Monitoring Your Own Blood Glucose
If you have type 2 diabetes, as well as having your blood glucose level checked by a healthcare professional every two to six months, you may be advised to monitor your own blood glucose levels at home.
Even if you have a healthy diet and are taking tablets or using insulin therapy, exercise, illness and stress can affect your blood glucose levels.
Other factors that may affect your blood glucose levels include drinking alcohol, taking other medicines and, for women, hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle.
A blood glucose meter is a small device that measures the concentration of glucose in your blood. It can be useful for detecting high blood glucose or low blood glucose .
If blood glucose monitoring is recommended, you should be trained in how to use a blood glucose meter and what you should do if the reading is too high or too low.
Blood glucose meters aren’t currently available for free on the NHS but, in some cases, blood monitoring strips may be. Ask a member of your diabetes care team if you’re unsure.
Read about diabetic eye screening.
When Should I Call My Doctor
Its important to monitor diabetes very closely if youre sick. Even a common cold can be dangerous if it interferes with your insulin and blood sugar levels. Make a sick day plan with your healthcare provider so you know how often to check your blood sugar and what medications to take.
Contact your provider right away if you experience:
- Confusion or memory loss.
- Nausea and vomiting for more than four hours.
- Problems with balance or coordination.
- Severe pain anywhere in your body.
- Trouble moving your arms or legs.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Type 2 diabetes is a disease where your body doesnt make enough insulin and cant use sugar the way it should. Sugar, or glucose, builds up in your blood. High blood sugar can lead to serious health complications. But Type 2 diabetes is manageable. Regular exercise and a healthy diet can help you manage your blood sugar. You may also need medication or insulin. If you have Type 2 diabetes, you should monitor your blood sugar at home regularly and stay in close communication with your healthcare provider.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 03/25/2021.
References
Accuracy Of Diabetes Test Results
Depending on the test used, the level of blood glucose can be affected by many factors including:
- eating or drinking
- taking medications that are known to raise blood glucose levels, such as oral contraceptives, some diuretics and corticosteroids
- physical illness or surgery that may temporarily alter blood glucose.;
If you think any of the above may have influenced your result, then it is important to discuss this further with your doctor.
If you don’t have diabetes, but your glucose levels are higher than normal, this is called pre-diabetes and it includes one or both of:
- impaired fasting glucose IFG
- impaired glucose tolerance IGT .
Diabetes can be delayed or prevented in some people with pre-diabetes by:
- increasing physical activity
- following a healthy eating plan developed by a dietitian;
- losing 510 per cent of their body weight, if they are overweight.
Talk to your doctor about how you can reduce your risk of developing diabetes.
Also Check: Diabetes Weight Loss Diets
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms, treatment, and complications from type 2 diabetes may vary from person to person. The following information will help you learn more about this disease and provide you with helpful tools, assessments and resources.
-
If left untreated or improperly managed, diabetes can lead to a variety of life-threatening complications.
Prognosis In Intensive Therapy
In the UKPDS, more than 5000 patients with type 2 diabetes were followed up for up to 15 years. Those in the intensely treated group had a significantly lower rate of progression of microvascular complications than did patients receiving standard care. Rates of macrovascular disease were not altered except in the metformin-monotherapy arm in obese individuals, in which the risk of myocardial infarction was significantly decreased.
In the 10-year follow-up to the UKPDS, patients in the previously intensively treated group demonstrated a continued reduction in microvascular and all-cause mortality, as well as in cardiovascular events, despite early loss of differences in glycated hemoglobin levels between the intensive-therapy and conventional-therapy groups. The total follow-up was 20 years, half while in the study and half after the study ended.
Other, shorter studies, such as Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease: Preterax and Diamicron Modified Release Controlled Evaluation and the Veterans Affairs Diabetes Trial , showed no improvement in cardiovascular disease and death with tight control .
A British study indicated that the HbA1c level achieved 3 months after the initial diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus predicts subsequent mortality. In other words, according to the report, aggressive lowering of glucose after diagnosis bodes well for long-term survival.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take Metformin To Lower A1c
Doctor On Mission To Stop Preventable Amputations In Diabetic Black Americans
As part of the new study, 12 men and women who had Type 2 diabetes and were of normal weight with an average BMI of 24.5 were asked to eat only 800 calories a day for two weeks. Their diet consisted mostly of low-calorie soups, shakes and non-starchy vegetables.
When those two weeks were over, they entered a maintenance phase for about a month, gradually returning to their regular eating regimen, but aiming to keep off the weight they lost, according to Diabetes UK.
They repeated this pattern up to three times until they had lost 10%-15% of their body weight.
Eight of the 12 participants achieved remission of their Type 2 diabetes, researchers reported. On average, the people in the study lost 18 pounds and reduced their body fat from 33% to 27%. Scans showed the amount of fat in their organs also fell.
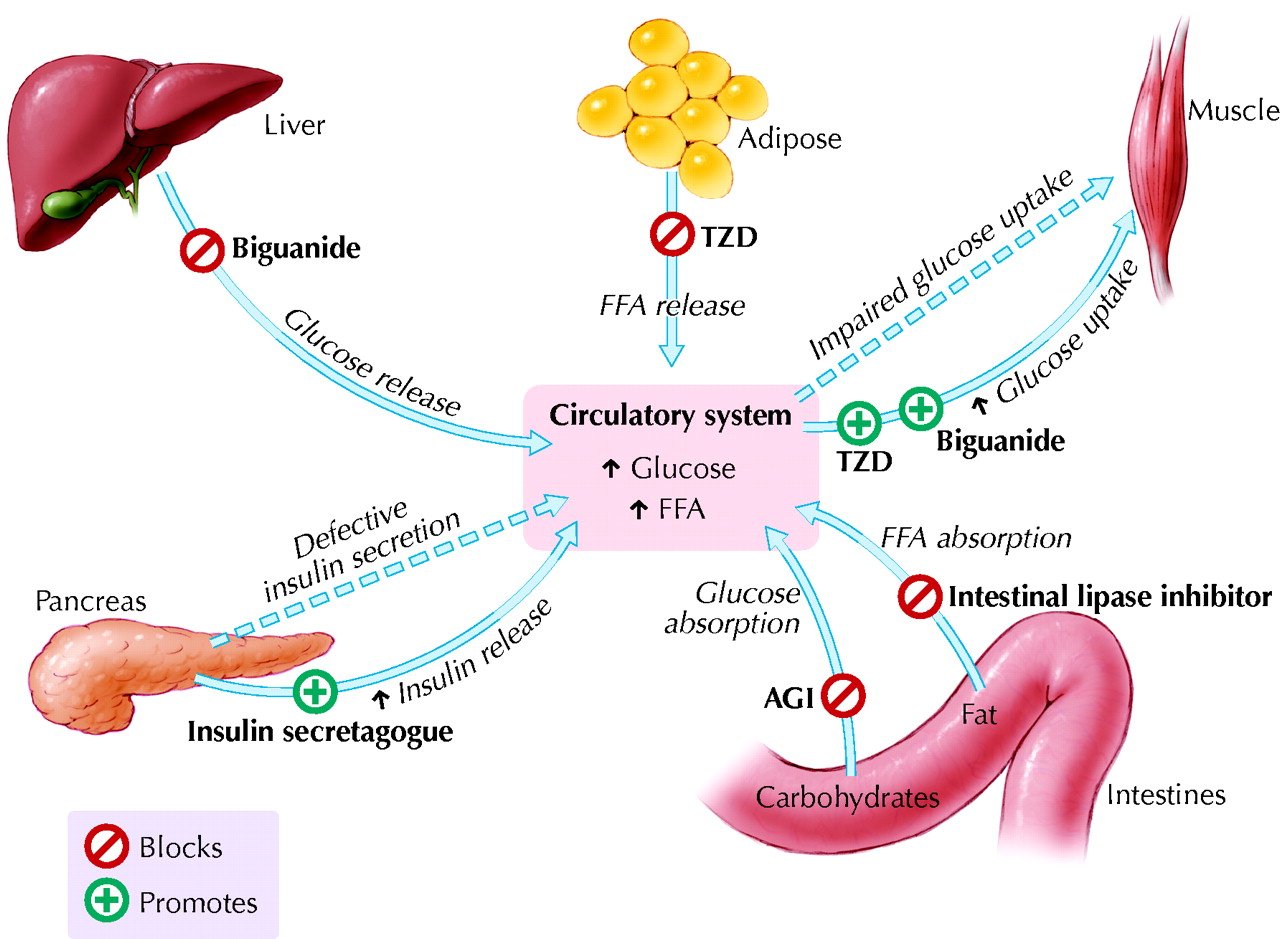
Medicines For Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a progressive condition and;usually gets worse over time. Making lifestyle changes, such as adjusting your diet and taking more exercise, may help you control your blood glucose levels at first, but may not be enough in the long term.
You may eventually need to take medication to help control your blood glucose levels.
Initially, this will usually be in the form of tablets and can sometimes be a combination of more than one type of tablet. It may also include insulin or another medication that you inject.
Read Also: How Can Diabetics Improve Circulation
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
If you have type 2 diabetes, your GP or diabetes care team will need to take a reading of your blood glucose level about every two to six months.
This will show how stable your glucose levels have been in the recent past and how well your treatment plan is working.
The HbA1c test is used to measure blood glucose levels over the previous two to three months.
HbA1c is a form of haemoglobin, the chemical that carries oxygen in red blood cells, which also has glucose attached to it.
A high HbA1c level means that your blood glucose level has been consistently high over recent weeks, and your diabetes treatment plan may need to be changed.
Your diabetes care team can help you set a target HbA1c level to aim for. This will usually be less than 53 mmol/mol or individualised as agreed with your diabetes team.
Read more about the HbA1c test
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Managed
Theres no cure for Type 2 diabetes. But you can manage the condition by maintaining a healthy lifestyle and taking medication if needed. Work with your healthcare provider to manage your:
- Blood sugar: A blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring can help you meet your blood sugar target. Your healthcare provider may also recommend regular A1c tests, oral medications , insulin therapy or injectable non-insulin diabetes medications.
- Blood pressure: Lower your blood pressure by not smoking, exercising regularly and eating a healthy diet. Your healthcare provider may recommend blood pressure medication such as beta blockers or ACE inhibitors.
- Cholesterol: Follow a meal plan low in saturated fats, trans fat, salt and sugar. Your healthcare provider may recommendstatins, which are a type of drug to lower cholesterol.
You May Like: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
Build Your Health Care Team
There are many medical professionals who can help you live well with diabetes, including:
- Endocrinologists
NHS Inform: âType 2 diabetes.â
American Diabetes Association: âSkin Complications,â âDiabetes and Hearing Loss.â
Alzheimerâs Association: âAlzheimerâs disease and type 2 diabetes: A growing connection.â
UpToDate: âSodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors for the treatment of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Diabetes Care: “Investigation of the Accuracy of 18 Marketed Blood Glucose Monitors.â
Diatribe.org: âFDA Publishes Final Recommendations on Blood Glucose Meter Accuracy.â
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology: “Lot-to-lot variability of test strips and accuracy assessment of systems for self-monitoring of blood glucose according to ISO 15197.â
MIT School of Engineering: “How do glucometers work?â
National Institute of Mental Health: “Depression.”
American Diabetes Association: “Depression.”
Type 2 Diabetes In Children And Teens
Childhood obesity rates are rising, and so are the rates of type 2 diabetes in youth. More than 75% of children with type 2 diabetes have a close relative who has it, too. But its not always because family members are related; it can also be because they share certain habits that can increase their risk. Parents can help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by developing a plan for the whole family:
- Drinking more water and fewer sugary drinks
- Eating more fruits and vegetables
- Making favorite foods healthier
- Making physical activity more fun
Healthy changes become habits more easily when everyone makes them together. Find out how to take charge family style with these healthy tips.
Also Check: Low A1c In Nondiabetic
Prognosis Of Type 2 Diabetes
Dont lose hope, though. You dont have to be a statistic. Receiving a prompt diagnosis can help you get your health on track and reduce your risk for complications.
Indeed, if you take care to manage your blood sugar by following a healthy diet, exercising regularly, taking your prescribed medication, and losing weight, you may find your quality of life to be better with diabetes than it was before your diagnosis.
FEATURED
What Kind Of Doctor Treats Diabetes
Endocrinology is the specialty of medicine that deals with hormone disturbances, and both endocrinologists and pediatric endocrinologists manage patients with diabetes. People with diabetes may also be treated by family medicine or internal medicine specialists. When complications arise, people with diabetes may be treated by other specialists, including neurologists, gastroenterologists, ophthalmologists, surgeons, cardiologists, or others.
You May Like: What A1c Level Requires Medication
These Are Some Of The Statistics:
- 80-90% of people with Type 2 diabetes have other family members with diabetes.
- 10-15% of children of a diabetic parent will develop diabetes.
- If one identical twin has type 2 diabetes, there is up to a 75% chance that the other will also be diabetic.
- There are many genetic or molecular causes of type 2 diabetes, all of which result in a high blood sugar.
- As yet, there is no single genetic test to determine who is at risk for type 2 diabetes.
- To develop type 2 diabetes, you must be born with the genetic traits for diabetes.
- Because there is a wide range of genetic causes, there is also a wide range in how you will respond to treatment. You may be easily treated with just a change in diet or you may need multiple types of medication.
The hallmark of type 2 diabetes is resistance to the action of insulin and insufficient insulin to overcome that resistance
Causes Of Type 2 Diabetes
Your pancreas makes a hormone called insulin. It helps your cells turn glucose, a type of sugar, from the food you eat into energy. People with type 2 diabetes make insulin, but their cells don’t use it as well as they should.
At first, your pancreas makes more insulin to try to get glucose into your cells. But eventually, it can’t keep up, and the glucose builds up in your blood instead.
Usually, a combination of things causes type 2 diabetes. They might include:
You May Like: How To Mix Nph And Regular Insulin
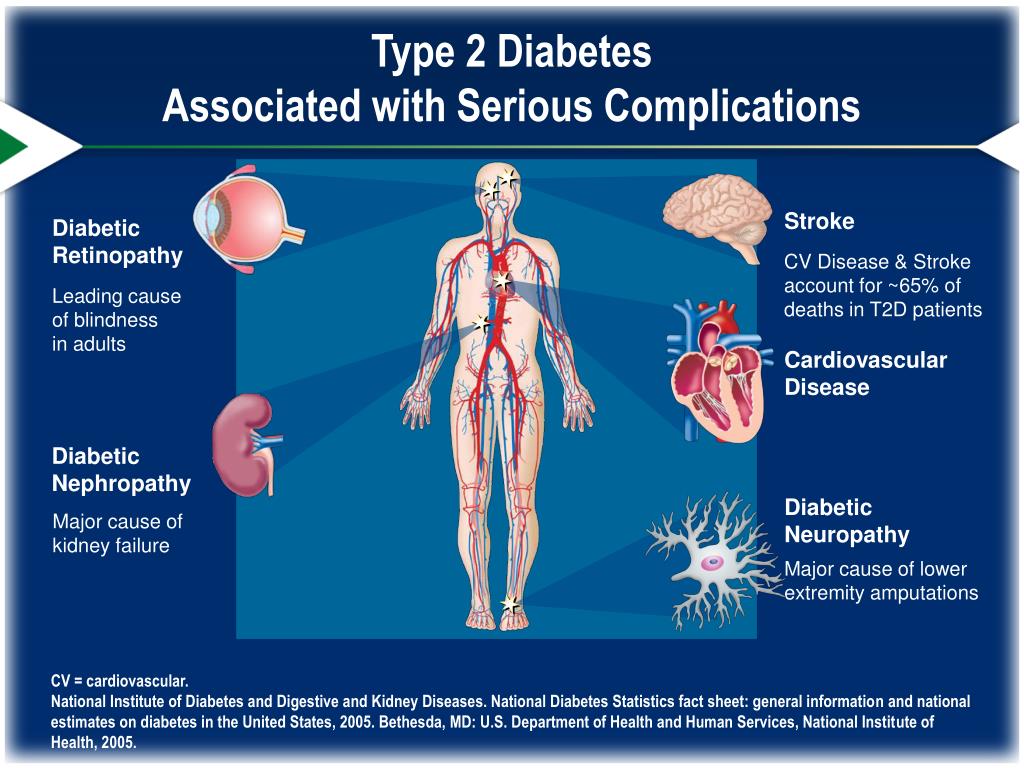
Microvascular And Macrovascular Complications
Longer survival times and development of type 2 diabetes at younger ages increase the risk of developing duration-dependent complications. In UKPDS 16, 18% of patients, all of whom were presumed to be clinically healthy, had a clinical end point within 6 years of diagnosis.
UKPDS 35 showed highly significant associations between development of diabetes complications, including death, across the broad range of exposure to glycemia, with no evidence of a threshold. Conversely, each 1% reduction in mean A1C was associated with reduction in risk of 21% for any end point related to diabetes .
The role of complications on disease progression and failure has not been well studied. A change in insulin sensitivity and clearance is well recognized in renal failure and clearance is well recognized. However, the impact of these changes on the natural history of diabetes itself needs to be studied. Many patients with established complications tend to be poorly controlled, and factors such as glucose toxicity may play a role in disease progression as discussed above. In addition, various cardiovascular drugs such as diuretics and -blockers may affect -cell function adversely.
Receiving A Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosis
Whether or not you have prediabetes, you should see your doctor right away if you have the symptoms of diabetes. Your doctor can get a lot of information from blood work. Diagnostic testing may include the following:
- Hemoglobin A1C test.This test measures average blood glucose levels for the previous two or three months. You dont need to fast for this test, and your doctor can diagnose you based on the results. Its also called a glycosylated hemoglobin test.
- Fasting plasma glucose test. This test measures how much glucose is in your plasma. You may need to fast for eight hours before having it.
- Oral glucose tolerance test. During this test, your blood is drawn three times: before, one hour after, and two hours after you drink a dose of glucose. The test results show how well your body deals with glucose before and after the drink.
If you have diabetes, your doctor will provide you with information about how to manage the disease, including:
- how to monitor blood glucose levels on your own
- dietary recommendations
- physical activity recommendations
- information about any medications that you need
You may need to see an endocrinologist who specializes in the treatment of diabetes. Youll probably need to visit your doctor more often at first to make sure your treatment plan is working.
If you dont already have an endocrinologist, the Healthline FindCare tool can help you find a physician in your area.
Read Also: Ideal A1c Levels For Diabetes
Heres How You Can Get Started:
- Work with your doctor to determine what level of physical activity you should engage in
- Figure out how much time per day you can devote to exercise
- Set fitness goalshaving clear goals can help you stay motivated
- Consider where youll start working outthe gym, in your neighborhood, in a park?
- Build different activities;into your daily routine
- Start slowly and allow for recovery time
- Keep track of what you do and stay focused on your goals
- Listen to your body
Who Gets Type 2 Diabetes
No one knows for sure what causes type 2 diabetes. But many kids who develop it have at least one parent with diabetes and a family history of the disease, so there seems to be a genetic risk.
Most people with type 2 diabetes are overweight. Excess fat makes it harder for the cells to respond to insulin, and not being physically active makes this even worse. Type 2 diabetes used to mostly affect adults, but now more and more U.S. kids and teens, especially those who are overweight, are developing the disease.
Also, kids in puberty are more likely to have it than younger kids, probably because of normal rises in hormone levels that can cause insulin resistance during this stage of fast growth and physical development.
p
Read Also: What Are The First Signs Of Diabetes
Highlights From The Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects Canadians of all ages. If left uncontrolled, diabetes results in consistently high blood sugar levels , which can lead to serious complications such as cardiovascular disease, vision loss, kidney failure, nerve damage, and amputation. Fortunately, it is possible to remain healthy with diabetes through appropriate management and care.
The Public Health Agency of Canada , in collaboration with all provinces and territories, conducts national surveillance of diabetes to support the planning and evaluation of related policies and programs. This fact sheet presents an overview of diagnosed diabetes data from the Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System .
Viola Davis And Sisters On Tackling Diabetes In A Touch Of Sugar Doc
Most people with Type 2 diabetes a disease in which the body doesn’t use insulin properly and blood sugar levels are too high develop it in part because of obesity.
But about 10% of people with Type 2 diabetes are at a healthy BMI. The risk differs by race and ethnicity: the prevalence of the disease in this group was 5% in whites, 10% in Asians and American Indians/Alaskan Natives, 13% in Hispanics, 13.5% in Blacks and 18% in Hawaiians/Pacific Islanders, research has found.
The theory is that each person has a personal fat threshold, which if exceeded may cause fat to be stored in harmful places in the body and can lead to Type 2 diabetes, even if that person is slim. Internal fat around the pancreas and liver could be one of the reasons why people with a normal BMI can develop the disease, noted Diabetes UK, the charity that funded the study.
It turns out that the fat in the abdominal cavity, around the organs, what we call visceral fat, is the fat that is most effective in causing insulin resistance, Gabbay added.
Read Also: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic

