Can Type 2 Diabetes Be Cured
There is no cure for type 2 diabetes, but some people are able to put their diabetes into remission. This means that your blood sugar levels are healthy and you dont need to take diabetes medication any more. Remission can be life-changing, but its not possible for everyone.
Learn more about diabetes remission.
Social And Personality Characteristics
For some, marital satisfaction remains intact, but other family relationships can be more difficult. Career satisfaction focuses more on inner satisfaction and contentedness and less on ambition and the desire to advance. Even so, career changes occur often. Middle adulthood or middle age can be a time when people re-examines their lives by taking stock and evaluating their accomplishments. Morality may change and become more conscious. The perception that those in this stage of development of life undergo a “mid-life” crisis is largely false. This period in life is usually satisfying and tranquil. Personality characteristics remain stable throughout this period. The relationships in middle adulthood may continue to evolve into connections that are stable.
Is Type 2 Diabetes Increasing
Type 2 diabetes is increasing at an epidemic rate, and is being diagnosed at younger and younger ages. The most likely reason for this increase is that individuals with a genetic susceptibility to type 2 diabetes are developing the disease due to lifestyle changes namely less physical activity, weight gain, and longer life span.
The good news is that scientific research confirms that by eating healthy foods, exercising regularly and maintaining an ideal body weight, you can delay or prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes.
Also Check: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
How Can I Manage My Type 2 Diabetes
Managing your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol, and quitting smoking if you smoke, are important ways to manage your type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle changes that include planning healthy meals, limiting calories if you are overweight, and being physically active are also part of managing your diabetes. So is taking any prescribed medicines. Work with your health care team to create a diabetes care plan that works for you.
What Is Type 2 Diabetes
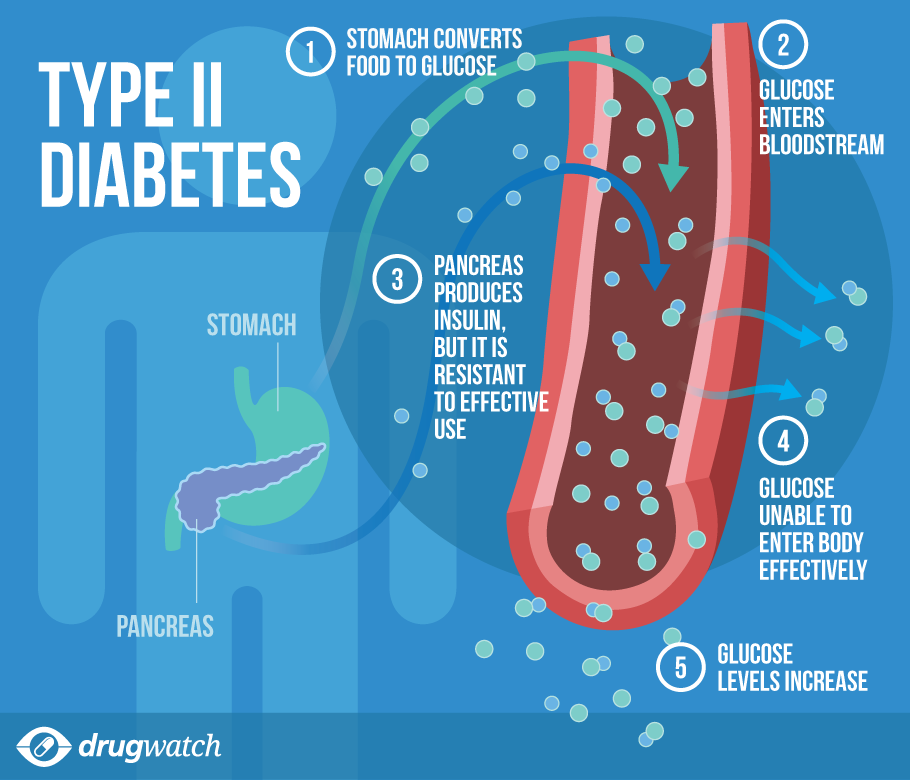
Type 2 diabetes, the most common type of diabetes, is a disease that occurs when your blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high. Blood glucose is your main source of energy and comes mainly from the food you eat. Insulin, a hormone made by the pancreas, helps glucose get into your cells to be used for energy. In type 2 diabetes, your body doesnt make enough insulin or doesnt use insulin well. Too much glucose then stays in your blood, and not enough reaches your cells.
The good news is that you can take steps to prevent or delay the development of type 2 diabetes.
Read Also: What Happens If You Stop Taking Diabetes Medication
Keep Your Blood Pressure Down
It is very important to have your blood pressure checked regularly. The combination of high blood pressure and diabetes is a particularly high risk factor for complications. Even mildly raised blood pressure should be treated if you have diabetes. Medication, often with two or even three different medicines, may be needed to keep your blood pressure down but remember weight loss and exercise can really help with this too.
Treatment For Low Blood Glucose
If you have type 2 diabetes that’s controlled using insulin or certain types of tablets , you may experience episodes of hypoglycaemia.
Hypoglycaemia is where your blood glucose levels become very low.
Mild hypoglycaemia can make you feel shaky, weak and hungry, but it can usually be controlled by eating or drinking something sugary.
If you have a hypo, you should initially have a form of carbohydrate that will act quickly, such as a sugary drink or glucose tablets.
This should be followed by a longer-acting carbohydrate, such as a cereal bar, sandwich or piece of fruit.
In most cases, these measures will be enough to raise your blood glucose level to normal. You should aim for a hypo to be treated and to recheck your blood glucose level within 15 minutes.
If blood glucose still less than 4mmol/l then repeat the treatment using a fast acting carbohydrate. When your blood glucose returns to normal then have your longer acting carbohydrate.
If you develop severe hypoglycaemia, you may become drowsy and confused, and you may even lose consciousness.
If this occurs, you may need to have an injection of glucagon into your muscle or glucose into a vein. Glucagon is a hormone that quickly increases your blood glucose levels.
You may require input from a health care professional. If the glucagon is not successful, you may require an injection of dextrose into your vein.
Your diabetes care team can advise you on how to avoid a hypo and what to do if you have one.
Also Check: Can You Be Born With Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes Treatment
First line treatment for type 2 diabetes typically includes a combination of diet modification with regular and appropriate exercise.
The NICE guidelines state that treatment for type 2 diabetes should take into account an individuals needs and preferences into account. People with diabetes should be given the opportunity to make informed decisions about their care and work together with healthcare professionals.
The NICE guidelines encourage having high-fibre, low-glycemic-index carbohydrate in the diet. This allows a good amount of flexibility and it is possible to follow a range of diets, including lower-carb and low-calorie, whilst ensuring you get a good source of low-GI foods such as vegetables, beans and pulses.
Your health team should help you with setting recommendations for carbohydrate and alcohol intake that work for you.
Prognosis In Intensive Therapy
In the UKPDS, more than 5000 patients with type 2 diabetes were followed up for up to 15 years. Those in the intensely treated group had a significantly lower rate of progression of microvascular complications than did patients receiving standard care. Rates of macrovascular disease were not altered except in the metformin-monotherapy arm in obese individuals, in which the risk of myocardial infarction was significantly decreased.
In the 10-year follow-up to the UKPDS, patients in the previously intensively treated group demonstrated a continued reduction in microvascular and all-cause mortality, as well as in cardiovascular events, despite early loss of differences in glycated hemoglobin levels between the intensive-therapy and conventional-therapy groups. The total follow-up was 20 years, half while in the study and half after the study ended.
Other, shorter studies, such as Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease: Preterax and Diamicron Modified Release Controlled Evaluation and the Veterans Affairs Diabetes Trial , showed no improvement in cardiovascular disease and death with tight control .
A British study indicated that the HbA1c level achieved 3 months after the initial diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus predicts subsequent mortality. In other words, according to the report, aggressive lowering of glucose after diagnosis bodes well for long-term survival.
You May Like: Metformin Purpose
How Can I Lower My Chances Of Developing Type 2 Diabetes
Research such as the Diabetes Prevention Program, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, has shown that you can take steps to reduce your chances of developing type 2 diabetes if you have risk factors for the disease. Here are some things you can do to lower your risk:
- Lose weight if you are overweight, and keep it off. You may be able to prevent or delay diabetes by losing 5 to 7 percent of your current weight.1 For instance, if you weigh 200 pounds, your goal would be to lose about 10 to 14 pounds.
- Move more. Get at least 30 minutes of physical activity, such as walking, at least 5 days a week. If you have not been active, talk with your health care professional about which activities are best. Start slowly and build up to your goal.
- Eat healthy foods. Eat smaller portions to reduce the amount of calories you eat each day and help you lose weight. Choosing foods with less fat is another way to reduce calories. Drink water instead of sweetened beverages.
Ask your health care team what other changes you can make to prevent or delay type 2 diabetes.
Most often, your best chance for preventing type 2 diabetes is to make lifestyle changes that work for you long term. Get started with Your Game Plan to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes.
What Causes Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin is a hormone made by your pancreas that acts like a key to let blood sugar into the cells in your body for use as energy. If you have type 2 diabetes, cells dont respond normally to insulin this is called insulin resistance. Your pancreas makes more insulin to try to get cells to respond. Eventually your pancreas cant keep up, and your blood sugar rises, setting the stage for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar is damaging to the body and can cause other serious health problems, such as heart disease, vision loss, and kidney disease.
Don’t Miss: Banana Bad For Diabetics
What Health Problems Can People With Diabetes Develop
Following a good diabetes care plan can help protect against many diabetes-related health problems. However, if not managed, diabetes can lead to problems such as
- heart disease and stroke
- gum disease and other dental problems
- sexual and bladder problems
Many people with type 2 diabetes also have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease . Losing weight if you are overweight or obese can improve NAFLD. Diabetes is also linked to other health problems such as sleep apnea, depression, some types of cancer, and dementia.
You can take steps to lower your chances of developing these diabetes-related health problems.
What Are The Different Types Of Diabetes
There are two major types of diabetes, called type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes was also formerly called insulin dependent diabetes mellitus , or juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus. In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas undergoes an autoimmune attack by the body itself, and is rendered incapable of making insulin. Abnormal antibodies have been found in the majority of patients with type 1 diabetes. Antibodies are proteins in the blood that are part of the body’s immune system. The patient with type 1 diabetes must rely on insulin medication for survival.
Recommended Reading: How Does High Blood Sugar Make You Feel
Can Type 2 Diabetes Be Reversed
Yes! The good news is that several studies have shown that type 2 diabetes can be reversed. You are considered in remission from type 2 diabetes when you have had normal blood sugar levels for a year without medication.
One of the most important components in reversing type 2 diabetes is early detection. Dr. Bergquist explains, The pancreas produces insulin. The longer you have diabetes, the more damage your insulin resistance causes to your pancreas, and the less likely your pancreas is to recover. Hence, the possibility for remission decreases the longer you have diabetes. But theres a wide window during which you can be successful.
Microvascular And Macrovascular Complications
Longer survival times and development of type 2 diabetes at younger ages increase the risk of developing duration-dependent complications. In UKPDS 16, 18% of patients, all of whom were presumed to be clinically healthy, had a clinical end point within 6 years of diagnosis.
UKPDS 35 showed highly significant associations between development of diabetes complications, including death, across the broad range of exposure to glycemia, with no evidence of a threshold. Conversely, each 1% reduction in mean A1C was associated with reduction in risk of 21% for any end point related to diabetes .
The role of complications on disease progression and failure has not been well studied. A change in insulin sensitivity and clearance is well recognized in renal failure and clearance is well recognized. However, the impact of these changes on the natural history of diabetes itself needs to be studied. Many patients with established complications tend to be poorly controlled, and factors such as glucose toxicity may play a role in disease progression as discussed above. In addition, various cardiovascular drugs such as diuretics and -blockers may affect -cell function adversely.
Also Check: Can People With Diabetes Eat Bananas
What Is Type 1 Diabetes
In autoimmune diseases, such as type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakenly manufactures antibodies and inflammatory cells that are directed against and cause damage to patients’ own body tissues. In persons with type 1 diabetes, the beta cells of the pancreas, which are responsible for insulin production, are attacked by the misdirected immune system. It is believed that the tendency to develop abnormal antibodies in type 1 diabetes is, in part, genetically inherited, though the details are not fully understood.
Exposure to certain viral infections or other environmental toxins may serve to trigger abnormal antibody responses that cause damage to the pancreas cells where insulin is made. Some of the antibodies seen in type 1 diabetes include anti-islet cell antibodies, anti-insulin antibodies and anti-glutamic decarboxylase antibodies. These antibodies can be detected in the majority of patients, and may help determine which individuals are at risk for developing type 1 diabetes.
How Is The Blood Glucose Level Monitored
The blood test that is mainly used to keep a check on your blood glucose level is called the HbA1c test. This test is commonly done every 2-6 months by your doctor or nurse.
The HbA1c test measures a part of the red blood cells. Glucose in the blood attaches to part of the red blood cells. This part can be measured and gives a good indication of your average blood glucose level over the preceding 1-3 months.
Treatment aims to lower your HbA1c to below a target level. Ideally, it is best to maintain HbA1c to less than 48 mmol/mol . However, this may not always be possible to achieve and your target level of HbA1c should be agreed between you and your doctor.
If your HbA1c is above your target level then you may be advised to step up treatment to keep your blood glucose level down.
Some people with diabetes check their actual blood glucose level regularly with a blood glucose monitor. If you are advised to do this then your doctor or nurse will give you instructions on how to do it.
Also Check: Quaker Oats For Diabetes
What Are The Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
Many people with type 2 diabetes have no symptoms at all. If you do have them, the symptoms develop slowly over several years. They might be so mild that you do not notice them. The symptoms can include
- Increased thirst and urination
- Numbness or tingling in the feet or hands
- Sores that do not heal
- Unexplained weight loss
Can Obesity Cause Type 2 Diabetes
How we understand obesity and type 2 diabetes matters as they are the most widespread metabolic disorders. Though theyre separate conditions, they often overlap.
Weight and nutrition specialist Caroline Apovian MD explains, Although lifestyle is very important for both obesity treatment and diabetes, there are people who never develop obesity, and there are people who do have obesity for whom lifestyle changes dont always work, because obesity is a disease and the body defends a higher body weight set point. Even after weight loss, the hormonal changes involved in obesity can force a patient to regain the weight.
Type 2 diabetes patients did not bring it on themselves, emphasizes diabetes and metabolism expert Elena Christofides MD. This is not a moral failing.
But both the prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes is increasing. Why? Researchers believe its our environment. There has been an increased availability of high-fat, high-sugar, highly processed foods. These foods often contain other non-food items.
Some of these ingredients have been found to act as endocrine disrupters and change the way our bodies store fat and process energy. While there have not been sufficient studies to prove a causal relationship, most doctors and nutritionists recommend avoiding them.
Read Also: What Happens In Type 1 Diabetes
Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes symptoms often take several years to develop. Some people dont notice any symptoms at all. Type 2 diabetes usually starts when youre an adult, though more and more children and teens are developing it. Because symptoms are hard to spot, its important to know the risk factors for type 2 diabetes. Make sure to visit your doctor if you have any of them.
What Is Type 2 Diabetes And Why Does It Occur
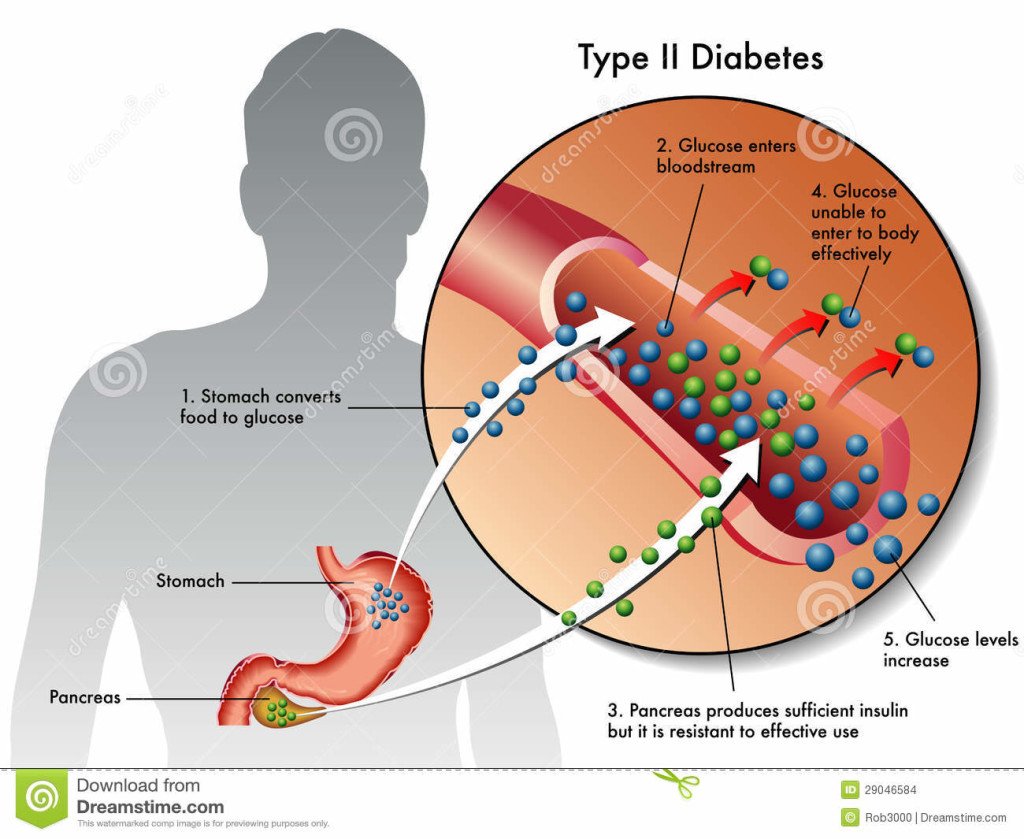
There are two main types of diabetes, known as “Type 1 Diabetes” and “Type 2 Diabetes”.
These two conditions are generally considered to be 2 different and separate conditions, so it is important to understand the differences between the two.
Some old names for Type 2 Diabetes include: Adult Onset Diabetes, Non Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus and NIDDM. These old names should not be used, as they are no longer considered correct.
Important Stuff to Know
Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes. Of all people with diabetes, 90% have Type 2 diabetes.
Some ethnic groups, like the South African Indian population, are more prone to developing diabetes, and in these groups, the percentage is even higher.
Type 2 diabetes usually happens in older people, but recently, more and more younger people, and sometimes even children, develop Type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes is a disorder of a person’s metabolism, and its primary characteristic is high blood glucose. There are two main reasons for the high blood glucose:
- Insulin resistance
- Lack of insulin
Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance means that the cells of the body do not fully respond to insulin that is released. In other words, the insulin that is present, does not work as well as it should.
Lack of insulin
This occurs as the condition progresses. Over time, the pancreas produces less and less insulin, and eventually, the pancreas will stop producing insulin.
- Obesity
- Poor diet
Recommended Reading: Insulin Is Produced By The Pancreatic Beta Cells In The Islets Of Langerhans.

