What Causes Ketoacidosis In Diabetes
You are diagnosed with diabetes when your blood sugar levels are higher than normal. There are many causative factors of this serious and life-threatening condition.
Diabetic ketoacidosis can occur due to varied reasons such as:
- Not enough insulin in the body
- Certain medications that trigger DKA
- You dont know that you have type 1 diabetes DKA can be the first sign of insulin-dependent diabetes
- You experience some physical stress like infection or illness
- Stroke, heart attack, or pancreatitis can also cause DKA
- Drinking a lot of alcohol
- Indulging in high doses of narcotic drugs like cocaine
If you have undiagnosed diabetes, you must look out for signs and symptoms that could potentially signal this condition. In case youve already been diagnosed with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, you should be aware of the warning signs of DKA, so you can take action quickly.
At any time, if you are ill or have a serious infection, do inform your doctor about your diabetes. You should also be wary about taking medicine and supplements on your own, even supposedly natural and herbal products, as they can interact with any diabetic medications and cause problems.
Follow Your Treatment Plan
You can lower your risk of DKA with proper management of your diabetes:
- Take your medications as directed, even if youre feeling fine.
- Follow your meal plan.
- Test your blood sugar consistently, as recommended by your doctor. This will help you get in the habit of making sure your numbers are in range. If you notice a problem, you can talk with your doctor about adjusting your treatment plan.
- Talk with your doctor about adjusting your insulin dosage levels based on your activity level, illnesses, or other factors, such as what youre eating.
- If you have high blood sugar and your blood or urine test detects ketones, do not exercise. Exercising with high blood sugar can be dangerous when you have diabetes. Its best to talk with your doctor about how to manage this situation.
- Sometimes the cost of insulin can make it to follow a diabetes treatment plan. Read more about how to access insulin at a reduced cost.
Are There Any Possible Complications From Dka
As DKA is life-threatening, its important to seek emergency care as soon as you suspect youre suffering from the condition. Fluid loss from DKA can lead to kidney and organ damage, brain swelling that can eventually cause a coma, and fluid buildup in your lungs. The sooner youre treated for DKA, the less likely you are to suffer from these major complications.
Read Also: Cottage Cheese For Diabetes
How Do I Avoid Diabetic Ketoacidosis
The best way to prevent diabetic ketoacidosis is to keep good blood glucose control at all times. Regularly testing your blood sugar levels at home will help you to manage your glucose levels.
If you experience difficulty in controlling your diabetes, speak to your GP or consultant who can advise you or may refer you to go on a structured diabetes education course.
If you ever feel unwell or abnormal, you should test your blood sugar levels at once.
Symptoms Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
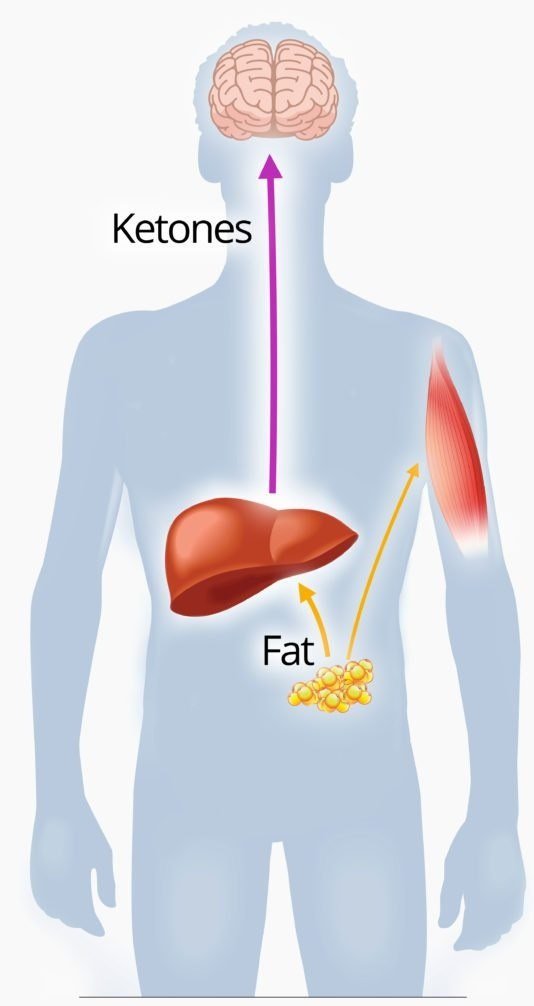
- needing to pee more than usual
- feeling very thirsty
- breath that smells fruity
- deep or fast breathing
- confusion
- passing out
You can get DKA if you have high blood sugar and a high level of ketones in your blood or urine. You can check your ketone levels using a home-testing kit.
Symptoms usually start over a 24-hour period, but they can happen faster.
Recommended Reading: Normal A1c Level For Nondiabetic
What Can You Do To Avoid Dka
You can help avoid DKA by monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly and altering your insulin dose in response to your blood sugar levels and what you eat.
Your blood sugar levels could be higher than normal when you are unwell. So, its a good idea to work with your healthcare team to come up with some sick day rules for when you are ill. You may need to drink more fluids, take more insulin and check your blood sugars more than you would usually. The amount of extra insulin needed will vary from person to person. Your diabetes team will help you to work out the correct dose for you .
It is still a good idea to contact your GP or diabetes team if:
- You feel fine but are getting higher than usual readings for blood glucose and ketones.
- You feel unwell but your blood glucose and ketones are only slightly higher than normal.
“The experience has taught me that its so important to listen to your body. No matter how many HCPs you visit, whether theyre a GP or a diabetes specialist or a family friend who works in the field, you know your body and you know what feels right and what doesnt feel right. When it comes to diabetes, its so important to trust your instincts.” Amber, 21, had DKA
Can Diabetic Ketoacidosis Be Prevented Or Avoided
If you have diabetes, there are some things you can do to watch for diabetic ketoacidosis. When youre sick, watch your blood sugar level very closely so it doesnt get too high or too low. Ask your doctor what your critical blood sugar level is. Most patients should watch their glucose levels closely when they are more than 250 mg per dL.
When youre sick or stressed, you should check your blood sugar level more often than normal . If your blood sugar reaches a critical level, check it every 1 to 2 hours. Ask your doctor if you should test your blood sugar level during the night.
You should also test your urine for ketones every few hours if youre sick, stressed, or if your blood sugar level is more than 250 mg per dL.
You should talk to your doctor to develop a plan if your blood sugar level gets too high. Make sure that you know how to reach your doctor in an emergency.
Recommended Reading: Ribbon Color For Diabetes
Should I Keep Taking Insulin When Im Sick
You should keep taking your insulin, even if you are too sick to eat. Your body needs insulin even if youre not eating. Ask your doctor whether its necessary to adjust your dose or take extra insulin.
If you use an insulin pump, keep a variety of supplies on hand. Make sure that you have short-acting insulin, long-acting insulin, and needles in case your pump is not working right. You also should have an emergency phone number to call for help with your pump.
Who Is At Risk For Developing Diabetic Ketoacidosis
People with type 1 diabetes who are not taking their insulin or are getting ill with an infection or other disease are at risk for diabetic ketoacidosis.
Usually it occurs in people who have type 1 diabetes that are at risk for diabetic ketoacidosis. Although it is rare in people with type 2 diabetes, it can occur.
Also Check: Insulin Secretion Would Be Highest
Who Does Diabetic Ketoacidosis Affect
Diabetic ketoacidosis can develop in people of any age who have diabetes or undiagnosed diabetes.
- Individuals who have undiagnosed Type 1 diabetes: For some people, diabetic ketoacidosis is how they find out that they have Type 1 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune disease in which your immune system attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in your pancreas. Oftentimes people are in DKA when they’re first diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes because they no longer have enough insulin in their body to use glucose for energy. Type 1 diabetes typically develops during childhood or adolescence but can also develop in adulthood. You can develop Type 1 diabetes even if you dont have a family history of diabetes. Approximately 20% to 40% of DKA cases are from people who are newly diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes.
- Individuals who have Type 1 diabetes: People who have been diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes can develop DKA at any point throughout their life if their body does not get as much insulin as it needs.
- Individuals who have Type 2 diabetes: Although its not as common, people with Type 2 diabetes who have ketosis-prone diabetes can develop diabetic ketoacidosis .
What Are The Causes Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis usually happens to people with type 1 diabetes. It is triggered by low insulin levels, most often caused by one of the following:
- Missed doses of insulin.
- Insulin not being given correctly. This may be because of problems with your insulin pen, insulin cartridge or insulin pump.
- An illness or hormonal change. Insulin in your body may not work well if you have an infection such as gastroenteritis , urinary tract infection, a chest infection or skin infection, or if you have stress or are pregnant. This is due to your body producing higher levels of other hormones, such as adrenaline or cortisol, which reduce the effect of insulin.
- An injury or surgery.
People with type 2 diabetes are at risk if they are taking empagliflozin.
Other causes include:
- alcohol or drug abuse, in particular, cocaine
- certain medicines, such as corticosteroids and some diuretics.
Sometimes there is no obvious cause.
Don’t Miss: Metformin Medicine Side Effects
Treatments For Diabetic Ketoacidosis
DKA is usually treated in hospital.
Treatments for DKA include:
- insulin, usually given into a vein
- fluids given into a vein to rehydrate your body
- nutrients given into a vein to replace any you’ve lost
You’ll also be closely monitored for any life-threatening problems that can happen, such as problems with your brain, kidneys or lungs.
You can leave hospital when you’re well enough to eat and drink and tests show a safe level of ketones in your body. It’s common to stay in hospital for around 2 days.
Before leaving hospital, ask to speak to a diabetes nurse about why you got DKA and what you can do to stop it happening again.
Page last reviewed: 01 May 2020 Next review due: 01 May 2023
Check Your Blood Sugar And Ketone Levels
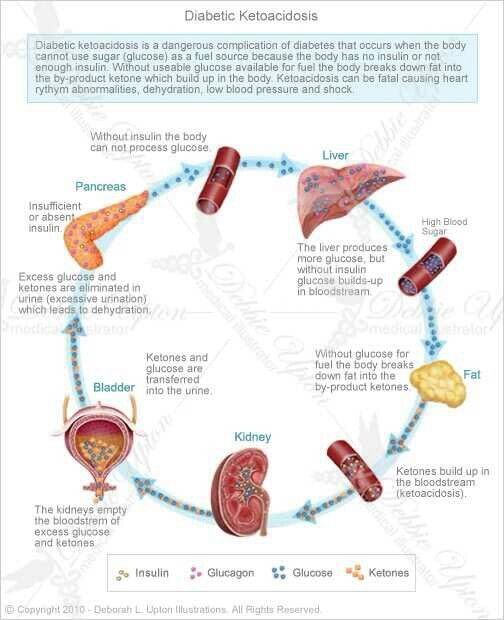
Check your blood sugar level if you have symptoms of DKA.
If your blood sugar level is 11mmol/L or above, and you have a blood or urine ketone testing kit, check your ketone level.
If you do a blood ketone test:
- lower than 0.6mmol/L is a normal reading
- 0.6 to 1.5mmol/L means you’re at a slightly increased risk of DKA and you should test again in 2 hours
- 1.6 to 2.9mmol/L means you’re at an increased risk of DKA and should contact your diabetes team or GP as soon as possible
- 3mmol/L or above means you have a very high risk of DKA and should get medical help immediately
If you do a urine ketone test, a result of more than 2+ means there’s a high chance you have DKA and you should get medical help immediately.
You May Like: Side Effects Of Diabetes Medication Metformin
Diabetic Ketoacidosis : Symptoms And Prevention
Diabetic Ketoacidosis is a serious condition in which an insulin-deprived body seeks energy from stored fat. Ketones are caused by the breakdown of fat when there isnt enough insulin to allow the glucose into your cells for energy. When ketones build up, the result is acidosis . If not treated, this can lead to death. Usually blood glucose levels are elevated but not always. This article will help you be aware of the symptoms of DKA, what signs to look for and how to prevent it.
Rare Symptoms Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
DKA-related deaths are usually low among those who receive standardized treatment, which includes:
- Administration of insulin
- Correction of hydroelectrolytic disorders
- Management of the triggering factor, which is often cessation of insulin therapy, an infection, or a heart attack
The symptoms of DKA develop quickly and can lead to a coma. It is unknown why the progression to rare symptoms like coma happens more quickly in some people than others, but those who develop DKA following an infection may be at higher risk.
Additionally, cerebral edema is a rare but severe complication that occurs predominantly in children. Symptoms of cerebral edema include:
- Headache
Recommended Reading: How Long Do Type 2 Diabetics Live
What Are The Risk Factors For Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Risk factors for developing DKA include:
- Family history of diabetes: If you have a family history of diabetes, you could be at risk for developing Type 1 diabetes. If you have undiagnosed Type 1 diabetes and miss the early signs and symptoms of the disease, you could develop DKA.
- Family history of autoimmune diseases: If you have a family history of autoimmune diseases, you could be at risk for developing Type 1 diabetes. Undiagnosed Type 1 diabetes could result in DKA.
- Poorly managed Type 1 diabetes: If you have Type 1 diabetes and have frequent high blood sugar, don’t take your insulin regularly and dont check your blood sugar often, you’re at a higher risk of developing DKA.
- Poorly managed Type 2 diabetes: DKA is not as common in people with Type 2 diabetes, but those who have ketosis-prone Type 2 diabetes can develop DKA. This is more likely to happen if you have frequent high blood sugar, don’t take your medication regularly and don’t check your blood sugar often.
How Can You Check For High Ketone Levels In The Blood
If you have diabetes or symptoms of DKA, your doctor may ask you to monitor your ketone levels at home every 4-6 hours using at-home test kits.
Your doctor may also order a ketone test if:
- Your blood sugar levels are above 250 mg/dL for 2 days in a row
- You want to do heavy workouts and are at risk for diabetes complications
When doing a ketones in blood test at your doctors office, they will collect a blood sample from a vein in your arm and send it to a lab to check for ketone levels in your blood. Your doctor may also want to check for the presence of ketones in urine, blood sugar levels and HbA1C.
Read Also: Low Blood Pressure High Blood Sugar
What Are The Treatment Options Of Dka
Even if youre treated in a hospital, you should be aware of the treatment protocols. The aim of the treatment is to get you out of diabetic ketoacidosis as quickly as possible. So you will be given fluids, either orally or via I.V. so that your body is no longer dehydrated. Hydration is an important method to reduce hyperglycemia.
You will be given insulin so that your blood sugar levels normalize. These should be below 240mg/dL.
Electrolyte imbalance often occurs with DKA. As sodium and potassium levels are not normal, they can affect the functioning of your body. You will be given electrolytes, again via I.V.
Key takeaways:
- Diabetes invariably carries some risks diabetic ketoacidosis is a complication when you are severely hyperglycemic. It can occur if you have undiagnosed or poorly controlled diabetes.
- Familiarize yourself with the symptoms of DKA when you know what the signs of this complication are, you can take steps to save your health and prevent organ damage or worse.
- Always aim to keep blood sugar levels under control balance your insulin or medications, your diet, and activity levels and monitor your blood sugar levels regularly, several times a day, if necessary, so that you can manage your diabetes better.
Braden G. Barnett, MD
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a life-threatening complication of diabetes, and any delay in treatment can lead to death. The disorder can present with varied signs and symptoms and affects many organs thus, it is best managed by an interprofessional team dedicated to the management of patients with diabetes mellitus. The majority of patients first present to the emergency department, and it is here that the treatment usually starts.
The triage nurse has to be familiar with the signs and symptoms of DKA and immediately admit the patient and notify the emergency department physician. While the patient is being resuscitated, placed on a monitor, and having blood drawn, the intensivist and an endocrinologist should be consulted.
Immediate blood work is necessary to determine the state of ketoacidosis, and imaging may be necessary to rule out pneumonia. If the mental status is altered, a CT scan may be required, and thus the radiologist must be notified about the patient’s hemodynamic status. No patient with DKA should go unmonitored to a radiology suite.
The infectious disease expert and cardiologist should be consulted if there is suspicion of infection or MI as the trigger.
Outcomes
Read Also: Can Metformin Cause Heart Problems
Causes Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
There are several potential causes of diabetic ketoacidosis:
- Lack of insulin. You may develop DKA if your body doesnt produce enough insulin to help your cells use blood sugar for energy. If you lack insulin, it can lead to the breakdown of fat and the production of ketones.
- Too much blood sugar. You may develop DKA if your liver makes too much blood sugar.
- Lack of food. You dont eat enough food due to illness, making it difficult to manage your blood sugar levels.
- Infection. Bacterial or viral infection can trigger DKA, as your body needs more insulin than usual to fight the infection.
- Increased stress. Emotional or physical stress increases the production of stress hormone cortisol, which impacts how your body uses insulin.
- Insulin pump failure. The pump delivering insulin through a tube inserted under the skin can stop working, leading to DKA.
Complications Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
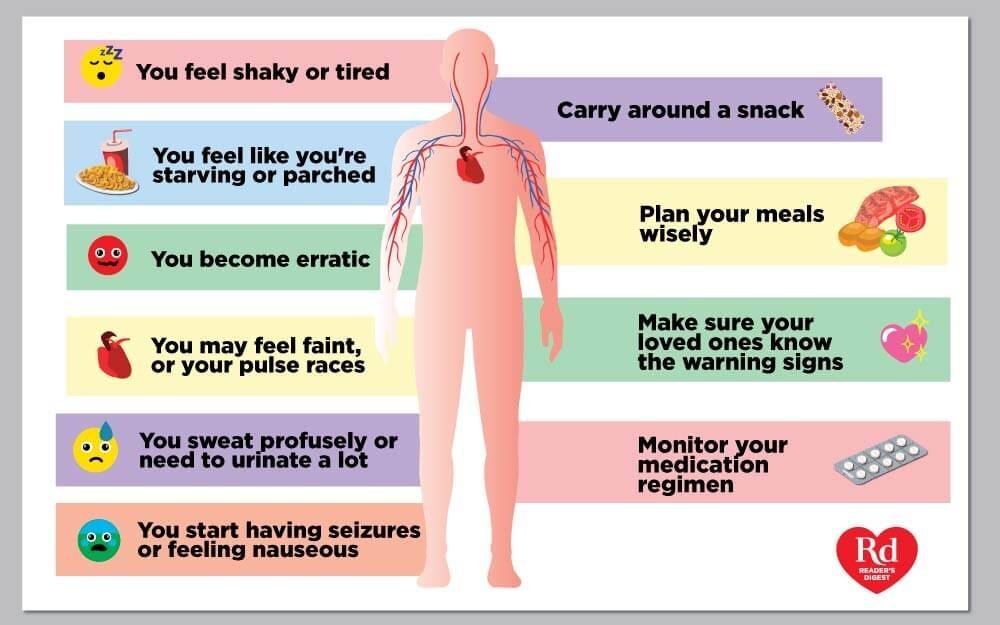
Complications from DKA result from the bodys inability to produce insulin.
When insulin is not present to break down sugars to use for energy, your body begins to break down fat instead. Fat breakdown produces ketones that spill into the urine and cause glucose to build up in the blood, acidifying the body.
Because sugar is not entering the bodys cells for energy breakdown, the sugar is processed by the kidneys and excreted through the urine. As a result, dehydration occurs and the blood becomes even more acidic.
When blood sugars are sky-high, hydrating with water or caffeine-free, sugar-free liquids may not be enough to ameliorate the problem, leading to sickness and hospitalization.
If left untreated, complications can include:
Low potassium levels are especially dangerous because potassium is needed for the heart to function properly.
When higher blood sugar and ketone levels damage the kidneys, potassium is lost, sometimes at a level that may negatively impact the heart. This is especially problematic in older adult populations with pre-existing heart conditions and those who are severely overweight because their heart cannot meet the increased physiological demands placed on the body.
You May Like: Banana Carbs Diabetes

