What Are The Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes In A Child
Type 1 diabetes often appears suddenly. In children, type 1 diabetes symptoms may be like flu symptoms. Symptoms can occur a bit differently in each child. They can include:
- High levels of glucose in the blood and urine when tested
- Unusual thirst
- Dehydration
- Frequent urination
- Extreme hunger but weight loss
- Loss of appetite in younger children
- Blurred vision
- Serious diaper rash that does get better with treatment
- Fruity breath and fast breathing
- Yeast infection in girls
The symptoms of type 1 diabetes can be like other health conditions. Make sure your child sees his or her healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
How Is Type 1 Diabetes Diagnosed
Because the symptoms can develop rapidly, a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes is usually made by a pediatrician or a physician in the emergency room. Pediatricians might check a childs glucose levels if there is unexplained weight loss or sudden bedwetting. Glucose tests are also commonly run when a person with type 1 diabetes symptoms arrives at the hospital.
Doctors can also diagnose type 1 diabetes by running several tests to check blood-sugar levels. The primary screening test for type 1 diabetes is the random blood-sugar test, which tells physicians the amount of glucose circulating in a persons blood at a specific moment in time. A blood-sugar level of 200 milligrams per deciliter suggests diabetes.
The secondary test is a glycated hemoglobin test, or A1C test. This test measures the average amount of glucose in a persons bloodstream over the past 90 days as a percentage.
A normal A1C level is between 5 and 5.5%, while anything higher than 5.7% indicates diabetes. When diabetes is controlled, a persons A1C levels will be low.
Its a useful test because you dont want to overreact, says Dr. Christofides. If someone has hyperglycemia for a week or a couple days, their A1C isnt going to rise. This gives us a good reflection of what the glucose level was for the past three months.
Testing For Type 1 Diabetes
A simple blood test will let you know if you have diabetes. If youve gotten your blood sugar tested at a health fair or pharmacy, follow up at a clinic or doctors office to make sure the results are accurate.
If your doctor thinks you have type 1 diabetes, your blood may also be tested for autoantibodies that are often present with type 1 diabetes but not with type 2. You may have your urine tested for ketones , which also indicate type 1 diabetes instead of type 2.
You May Like: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
What Are The Possible Complications Of Type 1 Diabetes In A Child
Type 1 diabetes can cause:
- Ketoacidosis. This is when blood sugar levels are very high and the body starts making ketones. This is a very serious condition that needs to be treated right away in the hospital, sometimes in the intensive care unit. If your child is not treated right away, they are at risk for diabetic coma. A child with a diabetic coma loses consciousness because of brain swelling. The brain swells because of the very high blood sugar levels.
- Low blood sugar . This is also sometimes called an insulin reaction. This occurs when blood glucose drops too low.
Your childs healthcare provider will tell you how to avoid these problems.
Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels. Balancing insulin, diet, and activity can help keep blood sugar levels in the target range and help prevent complications such as:
- Eye problems
- Heart and blood vessel disease
What Medicines Do I Need To Treat My Type 1 Diabetes
If you have type 1 diabetes, you must take insulin because your body no longer makes this hormone. Different types of insulin start to work at different speeds, and the effects of each last a different length of time. You may need to use more than one type. You can take insulin a number of ways. Common options include a needle and syringe, insulin pen, or insulin pump.
Some people who have trouble reaching their blood glucose targets with insulin alone also might need to take another type of diabetes medicine that works with insulin, such as pramlintide. Pramlintide, given by injection, helps keep blood glucose levels from going too high after eating. Few people with type 1 diabetes take pramlintide, however. The NIH has recently funded a large research study to test use of pramlintide along with insulin and glucagon in people with type 1 diabetes. Another diabetes medicine, metformin, may help decrease the amount of insulin you need to take, but more studies are needed to confirm this. Reseachers are also studying other diabetes pills that people with type 1 diabetes might take along with insulin.
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can occur if you take insulin but dont match your dose with your food or physical activity. Severe hypoglycemia can be dangerous and needs to be treated right away. Learn more about hypoglycemia and how to prevent or treat it.
Read Also: What Is A High Blood Sugar Reading
Excessive Thirst Frequent Urination And Dehydration
When your blood glucose levels are high, a lot of the glucose passes into the urine. Because you lose so much glucose in your urine, it also attracts water, meaning that you are making a lot of urine, causing you to need to pee a lot! If you are going to the toilet a lot and losing a lot of urine, then you are quickly becoming dehydrated. If you are dehydrated, you become thirsty. People who feel they need to constantly drink lots of water may have diabetes and it needs to be tested for.
If a person with high sugar tries to deal with their thirst by drinking sugar containing fruit juice or soft drinks, then the blood sugar can become even higher, resulting in even more sugar in the urine, even more urine production, and worsening dehydration. Its a vicious cycle.
How Is The Blood Glucose Level Monitored
It is likely you will need to monitor your blood sugar levels by using a monitor at home. If you check your blood glucose level, ideally you should aim to keep the level between 4 and 7 mmol/L before meals and less than 9 mmol/L two hours after meals.
It may be best to measure your blood glucose level at the following times:
- At different times in the day.
- After a meal.
- During and after vigorous sport or exercise.
- If you think you are having an episode of low blood glucose .
- If you are unwell with another illness .
Another blood test is called HbA1c. This test measures a part of the red blood cells. Glucose in the blood attaches to part of the red blood cells. This part can be measured and gives a good indication of your blood glucose control over the previous 1-3 months. This test is usually done regularly by your doctor or nurse. Ideally, the aim is to maintain your HbA1c to less than 48 mmol/mol . However, this may not always be possible to achieve and your target level of HbA1c should be agreed between you and your doctor.
Read Also: Glucagon Action
High Blood Pressure Risks
Type 1 diabetes damages arteries and makes them susceptible to hardening , which can lead to high blood pressure and other heart and circulation problems. Unfortunately, undiagnosed or prolonged high blood sugar levels can result in damage to organ systems in the body over time. People with type 1 diabetes have a high risk of vision problems, heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, gum disease, tooth loss, and nerve damage . Other organs may also be damaged.
Types Of Diabetes Tests
- Fasting blood glucose test blood glucose levels are checked after fasting for between 12 and 14 hours. You can drink water during this time, but should strictly avoid any other beverage. People with diabetes may be asked to delay their diabetes medication or insulin dose until the test is completed.
- Random blood glucose test blood glucose levels are checked at various times during the day, and it doesnt matter when you last ate. Blood glucose levels tend to stay constant in a person who doesnt have diabetes
- Oral glucose tolerance test a high-glucose drink is given. Blood samples are checked at regular intervals for two hours.
You May Like: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
In diabetes mellitus, symptoms that you experience are related to:
a) the severity of diabetes, i.e. how high your blood glucose levels are,
b) how long you have had the condition, i.e. how long you have had high blood glucose levels for.
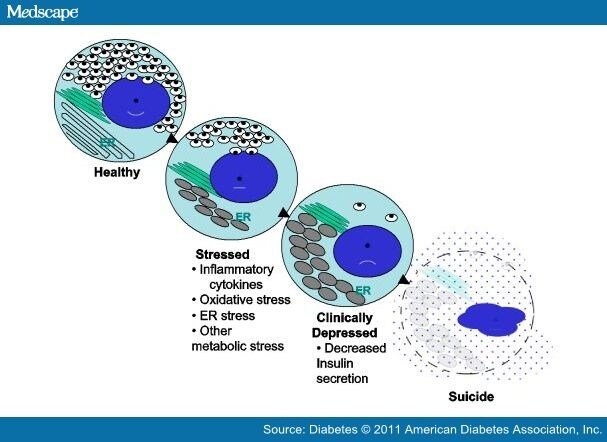
When a person initially develops type 1 diabetes, the beta cells of the pancreas rapidly fail to produce adequate amounts of insulin. Since there is little insulin, blood glucose levels rise very quickly. The symptoms of diabetes happen rapidly, are severe, and people notice that they are unwell quite quickly. If a person develops type 1 diabetes slowly, then these symptoms may take months to develop but often it is weeks.
Diabetes And Your Child
For a parent whose child is diagnosed with a life-long condition, the job of parenting becomes even tougher.
Although being diagnosed with type 1 diabetes will involve coming to terms with the diagnosis, getting used to treatment and making changes to everyday life, your child can still lead a normal and healthy life.
The Diabetes UK website has information and advice about your child and diabetes.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If You Take Too Much Glipizide
Eating A Healthy Balanced Diet
What you eat can make a difference to how you feel and how you manage your condition. Thats why weve got a huge range of tasty and nutritious recipes ready for you to try.
Whether youre cooking up a feast for dinner, or looking for something lighter for lunch, weve got you covered. Simply search by ingredient, meal type or dietary requirement and enjoy eating with diabetes.
Financial Support And Benefits
Some people with diabetes may be eligible to receive disability benefits and incapacity benefits, depending on the impact the condition has on their life.
The main groups likely to qualify for welfare benefits are children, elderly people, people with learning disabilities or mental health problems, and those with complications of diabetes.
People over 65 who are severely disabled, may qualify for a type of disability benefit called Attendance Allowance.
Carers may also be entitled to some benefit too, depending on their involvement in caring for the person with diabetes.
Staff at your local Citizens Advice Bureau can check whether you’re getting all of the benefits you’re entitled to. Both they and your diabetes specialist nurse should also be able to give you advice about filling in the forms.
GOV.uk has more information about benefits, and the Diabetes UK website has further advice about the Disability Living Allowance .
You May Like: Metformin Mg
Incidence And Prevalence Of Type 1 Diabetes
The exact number of individuals with type 1 diabetes around the world is not known, but in the U.S., there are estimated to be up to 3 million . Although it has long been called juvenile diabetes due to the more frequent and relatively straightforward diagnosis in children, the majority of individuals with type 1 diabetes are adults.
Most children are referred and treated in tertiary centers, where clinical data are more readily captured. The SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study estimated that, in 2009, 18,436 U.S. youth were newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes . Worldwide, 78,000 youth are diagnosed with type 1 diabetes annually. Incidence varies tremendously among countries: East Asians and American Indians have the lowest incidence rates as compared with the Finnish who have the highest rates . In the U.S., the number of youth with type 1 diabetes was estimated to be 166,984 .
The precise incidence of new-onset type 1 diabetes in those over 20 years of age is unknown. This may be due to the prolonged phase of onset and the subtleties in distinguishing the different types of diabetes. In one European study of adults aged 3070 years, 9% tested positive for GAD antibodies within 5 years of a diabetes diagnosis, consistent with other studies .
Type 1 Diabetes Through The Life Span: A Position Statement Of The American Diabetes Association
Type 1 diabetes is characterized by an immune-mediated depletion of -cells that results in lifelong dependence on exogenous insulin. While both type 1 and type 2 diabetes result in hyperglycemia, the pathophysiology and etiology of the diseases are distinct and require us to consider each type of diabetes independently. As such, this position statement summarizes available data specific to the comprehensive care of individuals with type 1 diabetes. The goal is to enhance our ability to recognize and manage type 1 diabetes, to prevent its associated complications, and to eventually cure and prevent this disease.
You May Like: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Are There Other Ways To Manage Type 1 Diabetes
People with Type 1 diabetes need to monitor their blood sugar closely. Maintaining a healthy blood sugar range is the best way to avoid health complications. You can monitor your blood sugar in the following ways:
- Blood glucose meter: You prick your finger and put a small drop of blood on the meters test strip. Your blood glucose level appears on the meter. A blood glucose meter is usually the least expensive home testing option, but it only reports your blood sugar at the time of the check.
- Continuous glucose monitoring : There are different types of CGMs. Most CGMs require you to insert a small sensor under your skin at home every seven to 14 days. Some CGMs are implanted by a healthcare provider. The sensor continuously records your blood glucose levels. People using a CGM require fewer finger sticks. CGM systems can be more expensive than fingerstick blood glucose meters, but they provide much more information about your glucose levels, including where they have been and where they are going.
When To Contact A Medical Professional
- Chest pain or pressure, shortness of breath, or other signs of angina
- Loss of consciousness
Also call your provider if you have:
- Blood sugar levels that are higher than the goals you and your provider have set
- Numbness, tingling, or pain in your feet or legs
- Problems with your eyesight
- Sores or infections on your feet
- Frequent feelings of depression or anxiety
- Symptoms that your blood sugar is getting too low
- Symptoms that your blood sugar is too high
- Blood sugar readings that are below 70 mg/dL
You can treat early signs of hypoglycemia at home by drinking orange juice, eating sugar or candy, or by taking glucose tablets. If signs of hypoglycemia continue or your blood glucose level stays below 60 mg/dL , go to the emergency room.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Diabetes If You Re Skinny
Type 1 Diabetes Treatment: Artificial Pancreas
Researchers are developing an artificial pancreas. This device is a combination of an insulin pump and continuous glucose monitoring system controlled by a computer program. The goal for the system is to have a device that mimics the function of a normal pancreas.
Additional Information on Diabetes
What Are The Aims Of Treatment
Although diabetes cannot be cured, it can be treated successfully.
If a high blood sugar level is brought down to a normal or near-normal level, your symptoms will ease and you are likely to feel well again. However, you still have some risk of complications in the long term if your blood glucose level remains even mildly high – even if you have no symptoms in the short term. Studies have shown that people who have better glucose control have fewer complications compared with those people who have poorer control of their glucose level.
Therefore, the main aims of treatment are:
- To keep your blood glucose level as near to normal as possible.
- To reduce any other risk factors which may increase your risk of developing complications. In particular, to reduce your blood pressure if it is high and to lead a healthy lifestyle.
- To detect any complications as early as possible. Treatment can prevent or delay some complications from becoming worse.
Also Check: Can You Be Born With Type 2 Diabetes
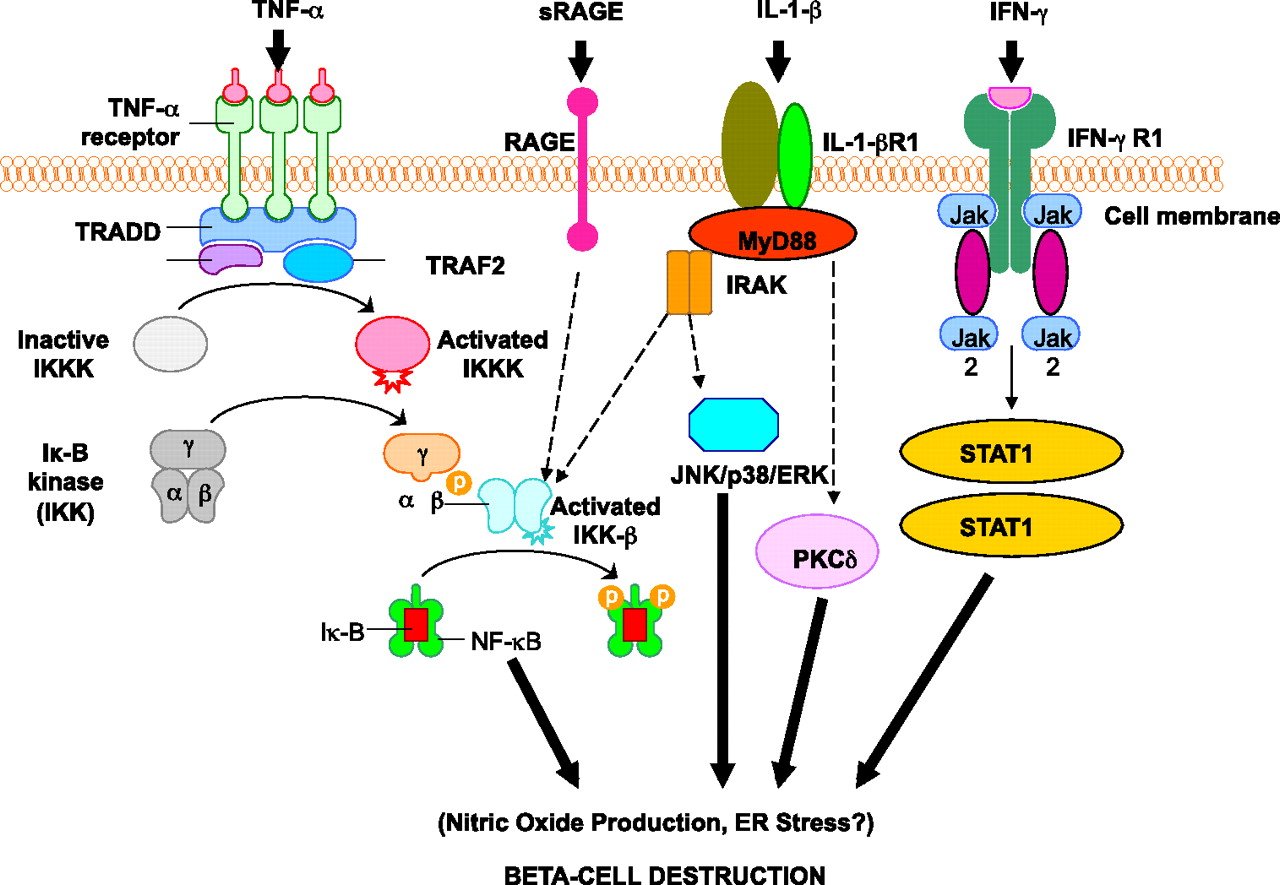
Is Type 1 Diabetes An Autoimmune Disease
When type 1 diabetes is triggered by a virus, someone predisposed to autoimmune conditions may develop an autoimmune response. This means that their bodys immune system will start attacking its own cells. In type 1 diabetes, the body attacks the beta cells in the pancreas that are responsible for producing insulin.
Who Gets Type 1 Diabetes

Type 1 diabetes can’t be prevented, and there is no real way to predict who will get it. Nothing that either a parent or the child did caused the disease.
Once a person has type 1 diabetes, it does not go away and requires lifelong treatment. Kids and teens with type 1 diabetes depend on daily insulin injections or an insulin pump to control their blood glucose levels.
Page 2
Recommended Reading: What Can You Eat When You Have Diabetes

