Diabetic Ulcer Treatment And Healing Process
Diabetes interrupts the bodys healing process by restricting its efficiency and slowing its speed. Chronically high blood sugar levels act like a stranglehold to white blood cells and impair their function. Without white blood cells to fight away bacteria, infection can effortlessly take root and spread throughout any wound.
Diabetes is also correlated with poor circulation, which exacerbates an already compromised wound-healing process. ;Consistently strong circulation is essential to help red blood cells deliver nutrients to the wound. Without strong circulation, diabetic patients become even more vulnerable to infections and ulcers.
Of course, diabetes also causes overwhelming nerve damage. This means that you might not be able to feel or sense the infected, slow-healing wound on your body, even as it causes you significant harm. Since the feet endure so much pressure on a regular basis and often remain trapped in dark, moist shoes and socks, theyre the first place where diabetic ulcers develop.
How Can You Prevent Foot Ulcers
Here are some tips to preventing foot ulcers:
- Watch your blood sugar. The best way to prevent diabetic foot ulcers is to keep your blood sugar levels under control. Uncontrolled glucose is often behind neuropathy, which causes loss of feeling in the feet and may allow a sore to go unnoticed. Maintaining normal glucose levels will also help any sores on the foot heal faster. This can help keep ulcers from developing.
- Pay attention to your feet. Dr. Scott says its important to conduct daily foot inspections;if you have diabetes.;Catching a sore early can go a long way in preventing major problems. Cant see the bottoms of your feet? Try this: Put a mirror on the floor and hold each foot over it. Or ask a family member to check all areas of your feet regularly.
Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Prevention Diagnosis And Classification
DAVID G. ARMSTRONG, D.P.M., and LAWRENCE A. LAVERY, D.P.M., M.P.H., University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio and the Diabetic Foot Research Group, San Antonio, Texas
Am Fam Physician.;1998;Mar;15;57:1325-1332.
;See related patient information handout on maintaining healthy feet in diabetics, written by the authors of this article.
Diabetic foot complications are the most common cause of nontraumatic lower extremity amputations in the industrialized world. The risk of lower extremity amputation is 15 to 46 times higher in diabetics than in persons who do not have diabetes mellitus.1,2 Furthermore, foot complications are the most frequent reason for hospitalization in patients with diabetes, accounting for up to 25 percent of all diabetic admissions in the United States and Great Britain.35
The vast majority of diabetic foot complications resulting in amputation begin with the formation of skin ulcers. Early detection and appropriate treatment of these ulcers may prevent up to 85 percent of amputations.6,7 Indeed, one of the disease prevention objectives outlined in the Healthy People 2000 project of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services is a 40 percent reduction in the amputation rate for diabetic patients. Family physicians have an integral role in ensuring that patients with diabetes receive early and optimal care for skin ulcers.
Don’t Miss: Why Does My Blood Sugar Go Up At Night
Where Does An Ulcer Appear
There are many different kinds of ulcers. While peptic ulcers form in the stomach or upper intestine lining, ulcers can also occur almost anywhere on the body.
Ulcers that are found outside the body can include leg and foot ulcers. These ulcers are generally swollen or tender and can cause itchiness or pain. Skin discoloration and changes in texture are also common in ulcers found outside the body.
Whether they are found inside or on the skin’s surface, ulcers are sores that are often slow to heal. Once they have disappeared, ulcers can return if not treated properly. Depending on the cause of the ulcers, they can require different treatment options.
Diabetes Peripheral Arterial Disease And Foot Ulcers
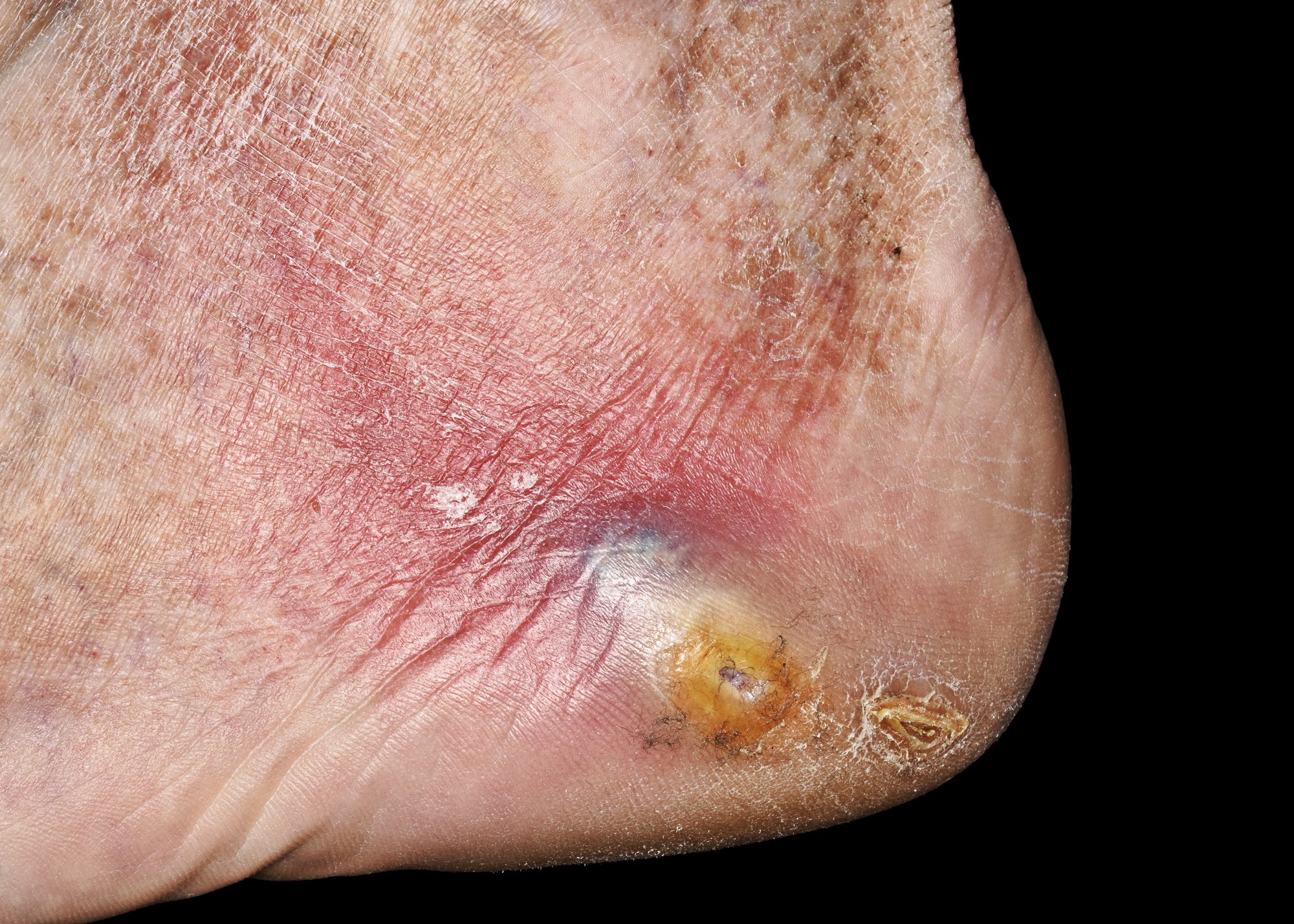
Learn about diabetic foot ulcers, a common and costly complication of diabetes that often leads to lower limb amputation, and the role peripheral arterial disease plays in its development and severity.
Dr. Edward Boyko and Dr. Matilde Monteiro-Soares are co-authors of the chapter, Peripheral Arterial Disease, Foot Ulcers, Lower Extremity Amputations, and Diabetes, in the NIDDK publication Diabetes in America, 3rd Edition. Here, they discuss how health care professionals can diagnose PAD and prevent foot complications in patients with diabetes.
Q: What are diabetic foot ulcers? How are diabetes, PAD, and foot ulcers related?
Dr. Monteiro-Soares: Theres still some debate about a specific definition for diabetic foot ulcers. However, experts agree that a diabetic foot ulcer is a break in the skin that must involve at least the epidermis and a part of the dermis, but it can reach more deeply to tendons or even bone. A diabetic foot ulcer may occur anywhere on the foot, but it must be located below the ankle. An ulcer on the ankle would not be classified as a diabetic foot ulcer. Also, the foot ulcer must occur in a person who has a diagnosis of diabetes, of course.
Q: How common are PAD and foot ulcers among people who have diabetes?
Q: For health care professionals caring for patients who have diabetes, what are the challenges involved in diagnosing and managing PAD?
Q: What challenges are involved in preventing or treating diabetic foot ulcers?
You May Like: Average Life Expectancy Type 1 Diabetes
Keep Your Nails Clean
Whether you have diabetes or not, neglecting your toenails unclean and unhygienic. It is not advisable for diabetic patients to trim their nails. But dont let this be an excuse for you to go on with unclean toenails, as bacteria could easily reproduce and reach your wound, leading to infection. There are doctors who specialize in foot care called podiatrists, and they will help you keep your foot maintained and your foot ulcer safe.
How Can You Treat Foot Ulcers
Typical wound care for a foot ulcer is debridement . Taking this tissue off sparks the bodys natural healing mechanism, Dr. Scott says.
Your doctor will then apply a dressing to the wound, which youll need to change regularly.
Youll also have to offload the affected part of the foot, he says. Continued pressure on the sore will only worsen it. So youll likely wear a cast, surgical shoe or boot that keeps weight off the injured site while the wound heals.
If the ulcer hasnt healed in four weeks or you have a bone infection, your doctor may recommend more advanced therapies.
These may include:
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy to promote healing
You May Like: How To Determine If You Have Diabetes
Why Is Wound Care So Important For Diabetic Foot Ulcers
According to our diabetic foot specialists in Hialeah and Miami, the goal of treatment is to ensure that a foot ulcer heals. When treating foot ulcers, doctors may deem it necessary to remove dead tissue from the wound. This is done under anesthesia. After the wound has been cleaned, covered, and bandaged it is important that you keep the foot clean.
It is known that people with diabetes are more prone to infections, so you should keep an eye on your wounds to ensure they don’t develop into something worse. If any of your wounds seem to worsen, it is imperative for you to see a doctor right away. If the wound becomes infected with bacteria, and the healing process does not take place, amputation may be required to prevent additional complications.
Diabetes Causes Peripheral Artery Disease
Due to diabetes, blood vessels become inflamed and hardened. It also leads to the narrowing of the arteries due to which the flow of oxygen, glucose, and essential nutrients to the wounded tissues are obstructed. Due to lack of oxygen, the wound becomes more prone to infections, and ulcers can easily develop.
Also Check: What Causes Diabetics To Lose Their Legs
How Are Diabetic Foot Ulcers Treated
If you have diabetes and notice a blister, cut, callus, sore, or other foot issues, seek immediate medical care to avoid the development of a foot ulcer. Once an ulcer develops, it is difficult to heal and your risk of developing a serious infection increases.;
Your doctor at Arlington/Mansfield Foot & Ankle Centers evaluates your feet and conducts important vascular and nerve testing. If a foot ulcer presents, your provider creates a customized care plan for you. Treatment may include:
- Medical care or dressings to prevent infection
- Debriding the wound to remove dead skin/tissue
- Medication to promote healing
- Off-loading to alleviate pressure from wounds or ulcers
If your doctor determines off-loading is needed, youll be outfitted with special footgear, a brace, casting, or a wheelchair to help take the pressure off the ulcer so it can heal.;
Ready to learn more about diabetic foot care or treatment for diabetic foot ulcers? Contact the Arlington/Mansfield Foot & Ankle Center nearest to you or request an appointment online now!
You Might Also Enjoy…
Can I Avoid Diabetic Foot Ulcers
The best way to treat diabetic foot ulcers is to avoid them in the first place. The first step in preventing a foot ulcer is to control your blood sugar. Elevated blood sugar creates nerve damage, which can trigger foot problems.;
Diabetic feet often have increased pain and swelling, and cold and warm baths can help. Warm water increases blood flow while cold water baths reduce inflammation. You can alternate between the two or add ice massages for optimal relief.;
Staying active helps improve circulation and decrease your risk of developing nerve damage. Regular walking helps manage your blood sugar and prevent diabetic neuropathy, which is associated with diabetic foot ulcers.;
Be sure to wear proper footwear and avoid shoes that cause the blisters, calluses, and sores that lead to diabetic ulcers. Our podiatrists can help fit you for diabetic shoes or inserts to ensure the best preventive care for your feet.
Finally, if you have diabetes its important to develop a healthy foot care routine with the help of a diabetic foot care specialist. Specialized care includes:
- Regular foot examinations
- Professional care of calluses and corns
- Treating wounds and blisters
- Trimming toenails to prevent injury
Recommended Reading: What Makes Insulin In The Body
The Bottom Line: Choose A Wound Healing And Hbot Specialist Near You
R3 Wound Care and Hyperbarics opened its first location in San Antonio to answer the communitys growing need for high-quality outpatient wound care services. Not just standard wound care, but care provided in a comfortable, refreshing, and attractive environment.
Now R3 Wound Care is located at five convenient locations throughout Texas to provide the advanced wound care and hyperbaric oxygen therapy that was previously only available at large medical institutions. R3 acts on its mission to make wound healing as pleasant and successful as possible.
When you trust your diabetic foot ulcer treatment to the professionals at R3, youll benefit from R3s private setting with the latest hyperbaric technology. Every;HBOT treatment;occurs in a clear acrylic chamber where you relax, recline, and enjoy a good book or movie for a few hours. You can hear and speak throughout your treatment, and the entire process is painless.
Visit the R3;wound care clinic location near you today to learn more about this natural alternative healing treatment and its potential to save your limb or your life! We have 4 locations across the Dallas Fort Worth and San Antonio areas.
How To Treat Ulcers
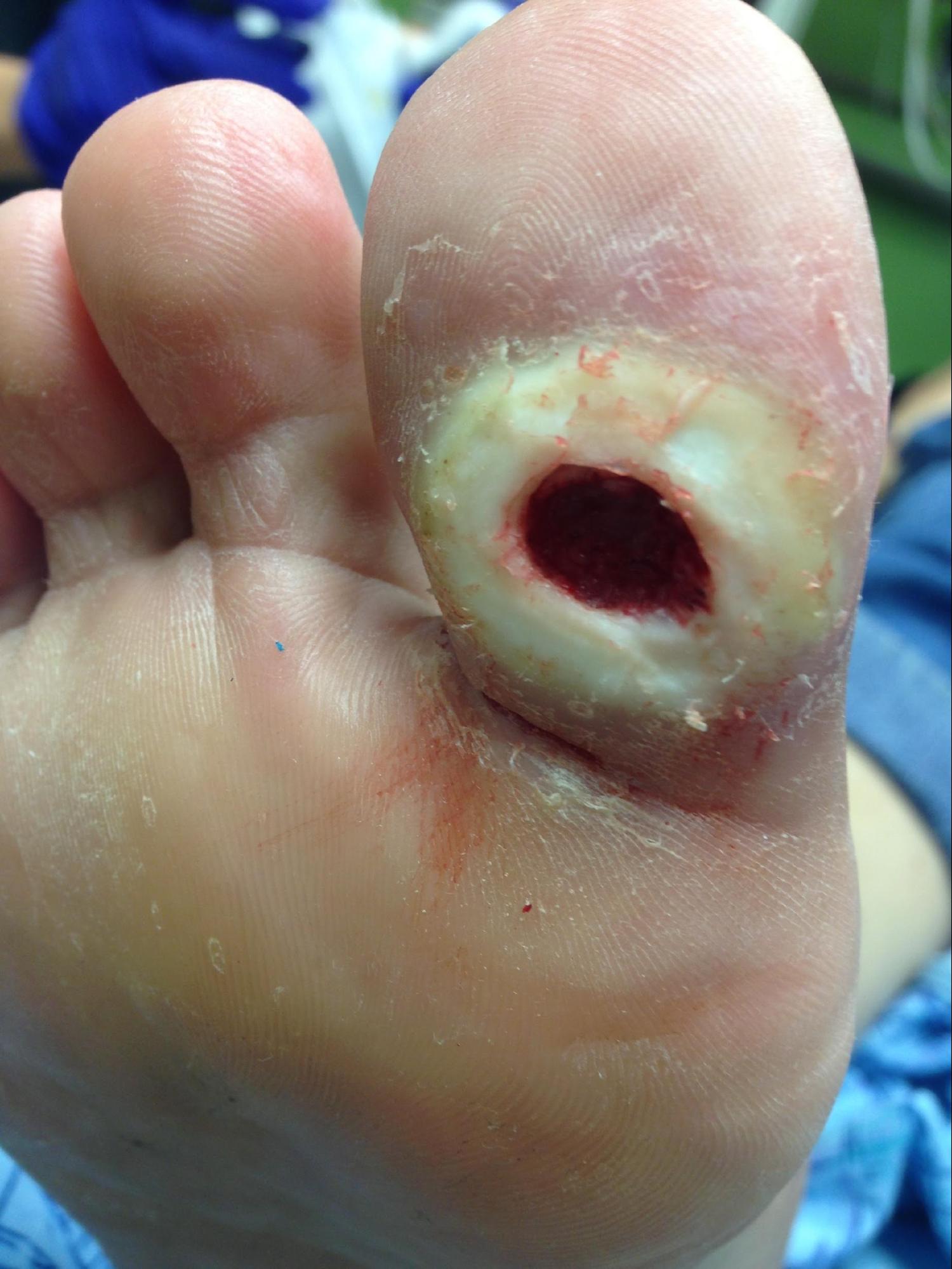
If you do get an ulcer or notice a change in your skin that youâre not sure about, tell your doctor right away. Youâll likely get a procedure called debridement, which removes unhealthy tissue from the wound to spur healing.
Your doctor will also work with you to try to keep your sore or ulcer from getting infected and becoming bigger. Some of the steps they may recommend include:
Clean your ulcer daily. Use soap and water, unless your doctor recommends another cleanser. Donât use hydrogen peroxide or soak your wound in a bath or whirlpool, because this could reduce healing and may boost your odds of infection.
Keep your ulcer bandaged or covered with a wound dressing. While you may have heard that itâs important to âair outâ wounds, experts now know that not covering a wound actually increases the odds of infection and slows healing.
Keep pressure off your ulcer, especially if itâs on your foot. This may mean you need to use crutches, special footwear, a brace, or other devices. Reducing pressure and irritation helps ulcers heal faster.
Use the topical medications your doctor recommends. These may be saline, growth factors, and/or skin substitutes.
Keep your blood sugar under control. In addition to reducing your risk of ulcers, tight blood sugar control helps your body heal existing ulcers.
Recommended Reading: How To Increase Blood Flow To Feet For Diabetics
Why Are Diabetics Prone To Foot Ulcers And Other Chronic Wounds
Diabetic patients are more prone to developing chronic wounds for a few reasons. Two of the most influencing factors are nerve damage and blood circulation issues that are common among diabetic patients.
Nerve damage, or neuropathy, tends to occur in patients who have a longer history with diabetes because elevated blood glucose levels damage nerves over time. Neuropathy causes patients to experience reduced, or lack of, sensation in the areas affected.
Many patients can sustain trauma or develop an infection without realizing it because theyre unable to feel pain in the area. Further, neuropathy commonly affects the feet, so a wound on the bottom of the foot can escalate quickly because the patient cannot feel or see the wound easily.
Blood circulation issues also can increase the risk for developing chronic wounds, as well as making the wounds more prone to infection. High blood glucose levels cause the narrowing of blood vessels, which constricts blood supply, Estocado said. Adequate blood supply is essential to normal wound healing. The secondary effect of impaired blood supply is a decrease in white blood cells, which are responsible for fighting infection and maintaining a strong immune system.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Diabetic Ulcer
Since diabetic ulcers often occur on the foot, pain can usually be felt while walking or standing. Wounds that come from diabetic ulcers may look like craters and can leak if they become infected. While the signs of a diabetic ulcer may seem obvious, but to many, they are not.
Diabetic ulcers can be complicated by poor circulation. When the blood does not properly circulate throughout the body, the effects can vary from mild to severe. One problem that can commonly occur with diabetes is the loss of sensation created from poor blood circulation. When the foot becomes desensitized to pain, detecting a diabetic ulcer can be much more difficult.
Poor circulation can also slow the healing process of a foot wound. While some scars may heal without treatment, diabetic ulcers are more likely to become infected. When this happens, the wound may look slightly different from a regular skin ulcer.
An infected diabetic ulcer can create symptoms such as swelling, an elevated skin temperature when touched, and pain. Pus, a foul odor, and other secondary wound signs are also common in a diabetic ulcer infection.
You May Like: Where Should Your Blood Sugar Be
Complications Of Untreated Diabetic Ulcers
If a diabetic ulcer is not adequately treated, the risk of infection can significantly increase. Abscesses, the spread of disease, gangrene, and eventual amputation are all possible outcomes of poorly treated or neglected diabetic ulcers.
Diabetic foot ulcers can quickly become severe conditions. By treating them as soon as possible, the condition can be remedied before the chance of infection. Serious wounds will not go away on their own and will require prompt attention.
Fortunately, diabetic ulcers can be easily detected. Unlike ulcers that form on the inside of the body, these wounds can be seen and felt. A diabetic ulcer’s symptoms include foot pain, discoloration or numbness, and a deepening wound that will not heal with time. Diabetic ulcers occur in those who have diabetes. The diagnosis of diabetes combined with painful wounds on the bottom of the feet is a good indication that a diabetic ulcer needs treatment.
Structural Deformity And Limited Joint Mobility
Foot deformities, which are common in diabetic patients, lead to focal areas of high pressure. When an abnormal focus of pressure is coupled with lack of sensation, a foot ulcer can develop. Most diabetic foot ulcers form over areas of bony prominences , especially when bunions, calluses or hammer-toe formations lead to abnormally prominent bony points. Foot deformities are believed to be more common in diabetic patients due to atrophy of the intrinsic musculature responsible for stabilizing the toes.20
FIGURE 2.
Usual locations of ulcers in the diabetic foot. Ulceration is particularly likely to occur over the dorsal portion of the toes and on the plantar aspect of the metatarsal heads and the heel.
FIGURE 2.
Usual locations of ulcers in the diabetic foot. Ulceration is particularly likely to occur over the dorsal portion of the toes and on the plantar aspect of the metatarsal heads and the heel.
Rigid deformities or limited range of motion at the subtalar or metatarsophalangeal joints have also been associated with the development of diabetic foot ulcers.26,27 Other mechanisms of skin breakdown in the insensate diabetic foot include puncture wounds and thermal injuries from, for example, hot water soaks.
Also Check: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
How Do Diabetic Foot Ulcers Form
Ulcers form due to a combination of factors, such as lack of feeling in the foot, poor circulation, foot;deformities, irritation , and trauma, as well as duration of diabetes. Patients who have diabetes for many years can develop neuropathy, a reduced or complete lack of;ability to feel pain;in the feet due to nerve damage caused by elevated blood glucose levels over time. The nerve damage often can occur without pain and one may not even be aware of the problem. Your podiatric physician can test feet for neuropathy with a simple and painless tool called a monofilament.
Vascular disease can complicate a foot ulcer, reducing the bodys ability to heal and increasing the risk for an infection. Elevations in blood glucose can reduce the bodys ability to fight off a potential infection and also retard healing.;

