How To Enjoy A Healthy Type 1 Diabetes Diet
There’s no such thing as a ‘diabetic diet for type 1. Your diet should include making healthier food choices that are lower in saturated fat, sugar and salt.
Doing this will help you to:
- control blood fats
- control blood pressure
- maintain a healthy weight.
This can also help to reduce your risk of diabetes complications, including heart disease and stroke. As with any lifestyle changes, making gradual and realistic changes over a longer period of time is more likely to lead to success. See a registered dietitian for specific advice and an eating plan that is tailored to your individual needs and lifestyle.
Your diet and insulin
If you are using a basal bolus insulin regime, injecting several times a day, or youre on an insulin pump then it’s possible to be much more flexible in how many carbs you can eat and when.
Most people who follow this regime will count the carbohydrates that they eat and drink, and then calculate how much insulin they need to take. The amount of insulin will be adjusted depending on how much carbohydrate they are eating and other factors, such as physical activity, blood sugar levels or illness.
This can let you be more flexible with your food choices and meal times, without compromising your blood glucose control.
If you are on a twice-daily fixed insulin regimen you need to have regular meal times and eat roughly the same carbohydrate portion at these meals from day to day.
How Should I Draw Up The Insulin
Insulin is a suspension not a solution, so before administering it you must mix it. Some insulins should be gently rolled and not shaken, while others should be shaken thoroughly. Your veterinarian will advise you on how to handle the insulin. Some insulin has more of a tendency to settle out of suspension, so mixing is very important for accurate dosing.
“The trick is to mix it vigorously enough to blend it without creating foam.”
The trick is to mix it vigorously enough to blend it without creating foam. When you have finished mixing the insulin, turn the bottle upside down to see if any of the white insulin molecules still adhere to the bottom of the bottle. If so, more mixing is needed.
Have the needle and syringe, insulin bottle, and dog ready. Then, follow these steps:
Obligations That Come With Insulin
Insulin needs to be administered twice a day.
After your dog is diagnosed with diabetes, it will take some time until the vet is able to prescribe an adequate dosage of insulin, and there’s going to be some trial and error.
You or your vet will run tests on the dog’s glucose level several times a day or a week in order to see the reaction of your dogs organism to a particular dosage. The positive thing is that once a good dosage is established, the dog wont need the check-ups as often.
Insulin needs to be administered around the same time.
This means creating a schedule around your dogs injections. If you have frequent business trips, irregular working hours, or stay overtime often, you would need to think about the alternatives for keeping up with the schedule. You can ask a friend, family member or a pet sitter to administer it to your dog when you are unable.
Some dog owners feel anxious about giving a shot to their dog, especially because the dog is not thrilled about it either. But giving injections to dogs is fairly simple, and most people get used to it very quickly it becomes a regular routine for them and their pet.
You May Like: Metformin Dose Range
How To Reverse Insulin Resistance
If you have insulin resistance, you want to become the oppositemore insulin sensitive .
Physical activity makes you more sensitive to insulin, one reason why its a cornerstone of diabetes management . Dont wait until youre diagnosed with diabetes to start moving more. The earlier you take action , the better off youll be.
Weight loss is important too, as is avoiding high blood sugar, reducing stress, and getting enough sleep .
These lifestyle changes really work. Talk with your health care provider about how to get started.
What Are The Risk Factors For Diabetic Coma

While anyone who has diabetes is at risk for a diabetic coma, the causes depend on the type of diabetes:
- People with Type 1 diabetes have a greater chance of going into a diabetic coma as a result of diabetic ketoacidosis or hypoglycemia. This is because people with Type 1 diabetes always need insulin and have a wider range in their blood glucose levels than people with Type 2 diabetes.
- People with Type 2 diabetes have a greater chance of going into a diabetic coma from diabetic hyperosmolar syndrome than from diabetic ketoacidosis or hypoglycemia.
Other risks that can lead to diabetic coma in anyone who has diabetes include:
- Surgery.
Recommended Reading: Side Effect Of Insulin
Incretin Mimetics And Non
These medications come in oral pill form, or in injectable form, and include the GLP-1 and DPP-4 inhibitors. They slow down digestion and signal the pancreas to make more insulin. These have a desired side effect of weight loss, and can lower A1C, while using the bodys natural blood glucose lowering mechanisms.
Injectables that are for diabetes, but are not insulin help the pancreas to produce more insulin. However, they may cause a side effect of nausea. Extended release injectable medications are given once weekly.
How Long Can A Type 1 Diabetic Go Without Insulin
Answer:
In the absence of insulin, people with type 1 diabetes become very sick within a day or two and will die without immediate medical attention.
Friday, January 21, 2022 20:04:20 UTC
This internet site provides information of a general nature and is designed for educational purposes only. If you have any concerns about your own health or the health of your child, you should always consult with a physician or other health care professional.
This site is published by T-1 Today, Inc. , a 501c3 not-for-profit organization, which is responsible for its contents. By using this site, you agree to our Terms of Use, Legal Notice and Privacy Policy.
Children with Diabetes.com © 1995-2021 Children with Diabetes, Inc. | | All Rights Reserved.
Social
Also Check: Insulin To Glucagon Ratio
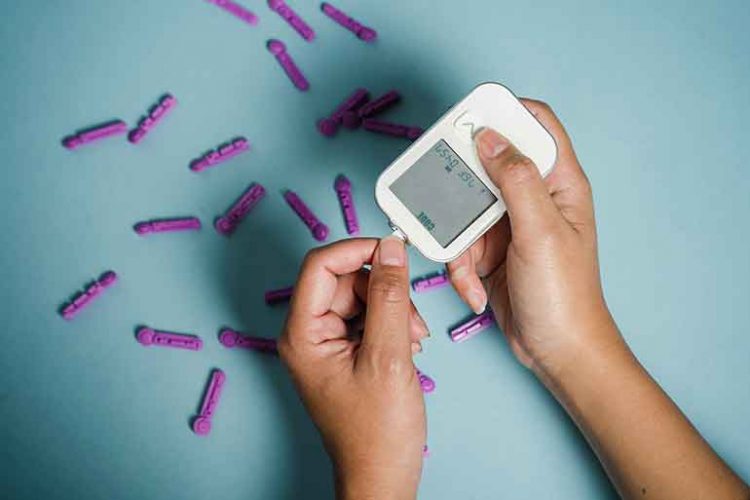
Having Your Blood Glucose Levels Checked
You’ll be measuring your blood glucose yourself every day, to check your levels.
Your GP or diabetes care team will also carry out a different blood test every two to six months, called the HbA1c test.
This gives a clearer idea of how well your treatment plan is working, by measuring how stable your glucose levels have been over the past 6-12 weeks.
It measures the amount of haemoglobin, which is the oxygen-carrying substance in red blood cells that has glucose attached to it. A high HbA1c level may indicate that your blood glucose level is consistently high and that your diabetes treatment plan needs to be altered.
The ideal HbA1c target for people with diabetes is below 53 mmol/mol.
Symptoms Causes Diagnosis And Treatments
For those with Type 1 Diabetes, this is an insulin emergency, developing in mere hours and having life-threatening consequences. Scary? Yes. Can you prevent it? Absolutely. Were here to empower you with clear answers to all your pressing Qs.
In This Article:
Elena Christofides MD, David Klonoff MD, and Guillermo Umpierrez MD
Also Check: Metformin For Hypoglycemia
Annual Health Checks If You’re In Remission
Youll also want to ensure that your HbA1c levels stay below 48mmol/l or 6.5%.
Be sure to have regular health checks with your healthcare team at least once a year, including retinal screening. That way, your healthcare team can follow up on existing complications, pick up on new complications and give you support as soon as possible if your HbA1c levels go up again.
What Foods Type 1s Should Avoid
Before your diagnosis of diabetes, it is likely that you experienced extreme thirst. It is a good idea to avoid sugary drinks and fruit juices as a way of quenching your thirst. They usually put blood glucose levels up very high and very quickly which is why they can be a useful treatment for a hypo .
Instead, drink water, sugar-free and diet soft drinks. Tea and coffee are still OK to include, too. Read more about what to drink when you have diabetes.
Dont bother with foods labelled diabetic or suitable for diabetics. These foods contain similar amounts of calories and fat, and they can affect your blood glucose levels. They are usually more expensive and can have a laxative effect. Stick to your usual foods. If you want to have an occasional treat, go for your normal treats and watch your portion sizes.
Also Check: How Many Carbs Per Day Diabetic
Exercise Physical Activity And Weight Loss
Its important for people with Type 2 diabetes to be physically active. They should aim to get in at least 30 minutes of physical activity five days per week. If weight loss is desired, a modest goal for weight loss of five to seven percent of body weight will help decrease insulin resistance, and protect remaining beta cells in the pancreas.
Research in the United Kingdom has shown that just a small amount of weight loss around the pancreas will greatly reduce insulin resistance. Overall weight loss can help reduce visceral fat.
Causes Of Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition, where the immune system mistakes the cells in your pancreas as harmful and attacks them.
Without insulin, your body will break down its own fat and muscle, resulting in weight loss. This can lead to a serious short-term condition called diabetic ketoacidosis. This is when the bloodstream becomes acidic, you develop dangerous levels of ketones in your blood stream and become severely dehydrated.
This results in the body being unable to produce insulin, which is required to move glucose out of the blood and into your cells to be used for energy. This is called Type 1 diabetes.
Read more about the causes of type 1 diabetes
Don’t Miss: Does Metformin Dehydrate You
Insulin Blood Sugar And Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin is a key player in developing type 2 diabetes. This vital hormoneyou cant survive without itregulates blood sugar in the body, a very complicated process. Here are the high points:
- The food you eat is broken down into blood sugar.
- Blood sugar enters your bloodstream, which signals the pancreas to release insulin.
- Insulin helps blood sugar enter the bodys cells so it can be used for energy.
- Insulin also signals the liver to store blood sugar for later use.
- Blood sugar enters cells, and levels in the bloodstream decrease, signaling insulin to decrease too.
- Lower insulin levels alert the liver to release stored blood sugar so energy is always available, even if you havent eaten for a while.
Thats when everything works smoothly. But this finely tuned system can quickly get out of whack, as follows:
- A lot of blood sugar enters the bloodstream.
- The pancreas pumps out more insulin to get blood sugar into cells.
- Over time, cells stop responding to all that insulintheyve become insulin resistant.
- The pancreas keeps making more insulin to try to make cells respond.
- Eventually, the pancreas cant keep up, and blood sugar keeps rising.
Before You Try Fasting
Talk to your doctor first. If you have type 1 diabetes, other health problems due to diabetes, or have had hypoglycemia, your doctor may recommend you not fast.
If your doctor says itâs OK to try, ask if you need to check your blood sugar more often or adjust your diabetes medication during and after fasting.
Watch for signs of low blood sugar. If you start to feel shaky, sweaty, or confused, your blood sugar may be too low. Stop fasting right away and do what you normally would to treat hypoglycemia. For example, eat a glucose gel or have a sugary drink followed by a small, balanced meal when your blood sugar level is back to normal.
Be careful about what you eat after fasting. Eating too many carbohydrates after fasting can cause your blood sugar levels to become too high. Choose healthy, balanced meals and snacks.
Use caution. Donât do tough workouts while youâre fasting. Hard exercise can make your blood sugar levels dip, which can lead to hypoglycemia. Ask your doctor what activities are OK to do, or just take a break.
Stay hydrated. Having diabetes puts you at risk of dehydration, which can make your blood sugar harder to manage. Drink lots of water and calorie-free beverages when you fast.
Show Sources
Recommended Reading: Is Pasta Good For Diabetics
What Is Diabetes Mellitus
In dogs, diabetes mellitus is caused by the failure of the pancreas to produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar. This is insulin dependent diabetes mellitus . This type of diabetes usually results from destruction of most or all of the beta-cells that produce insulin in the pancreas. As the name implies, dogs with this type of diabetes require insulin injections to stabilize blood sugar levels.
How Long Can Someone Live Without Insulin
Answer:
The fact that you are asking the question has me suspiciously worried! I hope you are not trying to hurt yourself or planning to see how long you can go without insulin.
The answer, perhaps, mostly lies in how long the person has had type 1 diabetes. For someone like yourself, who indicated that you have had diabetes for more than 10 years, you MIGHT be able to live for 7 to 10 or so days without insulin. But, the death would be awful and difficult and not peaceful. You would begin to have much urination and be extremely thirsty but, you would also develop abdominal pain and get nauseated and vomit so you might drink but not be able to keep anything down with all the vomiting. You would start to get achy and sore and could have a terrible headache as your brain began to swell! You would have blurred vision and would begin to become delirious before you probably would go into a coma and become brain dead. The death would be awful to watch and impossible to bear by those that love you. And even if you did not progress that far to death, if there were too much delay before you could get taken to an emergency room, the damage may already have been done and it might be too late to reverse matters back to normal.
DO NOT OMIT YOUR INSULIN DOSES.
DSAdditional comments from Dr. Tessa Lebinger:
A teenager who has had diabetes since infancy and for 10 years probably is making very little insulin now and could get very sick and die VERY quickly if they miss their insulin.
Also Check: Can Diabetics Eat Mac And Cheese
Faqs: Frequently Asked Questions
Can DKA recur?
Yes, DKA will happen whenever insulin levels are too low and not enough glucose is being produced to provide energy to your muscles and other tissues. If you miss a dose, underdose, or suffer from trauma or illness that depletes your insulin, DKA can recur.
Can DKA cause a heart attack or stroke?
Complications of DKA can include a heart attack or stroke because of the buildup of ketones in your body, so take it seriously and get emergency treatment as soon as you recognize the signs.
What causes a coma in DKA?
When blood-sugar levels become too low, triggering hypoglycemia, severe dehydration can then cause a diabetic coma.
How long does it take to recover from diabetic ketoacidosis?
Finally, some good news! Once youre safely admitted to the hospital for DKA, recovery is usually complete in one to three days.
What Significance Do These Findings Have For Type 1 Diabetes
Our findings indicate that patients diagnosed with type 1 diabetes may have another option to choose, said Dr. Tóth.
The boy in the study went without insulin for 24 months. The success is undoubtedly remarkable, even if he moved on to insulin injections afterwards.
This is a treatment requiring much more from the patient and his/her environment in terms of motivation, cooking techniques, personal burden of resisting against the mainstream etc. However, once realised, the method may offer a much better outcome of the disease.
It should be noted, though, that when Dr. Tóth says the Paleolithic ketogenic diet could be a treatment option for type 1 diabetes, he doesnt mean as a replacement for insulin injections.
The diet could help newly diagnosed type 1 patients with residual insulin secretion be without insulin for a short-term period, but the benefits that extend to people with long-standing type 1 include better glycemic control and the potential to prevent diabetic complications.
Of course, these findings refer to just one boy. Further research on a larger scale will be needed to confirm the results among people with type 1 diabetes of different durations. However, the Paleolithic ketogenic diet appears to be a fascinating area for future type 1 diabetes research.
Do you have any experience of the Paleolithic ketogenic diet? Has it helped improve your blood glucose levels?
Picture: thepaleodiet.com
Also Check: Does Hypertension Cause Diabetes
Treating Type 1 Diabetes
It’s important that diabetes is diagnosed as early as possible. If left untreated, type-1 diabetes is a life-threatening condition. It’s essential that treatment is started early.
Diabetes can’t be cured, but treatment aims to keep your blood glucose levels as normal as possible and control your symptoms, to prevent health problems developing later in life.
If you’re diagnosed with diabetes, you’ll be referred to a diabetes care team for specialist treatment and monitoring.
As your body can’t produce insulin, you’ll need regular insulin injections to keep your glucose levels normal. You’ll be taught how to do this and how to match the insulin you inject to the food you eat, taking into account your blood glucose level and how much exercise you do.
Insulin injections come in several different forms, with each working slightly differently. You’ll most likely need a combination of different insulin preparations.
Insulin is given to some patients by a continuous infusion of fast acting insulin . This is where a small device constantly pumps insulin into your bloodstream through a plastic tube that’s inserted under the skin with a needle.
There are alternatives to insulin injections and pumps, but they’re only suitable for a small number of patients. They are:
Read more about diagnosing diabetes and treating type 1 diabetes

