What Can Cause Low Blood Sugar Levels
Some things that can make low blood sugar levels more likely are:
- skipping meals and snacks
- not eating enough food during a meal or snack
- exercising longer or harder than usual without eating some extra food
- getting too much insulin
- not timing the insulin doses properly with meals, snacks, and exercise
Also, some things may increase how quickly insulin gets absorbed into the bloodstream and can make hypoglycemia more likely. These include:
- taking a hot shower or bath right after having an insulin injection increases blood flow through the blood vessels in the skin, which can make the insulin be absorbed more quickly than usual
- injecting the shot into a muscle instead of the fatty layer under the skin
- injecting the insulin into a part of the body used a lot in a particular sport .
All of these situations increase the chances that a person may get hypoglycemia.
page 1
Exercise Food And Alcohol
For people with type 1 diabetes, maintaining the correct blood glucose level involves balancing how much insulin you inject, the amount of food you eat, and how much energy you burn during exercise.
Hypoglycaemia may occur if you’ve taken your dose of insulin as usual, but your carbohydrate intake is lower than normal or has been used up more quickly. This may happen if you delay or miss a meal or snack, don’t eat enough carbohydrate, or exercise more than usual.
People with diabetes who’ve drunk too much alcohol, or drank alcohol on an empty stomach, can also get hypoglycaemia.
However, it’s not always possible to identify why a particular episode of hypoglycaemia has occurred, and sometimes it happens for no obvious reason.
What To Do If You Have Low Blood Sugar Symptoms
If you have diabetes and are experiencing mild to moderate hypoglycemia symptoms, you need to immediately eat or drink 15 grams of easily digestible carbohydrates.
Very low blood sugar is a medical emergency. If you or someone else with diabetes is experiencing severe symptoms, such as unconsciousness, its important to administer a medication called glucagon and contact emergency services immediately.
If youre at risk for low blood sugar, its important to talk with your doctor about getting a prescription for glucagon.
You should never give an unconscious person anything by mouth, as it could cause them to choke. If you have diabetes, make sure your family and friends know not to do this if you lose consciousness.
Low blood sugar can occur for a number of reasons. Its usually a side effect of diabetes treatment.
Don’t Miss: Metformin And Hypoglycemia
Possible Causes With Diabetes
Diabetes affects your bodys ability to use insulin. Think of insulin as the key that unlocks your cells, letting in glucose for energy.
If you have diabetes, a variety of treatments can help the cells in your body use the glucose in your blood. Among these are insulin injections and oral medications that increase insulin production.
If you take too much of these types of medications, your blood sugar may drop too low. You may also sometimes experience low blood sugar if you plan to eat a big meal but then do not eat enough.
Skipping meals, eating less than usual, or eating later than usual but taking your medication at your usual time can also lead to low blood sugar levels.
Unplanned excess physical activity without eating enough can also cause a drop in blood sugar levels.
Drinking alcohol when youre on these medications can also lead to low blood sugar, especially if it replaces food. When your body is trying to get rid of alcohol, it becomes worse at managing blood sugar levels.
How Do I Treat An Episode Of Hypoglycemia

The American Diabetes Association recommends the 15-15 rule for an episode of hypoglycemia:
- Eat or drink 15 grams of carbs to raise your blood sugar.
- After 15 minutes, check your blood sugar.
- If its still below 70 mg/dL, have another 15 grams of carbs.
- Repeat until your blood sugar is at least 70 mg/dL.
If you have symptoms of hypoglycemia but cant test your blood sugar, use the 15-15 rule until you feel better.
Note: Children need fewer grams of carbs. Check with your healthcare provider.
Recommended Reading: Drug Class Metformin
How To Treat Low Blood Sugar
If you think you have low blood sugar, be sure to check it.
Keeping your blood sugar levels on target as much as possible can help prevent or delay long-term, serious health problems. While this is important, closely managing your blood sugar levels also increases your chance for low blood sugar . Blood sugar below 70 mg/dL is considered low. If you think you have low blood sugar, check it. If you arent able to check it, go ahead and treat it.
Untreated low blood sugar can be dangerous, so its important to know what to do about it and to treat it immediately.
Does Everyone Have Symptoms From Hypoglycemia
Some people dont have symptoms or dont notice them. Healthcare providers call that situation hypoglycemia unawareness. People with such a challenge arent aware when they need to do something about their blood sugar. Theyre then more likely to have severe episodes and need medical help. People with hypoglycemia unawareness should check their blood sugar more often.
Read Also: How Long Does It Take To Get Diabetes
Preventing A Low Blood Sugar Level
If you have diabetes, you can reduce your chance of getting a low blood sugar level if you:
- Check your blood sugar level regularly and be aware of the symptoms of a low blood sugar level so you can treat it quickly.
- Always carry a sugary snack or drink with you, such as glucose tablets, a carton of fruit juice or some sweets. If you have a glucagon injection kit, always keep it with you.
- Do not skip meals.
- Be careful when drinking alcohol. Do not drink large amounts, check your blood sugar level regularly, and eat a carbohydrate snack afterwards.
- Be careful when exercising eating a carbohydrate snack before exercise can help to reduce the risk of a hypo. If you take some types of diabetes medicine, your doctor may recommend you take a lower dose before or after doing intense exercise.
- Have a carbohydrate snack, such as toast, if your blood sugar level drops too low while you’re asleep
If you keep getting a low blood sugar level, talk to your diabetes care team about things you can do to help prevent it.
How Common Is Low Blood Glucose
Low blood glucose is common among people with type 1 diabetes and among people with type 2 diabetes who take insulin or some other diabetes medicines. In a large global study of people with diabetes who take insulin, 4 in 5 people with type 1 diabetes and nearly half of those with type 2 diabetes reported a low blood sugar event at least once over a 4-week period.2
Severely low blood glucose, defined as when your blood glucose level drops so low you cant treat it yourself, is less common. Among U.S. adults with diabetes who take insulin or some diabetes medicines that help the pancreas release insulin into the blood, 2 in 100 may develop severely low blood glucose each year.3
Read Also: What Happens When Your Blood Sugar Gets Too High
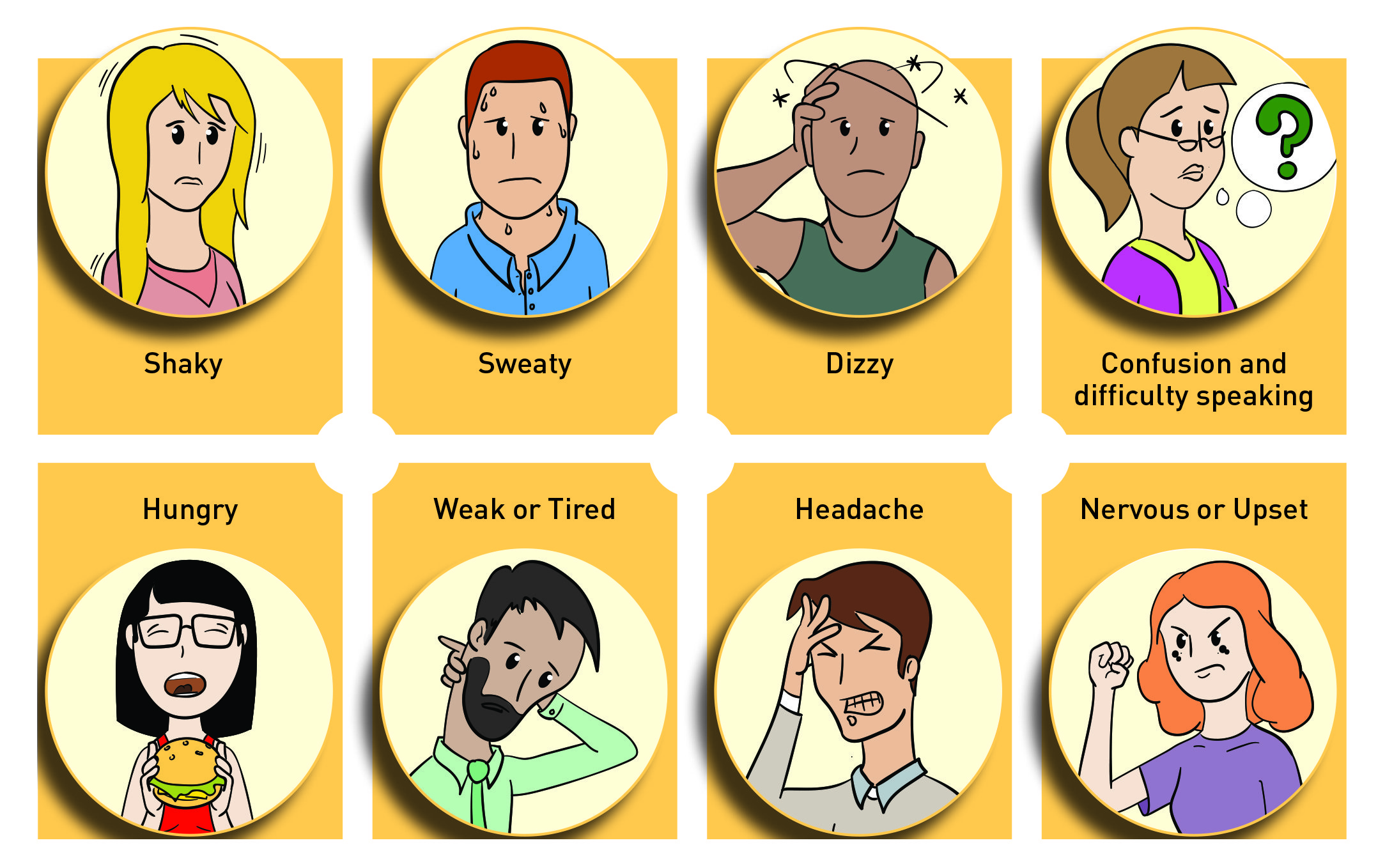
Signs & Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar
Keeping blood glucose levels in a healthy range can be challenging.
When the amount of sugar in your blood has dropped below your target range , it is called low blood sugar .
If your blood sugar has dropped, you may feel:
- shaky, light-headed, nauseated
- an increase in heart rate
- sweaty, headachy
- weak, drowsy
- numbness or tingling on your tongue or lips
Symptoms of very low blood sugar are more severe and can make you:
- confused and disoriented
- lose consciousness
- have a seizure
Make sure you always wear your MedicAlert® identification and talk to your doctor or diabetes educator about prevention and emergency treatment for severe low blood sugar.
Warning Signs Of Low Blood Sugar
Hypoglycemia can cause both short- and long-term complications. Know the signs so that you can treat the condition as soon as you’re aware of it.
As a person living with diabetes, you know how important it is to reduce blood sugar when it is too high, a phenomenon called hyperglycemia. But blood sugar that is too low, or hypoglycemia, is equally critical to avoid.
“Hypoglycemia happens when the amount of blood glucose drops to a level that’s too low to sustain normal functioning,” says Erin Palinski-Wade, RD, CDCES, who is based in Sparta, New Jersey. “In most people, this is defined as a blood sugar level at or below 70 milligrams per deciliter .”
Hypoglycemia is common among people with type 2 diabetes, according to a review published in June 2015 in the journal PLoS One. Individuals with the condition had an average of 19 mild or moderate episodes of hypoglycemia per year and nearly one severe episode per year on average, according to the researchers. Low blood sugar was particularly common among those taking insulin.
RELATED: What to Know Before You Use OTC Insulin
This decrease in blood sugar levels can cause both short-term complications, like confusion and dizziness, as well as more serious issues, including seizures, coma, and, rarely, death, according to the American Diabetes Association .
Hypoglycemia is usually the result of a too-high dose of insulin or a change in diet or exercise habits, according to Harvard Health Publishing.
Also Check: Average A1c Non Diabetic
Treating An Episode Of Hypoglycaemia
The immediate treatment for hypoglycaemia is to have some sugary food or drink to end the attack.
For example, this could be:
- a glass of fruit juice or non-diet soft drink
- between three and five dextrose tablets
- a handful of sweets
At first you should avoid fatty foods and drinks, such as chocolate and milk, because they don’t usually contain as much sugar and the sugar they do contain may be absorbed more slowly.
After having something sugary, you should have a longer-acting carbohydrate food, such as a few biscuits, a cereal bar, a piece of fruit or a sandwich.
It will usually take around 15 minutes to recover from a mild episode of hypoglycaemia. If you have a blood glucose meter, measure your blood sugar again after 15 to 20 minutes. If it’s still too low , you should have some more sugary food or a drink before testing your levels again in another 15 to 20 minutes.
When treating someone else with hypoglycaemia, if the above treatment isn’t effective, you may be able to help them by applying glucose gel to the inside of their cheeks, and gently massaging the outside of their cheeks.
It may take 10 to 15 minutes before they feel better. This shouldn’t be done if the person is drowsy or unconscious because of the risk of choking.
Treating Low Blood Sugar
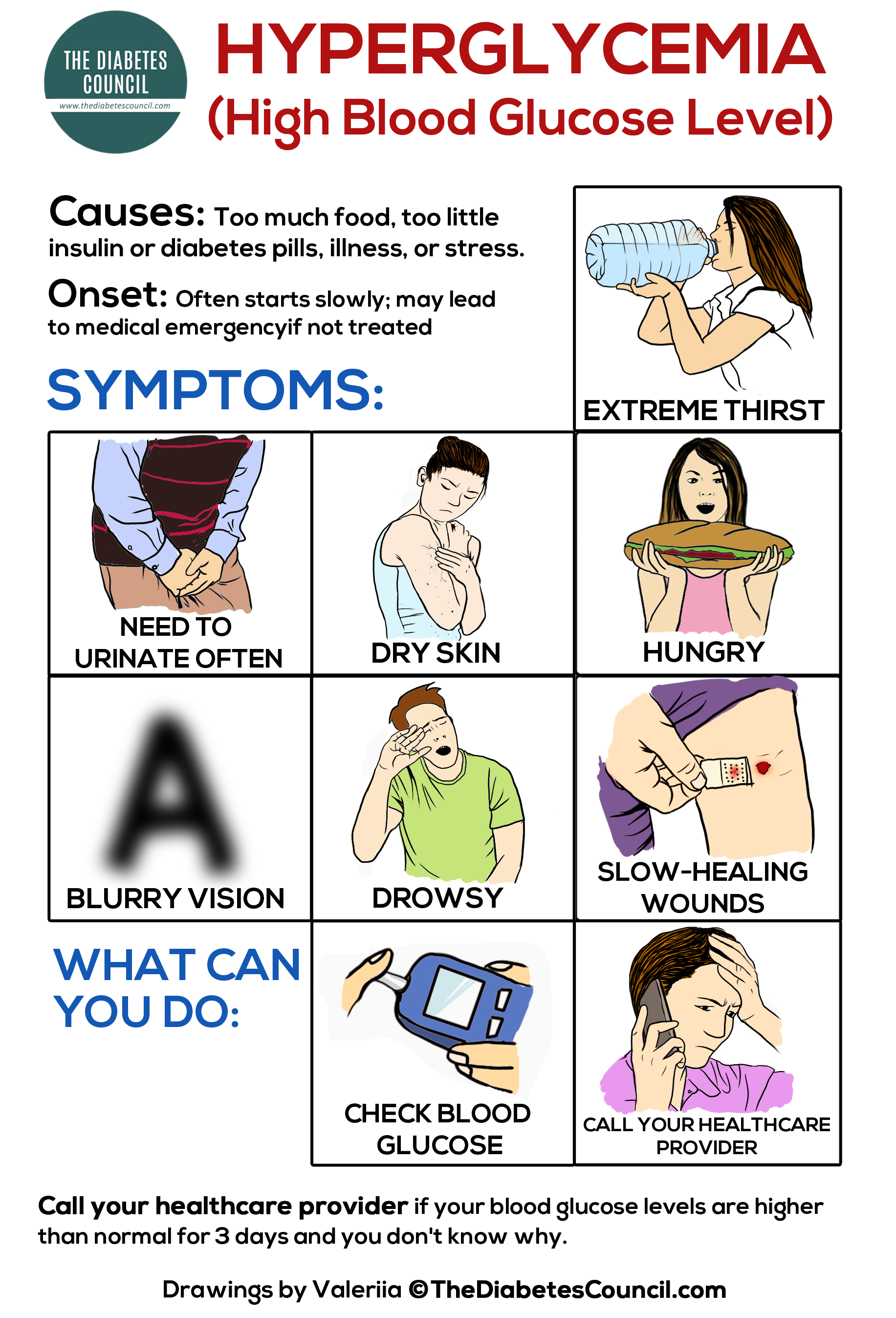
You are at risk of having a low blood sugar reaction if you:
- Skip or delay a meal or snack
- Take too much insulin or eat too few carbohydrates
- Exercise
- Drink alcohol, especially without eating carbohydrates
Check your blood sugar if you have any of these symptoms:
- Weakness and/or fatigue
If your blood sugar is less than 70 milligrams per deciliter :
- Eat 15 to 30 grams of carbohydrate
- Wait 15 minutes and then recheck your blood sugar
- If your blood sugar is still less than 100 mg/dl, take another 15 grams of carbohydrate and retest your blood sugar in another 15 minutes. Repeat if necessary.
Important: If you have frequent low blood sugars speak to your doctor. You may need changes in your medication and/or meal plan.
Recommended Reading: Metformin Onset Peak Duration
Take Medications As Prescribed
Certain diabetes medications can cause low blood sugar. The most common diabetes medications with a risk of hypoglycemia are insulin and sulfonylureas. Avoid changing your medication doses on your own, which might cause low blood sugar.
If you have type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes and you take insulin, your risk of low blood sugar is greater than people taking only oral medications.
Insulin is the most effective medication at lowering blood sugar, which is why it comes with a risk of hypoglycemia.
Signs And Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar
Each person’s reaction to low blood sugar is different. Learn your own signs and symptoms of when your blood sugar is low. Taking time to write these symptoms down may help you learn your own symptoms of when your blood sugar is low. From milder, more common indicators to most severe, signs and symptoms of low blood sugar include:
- Feeling shaky
- Color draining from the skin
- Feeling sleepy
- Feeling weak or having no energy
- Blurred/impaired vision
- Tingling or numbness in the lips, tongue or cheeks
- Headaches
- Nightmares or crying out during sleep
- Seizures
The only sure way to know whether you are experiencing low blood sugar is to check your blood sugar, if possible. If you are experiencing symptoms and you are unable to check your blood sugar for any reason, treat the hypoglycemia.
A low blood sugar level triggers the release of epinephrine , the fight-or-flight hormone. Epinephrine is what can cause the symptoms of hypoglycemia such as thumping heart, sweating, tingling and anxiety.
If the blood sugar level continues to drop, the brain does not get enough glucose and stops functioning as it should. This can lead to blurred vision, difficulty concentrating, confused thinking, slurred speech, numbness, and drowsiness. If blood sugar stays low for too long, starving the brain of glucose, it may lead to seizures, coma and very rarely death.
Don’t Miss: Diabetes Concentration Problems
What Is Normal Blood Sugar
When we eat, glucose — which is our body’s main source of energy — enters our bloodstream from our food. Then our pancreas secretes a hormone called insulin in just the right amount to help the glucose go from the bloodstream to our body’s various cells to be used as energy. This process usually keeps the glucose in our bloodstream in a healthy range, being neither too high, nor too low.
This range is measured in milligrams of blood glucose per deciliter, or mg/dL. Dr. Saleh Aldasouqi, Chief of Endocrinology at Michigan State University, explains to CNET: “Normal blood sugar is defined as anywhere from 70 to 110 mg/dL within a healthy physiology, as a person without diabetes or other related diagnosed condition. Sugar below 70 is generally considered low, and above 110 is considered high .”
How Can I Prevent Insulin
- Check your blood sugar regularly.
- Know what causes low blood sugar.
- Eat at regular mealtimes. Do not delay or skip meals and do not eat partial meals.
- Take all medicines exactly as prescribed.
- Check your blood sugar more often when you are exercising more or eating less, or when you are sick, according to your healthcare provider’s recommendations.
- Keep your follow-up appointments with your provider.
Recommended Reading: Metformin Xr Side Effects
Overdose Of Diabetes Medication
A common cause of hypoglycaemia is taking too much insulin for your current needs. Insulin is a medication that helps control your blood glucose levels. It’s commonly used to treat type 1 diabetes and is also recommended for some people with type 2 diabetes.
A fall in blood glucose levels can also occur after taking too much oral hypoglycaemia medication, such as sulphonylurea, which causes a release of insulin. This medication is often used to lower blood glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes.
Checking For Low Blood Sugar Levels
The warning signs of hypoglycemia are the body’s natural response to low blood sugar levels. When blood sugar levels fall too low, the body releases the hormone adrenaline, which helps get stored glucose into the bloodstream quickly. This can make someone:
- pale
- start shaking
- have an increased heart rate
If the hypoglycemia isn’t treated, more serious symptoms may happen, such as drowsiness, confusion, seizures, and loss of consciousness.
The only way to know for sure if you’re having a low blood sugar level is to test. Blood sugar levels can be tested with a . This computerized device measures and displays the amount of glucose in a blood sample. But if you can’t quickly check your blood sugar level, it’s important to treat yourself for hypoglycemia immediately to prevent symptoms from getting worse.
Sometimes a person with diabetes may have symptoms of low blood sugar levels, but blood sugar levels are not actually low. This is a called a false reaction. The hormone adrenaline is not just released when blood sugar drops too low it’s also released when blood sugar levels fall quickly when they’re too high. If you’re having a false reaction, you might actually have blood sugar levels in a healthy range but feel as if you have low blood sugar. Testing blood sugar levels before treating yourself for hypoglycemia can help you figure out if you’re having a false reaction.
page 3
Recommended Reading: Metformin Average Dose
Your Hypoglycemia Action Plan
If you experience symptoms of hypoglycemia, its important to take action. Start with these steps:
Test your blood sugar. If you recognize any of these symptoms and believe your blood sugar may be too low, the first step you should take is to test your blood sugar with your glucose meter, Tan says. Anything less than 70 milligrams per deciliter is considered low blood sugar, according to the National Library of Medicine . However, target levels are often individualized, so talk with your healthcare provider about your optimal numbers, Tan adds.
Eat or drink fast-acting carbs. If you have low blood sugar, you need to take action right away. Your best bet is to consume about 15 grams of carbohydrates, the NLM says. Some options include:
- ½ cup or 4 ounces of orange juice
- ½ cup or 4 ounces of regular soda
- 1 tablespoon of sugar dissolved in water
- 1 tablespoon of honey or maple syrup
- 5 or 6 hard candies, jelly beans, or gumdrops
- 1 tablespoon of cake frosting
- 2 tablespoons of raisins
- ½ cup of applesauce
You can also take three to four glucose tablets or a tube of glucose gel. Everyone who takes medications for diabetes should always have glucose tablets with them, Galindo urges.
Wait, then retest. The next step is to wait 15 minutes, then test your blood sugar again. If blood sugar has reached 100 mg/dl or greater, youre fine. If not…

