Causes Of Type 2 Diabetes
People with type 2 diabetes have insulin resistance. The body still produces insulin, but its unable to use it effectively.
Researchers arent sure why some people become insulin resistant and others dont, but several lifestyle factors may contribute, including being inactive and carrying excess weight.
Other genetic and environmental factors may also play a role. When you develop type 2 diabetes, your pancreas will try to compensate by producing more insulin. Because your body is unable to effectively use insulin, glucose will accumulate in your bloodstream.
Type 2 diabetes is much more common than type 1.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Preventions , 34.2 million people in the United States were living with diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes in 2018. Thats a little over 1 in 10 people. Ninety to 95 percent of people with diabetes have type 2.
The percentage of people with diabetes increases with age.
About 10.5 percent of the general population has diabetes. Among those 65 years old and older, the rate reaches 26.8 percent. Only 25 out of every 10,000 Americans under 20 years old had been diagnosed with diabetes in 2018.
Men and women get diabetes at roughly the same rate. However, prevalence rates are higher among certain races and ethnicities.
Prevalence rates are higher for Hispanic Americans of Mexican or Puerto Rican descent than they are for those of Central and South American or Cuban descent.
Managing Type 1 Diabetes
People with type 1 diabetes may benefit from controlling and counting the amount of carbohydrates they eat because carbohydrates are the bodys primary source of glucose. Insulin levels can be predicted by determining how many grams of carbohydrates were eaten at each meal. It is recommended that people with type 1 diabetes stay active, but they may need to monitor their blood sugar levels and adjust their carbohydrate intake to prevent a low blood sugar condition called hypoglycemia.
Can You Be Misdiagnosed With Type 2 Diabetes
Its possible for someone with type 2 diabetes to be misdiagnosed. They may have many of the symptoms of type 2 diabetes, but actually have another condition that may be more closely related to type 1 diabetes. This condition is called latent autoimmune diabetes in adults .
Researchers estimate that between 4 and 14 percent of people diagnosed with type 2 diabetes might actually have LADA. Many physicians are still unfamiliar with the condition and will assume a person has type 2 diabetes because of their age and symptoms.
In general, a misdiagnosis is possible because:
- both LADA and type 2 diabetes typically develop in adults
- the initial symptoms of LADA such as excessive thirst, blurred vision, and high blood sugar mimic those of type 2 diabetes
- doctors dont typically run tests for LADA when diagnosing diabetes
- initially, the pancreas in people with LADA still produces some insulin
- diet, exercise, and oral drugs usually used to treat type 2 diabetes work well in people with LADA at first
As of now, theres still a lot of uncertainty over how exactly to define LADA and what causes it to develop. The exact cause of LADA is unknown, but researchers have identified certain genes that may play a role.
LADA may only be suspected after your doctor realizes that youre not responding well to oral type 2 diabetes medications, diet, and exercise.
Read Also: Normal A1c Levels For Seniors
Can Diabetes Be Prevented Or Cured
“As of now there is no way to prevent or cure type 1 diabetes,” Drincic notes. “There is lots of promising research, but it is still in the early stages.” Some of the initiatives involve targeting the cells in the immune system that cause the autoimmune response. Other possibilities include the use of stem cells or pancreas transplants.
Another area of research is diet and its effects on both prevention and diabetes maintenance. A study published in March 2017 in the British Journal of Nutrition reported that following a diet high in plant nutrients and low in meat consumption lowers a person’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The results indicated that certain compounds found in meat, rather than specific proteins, increased the risk of type 2 diabetes. Aside from eating healthy foods rich in plant nutrients, a large number of studies indicate that exercise is paramount not only for weight control, but also for maintaining a healthy, optimistic outlook.
Complications With Variable Evolution
Potential complications are similar with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Prolonged hyperglycemia will have damaging effects on the arteries, along with renal, cardiovascular or vision damage. Patients with Type 1 diabetes are exposed younger to diabetes complications.
Whereas patients with Type 2 diabetes are often older, and less aware of the risks of physical inactivity and obesity, which are added to high blood sugar levels. But, regardless of the type of diabetes, good blood sugar control with good follow-up will delay or even prevent complications.
Read Also: When Insulin Is Present Glucose Can Be Utilized By
Rick Factors: Who Is Affected
Only about 5% to 10% of diagnosed diabetes cases are type 1. The disease is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, although it can technically strike at any age. Scientists do not know yet exactly what causes type 1 diabetes but suspect the disease involves a combination of genetic, environmental, and autoimmune factors.
An overweight person who does not exercise, is over 30, and/or has close relatives who have type 2 diabetes, runs a very high risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Higher-risk ethnic groups include African Americans, Latinos and Hispanics, Native Americans, Alaskan Natives, Asians, and those with Pacific Islander American heritage.
People are more likely to get diabetes if they smoke, have high blood pressure or cholesterol, or, in women, if they had gestational diabetes or gave birth to a baby who weighed more than 9 pounds. A free diabetes risk test is provided by Diabetes.org and only takes a few minutes to complete.
What Is Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which your bodys immune system attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in your pancreas.
This drastically reduces the ability of your body to produce insulin, the hormone responsible for signaling tissues that glucose is available in your blood, and people with type 1 diabetes require exogenous insulin .
Sometimes called juvenile-onset diabetes, type 1 diabetes typically occurs in children and young adults under the age of 30, though this is not always the case.
Currently, researchers have been unable to isolate one specific cause of type 1 diabetes, and there is no known cure. However, through diet and lifestyle, this form of insulin-dependent diabetes can be controlled and managed.
For more in-depth information on type 1 diabetes, you can visit our comprehensive article on the topic.
Don’t Miss: Mac And Cheese Diabetes
When Should I Call My Doctor
Its important to monitor diabetes very closely if youre sick. Even a common cold can be dangerous if it interferes with your insulin and blood sugar levels. Make a sick day plan with your healthcare provider so you know how often to check your blood sugar and what medications to take.
Contact your provider right away if you experience:
- Confusion or memory loss.
- Nausea and vomiting for more than four hours.
- Problems with balance or coordination.
- Severe pain anywhere in your body.
- Trouble moving your arms or legs.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Type 2 diabetes is a disease where your body doesnt make enough insulin and cant use sugar the way it should. Sugar, or glucose, builds up in your blood. High blood sugar can lead to serious health complications. But Type 2 diabetes is manageable. Regular exercise and a healthy diet can help you manage your blood sugar. You may also need medication or insulin. If you have Type 2 diabetes, you should monitor your blood sugar at home regularly and stay in close communication with your healthcare provider.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 03/25/2021.
References
Overview Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Type 1An autoimmune disease occurs when there is an abnormal immune response to a normal part of the body. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder caused by destruction of the cells that secrete insulin from the pancreas. This results in too little insulin being produced to support the bodys needs. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, and was previously known as juvenile diabetes.
Without insulin, glucose from the carbohydrate foods you eat cannot enter cells. This causes glucose to build up in the blood, leaving your bodys cells and tissues starved for energy. While a variety of tissue transplantation and genetically-based treatments are being studied, at this point the only widely-available treatments for type 1 diabetes are the injection of insulin and inhaled insulin.
Image text:
Type 2Type 2 is the most common form of diabetes and can be caused by a combination of factors. One factor is that your body begins to make less insulin. A second is that your body becomes resistant to insulin. This means there is insulin in your body, but your body cannot use it effectively. Insulin resistance is often related to excess body fat. Medication, lifestyle changes, and monitoring can help control blood glucose levels in those with type 2 diabetes.
Read Also: How Long Does Nph Insulin Take To Work
Type 1 Diabetes Definition
Type 1 diabetes used to go by different names, including juvenile-onset diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes. This type of diabetes is a condition that causes the immune system to destroy islet cells, cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Over time, this causes the body to stop producing insulin. The body needs insulin, a hormone, because it helps turn blood glucose into energy for cells. Type 1 diabetes is less common than Type 2 diabetes about 5% of people with diabetes have Type 1. However, about 85% to 90% of children and adolescents with diabetes have Type 1.
The Differences Between Type 1 Diabetes And Type 2
What are the differences between Type 1 diabetes and Type 2? The general public often mistakenly assumes that there is only one type of diabetes, Type 2 diabetes. However, there are many differences between Type 1 diabetes, also known as Juvenile diabetes, and Type 2 diabetes. In fact, their causes and treatments make them two very distinct diseases.
Also Check: High Blood Sugar Symptoms Type 1
How Do You Treat Type 2 Diabetes
Once someone is diagnosed as prediabetic, it’s common for doctors to recommend healthy lifestyle changes as the first form of treatment. Being physically active, weight loss of about 5 to 7% , and eating a healthy diet can help prevent type 2 diabetes from developing, Dr. Kalyani says.
But if someone already has type 2, their doctor may suggest insulin injections or oral medications that can either make the body more sensitive to insulin, help the pancreas release more insulin , or prevent the stores of glucose in the liver from breaking down, Dr. Kalyani says. While medication is often necessary, Dr. Hirsch says that aggressive lifestyle changes may also help get blood sugar under control enough that some patients are able to reduce or get off of medication entirely.
While type 1 and type 2 diabetes have similar symptoms, ultimately their impact on the body is quite different, and the treatments can vary. Thats why it’s important that youre diagnosed correctly, so that you can receive care that fits the disease and gets you back on a path of feeling well.
In Type 2 Diabetes Your Body Produces Insulin But It Doesn’t Work Properly

“In type 2 diabetes, you produce insulin, but the main issue is that the rest of your body does not listen to it,” O’Malley explains. “We call this insulin resistance.” When blood sugar is high and insulin is released, your body ignores it. Just like in type 1 diabetes, your blood sugar stays high, your liver releases even more glucose, and other cells don’t get the energy they need.
“With time, some patients with type 2 diabetes may start to produce less insulin, but not to the same extent as with type 1,” O’Malley says.
Although some people are genetically predisposed to developing type 2 diabetes, lifestyle factors also play a role. According to the NIDDK, a person is more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if they are overweight or obese, have high blood pressure, have high cholesterol or are not physically active. People over the age of 45, or with a history of heart attack or stroke, are also more likely to develop the disease.
Although people with type 2 diabetes sometimes experience the same symptoms as those with type 1 diabetes prior to diagnosis, many have no symptoms at all . Doctors routinely test for diabetes using blood glucose tests in patients over 45, or patients with two or more other risk factors, according to the NIDDK. As in type 1 diabetes, glucose levels of 126 or above for the fasting plasma glucose test, or 200 or above for the oral glucose tolerance or random plasma glucose tests, are indicative of diabetes.
Read Also: Prognosis Of Diabetes Type 2
Can Type 1 Or Type 2 Be Cured Or Prevented
Unfortunately, theres currently no permanent cure for either type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
But theres evidence that some people with type 2 can put their diabetes into remission by losing weight. Following a very low-calorie diet under medical supervision, or having surgery are some ways you can put your type 2 diabetes into remission.
Were also funding some vital research projects to help transform treatment and care. And to help find a cure for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
What Are The Risk Factors For Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Risk factors for type 1 diabetes include:
- Family history: People with a parent or sibling with type 1 diabetes have a higher risk of developing it themselves.
- Age: Type 1 diabetes can appear at any age, but its most common among children and adolescents.
- Geography: The prevalence of type 1 diabetes increases the farther away you are from the equator.
- Genetics: The presence of certain genes points to an increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
Youre at risk of developing type 2 diabetes if you:
- have prediabetes, or slightly elevated blood sugar levels
- are carrying excess weight or have obesity
- are Black, Hispanic, American Indian, or Alaska Native
- have an immediate family member with type 2 diabetes
Also Check: 1500 Mg Metformin
Symptoms Of Type 1 And Type 2
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes share common symptoms. They are:
- going to the toilet a lot, especially at night
- being really thirsty
- feeling more tired than usual
- losing weight without trying to
- genital itching or thrush
- cuts and wounds take longer to heal
- blurred vision.
But where type 1 and type 2 diabetes are different in symptom is how they appear. Type 1 can often appear quite quickly. That makes them harder to ignore. This is important because symptoms that are ignored can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis .
But type 2 diabetes can be easier to miss. This is because it develops more slowly, especially in the early stages. That makes it harder to spot the symptoms. That is why it is important to know your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Some people have diabetes and dont know it. They can have it for up to 10 years without knowing.
Causes Of Type 1 Diabetes
The bodys immune system is responsible for fighting off foreign invaders, such as harmful viruses and bacteria.
In people with type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakes the bodys own healthy cells for foreign invaders. The immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. After these beta cells are destroyed, the body is unable to produce insulin.
Researchers dont know why the immune system sometimes attacks the bodys own cells. It may have something to do with genetic and environmental factors, such as exposure to viruses. Research into autoimmune diseases is ongoing.
You May Like: Complications Of Metformin
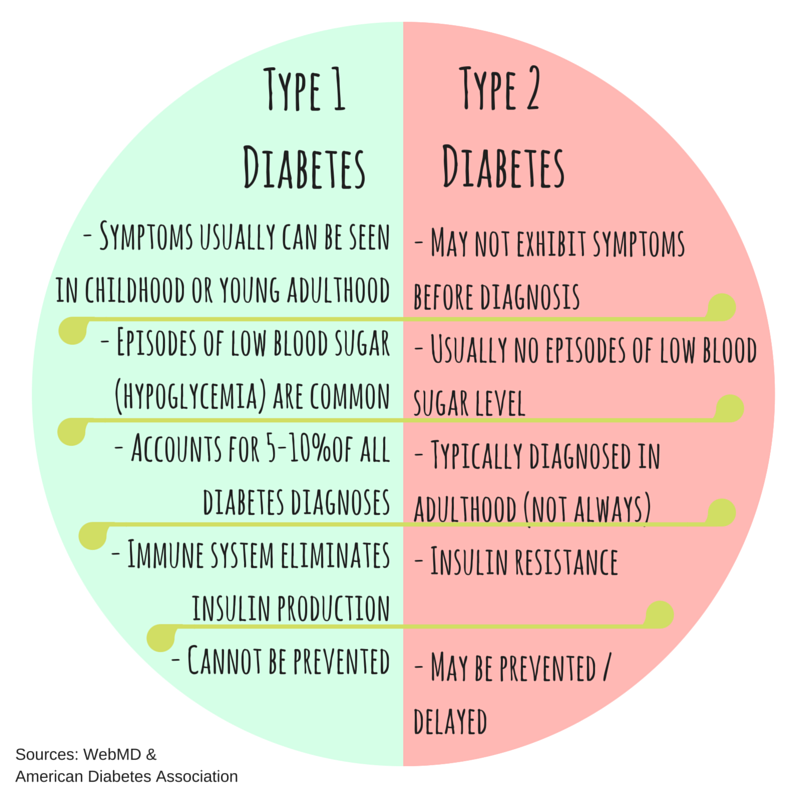
Type 1 Diabetes Vs Type 2 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes, which accounts for 5 to 10% of cases of diabetes, is an autoimmune disease, where the pancreas fails as a result of an autoantibody attack. Thus, even though the cause of Type 1 diabetes is still unknown, we do know that it is unrelated to a patients lifestyle. The disease often develops suddenly, from a young age, and requires immediate insulin treatment. This is why we also refer to it as insulin-dependent diabetes. However, diagnostic advances have shown us that it is not always that simple. For example, obese children are often misdiagnosed with Type 2 diabetes, even though it is sometimes actually Type 1.
Type 2 diabetes, which accounts for 90% of cases of diabetes, is caused by a decrease in insulin sensitivity associated with a dysfunction of the pancreatic beta cells responsible for secreting insulin. T2D often begins after the age of 40, has a strong genetic component and is traditionally considered to be linked to an unhealthy lifestyle. Even though obesity, diet and lack of physical inactivity are risk factors, the causes of T2D cannot be summed up in terms of lifestyle alone.
Read also: Type 1 diabetes: origin and causes

