When You Get Type 1 Diabetes As An Adult
Yes, you can get Type 1 diabetes as an adult. My husbands diagnosis at age 33 had a huge effect on our family, but with a positive attitude and a lot of trial and error, you can find your new normal and live life to the fullest!
Hi friends!
As many of you know if you follow me on social media, two weeks ago my husband was diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes at the age of 33. Since this is a major diagnosis, impacting pretty much all areas of our life, I wanted to take some time and write down our story. Ive discovered that many people dont actually know a lot about type 1 diabetes so I think its a good opportunity to use this platform to educate. Ive also realized just how much a diagnosis like this affects not only the person themselves, but family members and those around them as well.so I wanted to give you some insight into how its affecting him, me and our family in general.
Previously Healthy: Reegans Story
In 2013, Darice and Keith Oxendines 16-month-old daughter, Reegan, was life-flighted from Scotland Memorial Hospital to the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit at UNC Chapel Hill. Shed suffered complications following a misdiagnosis, despite having shown symptoms of Type 1 diabetes for three months prior.
By the time she arrived at UNC and was properly diagnosed, it was too late. The excess sugar in her blood had damaged her vital organs beyond repair. The official cause of death: Type 1 diabetes. Read Reegans story here.
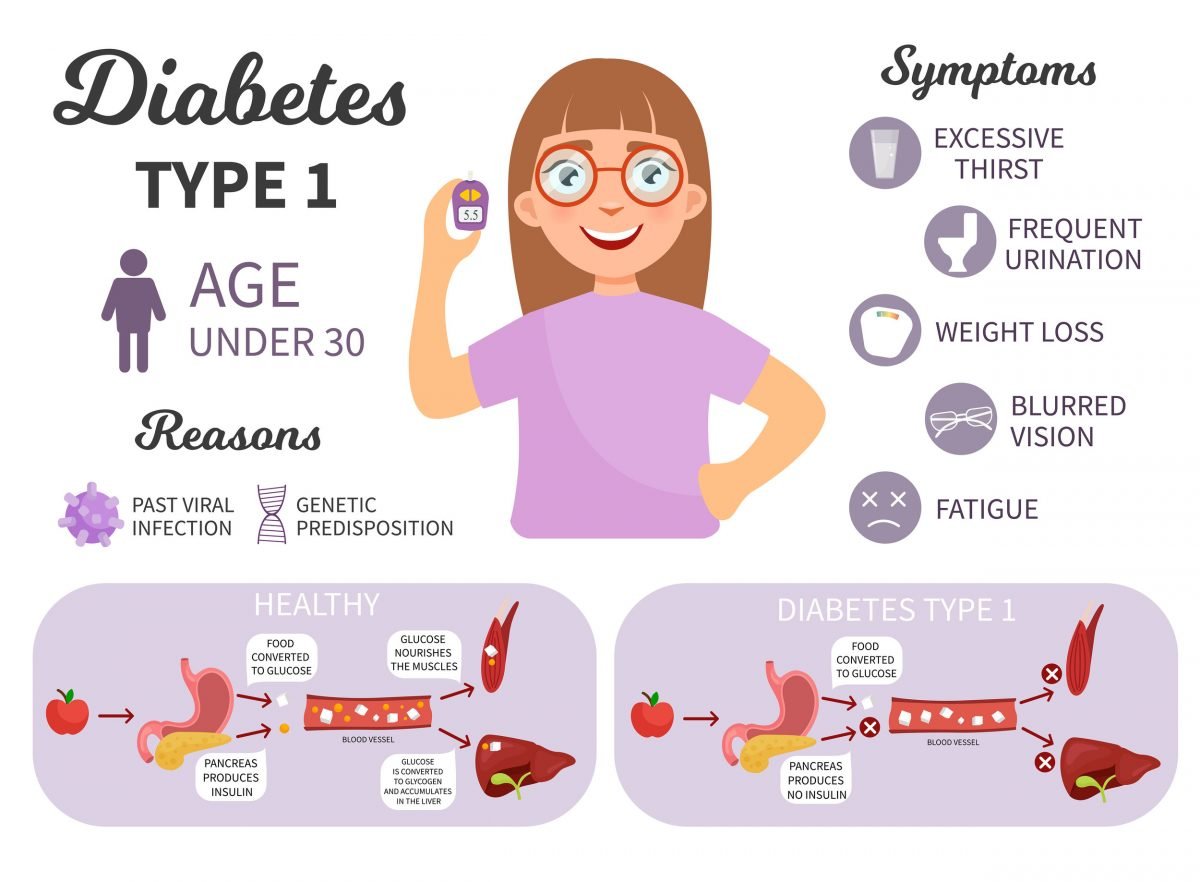
Signs And Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes can develop rapidly, especially in young people, says Sanjoy Dutta, PhD, vice president of research for the type 1 diabetes research organization JDRF. The NIDDK lists the following symptoms:
- Excessive thirst
- Blurry vision
- Unexplained weight loss
Dr. Dutta says sometimes the weight loss is very precipitous. In some cases, it might even be 10 kilos of weight loss within two weeks.
The onset of type 1 diabetes can be difficult to detect in very young children, says Dr. Thomas. The signs of something wrong may be more subtle, such as more wet diapers or heavier diapers, bedwetting, and increased thirst.
Also Check: What Is Normal A1c Level For Nondiabetic
The Surprising Truth About Prediabetes
Its real. Its common. And most importantly, its reversible. You can prevent or delay prediabetes from developing into type 2 diabetes with simple, proven lifestyle changes.
Amazing but true: approximately 88 million American adults1 in 3have prediabetes. Whats more, more than 84% of people with prediabetes dont know they have it. Could this be you? Read on to find out the facts and what you can do to stay healthy.
Does Type 1 Diabetes Get Worse With Age

Lower quality of life in adults with type 1 diabetes is related to worse glycemic control, the presence of chronic complications such as renal disease, and a history of severe hypoglycemia. All of these factors are important to consider in individualizing management plans for older adults with type 1 diabetes.
Read Also: D Cells Somatostatin
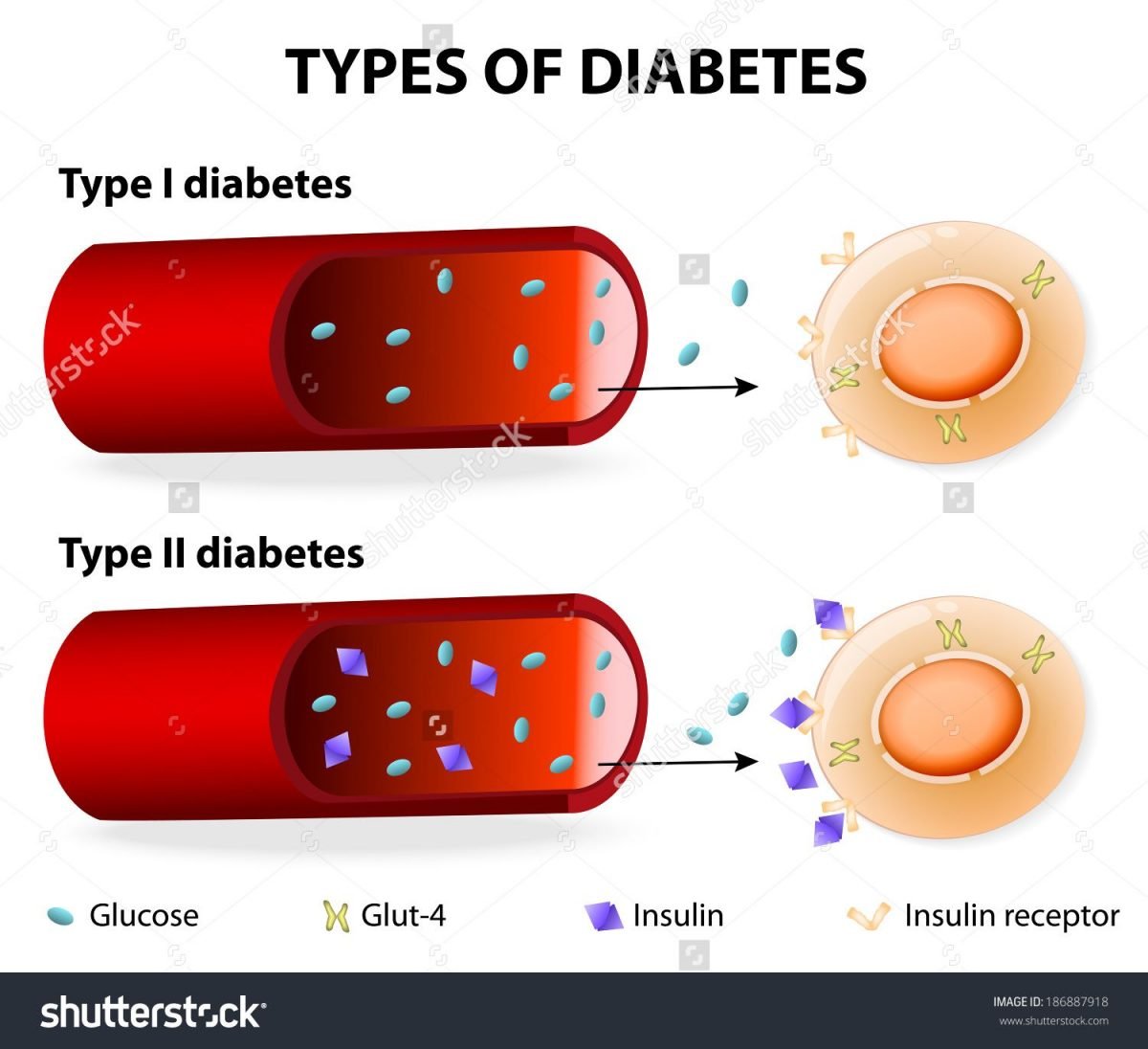
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes produce the same result: blood sugar that is too high. But they do it in very different ways.
As mentioned, type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder that results in the body being able to produce little or no insulin. It cannot be prevented, as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention explains.
Type 2 diabetes develops when liver, muscle, and fat cells don’t respond properly to insulin and become “insulin resistant,” the agency says. Glucose doesn’t enter the cells as efficiently as before, and instead builds up in the bloodstream.
In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas responds to these increased blood glucose levels by producing more insulin. Eventually, however, it can no longer make enough insulin to handle spikes in glucose levels, such as routine rises in blood sugar after a meal.
Type 2 diabetes accounts for 90 to 95 percent of all diagnosed cases of diabetes, according to the CDC. It can be prevented or delayed in many cases with diet and exercise changes.
Causes Of Type 2 Diabetes
People with type 2 diabetes have insulin resistance. The body still produces insulin, but its unable to use it effectively.
Researchers arent sure why some people become insulin resistant and others dont, but several lifestyle factors may contribute, including being inactive and carrying excess weight.
Other genetic and environmental factors may also play a role. When you develop type 2 diabetes, your pancreas will try to compensate by producing more insulin. Because your body is unable to effectively use insulin, glucose will accumulate in your bloodstream.
Type 2 diabetes is much more common than type 1.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Preventions , 34.2 million people in the United States were living with diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes in 2018. Thats a little over 1 in 10 people. Ninety to 95 percent of people with diabetes have type 2.
The percentage of people with diabetes increases with age.
About 10.5 percent of the general population has diabetes. Among those 65 years old and older, the rate reaches 26.8 percent. Only 25 out of every 10,000 Americans under 20 years old had been diagnosed with diabetes in 2018.
Men and women get diabetes at roughly the same rate. However, prevalence rates are higher among certain races and ethnicities.
Prevalence rates are higher for Hispanic Americans of Mexican or Puerto Rican descent than they are for those of Central and South American or Cuban descent.
You May Like: Hypoglycemia And Hypertension
We Know Some People Get Confused Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes And Were Often Asked About The Differences Between Them
Although type 1 and type 2 diabetes both have stuff in common, there are lots of differences. Like what causes them, who they affect, and how you should manage them. There are other types of diabetes like gestational and MODY. But this page is mainly about the differences between type 1 and type 2.
For a start, type 1 affects 8% of everyone with diabetes. While type 2 diabetes affects about 90%.
Lots of people get confused between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. This can mean you have to explain that what works for one type doesn’t work for the other, and that there are different causes.
The main thing to remember is that both are as serious as each other. Having high blood glucose levels can lead to serious health complications, no matter whether you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes. So if you have either condition, you need to take the right steps to manage it.
Bipoc And Type 1 Diabetes
Although type 1 diabetes is most prevalent in the United States among white people, Hispanic , non-Hispanic Asian and Pacific Islander , and Black children and youth saw the steepest annual percentage increases in cases between 2002 and 2015, according to the CDC.
Youth of the Black, Indigenous, and People of Color communities, particularly those who are socioeconomically disadvantaged, are more likely to have DKA at diagnosis, says Thomas. The authors of a 2018 study in Diabetes Care surmised that insurance access and parent education accounted for much of the difference.
Also Check: Metformin Highest Dose
Causes And Risk Factors Of Type 1 Diabetes
It’s unknown exactly what causes type 1 diabetes, but experts think it could be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. For instance, MedlinePlus states that the risk of type 1 diabetes in increased if you have certain variants of genes in the human leukocyte antigen complex. These genes are involved in making proteins that play a critical role in immune response.
Coxsackieviruses have been studied as possible triggers for type 1 diabetes, and prolonged viral infection may increase a childs risk for developing the disease, according to a June 2019 study in Nature Medicine.
Other possible risk factors for type 1 diabetes include:
- Being male. The risk of being diagnosed with type 1 diabetes is approximately 1.5 times higher for males than for females, says Thomas.
- Having autoantibodies that are associated with higher risk
- Being of European descent , per the CDC. Most white people with the disease have gene variants HLA-DR3 or HLA-DR4, according to the ADA.
- Having a close family relative who has type 1 diabetes.
In fact, the odds that a man with type 1 diabetes has a child who develops it are 1 in 17. For a woman who bears a child before age 25, that risk is 1 in 25, but it drops to 1 in 100 if the child is born after she is 25.
Yet 80 percent of people with type 1 diabetes have no family history of the disease, according to the JDRF.
More on Diabetes Causes
Treatment Of Type 1 Diabetes
- taking insulin daily by injections or by insulin pump
- self-monitoring of blood sugar levels by regularly testing droplets of blood in a glucose meter
- self-testing of urine with a test strip for high levels of ketones not routinely, but when problems are suspected
- regulating diet so intake is matched to insulin and exercise
- increasing the amount of slow carbohydrates in the diet, such as beans and fruit, which take longer to be absorbed by the body
- regular exercise
- maintaining regular checks for diabetes complications.
Recommended Reading: Metformin Dosage For Ketosis
Favorite Online Support Networks
Beyond Type 1
A frequent partner with JDRF, Beyond Type 1 is a social-media-savvy nonprofit focused on advocacy and insulin affordability. Join their social platform by connecting through Facebook or Apple, among other providers. Or, visit their GetInsulin.org guide for information about affording the medication and help devising an action plan to get it.
College Diabetes Network
This peer-support-focused nonprofit is focused on forging connections between and among students in high school and college with type 1 diabetes. Get advice for navigating care through the transition between high school and college, read blog posts written by college students, or find a college chapter to join.
Nutrition And Physical Activity
Nutrition education can improve metabolic control in ambulatory older people with diabetes . Although nutrition education is important, weight loss may not be, since moderate obesity is associated with a lower mortality in this population . Amino acid supplementation may improve glycemic control and insulin sensitivity in these people, although this is controversial .
Unfortunately, it appears difficult to maintain these healthy behaviour changes outside of a supervised setting .
Figure 1Clinical frailty scale.
Also Check: Long-term Side Effects Of Insulin Use
How Long Can A Child Live With Type 1 Diabetes
People who develop diabetes during childhood may die up to 20 years sooner than people without diabetes, according to research findings by scientists in Sweden and the U.K. A study of more than 27,000 individuals with type 1diabetes discovered that the average lifespan of women diagnosed with the disorder before
How Is Type 1 Diabetes Managed
Although there is currently no cure, type 1 diabetes can be managed with insulin and by having a healthy lifestyle.
If you have type 1 diabetes, you will need insulin replacement, through injections or an insulin pump, to control your blood glucose levels.
Having a healthy diet and being physically active can also help control your blood glucose levels and improve your health.
Also Check: Metformin Xr Dose
Prediabetes Flies Under The Radar
You can have prediabetes for years but have no clear symptoms, so it often goes undetected until serious health problems show up. Thats why its important to talk to your doctor about getting your blood sugar tested if you have any of the risk factors for prediabetes, which include:
- Being overweight
- Being 45 years or older
- Having a parent, brother, or sister with type 2 diabetes
- Being physically active less than 3 times a week
- Ever having gestational diabetes or giving birth to a baby who weighed more than 9 pounds
Race and ethnicity are also a factor: African Americans, Hispanic/Latino Americans, American Indians, Pacific Islanders, and some Asian Americans are at higher risk.
Ready to find out your risk? Take the 1-minute prediabetes risk test and be sure to share the results with your doctor.
What Is Diabetes
Our bodies turn a lot of the food we eat into sugar, called glucose, which gives us energy. To use glucose as energy, our body needs insulin, a hormone that helps glucose get into our cells. If you have diabetes, your body may not make enough insulin, may not use insulin in the right way, or both. That can cause too much glucose to stay in the blood, which can cause health problems over time. Your family doctor may refer you to a doctor who specializes in taking care of people with diabetes, called an endocrinologist. Often, your family doctor will work directly with you to manage your diabetes.
Also Check: Blood Sugar Over 600
How 2 Type 1
Do you live with type 1 diabetes? Do you care for someone who does? Whether you’ve been recently diagnosed or living with the disease for years, How 2 Type 1 is for you. This video, developed in partnership with the Diabetes Leadership Foundation, aims to provide support, knowledge, expert advice, and actionable steps to help you and others in the type 1 diabetes community thrive!
Managing And Treating Type 1 And Type 2
Managing and treating your diabetes is so important. This is because itll help you avoid serious health complications. And itll play a big part in your daily life regardless of if you have type 1 or type 2.
If you have type 1 diabetes, youll need to take insulin to control your blood sugar levels. Youll also need to test your blood glucose levels regularly. And count how many carbs you eat and drink. Counting carbs will help you work out how much insulin you should take when you inject with your meals.
And generally you should be trying to have a healthy lifestyle. That includes regular physical activity and a healthy balanced diet. These will help you reduce your risk of diabetes complications.
If you have type 2 diabetes, you also need to eat a healthy diet and be active. These things will help you manage your weight and diabetes.
But quite often people with type 2 also need to take medication. Such as tablets and insulin, or other treatments too. Whether you need to test your blood glucose level like someone with type 1, depends on the treatment you take. Your GP can tell you what you should do at home.
Don’t Miss: Insulin Inhibits Lipolysis
Can Symptoms Appear Suddenly
In people with type 1 diabetes, the onset of symptoms can be very sudden, while in type 2 diabetes, they tend to come about more gradually, and sometimes there are no signs at all.
Symptoms sometimes occur after a viral illness. In some cases, a person may reach the point of diabetic ketoacidosis before a type 1 diagnosis is made. DKA occurs when blood glucose is dangerously high and the body can’t get nutrients into the cells because of the absence of insulin. The body then breaks down muscle and fat for energy, causing an accumulation of ketones in the blood and urine. Symptoms of DKA include a fruity odor on the breath, heavy, taxed breathing and vomiting. If left untreated, DKA can result in stupor, unconsciousness, and even death.
People who have symptomsof type 1 or of DKAshould contact their health care provider immediately for an accurate diagnosis. Keep in mind that these symptoms could signal other problems, too.
Some people with type 1 have a “honeymoon” period, a brief remission of symptoms while the pancreas is still secreting some insulin. The honeymoon phase usually occurs after someone has started taking insulin. A honeymoon can last as little as a week or even up to a year. But its important to know that the absence of symptoms doesn’t mean the diabetes is gone. The pancreas will eventually be unable to secrete insulin, and, if untreated, the symptoms will return.
Types Of Diabetes Tests
- Fasting blood glucose test blood glucose levels are checked after fasting for between 12 and 14 hours. You can drink water during this time, but should strictly avoid any other beverage. People with diabetes may be asked to delay their diabetes medication or insulin dose until the test is completed.
- Random blood glucose test blood glucose levels are checked at various times during the day, and it doesnt matter when you last ate. Blood glucose levels tend to stay constant in a person who doesnt have diabetes
- Oral glucose tolerance test a high-glucose drink is given. Blood samples are checked at regular intervals for two hours.
You May Like: Postprandial Hypotension Diabetes
Symptoms Of Type 1 And Type 2
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes share common symptoms. They are:
- going to the toilet a lot, especially at night
- being really thirsty
- feeling more tired than usual
- losing weight without trying to
- genital itching or thrush
- cuts and wounds take longer to heal
- blurred vision.
But where type 1 and type 2 diabetes are different in symptom is how they appear. Type 1 can often appear quite quickly. That makes them harder to ignore. This is important because symptoms that are ignored can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis .
But type 2 diabetes can be easier to miss. This is because it develops more slowly, especially in the early stages. That makes it harder to spot the symptoms. That is why it is important to know your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Some people have diabetes and dont know it. They can have it for up to 10 years without knowing.

