Is Lada Diabetes Hereditary
LADA is known to be an autoimmune disease which requires people with the condition to ultimately go onto insulin. Their findings primarily showed that LADA has more in common genetically with type 1 than type 2 diabetes. One exception to this was in the HNF1A locus which is associated with type 2 diabetes.
Also question is, what causes Lada diabetes?
Latent autoimmune diabetes in adults is a slow-progressing form of autoimmune diabetes. Like the autoimmune disease type 1 diabetes, LADA occurs because your pancreas stops producing adequate insulin, most likely from some “insult” that slowly damages the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Subsequently, question is, is Type 1.5 diabetes genetic? Type 1.5 diabetes can be triggered by damage done to your pancreas from antibodies against insulin-producing cells. Genetic factors may also be involved, such as a family history of autoimmune conditions. When the pancreas becomes damaged in type 1.5 diabetes, the body destroys pancreatic beta cells, as with type 1.
Regarding this, is Lada Diabetes rare?
LADA, diabetes is rare and known as late-onset diabetes. Most adults diagnosed with LADA are older than 30 years of age. It’s progression is slow sometimes causing a misdiagnosis of Type 2 diabetes. This can take anywhere from a few months after diagnosis to several years.
What are the symptoms of Lada?
The first symptoms of LADA include:
You May Like Also
Do I Have Other Treatment Options For My Type 1 Diabetes
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases has played an important role in developing artificial pancreas technology. An artificial pancreas replaces manual blood glucose testing and the use of insulin shots. A single system monitors blood glucose levels around the clock and provides insulin or a combination of insulin and glucagon automatically. The system can also be monitored remotely, for example by parents or medical staff.
In 2016, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved a type of artificial pancreas system called a hybrid closed-loop system. This system tests your glucose level every 5 minutes throughout the day and night through a continuous glucose monitor, and automatically gives you the right amount of basal insulin, a long-acting insulin, through a separate insulin pump. You still need to manually adjust the amount of insulin the pump delivers at mealtimes and when you need a correction dose. You also will need to test your blood with a glucose meter several times a day. Talk with your health care provider about whether this system might be right for you.
The illustration below shows the parts of a type of artificial pancreas system.
Starting in late 2016 and early 2017, the NIDDK has funded several important studies on different types of artificial pancreas devices to better help people with type 1 diabetes manage their disease. The devices may also help people with type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes.
Bdiseases With An Immune Component
The immune disorders encompass arthritis, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease , systemic lupus erythematosus , chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , asthma, allergies, and atopic dermatitis.
Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus , atherosclerosis, and cancer also have an immune component. Type 1 diabetes arises from the destruction of beta cells of the pancreas by white blood cells . In atherosclerosis, the infiltration of macrophages in the coronary artery results in atherosclerotic plaques .
A distinguishing feature of cancer, on the other hand, is absence of an immune response, where this absence results from the fact that antigens of tumor cells are identical to, or have structures very similar to, antigens of normal host cells.
Immune disorders such as multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis are classified as autoimmune diseases because pathological lesions result from immune attack against the hosts own antigens. Other immune disorders, such as asthma and allergies, are merely classed as inflammatory disorders, because the pathology does not involve attack against specific host antigens. Inflammatory disorders also encompass collateral damage to the liver from an overly active immune system during immune response against hepatitis C virus.
Ji Qiu, Karen S. Anderson, in, 2013
Read Also: What Is The Lowest Dose Of Metformin
What Is Autoimmune Gastritis
Autoimmune gastritis, which can also be called Autoimmune Metaplastic Atrophic Gastritis or Type A Gastritis, is a chronic inflammatory disease. Having Type 1 diabetes increases the probability of being diagnosed with autoimmune gastritis 3-5 times more than the average person an estimated 6%-10% of the Type 1 diabetes population also has autoimmune gastritis. It is more common in older adults and is more common in women than men.
Autoimmune gastritis is an autoimmune disease in which the stomach deteriorates because the immune system attacks the healthy cells of the stomach lining. It affects the upper two-thirds of the stomach because the antibody that the body is mistakenly producing binds to a specific cell in that area of the stomachs inner lining. These cells, the parietal cells, loose their ability to effectively produce the hydrochloric acid that they are supposed to. This means that people with gastritis are unable to efficiently absorb the vitamin B12 and iron, which results in iron-deficiency anemia and vitamin B12 deficiency and can ultimately lead to pernicious anemia.
The Association Of Autoimmune Diseases With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus In Children Depends Also By The Length Of Partial Clinical Remission Phase
Gulsum Ozen
1Department of Pediatrics, University of Health Science, Ankara Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
2Regional Centre for Pediatric Diabetes, Department of Pediatrics, University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, Naples, Italy
3Department of Molecular Medicine and Biotechnology, CEINGE, Naples, Italy
4Faculty of Medicine, Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey
Abstract
1. Introduction
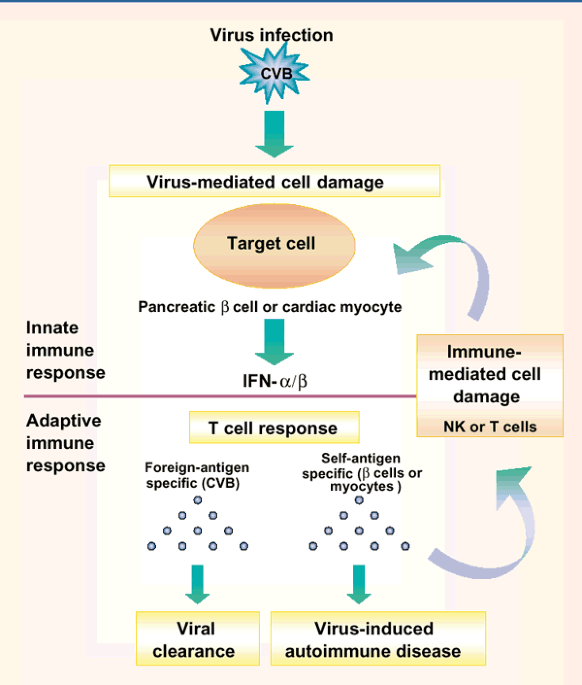
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a chronic illness known as insulin-dependent diabetes and characterized by irreversible, autoimmune, insulin producing islet -cell destruction. Exogenous insulin administration is the only treatment for patients.
The cause of Type 1 diabetes mellitus is unknown, although genetic, immunologic, and environmental factors are known to increase the risk for its development. These suspected factors are mainly determined by the HLA genes which are located on chromosome 6, viral infections such as German measles, coxsackie and mumps, geography, family history, diet, stress events, perinatal factors, and other autoimmune conditions such as Hashimoto thyroiditis, multiple sclerosis, pernicious anemia, Sjogrens syndrome, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, vitiligo, dermatitis herpetiformis, Addisons disease, and systemic lupus erythematosus.
2. Material and Methods
Celiac disease was diagnosed by elevated levels of certain antibodies and intestinal endoscopic biopsy.
3. Results
4. Discussion
| Mean |
Read Also: Loe Blood Pressure Diabetes
What Causes Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction that destroys the cells in the pancreas that make insulin, called beta cells. This process can go on for months or years before any symptoms appear.
Some people have certain genes that make them more likely to develop type 1 diabetes, though many wont go on to have type 1 diabetes even if they have the genes. Being exposed to a trigger in the environment, such as a virus, is also thought to play a part in developing type 1 diabetes. Diet and lifestyle habits dont cause type 1 diabetes.
What Are The Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes are serious and usually happen quickly, over a few days to weeks. Symptoms can include
- increased thirst and urination
- trouble breathing
- trouble paying attention or feeling confused
DKA is serious and dangerous. If you or your child have symptoms of DKA, contact your health care professional right away, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
Don’t Miss: Normal A1c Range For Seniors
Managing Blood Sugars On A Gluten
Many nutritious whole foods are naturally gluten-free. These include vegetables, fruits, gluten-free whole grains , most cheeses, yogurt, legumes, nuts, seeds, eggs, chicken, meat, fish, turkey, etc.
If you have T1D, you’ll need to know the carbohydrate amounts of all foods and aim to choose options that contain fiber, fat, and protein for blood sugar control. If you need help with meal planning, reach out to a registered dietitian specializing in T1D and CD.
Type 1 Diabetes Symptoms
Signs are often subtle, but they can become severe. They include:
- Extreme thirst
- Heavy, labored breathing
- Frequent infections of your skin, urinary tract, or vagina
- Crankiness or mood changes
- Bedwetting in a child whoâs been dry at night
Signs of an emergency with type 1 diabetes include:
- Shaking and confusion
- Loss of consciousness
You May Like: Insulin Medication Side Effects
Our Type 1 Diabetes Research
Our researchers are working to improve the prevention and treatment of type 1 diabetes. Their goals are to:
- Understand why immune cells attack insulin-producing cells.
- Understand the environmental factors that predispose to type 1 diabetes.
- Develop and trial new ways to prevent type 1 diabetes.
- Develop immune therapies to treat type 1 diabetes.
- Develop strategies to regenerate insulin-producing cells from stem cells as a cure for type 1 diabetes.
- Improve the success of pancreas transplantation as a cure for type 1 diabetes.
- Develop novel insulin analogues that will make life easier for patients with type 1 diabetes.
What Happens In The Body Of A Person With T1d
People are typically diagnosed with T1D after showing symptoms . As the body becomes incapable of creating insulin, which allows the body to use the sugar found in food, called glucose, as energy, people with T1D must work closely with their endocrinologists to determine the insulin doses and lifestyle changes needed to manage their blood-sugar levels.
If not treated properly, people with T1D are vulnerable to health issues ranging from minor to severe. Most people with T1D spend the majority of their time with blood-glucose levels outside the recommended healthy range, which can lead to potentially deadly episodes of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia . Chronic high blood sugar often causes devastating health complications later in life, including blindness, kidney failure, heart disease and nerve damage that can lead to amputations.
Don’t Miss: Diabetic Getting Dizzy
Symptoms Of Celiac Disease
Celiac disease can be hard to diagnose, as it often presents differently in different people and at different ages. While some people with CD have no symptoms at all, others can experience an array of symptoms that are gastrointestinal or throughout the body. Some common symptoms in kids include:
- Abdominal bloating and pain
- Canker sores inside the mouth
- Dermatitis herpetiformis
What Are The Most Common Autoimmune Diseases
Of the 80-plus autoimmune disorders, the most common ones include:
- Addisons disease immune system attacks the adrenal gland, disrupting production of steroid hormones aldosterone and cortisol.
- Coeliac disease autoimmune attack on substances found inside gluten damages the surface of the small bowel, disrupting the bodys ability to take in essential nutrients from food
- Hashimotos thyroiditis or Hashimotos disease similar to Graves disease, but this time damage to the thyroid gland lead to an underactive thyroid gland
- Multiple sclerosis myelin sheaths which protect the nerve fibres carrying messages to and from the brain are targeted by the immune system, causing behind scarring .
- Reactive arthritis immune system is tricked into thinking a previous infection is still present and attacks healthy tissue, causing it to become inflamed.
- Rheumatoid arthritis cells that line your joints are targeted by the autoimmune reaction, causing joints and surrounding tissues to become swollen, stiff and painful.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus immune system targets healthy tissue, causing inflammation of the skin and joints, and can affect internal organs
- Type 1 diabetes immune system destroys cells within the pancreas that produce the blood sugar-regulating hormone insulin.
You May Like: Mirico Low Carb Bread
Symptoms And Risk Factors
It can take months or years for enough beta cells to be destroyed before symptoms of type 1 diabetes are noticed. Type 1 diabetes symptoms can develop in just a few weeks or months. Once symptoms appear, they can be severe.
Some type 1 diabetes symptoms are similar to symptoms of other health conditions. Dont guessif you think you could have type 1 diabetes, see your doctor right away to get your blood sugar tested. Untreated diabetes can lead to very seriouseven fatalhealth problems.
Risk factors for type 1 diabetes are not as clear as for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes, though family history is known to play a part.
A Fifth Of People With Type 1 Diabetes May Have Additional Autoimmune Disease
medwireNews: People with type 1 diabetes should be screened for other autoimmune diseases, a Finnish research team suggests, after finding these individuals particularly vulnerable to additional disorders.
The study of more than 4000 Finnish individuals with type 1 diabetes revealed that 22.8% had at least one additional autoimmune disease, with the most prevalent being hypothyroidism, celiac disease, and hyperthyroidism.
And women were more than twice as likely as men to have at least one additional autoimmune disease, at a corresponding 31.6% versus 14.9%, the researchers note in Diabetes Care.
The risk for celiac disease was associated with early-onset diabetes, with the risk increasing by 1.5% with each decreasing year at onset. Children diagnosed before the age of 10 years were at greatest risk, being 1.38 times more likely to have celiac disease than other diabetic individuals.
Screening for celiac disease is important during childhood, since age 10 years at onset of but not ageing, per se, increases the risk of celiac disease, comment Per-Henrik Groop and co-workers.
Conversely, they note that the risk for hypothyroidism increased by 1.7% with each additional year of diabetes onset, and by 1.3% with each additional year of age.
FinnDiane participants had a mean age of 51.4 years by the end of follow-up or death in 2015 and a median diabetes duration of 35.5 years.
Also Check: Insulin Alpha Cells
Animal Models In Dm Type 1 Research
Animal models are used in autoimmune diabetes research to understand the pathogenesis and etiology of this disease, and to find and test predictive biomarkers and therapeutic interventions. Currently available models of T1D can be divided into spontaneously autoimmune, chemically induced, virus induced and genetically induced.
Spontaneous autoimmune
- Non-obese diabetic mouse
The NOD mouse is the best known and most widely used animal model for type 1 DM research. It is an inbred, genetically well characterized mouse strain that spontaneously develops T1D. The onset of insulitis occurs at 3â4 weeks of age. The islets of Langerhans are infiltrated by CD4+, CD8+ T lymphocytes, NK cells, B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages and neutrophils, similar to the disease process in humans. Insulitis leads to destruction of β-cells, resulting in the apparent occurrence of T1D, which varies by sex. The incidence is about 60-80% in females and 10-30% in males. In addition to sex, breeding conditions, gut microbiome composition or diet also influence the onset of T1D. NOD Mice are used to understand the pathogenesis and etiology of the disease, to identify novel autoantigens and biomarkers or to test new intervention strategies.
- BioBreeding Diabetes-Prone rat
- LEW -1AR1 / -iddm rat
Chemically induced
Genetically induced
Virally induced
What Medicines Do I Need To Treat My Type 1 Diabetes
If you have type 1 diabetes, you must take insulin because your body no longer makes this hormone. Different types of insulin start to work at different speeds, and the effects of each last a different length of time. You may need to use more than one type. You can take insulin a number of ways. Common options include a needle and syringe, insulin pen, or insulin pump.
Some people who have trouble reaching their blood glucose targets with insulin alone also might need to take another type of diabetes medicine that works with insulin, such as pramlintide. Pramlintide, given by injection, helps keep blood glucose levels from going too high after eating. Few people with type 1 diabetes take pramlintide, however. The NIH has recently funded a large research study to test use of pramlintide along with insulin and glucagon in people with type 1 diabetes. Another diabetes medicine, metformin, may help decrease the amount of insulin you need to take, but more studies are needed to confirm this. Reseachers are also studying other diabetes pills that people with type 1 diabetes might take along with insulin.
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can occur if you take insulin but dont match your dose with your food or physical activity. Severe hypoglycemia can be dangerous and needs to be treated right away. Learn more about hypoglycemia and how to prevent or treat it.
Don’t Miss: Banana Carbs Diabetes
Is Type 1 Diabetes Is Preventable
typediabetespreventabletype 1 diabetesType 1 diabetes
Similarly, what is the life expectancy of a Type 1 diabetic?
about 66 years77 yearsabout 68 years81 years
Can you be cured of type 1 diabetes?
curediabetestype 1diabetestypediabetescan
How do you control diabetes type 1?
type 1 diabetesdiabetessibling
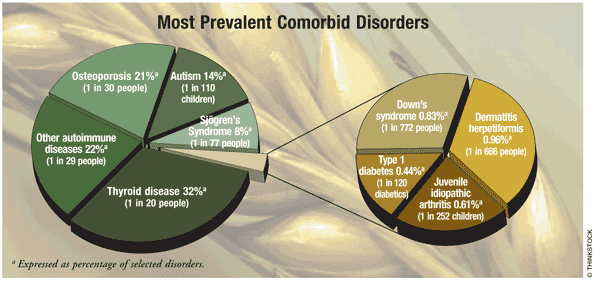
Type 1 Diabetes With Other Autoimmune Diseases
Editors Note: This content has been verified by Marina Basina, MD, a Clinical Associate Professor at Stanford University. Shes a clinical endocrinologist and researcher with a focus on diabetes management and diabetes technology. Dr. Basina is an active member of multiple medical advisory boards and community diabetes organizations, and she is on the Beyond Type 1 Science Advisory Council.
People with Type 1 diabetes, an autoimmune disease, are more likely to have a co-occurring autoimmune disorder. An autoimmune disease means that your immune system sees your bodys own tissue as foreign invaders and attacks itself. For example, if you have Type 1, your body mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing cells in your body. The reason that co-occurring autoimmune disorders are so common isnt exactly known, although we do know that genetics play a significant role.
Because we know that having Type 1 puts you at a higher risk of developing other autoimmune diseases, its important to be aware of what the signs and symptoms are. The following are warning signs that are common for all autoimmune diseases, including Type 1:
- Fever
Also Check: Insulin Secretion Would Be Highest

