Prediabetes Vs Diabetes: Whats The Real Difference
Have you ever been told you have borderline diabetes? What about actual diabetes? Terms like prediabetes, borderline diabetes, and type 1 and type 2 diabetes can be confusing and overwhelming. In this post, well compare prediabetes and diabetes. Is there a difference between them, and if so, what is it?
The Role Of Insulin In Your Body
Insulin is a natural hormone produced by your pancreas. It serves two primary functions: regulating blood sugar levels and aids in the storing of excess glucose for energy.
When your insulin levels are high, your body stores excess glucose in your liver in the form of glycogen. When your insulin levels get too low, the liver turns glycogen back into glucose to keep blood sugar levels within a narrow range.
When your body doesnt have insulin to regulate the amount of glucose going into your bloodstream it can cause an array of issues. Remember that your liver and kidneys work like filters. They keep toxins from getting into your bloodstream and allow the good to pass through. However, your liver and kidneys arent designed to handle high levels of glucose.
When your kidneys and liver have to filter out large amounts of sugar, they cant stop toxins from getting in the system. Over a long period of time, your liver and kidneys become exhausted and begin to fail. This is why diabetics who do not control their blood sugar levels go on dialysis, a process where toxic blood is removed from the body and replaced with clean blood. This can be prevented by managing your blood sugar levels through diet and exercise.
What Is Latent Autoimmune Diabetes In Adults
Many doctors consider LADA the adult form of type 1 diabetes because its also an autoimmune condition.
As in type 1 diabetes, the islet cells in the pancreas of people with LADA are destroyed. However, this process occurs much more slowly. Once it starts, it can take several months up to several years for the pancreas to stop being able to make insulin.
Other experts consider LADA somewhere in between type 1 and type 2 and even call it type 1.5 diabetes. These researchers believe that diabetes can occur along a spectrum.
Researchers are still trying to figure out the details, but in general, LADA is known to:
- develop in adulthood
- have a slower course of onset than type 1 diabetes
- often occur in people who arent overweight
- often occur in people who dont have other metabolic issues, such as high blood pressure and high triglycerides
- result in a positive test for antibodies against the islet cells
The symptoms of LADA are similar to those of type 2 diabetes, including:
- excessive thirst
Recommended Reading: Side Effects Of Diabetes Medication
What Should You Eat
If you have diabetes, you should focus on eating lean protein, high-fiber, less processed carbs, fruits, and vegetables, low-fat dairy, and healthy vegetable-based fats such as avocado, nuts, canola oil, or olive oil. You should also manage your carbohydrate intake. Have your doctor or dietitian provide you with a target carb number for meals and snacks. Generally, women should aim for about 45 grams of carb per meal while men should aim for 60. Ideally, these would come from complex carbs, fruits, and vegetables.
The American Diabetes Association offers a comprehensive list of the best foods for those with diabetes. Their recommendations include:
| Protein |
Both Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Have To Do With The Hormone Insulin
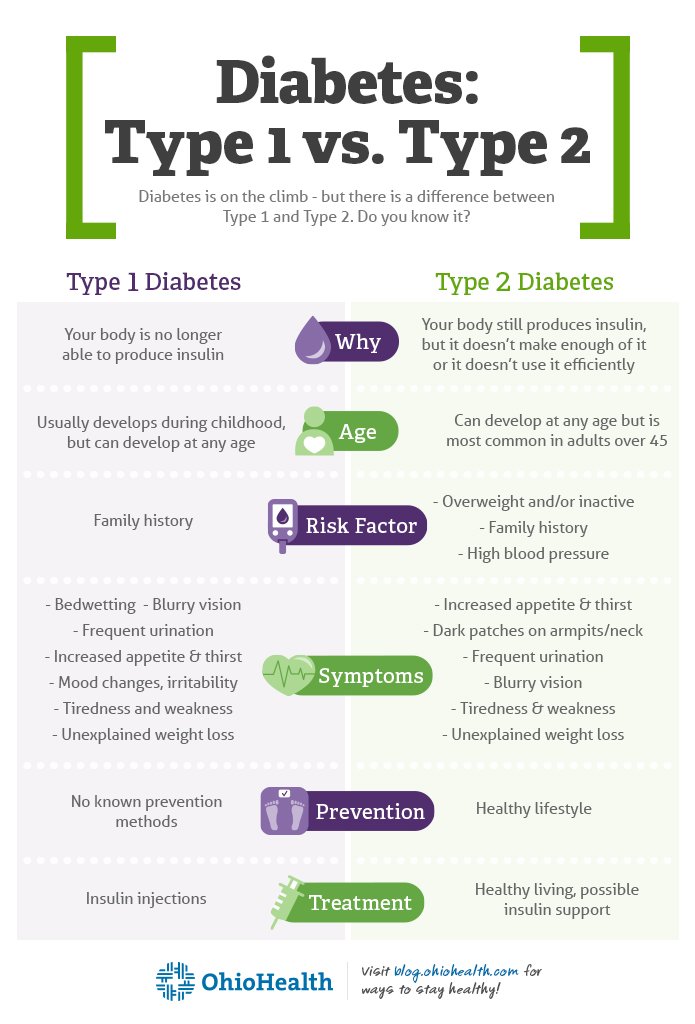
Without getting too deep in biochemistry, its important to know that insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas when levels of blood glucose in the body are high-that is, right after a meal or snack that contains carbohydrates, which are made of glucose and other sugars. In a nutshell, insulin tells your body to shuttle glucose to cells for energy, and to store glucose in the liver and other tissues. When this happens, your blood sugar levels lower, your body gets the energy it needs, and any leftover glucose is stored and saved for when you need energy between meals.
Read more:12 Healthy Ways to Lower Your Blood Sugar
Recommended Reading: Banana Good For Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors:
Your risk of developing type 2 diabetes is higher if your diet is high in carbs and fat but low in fiber, if youre not very physically active and/or if you have high blood pressure. High alcohol consumption and age are also risk factors. Though genes do play a role in the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes, it can be prevented with the right lifestyle choices, unlike type 1.
There Are A Few Ways To Treat Type 1 Diabetes:
- Monitor your blood sugar. Living with diabetes means getting familiar with healthy blood sugar levels and checking yours regularly. Depending on your health care providers specific recommendation, you might need to check it four to ten times daily. Youll use a small blood sugar meter called a glucometer to measure glucose levels in a pin-prick of blood on a disposable test strip. Another option is to have a continuous glucose monitor, which automatically measures your blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted underneath the skin.
- Take insulin. Because your body doesnt produce it on its own, youll have to get it another way. There are a few methods for taking insulin, including regular injections or a wearable insulin pump, which delivers small, steady doses of fast-acting insulin throughout the day through a thin tube. Though its certainly not the most convenient lifestyle, it often becomes second nature for people living with type 1 diabetes.
- Maintain a balanced diet. You dont have to be extremely restrictive, but carbohydrates are the foods youll want to watch, making sure to eat them consistently but not go overboard. If youre taking a fixed amount of insulin, keeping your carbohydrate intake consistent to match is important.
- Exercise. Staying active is always an important component of health, but for people with type 1 diabetes, it can help keep blood sugar levels in check and cause your body to use the insulin more efficiently.
Recommended Reading: Why Is Metformin Dangerous
Ultimately The Goal In Managing Both Types Of Diabetes Is To Keep Blood Sugar Levels Steady Over Time
The goal of diabetes treatment-whether through insulin injections, medication or proper diet-is to keep blood sugar levels as steady as possible to minimize potential complications. All people with diabetes should see a doctor for an A1C test two to four times a year, according to the NIDDK. The test results show average blood glucose level over the past three months, and the goal for many people with diabetes is for that level to remain below 7%.
Diabetes is a chronic condition, and both types of diabetes require long-term treatment. But with proper management, patients can lead long, healthy lives.
How Are These Diseases Different
|
Type 1 diabetes |
Type 2 diabetes |
|---|---|
|
Symptoms usually start in childhood or young adulthood. People often seek medical help, because they are seriously ill from sudden symptoms of high blood sugar. |
The person may not have symptoms before diagnosis. Usually the disease is discovered in adulthood, but an increasing number of children are being diagnosed with the disease. |
|
Episodes of low blood sugar level are common. |
There are no episodes of low blood sugar level, unless the person is taking insulin or certain diabetes medicines. |
|
It cannot be prevented. |
It can be prevented or delayed with a healthy lifestyle, including maintaining a healthy weight, eating sensibly, and exercising regularly. |
Also Check: When Is The Best Time To Test Your Blood Sugar
You May Like: Banana And Diabetes Type 2
How Are The Signs And Symptoms Similar
There isn’t a difference between the symptoms of either disease. The “classic” symptoms are the same for both diabetes type 1 and type 2:
- Increased urine output
- Unexplained weight loss
For both type 1 and type 2, early symptoms of untreated diabetes arise due to elevated blood sugar levels and the presence of glucose in the urine. High amounts of glucose in the urine can cause increased urine output and dehydration. Dehydration, in turn, causes increased thirst.
A lack of insulin or an inability of insulin to work properly affects protein, fat, and carbohydrate metabolism. Insulin normally encourages the storage of fat and protein, so when there is inadequate insulin or poorly functioning insulin, this eventually leads to weight loss despite an increase in appetite.
Some untreated diabetes patients also experience generalized symptoms like fatigue, nausea, and vomiting. People with diabetes are also at risk for infections of the bladder, skin, and vaginal areas. Changes in blood glucose levels can lead to blurred vision. When blood sugar levels are extremely high, lethargy and coma can result.
Can A Type 2 Diabetic Become A Type 1
It is not possible for type 2 diabetes to turn into type 1 diabetes. However, a person who originally receives a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes may still get a separate diagnosis of type 1 at a later date. Type 2 diabetes is the most common type, so a doctor might initially suspect that an adult with diabetes has type 2.
Don’t Miss: How Much Does Donating Blood Lower A1c
What Is A Diabetes Meal Plan
There’s no “magic” diabetes diet. However, there are dietary recommendations for people with diabetes. Diet methods for managing both type 1 and type 2 diabetes include:
- Carbohydrate counting
Signs and symptoms of diabetes, whether type 1 or type 2, do not differ.
- Early diabetes may not produce any symptoms at all.
- When symptoms do occur, the age of onset is typically different, with type 1 diabetes being diagnosed most often in younger people , while type 2 diabetes is diagnosed more commonly in adults. However, this is not always the case.
- The increasing incidence of obesity among children and adolescents has caused a rise in the development of type 2 diabetes in young people.
- Further, some adults with diabetes may be diagnosed with a form of late-onset type 1 diabetes.
How Do Diet And Exercise Effect Type1 And Type2 Diabetes Mellitus
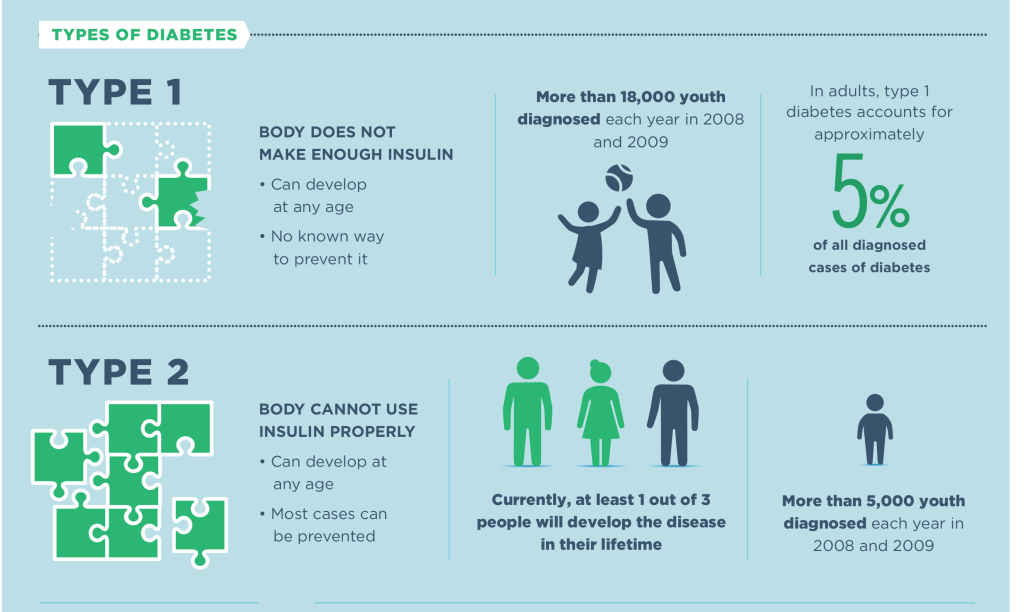
The food choices one make will affect the blood sugar control of a person with either type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Eating foods very high in sugar or simple carbohydrates will raise blood sugar significantly. A person needs to eat a balanced diet that includes some carbohydrates along with protein and fat. Proteins and fats eaten along with carbohydrates will slow the absorption for a less significant blood sugar rise. A nutritionist may be able to help create a food plan that will be beneficial.
Exercise is an important component of diabetes treatment. While helping to keep the cardiovascular system healthy, exercise can also lower blood sugar. For children, exercise can simply be outdoor games, dancing, or sports.
Don’t Miss: What Inhibits Insulin Secretion
What Happens When You Have Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
If you have either type 1 or type 2 diabetes, it means you have too much glucose in your blood. This is the same for both types. But the difference between them is how this happens.
If you have type 1 diabetes, it means you have an autoimmune condition. This means your body has attacked and destroyed the cells that make a hormone called insulin. So you cant make insulin anymore.
We all need insulin as it helps take the glucose from our blood into our bodys cells. We then use this glucose for energy. Without insulin, the glucose level in your blood gets too high.
Type 2 diabetes is different. If youve got type 2, either your body doesnt make enough insulin, or your insulin doesnt work properly. This is known as insulin resistance. Like type 1, this means the level of glucose in your blood is too high.
Diabetes Disrupts The Body’s Insulin Response
Diabetes, regardless of type, affects how your body produces insulin. Insulin is what helps your body convert the sugars from food into fuel for your cells.
Normally, the pancreas releases insulin after you eat. But people with diabetes don’t produce or use insulin properly, which means blood sugar, also called blood glucose, stays elevated at dangerously high levels. This can lead to a condition called hyperglycemia.
All diabetics can experience hyperglycemia, regardless of type. If not addressed, hyperglycemia can result in a life-threatening coma. Meanwhile, chronic cases can cause organ damage.
“These long-term complications can be severe and can lead to blindness, foot ulcers, gangrene requiring amputation, and kidney failure,” says Arnold Saperstein, MD, FACP, an endocrinologist and chief medical officer at Cecelia Health.
Also Check: Side Effects Of Metformin 500 Mg
The Emotional Impact Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Living with type 1 or type 2 diabetes can sometimes feel overwhelming.
Both types are different but feeling down or anxious because of your diabetes can affect anyone. It is important to understand that a long-term condition can come with an emotional impact, no matter how it has been caused or how you treat it.
If youre struggling with your diabetes, remember that youre not alone.
There is lots of support available to you, like our helpline. There you can speak to our highly trained advisors about how you’re feeling. And you can also speak to people who are going through similar experiences on our forum. There are lots of things you can do to help yourself and its just about finding what works for you.
It can be frustrating to explain the differences between type 1 and type 2.
Both types face confusion over what causes the condition and how it can be treated. This will be slightly different whether you’re type 1 or the more common type 2. Just because something is more common, doesn’t mean it is understood.
And while it is emotionally draining to constantly correct people, you should also know that you’re not alone. There are many people living with diabetes facing similar questions and struggles, regardless of type. You can reach out to them to give or receive support in the forum and at local groups.
Risk Factors For Type 2 Diabetes
- Obesity. Being overweight puts you at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The longer a person is obese, the more the risk for type 2 diabetes increases. In a 2014 study, a two-year duration of obesity increased the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by up to 14%.
- Inactivity. Physical activity aids in weight control and regular blood sugar levels. Thus, the less active you are, the higher your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Poor diet. A diet low in fiber and high in sugar and saturated/trans fats is linked to an increased risk for type 2 diabetes.
- Fat Distribution. Some research has found that people who store fat in their abdomen, as opposed to other places in the body, are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Family History. The risk for type 2 diabetes increases if a parent or sibling has it.
- Race. Those who are African-American, Hispanic, Indian, and Asian, are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Age. Type 2 diabetes is most common in adults, especially over the age of 45. However, type 2 diabetes is increasing dramatically among the younger population.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome . Women with PCOS have a higher chance of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes can be prevented by practicing healthy lifestyle habits.
Also Check: How Does Diabetes Cause Hypertension
How Are Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Treated
Theres no cure for type 1 diabetes. People with type 1 diabetes dont produce insulin, so it must be regularly injected into the body.
Some people take injections into soft tissue, such as the stomach, arm, or buttocks, several times per day. Other people use insulin pumps. Insulin pumps supply a steady amount of insulin into the body through a small tube.
Blood sugar testing is an essential part of managing type 1 diabetes, because levels can go up and down quickly.
Type 2 diabetes can be managed and even reversed with diet and exercise alone, but many people need extra support. If lifestyle changes arent enough, your doctor may prescribe medications that help your body use insulin more effectively.
Monitoring your blood sugar is an essential part of type 2 diabetes management too. Its the only way to know if youre meeting your target levels.
Your doctor may recommend testing your blood sugar occasionally or more frequently. If your blood sugar levels are high, your doctor may recommend insulin injections.
How Are Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed
The primary test used to diagnose both type 1 and type 2 diabetes is known as the A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, test.
This blood test determines your average blood sugar level for the past 2 to 3 months. Your doctor may draw your blood or give you a small finger prick.
The higher your blood sugar levels have been over the past few months, the higher your A1C level will be. Test results are expressed as a percentage. An A1C level of 6.5 percent or higher indicates diabetes.
The A1C test isnt accurate for people with sickle cell anemia or the sickle cell trait. If you have this condition or trait, then your doctor will have to use a different test.
Read Also: What Is The Ribbon Color For Type 1 Diabetes

