Causes Of Type 2 Diabetes
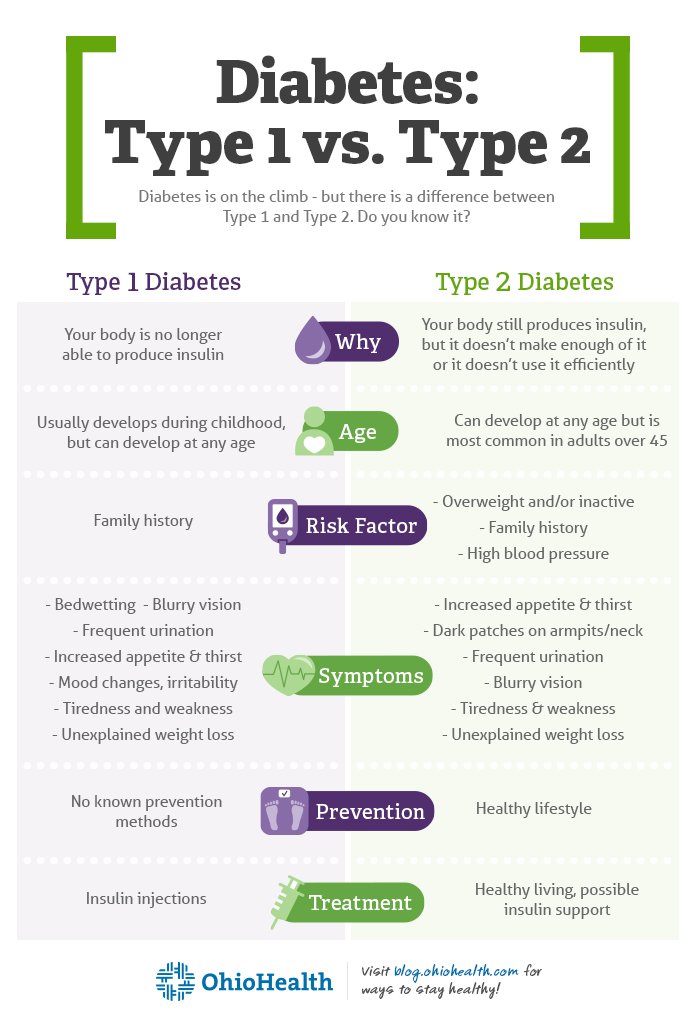
People with type 2 diabetes have insulin resistance. The body still produces insulin, but its unable to use it effectively.
Researchers arent sure why some people become insulin resistant and others dont, but several lifestyle factors may contribute, including being inactive and carrying excess weight.
Other genetic and environmental factors may also play a role. When you develop type 2 diabetes, your pancreas will try to compensate by producing more insulin. Because your body is unable to effectively use insulin, glucose will accumulate in your bloodstream.
Type 2 diabetes is much more common than type 1.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Preventions , 34.2 million people in the United States were living with diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes in 2018. Thats a little over 1 in 10 people. Ninety to 95 percent of people with diabetes have type 2.
The percentage of people with diabetes increases with age.
About 10.5 percent of the general population has diabetes. Among those 65 years old and older, the rate reaches 26.8 percent. Only 25 out of every 10,000 Americans under 20 years old had been diagnosed with diabetes in 2018.
Men and women get diabetes at roughly the same rate. However, prevalence rates are higher among certain races and ethnicities.
Prevalence rates are higher for Hispanic Americans of Mexican or Puerto Rican descent than they are for those of Central and South American or Cuban descent.
Risk Factors For Type 2 Diabetes
You can have type 2 diabetes without any obvious warning signs or symptoms. If you think you might be at risk for developing diabetes, donât ignore these risk factors. The earlier youâre diagnosed, the sooner you can take action to stay wellnow and in the future.
Some diabetes risk factors can be managed or reduced, while other factors may be beyond your control. For example, you have a greater risk of developing type 2 diabetes if you are over the age of 40 or if you have a parent, brother, or sister with diabetes. Your ethnic background is also a factor: being of African, Arab, Asian, Hispanic, Indigenous, or South Asian descent can increase your risk of living with type 2 diabetes.
Having any of the following conditions increases your chances of developing diabetes:
- high blood pressure
- obstructive sleep apnea
- darkened patches of skin called acanthosis nigricans
Lastly, if you have been prescribed a glucocorticoid medication by a doctor, you will also have an increased risk.
Also Check: Why Eat Sugar After Giving Blood
Other Causes Of Diabetes
Although more than 95% of people with diabetes have type 2 or type 1, there are some other rare causes of diabetes:
- Gestational diabetes: This is diabetes that develops when you are pregnant. After the baby is born, this diabetes may go away or remain. Having gestational diabetes increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later.
-
Drug-induced diabetes: This occurs when a medication increases your blood glucose levels to the point of diabetes. Examples of medications that can cause diabetes include:
- Glucocorticoids
- Antipsychotic medications
- Some HIV medications
In some cases, the diabetes goes away after stopping the medication. In other situations, diabetes may continue as a permanent condition.
Monogenetic diabetes: This is a rare form of diabetes that is caused by a mutation in a single gene. The main forms of monogenetic diabetes are neonatal diabetes mellitus , which affects newborns, and maturity-onset diabetes of the young , which usually affects teenagers or young adults.
Recommended Reading: Symptoms Of High Blood Sugar In The Morning
Can Type 2 Diabetes Turn Into Type 1
If you have type 2 diabetes, you might be wondering if it will ever turn into type 1 diabetes. Its understandable that you would think about this, especially if you take insulin. In short, however, the answer is no.
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes, two of the most common forms of diabetes, are actually two very different conditions. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease, which means that the body attacks the cells in the pancreas that make insulin. As a result, someone with type 1 needs to inject insulin in order to survive. Researchers believe that genetics or environmental factors are the cause of type 1. For the most part, type 1 diabetes is more common in children, adolescents and young adults but anyone at any age can develop type 1 diabetes.
So, type 2 diabetes does not become type 1 diabetes. But it is possible for someones type of diabetes to be misdiagnosed. In other words, someone may be told they have type 2 diabetes, but they actually have type 1 diabetes. Heres why: diabetes symptoms can be the same in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. For example, if your blood sugar is high, you may feel tired and thirsty and you might lose some weight. If you go to the doctor because of your symptoms, you may be quickly diagnosed with type 2 and prescribed a diabetes pill to take. This is more likely to happen if youre an adult and if youre overweight or obese .
Recommended Reading: How To Avoid Diabetes In Early Stages
What Are The Treatments For Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes must be treated with insulin. To do this, a person with type 1 diabetes must inject insulin under their skin where it can be absorbed into their bloodstream to help glucose access the cells that require it. Insulin cant be taken in pill form because the digestive juices in the stomach would destroy the insulin before it could work.
Treating T1D is all about the amount and timing of insulin, as well as the best way to get the right dose of this essential hormone to assure that the glucose circulating in your blood is able to be properly absorbed by your body. Having too much glucose in your body can cause serious complications as can having too little glucose in your blood .
Insulin can be delivered by:
Lexie, known as the divabetic, is a Black diabetes advocate who posts everything from giveaways to advice on dating with type 1 diabetes. She frequently shares posts about diabetes-friendly food and humor.
Don’t Miss: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
What Happens When You Have Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
If you have either type 1 or type 2 diabetes, it means you have too much glucose in your blood. This is the same for both types. But the difference between them is how this happens.
If you have type 1 diabetes, it means you have an autoimmune condition. This means your body has attacked and destroyed the cells that make a hormone called insulin. So you cant make insulin anymore.
We all need insulin as it helps take the glucose from our blood into our bodys cells. We then use this glucose for energy. Without insulin, the glucose level in your blood gets too high.
Type 2 diabetes is different. If youve got type 2, either your body doesnt make enough insulin, or your insulin doesnt work properly. This is known as insulin resistance. Like type 1, this means the level of glucose in your blood is too high.
What Should My Blood Glucose Level Be
Ask your healthcare team what your blood glucose level should be. They may have a specific target range for you. In general, though, most people try to keep their blood glucose levels at these targets:
- Before a meal: between 80 and 130 mg/dL.
- About two hours after the start of a meal: less than 180 mg/dL.
Recommended Reading: Genetics Of Diabetes Mellitus
Can Diabetes Cause Hearing Loss
Scientists dont have firm answers yet but there appears to be a correlation between hearing loss and diabetes. According to the American Diabetes Association, a recent study found that hearing loss was twice as common in people with diabetes versus those who didnt have diabetes. Also, the rate of hearing loss in people with prediabetes was 30% higher compared with those who had normal blood glucose levels. Scientists think diabetes damages the blood vessels in the inner ear, but more research is needed.
Can Thin People Get Type 2 Diabetes
Miller points to promising research on genetic risk scoring thats taking place through Trialnet, an international research consortium focused on type 1 diabetes that is supported by the National Institutes of Health and private organizations. For example, a Trialnet study published in July 2018 in Diabetes Care looked at the relatives of people with type 1 diabetes who did not have the disease themselves but did have one or more positive autoantibodies, and it found that a higher genetic risk score helped to predict their progression to developing type 1 diabetes.
The biggest challenge in that area of research that baffles most scientists is: Why do some patients who have demonstrated positive autoantibodies not go on to develop type 1 diabetes? Thats the area of greatest interest because if you can identify some factor in those patients that is protective, that keeps individuals with positive autoantibodies from killing off their beta cells, then perhaps you could prevent them from developing type 1 diabetes.
In the meantime, even without genetic testing, it is wise to pay attention to your family history and risk factors for diabetes. Not every case of diabetes is preventable, but neither is your DNA your destiny in every instance.
Don’t Miss: Metformin Highest Dose
Recognizing And Treating Double Diabetes
One of the early signs that you might be experiencing insulin resistance is a need for more and more insulin to meet your blood sugar control goals. However, there are treatment alternatives to continually ramping up your doses.
Its likely that patients should also be put on another medication to improve their response to insulin, but this is not yet standard of care, says Dr. Schauer. Metformin , which is often used to reduce insulin resistance in people who have type 2 diabetes, can be taken by people with type 1 diabetes as well.
What Is Type 1 Diabetes
An absolute lack of insulin, usually due to destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas, is the main problem in type 1 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes was formerly referred to as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus . Its causes are different from type II diabetes, as will be reviewed in this article.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If A Type 2 Diabetic Stops Taking Insulin
In Addition To Type 1 Type 2 And Gestational Diabetes There Are A Range Of Other Types Of Diabetes Which Are Just As Important
About 2% of people have these other types of diabetes. These include different types of monogenic diabetes, cystic fibrosis-related diabetes, and diabetes caused by rare syndromes. Certain medications such as steroids and antipsychotics could lead to other types of diabetes, as well as surgery or hormonal imbalances.
Unfortunately, many of these people are misdiagnosed leading to delays in getting the right treatment. Were proud of the research we have supported to ensure better diagnosis and treatments for all types of diabetes, and its taught us a lot about the condition. Get more information on other types of diabetes:
Latent Autoimmune Diabetes In Adults

LADA is a type of diabetes which seems to straddle type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Bits of it are more like type 1, and other bits are more like type 2. That’s why some people call it type 1.5 diabetes or type 1 ½ diabetes.
Its not actually classified as a separate type of diabetes at the moment, but there’s some medical research going on to try and pinpoint exactly what makes it different from type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Can You Be Skinny And Have Diabetes
Maturity Onset Diabetes Of The Young
MODY is a rare form of diabetes which is different from both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and runs strongly in families. MODY is caused by a mutation in a single gene. If a parent has this gene mutation, any child they have, has a 50 per cent chance of inheriting it from them. If a child does inherit the mutation they will generally go on to develop MODY before theyre 25, whatever their weight, lifestyle, ethnic group etc.
How Is Diabetes Diagnosed
Diabetes is diagnosed and managed by checking your glucose level in a blood test. There are three tests that can measure your blood glucose level: fasting glucose test, random glucose test and A1c test.
- Fasting plasma glucose test: This test is best done in the morning after an eight hour fast .
- Random plasma glucose test: This test can be done any time without the need to fast.
- A1c test: This test, also called HbA1C or glycated hemoglobin test, provides your average blood glucose level over the past two to three months. This test measures the amount of glucose attached to hemoglobin, the protein in your red blood cells that carries oxygen. You dont need to fast before this test.
- Oral glucose tolerance test: In this test, blood glucose level is first measured after an overnight fast. Then you drink a sugary drink. Your blood glucose level is then checked at hours one, two and three.
| Type of test |
|---|
You May Like: Which Pancreatic Cells Release Insulin And Glucagon
How Long Can You Live With Diabetes
It is not very uncommon to hear that diabetes will shorten the expected life of the concerned patient. But the question is: How much?
There are different opinions about the subject. As per a few types of research conducted, diabetes can shorten life by 8.5 years in a 50-year old individual. On the other hand, Diabetes UK estimates that the expected life span of type 1 diabetic patient is reduced by more than 20 years while a type 2 diabetes patient lives 10 years shorter as compared to the healthier counterparts.
Besides, the University of Pittsburg has estimated through various studies that people who are born after 1965 and are suffering from type 1 diabetes have a life expectancy of somewhere around 69 years.
Having said the above, we should not forget that with proper diabetes care and management, it is very much possible to extend the total life of a diabetes patient. In the following paragraphs, we shall dive into and analyze the causes and conditions which lead to deaths in the patients who suffer from the condition.
The Importance Of Insulin
Diabetes is a disease in which your body either can’t produce insulin or can’t properly use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone produced by your pancreas.
Insulin’s role is to regulate the amount of glucose in the blood. Blood sugar must be carefully regulated to ensure that the body functions properly. Too much blood sugar can cause damage to organs, blood vessels, and nerves. Your body also needs insulin in order to use sugar for energy.
Eleven million Canadians are living with diabetes or prediabetes. Chances are, diabetes affects you or someone you know.
Recommended Reading: Can You Take Too Much Metformin
What Insulin Medications Are Approved To Treat Diabetes
There are many types of insulins for diabetes. If you need insulin, you healthcare team will discuss the different types and if they are to be combined with oral medications. To follow is a brief review of insulin types.
- Rapid-acting insulins: These insulins are taken 15 minutes before meals, they peak at one hour and work for another two to four hours. Examples include insulin glulisine , insulin lispro and insulin aspart .
- Short-acting insulins: These insulins take about 30 minutes to reach your bloodstream, reach their peak effects in two to three hours and last for three to six hours. An example is insulin regular .
- Intermediate-acting insulins: These insulins reach your bloodstream in two to four hours, peak in four to 12 hours and work for up to 18 hours. An example in NPH.
- Long-acting insulins: These insulins work to keep your blood sugar stable all day. Usually, these insulins last for about 18 hours. Examples include insulin glargine , insulin detemir and insulin degludec .
There are insulins that are a combination of different insulins. There are also insulins that are combined with a GLP-1 receptor agonist medication .
Genes And Family History
As in type 1 diabetes, certain genes may make you more likely to develop type 2 diabetes. The disease tends to run in families and occurs more often in these racial/ethnic groups:
- African Americans
- Native Hawaiians
- Pacific Islanders
Genes also can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes by increasing a persons tendency to become overweight or obese.
You May Like: Can A Diabetic Eat Mac And Cheese
Can Prediabetes Type 2 Diabetes And Gestational Diabetes Be Prevented
Although diabetes risk factors like family history and race cant be changed, there are other risk factors that you do have some control over. Adopting some of the healthy lifestyle habits listed below can improve these modifiable risk factors and help to decrease your chances of getting diabetes:
- Eat a healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean or Dash diet. Keep a food diary and calorie count of everything you eat. Cutting 250 calories per day can help you lose ½ pound per week.
- Get physically active. Aim for 30 minutes a day at least five days a week. Start slow and work up to this amount or break up these minutes into more doable 10 minute segments. Walking is great exercise.
- Lose weight if you are overweight. Dont lose weight if you are pregnant, but check with your obstetrician about healthy weight gain during your pregnancy.
- Lower your stress. Learn relaxation techniques, deep breathing exercises, mindful meditation, yoga and other helpful strategies.
- Limit alcohol intake. Men should drink no more than two alcoholic beverages a day women should drink no more than one.
- Get an adequate amount of sleep .
- Take medications to manage existing risk factors for heart disease or to reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes as directed by your healthcare provider.
- If you think you have symptoms of prediabetes, see your provider.

