Type 2 Diabetes Flashcards
3. risk increases with age, obesity, and sedentary lifestyle, hx of gest diabetes, HTN, dyslipidemia 5. occurs more often in ethnic minorites: AA, native americans, hispanics, asian americans 2. impaired glucose tolerance, 2 hour values following glucose tolerance test: > 140-199 3. People with IFG or IGT are said to have pre-diabetes. Very high risk of developing in the future. OR a fasting plasma glucose > 126 OR a random plasma glucose of > 200 plus clinical signs and sx of diabetes 1. IFG –fasting blood glucose > 100 and < 125 2. IGT –2 hour plasma glucose 140-199 diabetes testing in undiagnosed pts-all patients should be considered in all individuals > 45 , if normal repeated then every 3 years. consider in overweight adults and who have at least one additional risk factor -first degree relative with diabetes -member of high risk ethnic population -on previous testing, had impaired GTT or IFG -other clinical conditions associated with insulin resistance diabetes testing undiagnosed-children suspected type 2 beginning at age 10 or at onset of puberty . Test every 3 years. A fasting blood glucose test is preferred. Consider in following: -overweight Plus any two of the following risk factors: -signs of insulin resistance or conditions associated with insulin resistance (HTN, PCOS, dyslipidemia, acanthContinue reading > >
New Ongoing And Published Research
VA researchers are studying innovative strategies and technologies, including group visits, telemedicine, peer counseling, and internet-based education and case management, to enhance access to diabetes care and to improve outcomes for patients.
In addition, VA researchers are working to develop better ways to prevent or treat diabetes, especially in special populations such as the elderly, amputees, minorities, spinal cord-injured patients, and those with kidney or heart disease.
For more on Diabetes, visit our Cardiovascular Disease topic page.
If you are interested in learning about joining a VA-sponsored clinical trial, visit our research study information page.
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes: Whats The Difference
Type 2 diabetes is not the same as Type 1 diabetes. In Type 1 diabetes, your pancreas doesnt make any insulin. In Type 2, your pancreas doesnt make enough insulin, and the insulin it is making doesnt always work as it should. Both types are forms of diabetes mellitus, meaning they lead to hyperglycemia .
Type 2 diabetes usually affects older adults, though its becoming more common in children. Type 1 diabetes usually develops in children or young adults, but people of any age can get it.
You May Like: Deficient Sugar In The Blood
Who Is More Likely To Develop Type 2 Diabetes
You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you are age 45 or older, have a family history of diabetes, or are overweight. Physical inactivity, race, and certain health problems such as high blood pressure also affect your chance of developing type 2 diabetes. You are also more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you have prediabetes or had gestational diabetes when you were pregnant. Learn more about risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Pathogenesis And Risk Factors
Multiple potential mechanisms unique to diabetes may contribute to the increased risk of UTI in diabetic patients. Higher glucose concentrations in urine may promote the growth of pathogenic bacteria., However, several studies did not find an association between HbA1c level, which serves as a proxy for glycosuria, and risk of UTI among diabetic patients also, sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, which increase glycosuria, were not found to increase the rate of UTI., High renal parenchymal glucose levels create a favorable environment for the growth and multiplication of microorganisms, which might be one of the precipitating factors of pyelonephritis and renal complications such as emphysematous pyelonephritis., Various impairments in the immune system, including humoral, cellular, and innate immunity may contribute in the pathogenesis of UTI in diabetic patients.,, Lower urinary interleukin-6 and -8 levels were found in patients with diabetes with ASB, compared to those without diabetes with ASB. Autonomic neuropathy involving the genitourinary tract results in dysfunctional voiding and urinary retention, decreasing physical bacterial clearance through micturition, thereby facilitating bacterial growth.,, Bladder dysfunction occurs in 26%85% of diabetic women, depending on age extent of neuropathy and duration of diabetic disease, and thus should be considered in all diabetic patients with UTI.
Also Check: Relationship Between Triglycerides And Blood Glucose
How Many Canadians Are Newly Diagnosed With Diabetes Each Year
In 20132014, close to 200,000 Canadians were newly diagnosed with diabetes . This represented 0.4 new cases per 1,000 population among children and youth and 7.6 new cases per 1,000 population among adults. Following a pattern similar to the prevalence of diagnosed diabetes, incidence generally increases with age and is higher among males than among females , both overall and in most age groups .
Figure 2: Incidence of diagnosed diabetes , by age group and sex, Canada, 20132014
| Age group | |
|---|---|
| 6.5 | 5.3 |
Note: The 95% confidence interval shows an estimated range of values which is likely to include the true value 19 times out of 20.Data source: Public Health Agency of Canada, using Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System data files contributed by provinces and territories, May 2017.
The Risk Of Uti In Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
All types of UTI are more frequent in patients with type 2 diabetes. Various studies have reported the overall incidence of UTI among these patients. An observational study of all patients with type 2 diabetes in the UK general practice research database found that the incidence rate of UTI was 46.9 per 1,000 person-years among diabetic patients and 29.9 for patients without diabetes. Women with previously diagnosed diabetes had a higher risk of UTI than those with recently diagnosed diabetes . A cohort study of over 6,000 patients enrolled in ten clinical trials found an incidence rate of 91.5 per 1,000 person-years in women and 28 per 1,000 person-years in men, and a cumulative incidence of 2% during 6 months. A recent American study performed on a health service data base with more than 70,000 patients with type 2 diabetes found that 8.2% were diagnosed with UTI during 1 year . Another American database study from 2014 found that a UTI diagnosis was more common in men and women with diabetes than in those without diabetes among 89,790 matched pairs of patients with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus.
In men, risk of acute bacterial prostatitis, prostatic abscess, progression to chronic prostatitis, and infections following prostatic manipulations, such as trans-rectal prostate biopsy, is increased in patients with diabetes mellitus.,
Also Check: How Long Does It Take To Lower Glucose Levels
Work Of Nobel Laureates
Two of VA’s three Nobel laureates have done important work to benefit Veterans with diabetes. The late Dr. Rosalyn S. Yalow received the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1977 for her work in developing the radioimmunoassay, an extremely sensitive way to measure insulin and other hormones in the blood. The technique made possible major advances in diabetes research and in diagnosing and treating hormonal problems related to growth, thyroid function, and fertility.
Dr. Andrew V. Schally also received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1977 for his discovery that the hypothalamus links the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. He is currently doing research, along with teams of national and international researchers, on growth hormone-releasing hormone . Among other possibilities opened up by Schally’s work with GHRH is the possibility of reducing or eliminating the need for diabetics to regularly inject insulin.
In 2013, an international research team including Schally devised a way to transplant healthy cells into the body without the usual risk of rejection. The study involved a middle-aged man with diabetes, but it may be relevant to a range of other diseases as well. The researchers developed what amounts to an artificial pancreas , which the patient tolerated well without taking drugs to suppress the immune system.
Type 2 Diabetes And Your Health
Type 2 diabetes, the most common form of diabetes, develops when the body becomes resistant to insulin, the hormone that controls the blood sugar levels. There are 32.6 million people in the United States living with type 2 diabetes. Unfortunately, this disease can lead to many serious health problems including heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure, kidney failure, blindness, skin wounds, nerve damage , erectile dysfunction, and cognitive decline among many others. Type 2 diabetes can contribute to premature death or a decreases in the number of years a person is expected to live. Obesity is one of the largest contributors to developing type 2 diabetes.
Initially, treatment of type 2 diabetes may focus on lifestyle changes such as weight-loss, exercise, dietary changes, and anti-diabetic medications. The goal is to stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent further damage to the body through blood sugar control. In many individuals, type 2 diabetes often worsens with time and requires higher doses and more types of medication to keep blood sugar levels under control. Type 2 diabetes tends to be a progressive disease and most people require treatment for the rest of their life.
If you are living with diabetes, you should know that one of the most important discoveries in the management of diabetes is that surgery can help control or improve type 2 diabetes in the large majority of patients.
Don’t Miss: What Happens In Type 1 Diabetes
Diabetes And Chronic Kidney Disease
Diabetes is the leading cause of kidney failure, accounting for 44% percent of new cases. Current research suggests that control of high blood pressure is a key factor in slowing this disease. Strict control of blood sugar levels and reduction of dietary protein intake are also important. Treatment to prevent diabetic kidney disease should begin early before kidney damage develops.
COVID-19 patients can become kidney patients.
You can provide lifesaving support today with a special monthly gift.
Highlights From The Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects Canadians of all ages. If left uncontrolled, diabetes results in consistently high blood sugar levels , which can lead to serious complications such as cardiovascular disease, vision loss, kidney failure, nerve damage, and amputation. Fortunately, it is possible to remain healthy with diabetes through appropriate management and care.
The Public Health Agency of Canada , in collaboration with all provinces and territories, conducts national surveillance of diabetes to support the planning and evaluation of related policies and programs. This fact sheet presents an overview of diagnosed diabetes data from the Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System .
You May Like: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
What Should A Type 2 Diabetes Meal Plan Include
Ask your healthcare provider or a nutritionist to recommend a meal plan thats right for you. In general, a Type 2 diabetes meal plans should include:
- Lean proteins: Proteins low in saturated fats include chicken, eggs and seafood. Plant-based proteins include tofu, nuts and beans.
- Minimally processed carbohydrates: Refined carbs like white bread, pasta and potatoes can cause your blood sugar to increase quickly. Choose carbs that cause a more gradual blood sugar increase such as whole grains like oatmeal, brown rice and whole-grain pasta.
- No added salt: Too much sodium, or salt, can increase your blood pressure. Lower your sodium by avoiding processed foods like those that come in cans or packages. Choose salt-free spices and use healthy oils instead of salad dressing.
- No added sugars: Avoid sugary foods and drinks, such as pies, cakes and soda. Choose water or unsweetened tea to drink.
- Non-starchy vegetables: These vegetables are lower in carbohydrates, so they dont cause blood sugar spikes. Examples include broccoli, carrots and cauliflower.
When Should I Call My Doctor
Its important to monitor diabetes very closely if youre sick. Even a common cold can be dangerous if it interferes with your insulin and blood sugar levels. Make a sick day plan with your healthcare provider so you know how often to check your blood sugar and what medications to take.
Contact your provider right away if you experience:
- Confusion or memory loss.
- Nausea and vomiting for more than four hours.
- Problems with balance or coordination.
- Severe pain anywhere in your body.
- Trouble moving your arms or legs.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Type 2 diabetes is a disease where your body doesnt make enough insulin and cant use sugar the way it should. Sugar, or glucose, builds up in your blood. High blood sugar can lead to serious health complications. But Type 2 diabetes is manageable. Regular exercise and a healthy diet can help you manage your blood sugar. You may also need medication or insulin. If you have Type 2 diabetes, you should monitor your blood sugar at home regularly and stay in close communication with your healthcare provider.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 03/25/2021.
References
You May Like: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Results In Relation To Other Studies
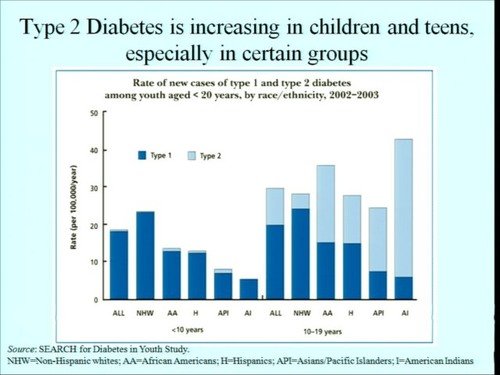
Continued monitoring of the prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes among adults is particularly important because both have increased substantially over time among children and adolescents.2229 In the United States, the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study reported that between 2001 and 2009 the prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes among children and adolescents increased from 1.48 to 1.93 per 1000 and from 0.34 to 0.46 per 1000, respectively.30 Moreover, among US children and adolescents during 2002-12 the annual incidence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes increased by 1.4% and 7.1%, respectively.31 It was projected that among US children and adolescents, the number of cases of type 1 diabetes would nearly triple, from 179388 in 2010 to 587488 in 2050 and the number of cases of type 2 diabetes would almost quadruple, from 22820 in 2010 to 84131 in 2050.32 As a result, cases of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in adults will substantially increase as the children and adolescents reach adulthood. Major risk factors for type 2 diabetes, including obesity, physical inactivity, and unhealthy diets are still problematic and without a notable declining trend.12 Although genetic disposition plays a critical part in type 1 diabetes, the potential role of environmental risk factors are increasingly recognized.1333
Diabetes Statistics By Age
Theres a greater prevalence of diabetes among older age groups, especially for Type 2 diabetes, which takes longer to develop.
- Of the Americans with diagnosed diabetes, 3.6 million are 18 to 44 years old, 11.7 million are 45 to 64 years old, and 11.5 million are older than 65.
- There are 210,000 cases of diagnosed diabetes among children and adolescents younger than 20, including 187,000 cases of Type 1 diabetes.
- Of the Americans with undiagnosed diabetes, 1.4 million are 18 to 44, 3.1 million are 45 to 64, and 2.9 million are older than 65.
- Approximately 24.2 million adults aged 65 and older have prediabetes.
Also Check: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Prevalence Of Diagnosed Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Among Us Adults In 2016 And 201: Population Based Study
- Accepted 27 August 2018
Box : What’s In The Data
The data used in this publication are from the Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System , a collaborative network of provincial and territorial chronic disease surveillance systems, led by the Public Health Agency of Canada . The CCDSS identifies chronic disease cases from provincial and territorial administrative health databases, including physician billing claims and hospital discharge abstract records, linked to provincial and territorial health insurance registry records using a unique personal identifier. Data on all residents eligible for provincial or territorial health insurance are captured in health insurance registries.
While CCDSS data reflect the health status of the Canadian population, they may also reflect changes in data collection methods, coding and classification systems, or clinical guidelines and billing practices. These factors must also be taken into consideration when interpreting time trends.
Definition of diagnosed diabetes in the CCDSSCanadians aged 1 year and older are identified as having diagnosed diabetes if they have: at least one hospitalization record or at least two physician claims in a two-year period with an International Classification of Diseases code for diabetes. Females aged 10 to 54 years diagnosed with diabetes 120 days preceding or 180 days following a pregnancy-related visit are removed, to exclude possible cases of gestational diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Side Effects Of Metaformin
What Causes Type 2 Diabetes And Other Forms Of Diabetes Mellitus
Many of the foods and beverages that you consume contain glucose, which your body processes to make energy. Your pancreas produces a hormone called insulin to help the glucose in your blood enter your muscles, fat, and liver to provide energy.

