Treating Type 1 Diabetes
It’s important that diabetes is diagnosed as early as possible. If left untreated, type-1 diabetes is a life-threatening condition. It’s essential that treatment is started early.
Diabetes can’t be cured, but treatment aims to keep your blood glucose levels as normal as possible and control your symptoms, to prevent health problems developing later in life.
If you’re diagnosed with diabetes, you’ll be referred to a diabetes care team for specialist treatment and monitoring.
As your body can’t produce insulin, you’ll need regular insulin injections to keep your glucose levels normal. You’ll be taught how to do this and how to match the insulin you inject to the food you eat, taking into account your blood glucose level and how much exercise you do.
Insulin injections come in several different forms, with each working slightly differently. You’ll most likely need a combination of different insulin preparations.
Insulin is given to some patients by a continuous infusion of fast acting insulin . This is where a small device constantly pumps insulin into your bloodstream through a plastic tube that’s inserted under the skin with a needle.
There are alternatives to insulin injections and pumps, but they’re only suitable for a small number of patients. They are:
Read more about diagnosing diabetes and treating type 1 diabetes
Key Points About Type 1 Diabetes In Children
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a long-term condition. It may start at any age. Only 5% of people with diabetes have type 1.
- Type 1 diabetes is a condition in which blood glucose levels are abnormally high.
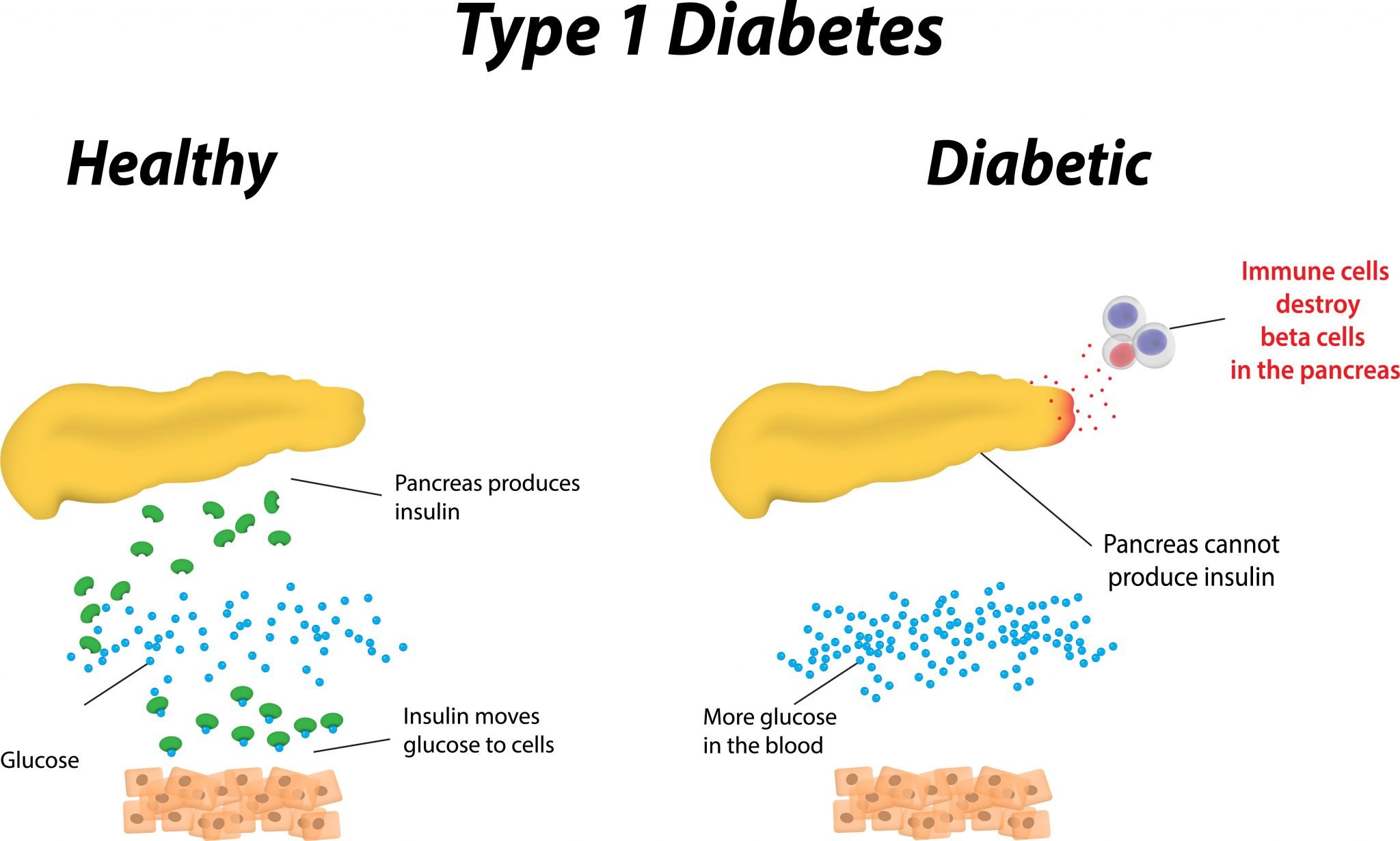
- It is most frequently caused by an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin.
- Children with type 1 diabetes must have daily injections of insulin to keep the blood glucose level within normal ranges.
- Without insulin, blood glucose levels continue to rise and death will occur.
- With the administration of insulin, and other management activities, children with type 1 diabetes can lead active, healthy lives.
How To Treat Type 2 Diabetes:
Unlike type 1, people with type 2 diabetes often do not need to take insulin, because their bodies still produce a small amount of it. Though there are medications like Metformin available to assist in lowering blood sugar, the primary ways to treat type 2 diabetes are:
- A balanced diet. Eating fruits and vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins while avoiding more than the occasional high-fat, high-sugar food is the first and most essential step to treating type 2 diabetes.
- Exercise. Staying active is also very important. There are so many ways to get exercise. Try different activities to find a type of exercise you enjoy and work it into your weekly routine.
- Weight loss. Of course, if you work toward eating healthier and exercising, this may be a byproduct. Losing weight is less about the number on the scale and more about taking care of your body and reducing the strain on your pancreas.
- Blood glucose monitoring. Checking your blood sugar regularly will become a part of your daily routine. It’s important to stay up-to-date on how your levels are doing throughout the day and adjust your food and activities accordingly. After a while you’ll figure out the regimen and balance that works best for you.
Don’t Miss: How Does Squeezing Finger Affect Blood Sugar
How Else Can I Manage Type 1 Diabetes
Along with insulin and any other medicines you use, you can manage your diabetes by taking care of yourself each day. Following your diabetes meal plan, being physically active, and checking your blood glucose often are some of the ways you can take care of yourself. Work with your health care team to come up with a diabetes care plan that works for you. If you are planning a pregnancy with diabetes, try to get your blood glucose levels in your target range before you get pregnant.
Are There Other Ways To Manage Type 1 Diabetes
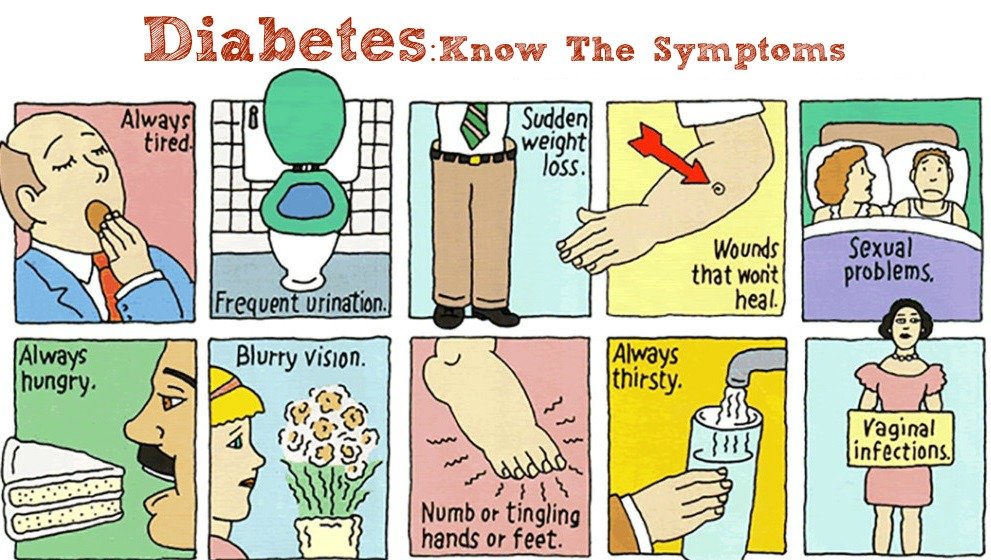
People with Type 1 diabetes need to monitor their blood sugar closely. Maintaining a healthy blood sugar range is the best way to avoid health complications. You can monitor your blood sugar in the following ways:
- Blood glucose meter: You prick your finger and put a small drop of blood on the meters test strip. Your blood glucose level appears on the meter. A blood glucose meter is usually the least expensive home testing option, but it only reports your blood sugar at the time of the check.
- Continuous glucose monitoring : There are different types of CGMs. Most CGMs require you to insert a small sensor under your skin at home every seven to 14 days. Some CGMs are implanted by a healthcare provider. The sensor continuously records your blood glucose levels. People using a CGM require fewer finger sticks. CGM systems can be more expensive than fingerstick blood glucose meters, but they provide much more information about your glucose levels, including where they have been and where they are going.
Recommended Reading: Can You Be Skinny And Have Diabetes
Treating & Managing Type 1 Diabetes
Understanding type 1 diabetes is the first step to managing it. Get information on type 1 diabetes causes, risk factors, warning signs, and prevention tips.
How Can I Best Balance My Type 1 Diabetes Symptoms And Daily Life
Fortunately, there are medications that can help keep T1D at bay and reduce the risk of long-term complications. Type 1 diabetics who cannot make their own insulin will need a way to deliver it to their bodies, either through a pump or through injections underneath the skin with syringes or pens.
When T1D is properly controlled, a person with the condition will show no signs or symptoms, because they are playing an active role in keeping their blood sugar levels steady.
Signs and symptoms of type 1 diabetes can come on quickly, and they arent always obvious. Many times, theyre mistaken for other conditions. Making yourself aware of the signs and symptoms of T1D is a great way to be proactive about your health and the health of your family members. If you notice any of these signs or symptoms in yourself or a loved one, get in touch with your doctor ASAP. They can make a diagnosis by checking blood glucose levels and A1C to start treatment before there are any complications.
Read Also: Side Effects Of Too Much Metformin
How Is Diabetes Diagnosed
The fasting blood glucose test is the preferred way to diagnose diabetes. It is easy to perform and convenient. After the person has fasted overnight , a single sample of blood is drawn and sent to the laboratory for analysis. This can also be done accurately in a doctor’s office using a glucose meter.
- Normal fasting plasma glucose levels are less than 100 milligrams per deciliter .
- Fasting plasma glucose levels of more than 126 mg/dl on two or more tests on different days indicate diabetes.
- A random blood glucose test can also be used to diagnose diabetes. A blood glucose level of 200 mg/dl or higher indicates diabetes.
When fasting blood glucose stays above 100mg/dl, but in the range of 100-126mg/dl, this is known as impaired fasting glucose . While patients with IFG or prediabetes do not have the diagnosis of diabetes, this condition carries with it its own risks and concerns, and is addressed elsewhere.
The oral glucose tolerance test
For the test to give reliable results:
- The person must be in good health .
- The person should be normally active , and
- The person should not be taking medicines that could affect the blood glucose.
- The morning of the test, the person should not smoke or drink coffee.
Evaluating the results of the oral glucose tolerance test
Glucose tolerance tests may lead to one of the following diagnoses:
Sign : Changes In Eyesight
A high blood glucose level causes fluid to be pulled from other body tissues, including eye lenses. This may lead to blurred vision or other eyesight problems. However, a young child may not complain to you about it.They dont know what normal is, the way adults would, says Clement. And some of them arent even reading yet.
Recommended Reading: What Happens In Type 1 Diabetes
Other Types Of Diabetes
Other forms of insulin-resistant diabetes also can be seen in gestational diabetes, polycystic ovary disease, acanthosis nigricans, and maturity-onset diabetes of the young or MODY. Insulin resistant diabetes can also be unmasked by medications like prednisone. In rare cases, a type similar to Type1 diabetes but without antibodies may be seen following trauma to the pancreas, following pancreatic surgery, or after exposure to toxins like Agent Orange. This type is insulin-dependent because no insulin can be produced once the pancreas is removed or severely damaged.
What Are The Risk Factors For Diabetes
Risk factors for type 1 diabetes are not as well understood as those for type 2 diabetes. Family history is a known risk factor for type 1 diabetes. Other risk factors can include having certain infections or diseases of the pancreas.
Risk factors for type 2 diabetes and prediabetes are many. The following can raise your risk of developing type 2 diabetes:
- Being obese or overweight
- Ethnic background: Hispanic/Latino Americans, African-Americans, Native Americans, Asian-Americans, Pacific Islanders, and Alaska natives are at greater risk.
Read Also: Diabetic Finger Food
More Severe Symptoms Of Untreated Type 1 Diabetes
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
When type 1 diabetes goes untreated, it can lead to organ failure, coma, and even death. This happens because the body can no longer turn glucose into fuel, and it starts burning fat, which then produces ketones in the blood and urine.
A small amount of ketones aren’t dangerous and can usually be detected if a person has been fasting or is on a low-carbohydrate diet. But too many ketones can actually change the bloods acidity and result in a life-threatening condition called diabetic ketoacidosis.
If you have one or more of these symptoms contact your doctor.
Symptoms of type1 diabetes tend to look different in children than adults, according to Dr. Christofides.
Recommendations For Distinguishing Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
- Consider a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes or one of its variants in AI/AN patients of any age or weight who present with a new onset of diabetes and an unclear clinical picture.
- Obtain laboratory studies and exams as needed to aid in diabetes classification.
Measurement of Endogenous Insulin Secretion
The results for tests to measure endogenous insulin secretion may be low in type 2 diabetes patients with glucose toxicity. If in doubt, measure the following after glycemic control has been restored for several weeks:
- Fasting insulin level if the patient is not on exogenous insulin
- C-peptide this is useful even if the patient is taking insulin injections.
Positive antibody tests denote an autoimmune process, but negative tests do not rule it out:
- IA-2
- GAD-65
- Other antibody tests have been used in research and clinical settings e.g., ZnT8 , thyroid peroxidase antibodies, insulin autoantibodies
Other Lab Tests and Exams
Although some overweight type 1 diabetes patients may have some signs of insulin resistance, in general, they will not have the usual type 2 diabetes measurements at diagnosis. Gauging the degree of insulin deficiency versus insulin resistance with the following tests can be helpful:
Don’t Miss: What Happens In Type 1 Diabetes
It Cant Be Cured With Lifestyle Changes
As with other autoimmune disorders, the exact cause of type 1 diabetes is not known. There is no cure or way for a person with type 1 to eliminate their need for insulin therapy, which is an important distinction between type 1 and type 2.
Morgan McKean, 29, who currently works abroad in health promotion for a charity foundation, sees a lack of knowledge about both types of diabetes. People think only overweight people get diabetes or that you can always get rid of it through a better diet and exercise. Thats not the case in type 1, and it isnt always true in type 2 diabetes either, she says.
What Are The Treatments For Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes must be treated with insulin. To do this, a person with type 1 diabetes must inject insulin under their skin where it can be absorbed into their bloodstream to help glucose access the cells that require it. Insulin cant be taken in pill form because the digestive juices in the stomach would destroy the insulin before it could work.
Treating T1D is all about the amount and timing of insulin, as well as the best way to get the right dose of this essential hormone to assure that the glucose circulating in your blood is able to be properly absorbed by your body. Having too much glucose in your body can cause serious complications as can having too little glucose in your blood .
Insulin can be delivered by:
Lexie, known as the divabetic, is a Black diabetes advocate who posts everything from giveaways to advice on dating with type 1 diabetes. She frequently shares posts about diabetes-friendly food and humor.
Recommended Reading: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Faqs: Frequently Asked Questions
Why did type 1 diabetes used to be called juvenile diabetes?
Most people with type 1 diabetes are diagnosed as children, although in rare cases some are not diagnosed until they are adults.
Are type 1 diabetes symptoms in adults different than in children?
No, adults and children experience the same symptoms.
Is there a type 1 diabetes cure?
Type 1 diabetes can be managed with insulin, but there is no cure.
In type 1 diabetes vs type 2, is diet as important?
Even though diet and lifestyle changes cannot reverse type 1 diabetes, and they have the potential of reversing type 2, learning what, how much, and when to eat can still help you have the most effective type 1 diabetes diet to manage your condition.
What type of doctor is best for type 1 diabetes treatment?
Even though an ER doctor or your primary care physician will likely be the one to first diagnose your type 1 diabetes, an endocrinologist is the best doctor to help you learn how to monitor your blood sugar and manage your condition.
A Short History Of Types
Described and treated since ancient times, diabetes has specific characteristics that were recognized long ago. Before the discovery of insulin, people found to have sugar in their urine under the age of 20 usually died in their youth. In contrast, those diagnosed when over the age of 40 could live for many years with this condition.
Beginning in the mid-1920s, those who got diabetes when young started on insulin, and those who got it when older often were not. However, the mechanisms that led to this difference in treatment were unknown. The only marker that differentiated the two types at that time was the presence in the urine of moderate or large levels of ketones when blood sugars were high. When significant ketones were present because the person could no longer make enough insulin, injected insulin was needed to control the glucose, and they were called insulin-dependent.
| Differences In The Three Major Types Of Diabetes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | |||
| insulin is vital, diet & exercise changes helpful | pills or insulin vital, diet & exercise changes helpful | pills helpful, diet & increased activity essential | |
| Late treatment | insulin, diet, exercise | insulin, pills, diet, exercise | insulin, pills, diet, exercise |
| * may occur at any age if all antibody-positive cases are included, i.e. Type 1 and Type 1.5 |
Read Also: Greek Yogurt And Diabetes
What Is Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is a condition in which your immune system destroys insulin-making cells in your pancreas. These are called beta cells. The condition is usually diagnosed in children and young people, so it used to be called juvenile diabetes.
A condition called secondary diabetes is like type 1, but your beta cells are wiped out by something else, like a disease or an injury to your pancreas, rather than by your immune system.
Both of these are different from type 2 diabetes, in which your body doesnât respond to insulin the way it should.
How Do I Keep My Blood Sugar Under Tight Control
Insulin helps people with type 1 diabetes keep the level of sugar in their blood at a normal level. Many people with type 1 diabetes take short-acting insulin before each meal. You can adjust the amount of insulin you take for each meal based on how many calories you eat and how physically active you plan to be in the next 3 to 4 hours. Most people with type 1 diabetes need to take about 8 to 10 units of insulin for every 500 calories they eat. You may need slightly less or slightly more insulin, depending on how your body reacts to insulin. Take enough insulin so your blood sugar level is usually between 80 and 120 mg and doesn’t go above 180 mg after meals.
To keep their blood sugar levels from rising during the night, most people with type 1 diabetes need to take 4 to 8 units of an intermediate-acting insulin before they go to sleep. If you carry a syringe of short-acting insulin wherever you go, you’ll always be ready if you need more insulin.
Also Check: Oatmeal Carbs Diabetes

