrients to help treat malnutrition, including:
- thiamine
- phosphorus
- magnesium
Your doctor may also admit you to the intensive care unit if you require ongoing care. The length of your hospital stay depends on the severity of the alcoholic ketoacidosis. It also depends on how long it takes to get your body regulated and out of danger. If you have any additional complications during treatment, this will also affect the length of your hospital stay.
One complication of alcoholic ketoacidosis is alcohol withdrawal. Your doctor and other medical professionals will watch you for symptoms of withdrawal. If you have severe symptoms, they may give you medication. Alcoholic ketoacidosis may lead to gastrointestinal bleeding.
Other complications may include:
- pancreatitis
- pneumonia
- encephalopathy
Be Patient A Person Emerging From A Coma Is Disoriented
As soon as the ICU staff allows: Every day write the date in large letters on a large piece of paper. Tape this where the patient can see it. This helps to orient the patient.
Remember the recovery of consciousness is a gradual process and is not just a matter of waking up as people often imagine.
Read Also: What Is The Function Of Insulin
Recommended Reading: What Can Diabetic People Eat
When Should You Call Your Doctor
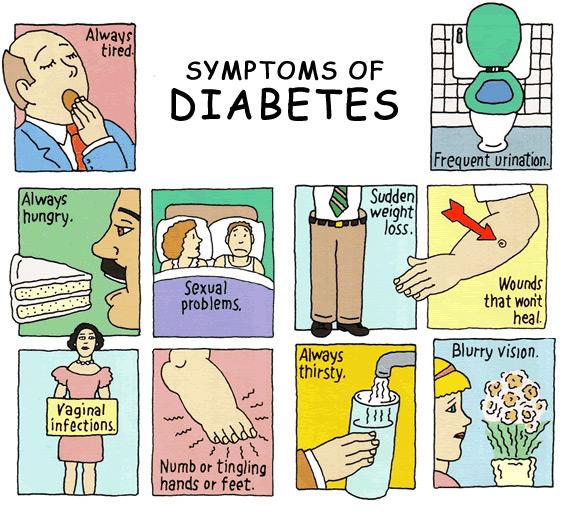
If you are aged over 45 years or are exposed to the risks of diabetes, then you should get tested. If you can spot the condition early on, you can avert issues like heart trouble, nerve damage, and other complications. You should, however, call your doctor when you notice the following conditions frequent urination, sickness of the stomach, deep breathing, and sweet breath.
You may like these articles as well:
Type 1 Diabetes Symptoms And Signs
Type 1 diabetes can be subtle or life threatening. Some people have no symptoms , and type 1 diabetes is not detected until blood or urine lab studies are done. If a person does have type 1 diabetes symptoms, early signs and symptoms include excessive urination, excessive thirst, and weight loss.
Don’t Miss: Blood Sugar Dropping At Night
Should I Put Down My Diabetic Cat
Euthanizing a diabetic cat is always the last resort and reserved only for the worst cases. Veterinarians and owners should first consider all possible treatments to save the kittys life.
If the prognosis for the diabetic cat is poor, the vet may advise that the feline be put to sleep. This is because the treatment is less likely to improve the cats condition and that it would be painfully expensive. Above all, it will put more suffering to the cat.
On the other hand, some diabetic cats are put to sleep if their owners are no longer financially capable to support their veterinary care. This is a heartbreaking decision, but many owners are left with no choice.
Organizations that provide assistance for diabetic cats
If youre struggling financially to support your diabetic cats vet bills, you can tap the help of various organizations. As much as possible, putting the cat down should be the last option.
The following are some of the organizations, charities, and groups that could help:
What Are The Risk Factors For Diabetic Coma
While anyone who has diabetes is at risk for a diabetic coma, the causes depend on the type of diabetes:
- People with Type 1 diabetes have a greater chance of going into a diabetic coma as a result of diabetic ketoacidosis or hypoglycemia. This is because people with Type 1 diabetes always need insulin and have a wider range in their blood glucose levels than people with Type 2 diabetes.
- People with Type 2 diabetes have a greater chance of going into a diabetic coma from diabetic hyperosmolar syndrome than from diabetic ketoacidosis or hypoglycemia.
Other risks that can lead to diabetic coma in anyone who has diabetes include:
- Surgery.
Also Check: High Blood Sugar Symptoms Type 2
But Keeping Hba1c In Check Can Mitigate This Early Mortality
The average British adult with type 1 diabetes loses about eight life-years compared with nondiabetic age peers, according to a modeling study.
Drawing upon national data from the U.K., the average person with type 1 diabetes age about 43 could expect to live 32.6 more years, reported Adrian Heald, MD, of Salford Royal Hospital in England, and colleagues.
Thats against an expectancy of 40.2 additional life years for an average 43-year-old without diabetes, the group reported in Cardiovascular Endocrinology & Metabolism and simultaneously at the virtual European Association for the Study of Diabetes 2020 meeting.
The extent of life-years lost also differed among the sexes. Specifically, women with type 1 diabetes lost about 8.5 years of life-expectancy versus a nondiabetic female in men the figure was about 7 years.
People with type 2 diabetes also had shorter life expectancy, albeit by less than those with type 1 diabetes.
The average person with type 2 diabetes age 65 can expect 18.6 years of additional life, versus 20.3 years for an equivalent population free of diabetes. These life years lost were similarly mediated by sex, as females with type 2 diabetes saw about a 2-year shorter lifespan while males saw a 1.4-year shorter lifespan.
The fact that women werent spared the shortened life expectancy with diabetes also came as a surprise.
Its actually something people can relate to, its tangible to them, Heald said.
Disclosures
When Is It Time To Put A Diabetic Dog Down
However, if your dog has been diagnosed with quite an advanced stage of diabetes, the kindest thing to do may be to put them to sleep. But when is the right time to put a diabetic dog down?
Just talk with your vet
You will be advised by your vet about the best course of action, but it is ultimately your choice. A lot of first-time owners, however, regret keeping their pet alive and suffering longer than they needed to.
It can be very hard to let go of your best friend, but youll need to consider whether they are living the best quality of life.
Diabetes in its advanced stages can lead to a plethora of other health issues including:
- Kidney failure
- Ketoacidosis
You May Like: What Is A High Blood Sugar Reading
Where Can I Find Support
Since DKA is a common and life-threatening condition, its important to seek out diabetes support in your community. Here are a few nonprofits and groups to check out:
An entire database of education and support groups through the ADAs Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support network to help you find the right one for you.
Avoiding Hyperglycemia & Preventing Diabetic Ketoacidosis
The best way to prevent diabetic ketoacidosis is to treat high blood sugar levels appropriately, which means following the diabetes management plan prescribed by the diabetes health care team.
Make sure your child:
- takes insulin and diabetes medicines as prescribed
- follows the meal plan and/or makes appropriate adjustments to diabetes medicines when changes to the meal plan are made
- monitors his or her blood sugar levels regularly and ketone levels when indicated
- follows the instructions and advice of the diabetes health care team and diabetes management plan, which should include instructions for sick days
Don’t Miss: Do Bananas Raise Your Blood Sugar
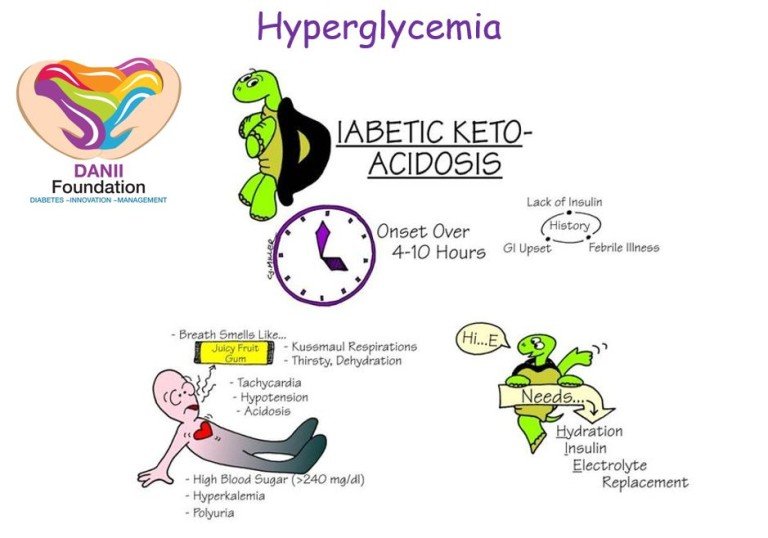
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Causes And Risk Factors
Diabetic ketoacidosis usually happens because your body doesn’t have enough insulin. Your cells can’t use the sugar in your blood for energy, so they use fat for fuel instead. Burning fat makes acids called ketones. If the process goes on for a while, they could build up in your blood. That excess can change the chemical balance of your blood and throw off your entire system.
People with type 1 diabetes are at risk for ketoacidosis, since their bodies don’t make any insulin. Your ketones can also go up when you:
- Miss a meal
- Have an insulin reaction
- Havenât injected enough insulin
DKA can happen to people with type 2 diabetes, but it’s rare. If you have type 2, especially when you’re older, you’re more likely to have a condition with some similar symptoms called HHNS . It can lead to severe dehydration.
Risk factors for DKA include:
- Having type 1 diabetes, even if itâs undiagnosed
- Missing your insulin dose often
- Not taking your insulin as prescribed
- Using illegal drugs, such as cocaine
Managing Type 1 Diabetes Takes Constant Work And Planning I Never Get A Break
Type 1 diabetes is very unique, says Ramage. If Ive been diagnosed with type 1, Ive had one of my organs fail. And the pancreas is a vital organ, not like an appendix. Its key for glucose metabolism, which we need to live. Imagine if my heart stopped beating properly and that every 10 beats I was the one responsible for making sure its of that gravity, she says.
Diabetes never takes a break. I check my blood sugar around six times a day, and probably in the middle of the night at least three nights a week, says McKean. I also give insulin when I first wake up, and then anytime I eat or my blood sugar goes high during the day.
Even more taxing can be the mental energy required to manage type 1 diabetes. Theres constant thinking that goes into diabetes calculating how many carbs youre eating, if its worth eating them, wondering if youre a bit tired because your blood sugar is high or if you just didnt sleep well, not to mention playing detective if your blood sugar is not what you expected, McKean says.
People with type 1 diabetes are just like the rest of us sometimes they wish they could just relax. My endocrinologist noted that my blood sugar levels are consistently in a good range during the week, but not so much on Saturday and Sunday, says Grady Cecile, 45, a senior services worker in North Carolina. I jokingly told him, Thats because I dont have diabetes on the weekend! In reality, having type 1 means being on every day of the week.
Also Check: What Happens In Type 1 Diabetes
The Importance Of Preventing Diabetes Progression And Heart Disease
Whats important to remember, in the absence of cardiovascular disease, is life expectancy is going to depend on the progression of diabetes, Rinker says. This means its important to eat well, exercise, and take medicine if recommended by your doctor.
Equally crucial, be sure to prevent or manage any additional conditions, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, or chronic inflammation. When a person is diagnosed with diabetes, their healthcare provider will require them to be examined for heart disease and take care to reduce their risk of developing it in the future. To that end, a diabetes diagnosis can be the first step to managing or reversing more life-threatening conditions, potentially leading to a longer life.
To someone who is depressed about the diagnosis of diabetes, Ill say, This disease is going to make you do things you should be doing anyway. You should be eating well and exercising anyway. It might actually prolong their lives because theyll be doing things they wouldnt have done before the diagnosis, Dr. Munshi says.
For some people, these measures can have incredible benefits: A report published in September 2017 in the British Medical Journal suggested maintaining a healthy weight and lowering blood glucose levels may even help reverse type 2 diabetes.
Complications Which Might Be A Cause Of Worry For Diabetes:
The following complications in diabetes might be a factor why people should beware and treat diabetes in the most effective manner.
Kidney Disease:
As per the American Diabetes Association, 44 percent of the diabetes patients tend to suffer from serious kidney disorders.
Heart-Related Condition:
There are several heart-related diseases which might affect our body if we suffer from diabetes. The blood vessels and the nerves supplying blood might get damaged resulting in serious conditions including death.
Nerve Damage:
The problem of high glucose and pressure levels can lead to damage in the various nerves of the body, including those that control the heart, kidney, arms, legs, amongst other nerves. When this condition occurs, there are chances that death might take place due to diabetes.
Diabetes Ketoacidosis:
Sometimes, there are chances that the problem of high blood glucose level might lead to high levels of ketone cells being developed in the body. This leads to the problem of Diabetes Ketoacidosis which is often very dangerous and might even lead to death.
Other Serious Complications:
Several other complications might lead to serious damage to the nerves and vessels leading to the death of diabetic patients. Some of these complications include gum diseases, amputations of different body parts, as well as other deadly complications.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Normal A1c For A Nondiabetic
Early Age Of Type 1 Diabetes Diagnosis Linked To Shorter Life Expectancy Compared To Later Diagnosis
Life-expectancy for individuals with younger-onset disease is on average 16 years shorter compared to people without diabetes, and 10 years shorter for those diagnosed at an older age
Being diagnosed with type 1 diabetes at a young age is associated with more cardiovascular complications and higher risk of premature death than being diagnosed later in life, independent of disease duration. The findings, published in The Lancet, come from a large observational study in Sweden that followed over 27,000 individuals with type 1 diabetes and more than 135,000 matched controls for an average of 10 years. With around half of individuals with type 1 diabetes diagnosed before the age of 14, the authors stress the need to consider wider and earlier use of cardioprotective measures such as statins and blood pressure lowering drugs in this high-risk population.
Although the relative risk of cardiovascular disease is increased after an early diabetes diagnosis, the absolute risk is low, says Dr. Araz Rawshani from the University of Gothenburg in Sweden who co-led the research. However, age at disease onset appears to be an important determinant of survival as well as cardiovascular outcomes in early adulthood, warranting consideration of earlier treatment with cardioprotective drugs.
The impact of type 1 diabetes on younger people should not be underestimated, and there is a need to consider adding recommendations about age of onset in future guidelines, say the authors.
Dka Signs And Symptoms
DKA usually develops slowly. Early symptoms include:
- Being very thirsty.
- Urinating a lot more than usual.
If untreated, more severe symptoms can appear quickly, such as:
- Fast, deep breathing.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Stomach pain.
Sometimes DKA is the first sign of diabetes in people who havent yet been diagnosed.
You May Like: Alcohol Insulin Response
What Are The Symptoms Of Gestational Diabetes
There is usually no symptom of High blood sugar during pregnancy. However, one may feel a bit more thirsty than usual in addition to frequent urination. Melissa Thompson of Diabetes Life Solutions suggests If thinking about getting pregnant, or recently discovered you are pregnant, meet with your Doctor. They can check your risk of gestational diabetes, and theyll continue to monitor as part of your prenatal care.
What Is The Icd 10 Code For Diabetic Ketoacidosis
4.7/5diabetesketoacidosis10ICD10codeICD10
Similarly, what is a DKA episode?
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes mellitus. Signs and symptoms may include vomiting, abdominal pain, deep gasping breathing, increased urination, weakness, confusion and occasionally loss of consciousness. Onset of symptoms is usually rapid.
Beside above, what is DKA in medical terms? Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when your body produces high levels of blood acids called ketones. The condition develops when your body can’t produce enough insulin. Without enough insulin, your body begins to break down fat as fuel.
Similarly, how do you get ketoacidosis?
It usually happens because your body doesn’t have enough insulin. Your cells can’t use the sugar in your blood for energy, so they use fat for fuel instead. Burning fat makes acids called ketones and, if the process goes on for a while, they could build up in your blood.
Can you code acidosis with DKA?
It would seem as though the classification is telling coders to code all types of acidosis to ‘lactic acidosis‘ when in a diabetic patient. However the Index entry under Diabetes does not give this impression. Respiratory, lactic, and metabolic acidosis, ketoacidosis and acidosis NEC are all indexed to E87.
Also Check: Can You Use Insulin Straight From The Fridge

