Right Before Lunch Or Dinner
Checking your blood sugar before your next meal can tell you two things:
- How well your body and/or medication dosages handled your last meal
- How well your body and/or medication dosages handled your blood sugar in the last few hours without food being digested.
Keep in mind that some meals take longer to digest than others. High-fat meals that are also high in carbohydrates can take many hours to digest, affecting your blood sugar for many hours, too.
A high blood sugar level before lunch or dinner could suggest:
- What you ate or drank at your last meal was more than your body could handle on your current diabetes management regimen.
- Your body may need some extra help from a diabetes medication.
- Your current diabetes medications may need a change in dosage.
- Your current diabetes medication may not be the right fit for you.
- Its time to try a different type of diabetes medication.
- Your overall insulin production or insulin resistance level has changed and your body needs more support from a new or current medication.
A low blood sugar level before your next meal could suggest:
- Youre getting too much of a certain diabetes medication .
- Your insulin sensitivity or insulin production has improved, which means your medication dosages need to be adjusted by your healthcare team.
Talk to your healthcare team about making any adjustments to your diabetes regimen to help you achieve your blood sugar goals.
What Are Blood Sugar Targets
A blood sugar target is the range you try to reach as much as possible. These are typical targets:
- Before a meal: 80 to 130 mg/dL.
- Two hours after the start of a meal: Less than 180 mg/dL.
Your blood sugar targets may be different depending on your age, any additional health problems you have, and other factors. Be sure to talk to your health care team about which targets are best for you.
How Many Times Do You Really Check Your Blood Sugars At The Early Stages Of Diabetes
You dont really have to check too many times. If your blood sugars are not very uncontrolledMeaning your A1c is below 7%, you can check it once a day in the mornings, just to keep an eye on your blood sugars overall. As we mentioned occasionally you can check it after meals to see where your blood sugars are. You can do that occasionally after meals. Lets say you think that you had too much carbs, and you want to check. This will help you understand how food affects you and so forth. For example,if your overall well controlled and youre waking up with you know say 100 Or 110 and then occasionally you check after meals and you never go more than 160 170 after meals then youre pretty well controlled.
Also Check: Side Effects Of Metformin 500 Mg
Overcoming Barriers To Blood Sugar Monitoring
Some people find it difficult to incorporate blood sugar monitoring into their daily or weekly routines. There are lots of reasons for this:
- If blood sugar readings are consistently high, it can be upsetting
- Monitoring seems pointless
- Finger pricks to get a drop of blood are uncomfortable
- Monitoring is inconvenient
Blood sugar monitoring is an important tool that can help you manage your diabetes effectively and prevent or delay complications.
Get The Best Use Out Of Your Strips
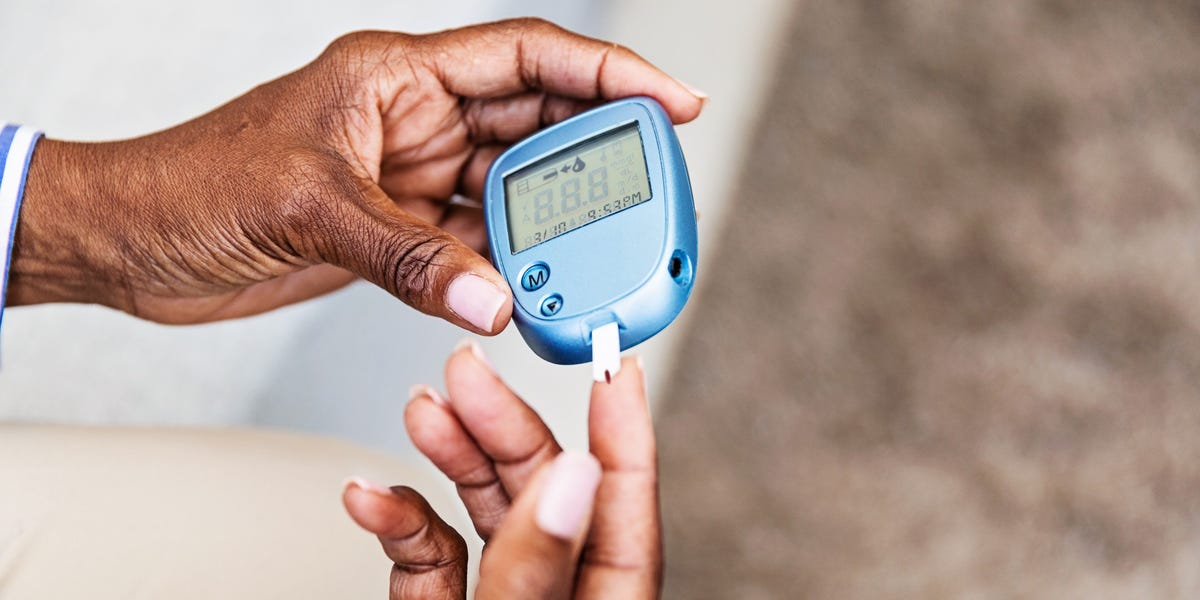
There are many times you could check. How often should you? “Everyone wants black-and-white answers,” says Mary M. Austin, R.D., CDE. “It’s not how often you do it it’s what you do with the information.”
Endocrinologist Tom Elasy says people and health care providers need to distinguish between the intensification stages of diabetes — when diabetes is newly diagnosed or when you and your provider make changes in your treatment plan — and the maintenance phase — when you are reaching your glucose goals and things are in a pretty steady state.
How to Make the Best Use of Your Strips: Medicare, for people who have Part B, covers 100 test strips every three months for a PWD who doesn’t take insulin.
For someone newly diagnosed with type 2, how can you make the best use of your strips? According to Elasy, use more strips when you’re diagnosed and learning about the impact of what you eat, your physical activity, and medications on your glucose levels. Once you get a sense of your fluctuating glucose levels, testing doesn’t need to happen as often. As type 2 diabetes progresses over time, renewed, more frequent testing often is necessary.
People who do not take any glucose-lowering medications might want to check at least once or twice a week just to keep track. It is recommended that you do monitor and use your allotted strips wisely. Monitoring can have a powerful, positive effect on how you subsequently eat or the likelihood that you’ll take a walk, Elasy notes.
You May Like: Does Squeezing Finger Affect Blood Sugar Reading
Monitoring Your Blood Sugar
Regular blood sugar monitoring is the most important thing you can do to manage type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Youll be able to see what makes your numbers go up or down, such as eating different foods, taking your medicine, or being physically active. With this information, you can work with your health care team to make decisions about your best diabetes care plan. These decisions can help delay or prevent diabetes complications such as heart attack, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, and amputation. Your doctor will tell you when and how often to check your blood sugar levels.
Most blood sugar meters allow you to save your results and you can use an app on your cell phone to track your levels. If you dont have a smart phone, keep a written daily record like the one in the photo. You should bring your meter, phone, or paper record with you each time you visit your health care provider.
Sometimes having high blood sugar can feel like a test you didnt pass. But numbers are just numbers. Think of them instead as information. Did a certain food or activity make your levels go up or down? Armed with that knowledge, you can make adjustments and get closer to your target range more often.
How Do Carbs Affect Blood Sugar
Carbs in food make your blood sugar levels go higher after you eat them than when you eat proteins or fats. You can still eat carbs if you have diabetes. The amount you can have and stay in your target blood sugar range depends on your age, weight, activity level, and other factors. Counting carbs in foods and drinks is an important tool for managing blood sugar levels. Make sure to talk to your health care team about the best carb goals for you.
Recommended Reading: Diabetic Feeling Dizzy
Why Monitor Your Blood Sugar Levels
Whether you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes, monitoring blood sugar is an important part of your management regimen. Blood sugar monitoring provides a lot of useful information, as it can help you:
- Judge how well youre reaching your blood sugar targets
- Know how diet and exercise affect your blood sugar levels
- Understand how other factors affect your blood sugar
- Monitor the effect of your diabetes medications on your blood sugar levels
- Identify highs and lows
Don’t Forget These Important Times To Test
You should also test your blood sugar if you:
Are sick or have an infection. Illness can send blood sugar levels up. Do a check every two to four hours. If it’s:
Over 250 mg/dl, check your urine for ketones if ketones are present in more than trace amounts, call your doctor.
* Over 250 mg/dl for more than six hours, call your doctor.
* Over 350 mg/dl even once, call your doctor.
Start a new blood glucose-lowering medication or change the dose of one. A prescription or over-the-counter medicine for a condition other than diabetes may affect blood sugar levels. Steroids are one example.
Are under a lot of stress. Emotional stress may lead to higher blood sugar numbers. Exercise — even just a walk around the block — can help reduce stress and glucose levels.
Feel as though your blood sugar level is too low. If your meter confirms it with a number of 70 mg/dl or less, eat 15-20 grams of pure glucose or drink 1/2 cup fruit juice or regular soda. Wait 15 minutes and check again to make sure it has come back into the normal range.
You May Like: Metformin Most Common Side Effects
When Should You Check Your Blood Sugar
People with diabetes are encouraged to check their blood sugars often, and with the latest technology like continuous glucose monitors , the frequency of checking has increased more than ever.
But what if youre using a glucometer, lancet device, and test strips? How often, and maybe more importantly, exactly when should you check your blood sugar?
This article will outline the importance of checking your blood sugar, how often, and when you really should check for better diabetes management.
How Can I Treat High Blood Sugar
Talk to your doctor about how to keep your blood sugar levels within your target range. Your doctor may suggest the following:
- Be more active. Regular exercise can help keep your blood sugar levels on track. Important: dont exercise if ketones are present in your urine. This can make your blood sugar go even higher.
- Take medicine as instructed. If your blood sugar is often high, your doctor may change how much medicine you take or when you take it.
- Follow your diabetes meal plan. Ask your doctor or dietitian for help if youre having trouble sticking to it.
- Check your blood sugar as directed by your doctor. Check more often if youre sick or if youre concerned about high or low blood sugar.
- Talk to your doctor about adjusting how much insulin you take and what types of insulin to use.
Recommended Reading: Metformin Blood Pressure Diabetes
Why Is My Blood Sugars Up And Down In The Mornings
You will never wake up with the same blood sugar. So forget about you trying to keep your blood sugar like on a flat line. That simply doesnt happen. You dont see a flat line in any human body. The moments you see a flat line means you are dead. Anyway, everything constantly is changing. Everything affects your blood sugar. So, its not like a heart rate. Even your heart rate gets up and down a little bit daily. A normal person wakes up around eighty or ninety blood sugar, but when youre diabetic you know theres a lot of factors playing into it. If you are waking up with a blood sugar of lets say less than 120 thats great. But we dont want to start at 200 at nighttime and wake up at 120 in the morning. That is not necessarily always good either when you are on insulin. So we want to make sure that your blood sugar is similar overnight on basal insulin.
What a lot of people do wrong is that they try to give too much basal insulin to try to control morning numbers. Well, thats a problem. Because we dont want you to go down like this overnight. Thats very dangerous. So, if you want to keep your blood sugar very stable when youre sleeping you want to keep it as straight as possible. Now if there is a 20-30 plus-minus range is ok. This difference is very acceptable. Because thats not going to put you to danger zone.
Whats My Target Range
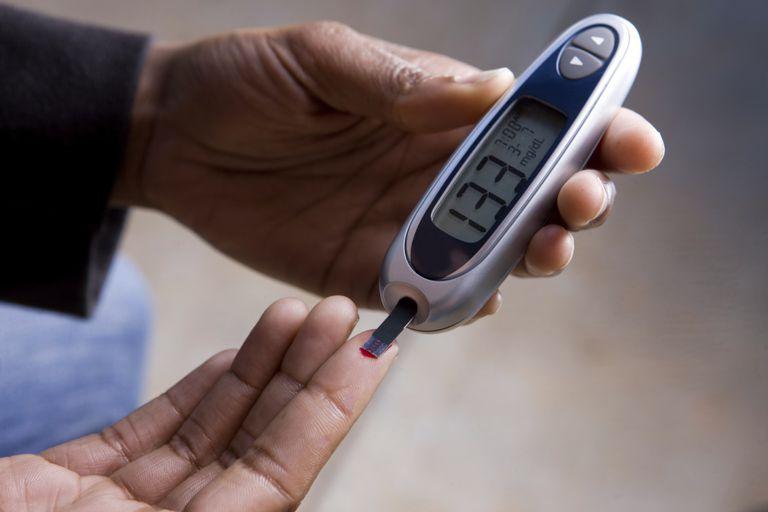
You might be asking, what’s the normal range for blood sugar levels? The answer is, there is a healthy range that you should ideally be aiming for. The infographics above show the general guidelines, but your individual target range for your blood sugar levels may be different. Youll healthcare team will agree with you what it is.
Youll get different readings at different times of the day, depending on things like what youve eaten and how much you are moving around. Heres a guide to help you get started on finding your target range:
If youre a child with Type 1 diabetes
- when you wake up and before meals: 4 to 7mmol/l
- after meals: 5 to 9mmol/l
If youre an adult with Type 1 diabetes
- when you wake up and before meals: 5 to 7mmol/l
- before meals at other times of the day: 4 to 7mmol/l
If you have Type 2 diabetes
- before meals: 4 to 7mmol/l
- two hours after meals: less than 8.5mmol/l
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Tattoos If Your Diabetic
Ways To Test Your Blood Sugar
Traditional home glucose monitoring
You prick your finger with a small, sharp needle called a lancet, put a drop of blood on a test strip, and then place the strip into a meter that displays your blood sugar levels. Record the test results so you can share them with your doctor. Based on your results, the two of you may adjust your diet, exercise, or medication.
Meters vary in features, portability, speed, size, cost, and readability . Devices deliver results in less than 15 seconds and store this information for future use.
Some meters also calculate an average blood sugar level over a span of time. Some also feature software kits that take information from the meter and display graphs and charts of your past test results. Blood sugar meters and strips are available at your local pharmacy.
Meters that test other parts of your body
Some devices let you test your upper arm, forearm, base of the thumb, and thigh.
These results may differ from the blood sugar levels gotten from a fingertip stick. Levels in the fingertips show changes more quickly. This is especially true when your sugar is changing fast, like after a meal or after exercise.
If you have symptoms of low blood sugar, donât rely on test results from other parts of your body.
Continuous glucose monitoring system
You’ll still need to check your levels throughout the day continuous glucose monitoring doesn’t replace that. It gives your doctor more information about trends that self-checking might not show.
How Can I Check My Blood Sugar
Use a blood sugar meter or a continuous glucose monitor to check your blood sugar. A blood sugar meter measures the amount of sugar in a small sample of blood, usually from your fingertip. A CGM uses a sensor inserted under the skin to measure your blood sugar every few minutes. If you use a CGM, youll still need to test daily with a blood sugar meter to make sure your CGM readings are accurate.
Don’t Miss: Nondiabetic Hyperglycemia Symptoms
What If I Cant Get A Drop Of Blood For A Fingerstick
If you want to get blood from your fingertip, try washing your hands in hot water to get the blood flowing. Then dangle your hand below your heart for a minute. Prick your finger quickly and then put your hand back down below your heart. You might also try slowly squeezing the finger from the base to the tip.
How To Check Blood Sugar
A glucometer is used to determine blood sugar levels. Only a drop of blood is needed. People with diabetes will use a specialized pen to prick a finger. The blood droplet will is placed on a disposable test strip and the glucometer relays the results on a computerized screen. Blood can be taken from any part of the body however, the results are most accurate when taken from the fingers.
Continuous glucose monitors are another option. A small sensor with a needle is attached to the skin. The sensor reads the blood glucose levels every few minutes. The information is relayed back to a data receiver. The data receiver can be carried in a pocket or purse. Alarms can be set to go off if glucose reaches certain levels. Many factors can affect insulin levels. CGMs relay more accurate results than finger pricks secondary to continuous glucose monitoring around the clock.
Also Check: Why Does My Glucose Go Up At Night
What Are The Target Ranges
Blood glucose targets are individualized based on:
- duration of diabetes
- conditions a person may have
- cardiovascular disease or diabetes complications
- hypoglycemia unawareness
- individual patient considerations
The American Diabetes Association suggests the following targets for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. A1C targets differ based on age and health. Also, more or less stringent glycemic goals may be appropriate for each individual.
- A1C: Less than 7%A1C may also be reported as eAG: Less than 154 mg/dL
- Before a meal : 80130 mg/dL
- 1-2 hours after beginning of the meal *: Less than 180 mg/dL
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis
If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms.
When too many ketones are produced too fast, they can build up in your body and cause diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA. DKA is very serious and can cause a coma or even death. Common symptoms of DKA include:
- Fast, deep breathing.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Stomach pain.
If you think you may have DKA, test your urine for ketones. Follow the test kit directions, checking the color of the test strip against the color chart in the kit to see your ketone level. If your ketones are high, . DKA requires treatment in a hospital.
DKA happens most in people with type 1 diabetes and is sometimes the first sign of type 1 in people who havent yet been diagnosed. People with type 2 diabetes can also develop DKA, but its less common.
You May Like: Metformin Dosage For Diabetes
What Else Can I Do To Help Manage My Blood Sugar Levels
Eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular physical activity can all help. Other tips include:
- Keep track of your blood sugar levels to see what makes them go up or down.
- Eat at regular times, and dont skip meals.
- Choose foods lower in calories, saturated fat, trans fat, sugar, and salt.
- Track your food, drink, and physical activity.
- Drink water instead of juice or soda.
- Limit alcoholic drinks.
- For a sweet treat, choose fruit.
- Control your food portions .

