What Happens During Exercise
The muscles need more energy during exercise, so the body releases extra sugar, or glucose. For people with diabetes, this can have some side effects. For example, if the body doesn’t have enough insulin to use the glucose that’s released during exercise, then the glucose stays in the blood, which leads to high blood sugar levels. This is called hyperglycemia .
Not having enough insulin to use the sugar in the blood can also cause the body to burn fat for fuel. When the body starts to burn fat for fuel, substances called ketones are produced. People with diabetes shouldn’t exercise if they have high levels of ketones in their blood because this can make them really sick. If you have type 1 diabetes, your doctor will tell you how to check for ketones and treat yourself to get back on track.
The body’s need for extra glucose during exercise can also cause low blood sugar levels . Low blood sugar can happen when the body uses up all the sugar that it’s stored so there’s no more to be released as glucose when the muscles demand it. This is especially true if insulin levels in the blood are still high after taking an injection.
You may need to check blood sugar levels and have an extra snack to prevent low blood sugar levels. If you’re starting a rigorous exercise schedule, like training for a sport, your doctor may recommend that you adjust your insulin dosage to prevent low blood sugar levels.
Aerobic Endurance And High
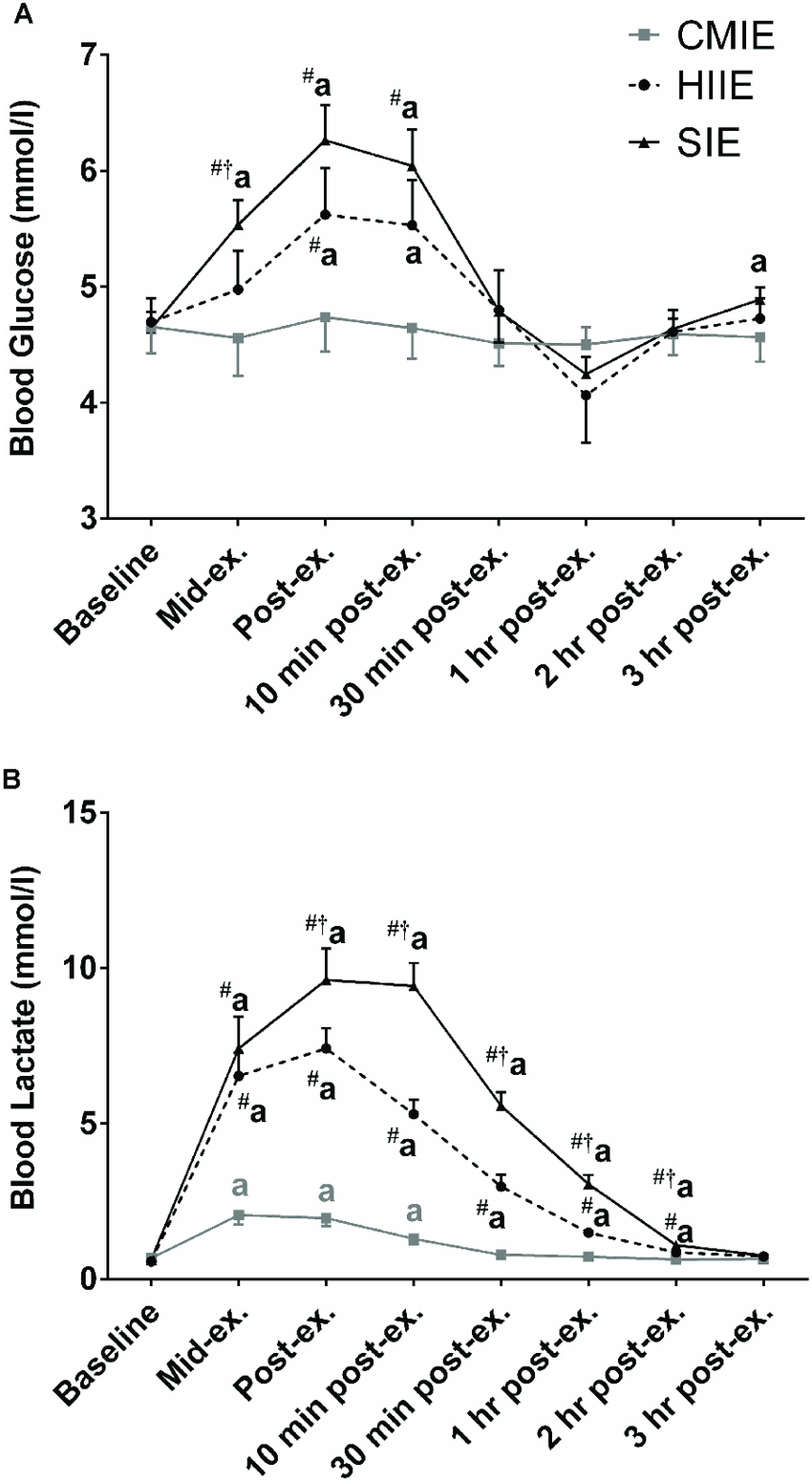
HIT is effective in improving aerobic endurance. In one study six all out SIT sessions over 2 weeks improved the mean cycle endurance time to fatigue while cycling at approximately 80% of pretraining VO2max by 100% . This required a total high-intensity exercise time of only 15 minutes with a total training time commitment of approximately 2.5 hours. In another study, a less intense version of HIT produced a similar improvement in VO2max after 4 weeks of training, as was seen in the more intense SIT group . The less intense HIT required only half the intensity but double the repetitions of the SIT, and may be more practical for the nonathlete.
Many people do not exercise despite the proven benefit of endurance exercise. An exercise program requiring less time commitment may appeal to some people. The aim of this paper is to review the impact of high-intensity exercise of short duration on blood glucose levels in diabetic and nondiabetic people.
What Is High Blood Glucose
To fully understand your blood glucose levels, itâs important to know: a) what values are actually considered high, and b) factors that can cause your elevated reading in the first place.
High blood glucose, also known as hyperglycemia, occurs when there is too much sugar in the bloodstream. Low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, is the result of too little glucose in the bloodstream. Hyperglycemia usually occurs because your body doesnât produce enough insulin or canât properly use the available insulin to remove the glucose from the bloodstream.
Using milligrams of glucose per deciliter of blood for measurement, high blood glucose readings after a meal indicating prediabetes can fall between 140 and 199 mg/dL. Levels reaching 200 mg/dL two hours after eating indicate you may already be insulin resistant or diabetic, though that diagnosis will need to come from your doctor. By comparison, the typical standard for normal glucose readings is to remain under 140 mg/dL throughout the day and under 100 mg/dL after eight hours of fasting.
A range of lifestyle factors, habits, and health conditions can cause high blood sugar. To debunk common hyperglycemia myths, review causes and symptoms, and discuss the best ways to address them, we spoke with two experts on high blood sugar levels: registered dietitian and For The Love of Diabetes creator Lori Zanini and registered dietitian nutritionist and diabetes management expert .
Also Check: Somatostatin Diabetes
Do I Opt For Weight Training If I Have Diabetes
Undergoing weight training is essential part if you have diabetes. Weight training increases your strength. Start with light weight and then jump to higher ones, but with the prior consultation of the gym instructor. You may use light dumbles each day and then go to heavier ones. Working on your muscles, back and butts will improve your posture.
You must take care of your diet in case you want to go for that six pack figure. Opting for a proper protein diet along with exercising and avoiding carbohydrates are essential.
Read Also:
People who have type2 diabetes must start with slow walking and then gradually speeded up. You should always keep in mind that unnecessary speeding up at the treadmill or cross trainer might hurt the joints. So, a slow and steady policy is a better one. Regular and efficient exercises will help to keep away from diabetes. Moreover, you will gain confidence, good posture, and a healthy body when you exercise.
Diabetes Exercise And Ketoacidosis
People with type 1 diabetes are at risk of developing a build-up of ketones if they are unwell or have forgotten to take their insulin.
If you have type 1 diabetes and you are unwell, avoid exercise until you feel better. If your BGL is above 15 mmol/L and you have positive blood or urine ketones, you need to clear the ketones from your blood before beginning exercise. Extra insulin is needed to clear ketones. Ask your diabetes health professional for an individual management plan.
People with type 2 diabetes are generally not at risk of developing dangerous levels of ketones and therefore do not need to check for them.
Also Check: High Sugar Symptoms Diabetes
If You Have Type 1 Diabetes
Here are a few extra strategies to help you avoid hypoglycemia during exercise:
- Dont exercise on an empty stomach and avoid delaying your meals.
- Do very short intervals at maximum intensity at the beginning or end of a moderate-intensity exercise session.
- Do your strength/weight training exercises immediately before your aerobic exercises .
- Avoid injecting insulin in an area of your body that will be worked during the activity . That would accelerate insulin absorption and could cause hypoglycemia.
Why Some Types Of Exercise Can Make Your Blood Sugar Increase
Have you ever wondered why your blood sugar falls during certain types of exercise whilst increasing during and types of exercise? Or why you sometimes get high blood sugars after exercise?
If youre curious about the scientific explanation of how exercise can raise blood sugar, read on.
I rarely come across scientific studies that explore how exercise affects blood sugar in people living with type 1 diabetes, so when I recently got my hands on just such a research paper, I dug in with great interest .
Well actually, Google and I dug in. This research paper is heavy reading. You know those scientific papers where you feel like you need an advanced degree just to understand the introduction? This is one of them.
The paper is titled Effect of intermittent high-intensity compared with continuous moderate exercise on glucose production and utilization in individuals with type 1 diabetes, and is written by a team of scientists from Australia. It was published in the American Journal of Physiology Endocrinology and Metabolism in 2007 .
I thought that the subject was relevant and interesting enough to spend the time reading and understanding it. So, since Ive done the heavy reading, let me share what Ive learned with you.
Recommended Reading: Diabetes Mac And Cheese
Diabetics Develop Higher Blood Sugar During Exercise
Nov. 18, 1999 — Insulin-dependent diabetics who take part in sports may need to take more insulin after intense exercise rather than less, contrary to conventional wisdom.
A new study, published in the November issue of the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, shows that insulin-dependent diabetics, known as type 1 diabetics, are likely to see an increase in their blood sugar, not a decrease, after an intense bout of physical exertion.
It is healthy for blood sugar to rise during exercise because the muscles need the excess fuel to compensate for the increased demand placed upon them. But in most people the body will adjust after exercising and bring the blood sugar levels back to normal. That is not the case for a type 1 diabetic, because their bodies will not circulate enough insulin, which is required to convert the sugar in the blood.
“Anyone who is competitive, who is doing a sprint, playing hockey, basketball … is at significant risk of developing high sugar as a consequence of their exercise,” study investigator Errol Marliss, MD, tells WebMD. Marliss is professor of medicine and director of the McGill Nutrition and Food Science Center at the Royal Victoria Hospital in Montreal.
How To Implement The Research Findings
Aside from me finding this super fascinating, what can we do with this information?
I think that this is a great piece of knowledge to have for trained athletes, those who are just starting out, and for parents managing their kids diabetes. It can serve as a guide when determining the amount of insulin and carbohydrates to safely administer prior to and post an activity.
The scientists compared interval training to sports like basketball and soccer where you have intense bursts of activity. I would add newer sports such as CrossFit, HIIT and HIT . It could also be boot camps, spinning classes, or if you just do a lot of cardiovascular interval training and heavy resistance training.
Armed with this scientific knowledge , I know that I dont need to reduce my insulin as much before and after an interval training or a resistance training session ), while I will need to make reductions if I do 40-60 minutes of steady state cardio.
For me, steady state cardio can be a long walk, a bike ride, or walking on an incline, Stairmaster or elliptical. With all of these activities, Ill see an almost instant drop in blood sugars. However, the improved glucose utilization wears off pretty quickly after I stop exercising, so I know to lower my insulin prior to steady state cardio but not after.
Read Also: What Can Type 2 Diabetics Eat
Is Eih A Sign Of Diabetes
EIH is not necessarily a sign of diabetes. Exercise alone can substantially lower blood glucose. However, people with diabetes have additional risk factors for hypoglycemia.
Untreated diabetes causes hyperglycemia, which is high blood glucose. Individuals who take medications to manage their diabetes are at increased risk of hypoglycemia if they take more than they need. Not eating enough food to match activity levels can also be a cause.
Also, people with diabetes may become hypoglycemic if they take medication for diabetes when fasting or starting a restrictive diet.
How Exercise Impacts Glucose In The Moment
When you exercise, your body relies on two sources of fuel: glucose and fat. How your blood sugar changes during exercise depends on the intensity level of your workout and the fuel source your body is using.
Steady-state cardio exercises, like jogging or gentle swimming, donât rely on your body having to produce quick bursts of energy. In these cases, it gets more of its energy from fat, so your blood sugar will usually stay at the same level or decrease.
Higher-intensity exercises like HIIT, strength training, and sprinting cause your body to release a surge of adrenaline. To ensure that you have enough energy readily available for this, your body releases glucose from your liver, increasing your blood sugar levels.
Put more simply, your body works through exercise using supply and demand. During high-intensity exercises, it doesn’t have the supply of energy on hand to fuel your workout. So, it releases glucose, immediately meeting the energy demand to fuel your workout while causing a short-term spike in blood sugar. During low-intensity exercise, your body has enough energy on hand to meet the demand, so blood glucose typically stays steady or decreases.
Short-term level changes like these are not harmful, just a standard part of our physiology.
You May Like: Does Smoking Raise Blood Sugar
Diabetes Precautions To Take Before Starting An Exercise Program
While exercise has many benefits it is also important to know about some guidelines for diabetes and exercise. This makes exercise safer and more enjoyable.
People with diabetes are at increased risk of heart and blood vessel disease and foot problems, so its important that your exercise is right for you.
People with type 1 diabetes and people with type 2 diabetes using insulin or some glucose-lowering medications called sulphonylureas are at risk of hypoglycaemia, and their risk increases during and after exercise. Speak with your doctor if you are unsure of the type of medication you are taking.
- Make sure you have an individualised diabetes management plan your diabetes health professional can help you with this.
- If you have never exercised before, start with low impact exercise such as walking and go slowly. This will help build exercise tolerance. You will also be more likely to continue doing regular exercise and prevent injuries.
- Consider seeing an exercise physiologist for an individualised exercise program. This is especially helpful if you have pain or limited movement.
- Discuss with your doctor or diabetes educator the most appropriate areas of the body to inject your insulin, especially during exercise.
Glucose Metabolism During Moderate
Skeletal muscle is responsible for most of the uptake of glucose after a meal, and transport of glucose into the muscle is considered the limiting step in glucose disposal., Glucose transport occurs primarily by diffusion utilizing glucose transporter carrier proteins . Both exercise and insulin regulate glucose transport mainly by the translocation of the GLUT4 isoform from an intracellular compartment to the plasma membrane and transverse tubules., GLUT4 levels are considered an important determinant of insulin sensitivity,
At rest and postprandially, glucose uptake is insulin-dependent, with the major purpose being the replenishment of muscle glycogen stores. Insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation is generally impaired in type 2 diabetes. During exercise, muscle utilizes glucose made available by intramuscular glycogenolysis and by increased glucose uptake. Both aerobic and resistance exercises increase GLUT4 abundance and translocation, and hence blood glucose uptake by a pathway that is not dependent on insulin. Glucose uptake into contracting muscle is therefore normal even in the presence of type 2 diabetes.,, Following exercise, glucose uptake remains elevated with the contraction-mediated pathway remaining active for several hours.
Read Also: Blood Sugars Too High
If My A1c Is Normal My Glucose Is Good
An A1C result thatâs below 5.7% is normal âs standards, but having a result below that number isnât the end of the story. Pregnancy, hemoglobin variants, anemia, liver disease, and certain medications can cause inaccurate A1C results.
Additionally, the A1C test is measuring your average glucose value over the past 3 months, but averages inherently do not capture highs and lows. So, you could have a normal average while also having abnormal glucose spikes. The A1C test should only supplement your regular blood sugar testing, not replace it completely.
Physical Activity And Hyperglycemia
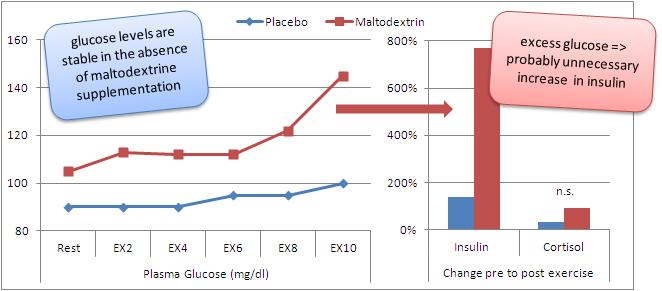
During and after nearly all types of exercise, blood sugar levels tend to drop, since the cells are more sensitive to insulin. However, a short-duration, but very intense physical activity can cause transient hyperglycemia because the body will produce more glucose than it uses due to the activation of stress hormones.
If you are in a hyperglycemia state before you start, physical activity could make it worse. Therefore, it is prudent to monitor your blood glucose levels more often if you start doing physical activity when in a state of hyperglycemia.
Elevated glycemia can be due to:
- dehydration, which increase the concentration of glucose in the blood
- stress hormones, such as adrenalin, secreted during high-intensity exercise
Be sure to hydrate before and during the activity to avoid increasing the concentration of glucose in the blood when you lose water through sweat, especially on hot, humid days.
Read Also: Metformin Maximum Dose Per Day
High Blood Sugar: 13 Reasons Your Glucose Levels Are Rising
May 2, 2021
Itâs a fact of life that blood sugar fluctuates throughout the day. These ups and downs depend on a handful of factors, like when you wake up, what you eat, the medications you take, and how you manage stress. So, some variation is normal, to the point that you might not even notice it.
Ignoring blood sugar level changes altogether, though, means youâre ignoring a valuable marker of your health. Especially if you start to have new or unfamiliar symptoms like fatigue, thirst, or brain fog . Learning these symptoms and their causes will give you the tools to better understand your own body, then take the right actions for better long-term metabolic health.
What Are The Common Types Of Exercises That I Must Practice To Get Rid Of Diabetes
- Exercise is the most efficient way to beat off diabetes. Might be going to the gym or regular yoga is not possible for each and everybody. But owing to your hectic schedule, you must be doing something that will boost your health forever.
- Walk some distance for getting your daily ration especially if itâs a walking distance, then avail on foot and avoid traveling by car.
- Walk the stairs to your office. It will boost some energy, burn calories and thereby make you feel fresh.
- Cycle some distance in the morning and evening. You will enjoy the cool breeze, and it will be your mood buster.
- Whenever you are in your garden, try to use a skipping rope. It will initiate and trigger your hormones efficiently.
- Do some gardening. It is a light activity and will boost your mood and enhance insulin levels to work
- Practice yoga day and night. There are various postures in yoga that cure diabetes like Pashchimottasana and sitting pose of Vajrasana. Dhanurashana and tree pose is good for a steady weight and also triggering insulin from the pancreas. Light aerobics is suitable for cutting down those extra kilos.
- Jump the trampoline to enhance your mood and make use of the extra glucose in your body.
You May Like: Long Term Effects Of Insulin

