What Is The Ketogenic Diet
Despite its recent rise in popularity for weight loss, diabetes and more, the ketogenic diet was developed as a medical nutrition therapy intervention for epilepsy in the 1920s. Though it may seem like a fad diet, this approach has true clinical application in the appropriate settings .
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, moderate-protein, low-carbohydrate diet. Usually 5 percent or less of energy intake is from carbohydrates. In contrast, the Dietary Guidelines recommend that 45-65 percent of daily calories come from carbohydrates.
The body prefers to use carbohydrates, broken down to glucose, as its main energy source. When your carb intake is extremely low and glucose is not available for energy, the body enters a metabolic state called ketosis where it breaks down fat for energy instead. In this state, the body uses ketone bodies for energy instead of glucose until you start eating carbohydrates again.
Listen To Your Body And Your Doctor
If you are taking insulin, you may immediately need to lower your intake anywhere from 30-50% as soon as you enter ketosis. For those living with Type 1, this can significantly help with controlling highs and hypos.
As with any diet, precautions need to be taken. Pregnant women and those with kidney disease are not good candidates for this diet, and some people with diabetes may find that the diet increases their insulin resistance. Dairy can often spike blood sugar, so avoiding the dairy in a keto diet and taking a Vitamin D supplement might be a better option for some people. Its important to pay attention to the way your body responds and realize that no diet is a one-size-fits-all model.
The trick to reaping the benefits of the keto diet is to stay in ketosis, which means keeping your carbs at 5% or less of your calories. The 5% can fall anywhere between 20-50 grams a day. However, if an insulin shot is missed while in deep ketosis, theres a good chance you will find yourself quite sick, so its probably best to avoid the risk and keep carbs on the upper end of this spectrum.
This diet might be untenable as a long-term way of life for many people, but if you have iron willpower and the desire to try a restrictive diet that still allows you to indulge yourself with fatty meats and oils, a keto diet might very well be the way for you to help manage your diabetes while managing weight.
What The Science Says
Several comprehensive studies and meta-analyses have demonstrated that after a few months or even a year of a low carb diet versus a moderate/high carb diet, there are no significant differences in the amount of weight lost .; I will say, however, most of these diets are NOT keto and are simply lower carb .; Also, long-term effects are not often studied due to budgetary constraints, so interpret results as you wish.
Verdict: A keto diet is not inherently better for weight loss than other diets but can be very effective if it:
- Helps you manage your blood sugar better than other diets
- Is easier for you to follow than other diets
- Works for your general lifestyle
As with most other diets, the main criteria for success is whether or not you can follow the diet for the long term. If you like the keto lifestyle, the diet works great. If you hate it, it probably wont work for you.
Recommended Reading: How Many Carbs Should A Diabetic Have In One Day
Fair Warning: There Are Challenges To Choosing A Keto Diet
- The first few days are extremely difficult as your body tries to acclimate to such a low level of carbs. During this adjustment to burning fat instead of glucose, the side effects will make you feel awful; hence the term, keto flu.
- Youll be depriving yourself in social situations
- Youll need to prepare meals ahead and take them with you since you are confined to eating specific foods.
3 Common Mistakes to Keep In Mind When On a Keto Diet
Adhering to the keto diet puts your body into a state of ketosis, which sounds similar to ketoacidosis. However, dont confuse these terms as ketosis and ketoacidosis are two very different physiological states, Dr. Goss explains.
Common Problems With A Ketogenic Diet
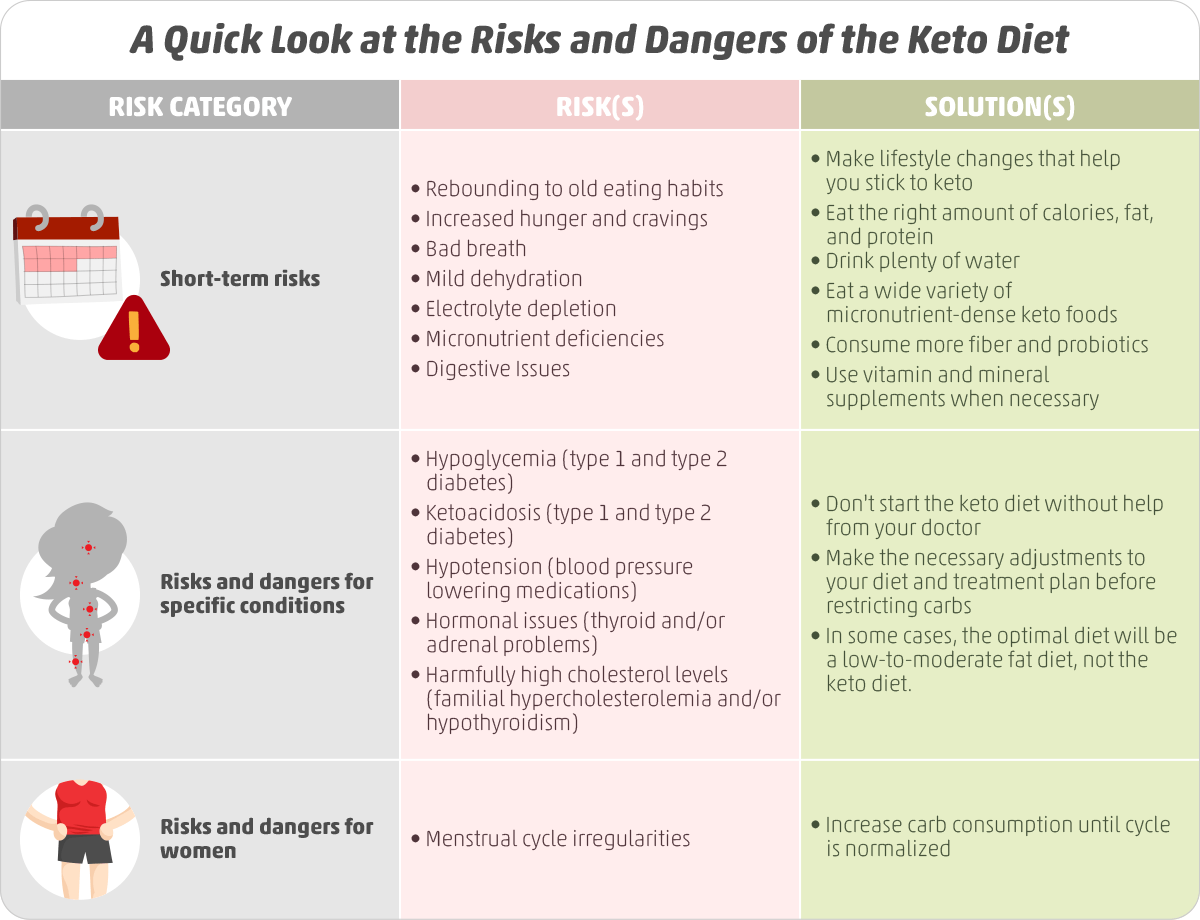
Adjusting to a lower intake of carbohydrate is often a significant change for most people. As , writes for Harvard Health, a keto diet can be hard to follow, and it can be heavy on red meat and other fatty, processed, and salty foods that are notoriously unhealthy.;He goes on to explain that we dont know much about the long-term effects of a keto diet because it can be very hard for people to stick with it for long periods of time.
The keto diet is not consistent with typical recommendations that have come from years of nutritional research. Although a keto diet may initially help with weight management and blood sugar control, it is not consistent with the recommendations for a heart-healthy diet and a diet to prevent cancer, since those eating patterns include whole grains and plenty of fruits and vegetables.
It is important to choose an eating pattern that promotes overall good health and is sustainable. A healthy eating pattern is not about cutting foods out, but rather adding in more healthy options such as whole grains, fruits and vegetables, lean protein sources, nuts, and healthy fats. When people add in these healthy foods, they dont have room for empty calorie processed snacks.
You May Like: How Long Does It Take To Lower Blood Sugar
Fix Your Keto Side Effects
- Drink more water– With the loss of water and sodium, your body will experience dizziness, nausea, headache, and cramps. Keeping the body hydrated and even adding some salt to the water will help ease the symptoms.
- Eat more fat- Remember, removing carbs is essentially starving your body of energy. Replacing it with more fat helps to supplement the missing carbs .
Pros Cons And Best Practices
Ask a wide range of expertsdoctors, dietitians, and nurseshow they feel about the ketogenic diet for diabetes and you’ll probably hear a wide range of answers. Some answers might be based on personal experience, others on scientific evidence about its efficacy, long-term benefits vs. risks, and so on.
Ask people with diabetes who’ve tried the ketogenic diet about their experience and you’ll also hear a wide range of answers. This is because a dietary approach that works for one may not work for someone else.
Ketogenic diets can serve a purpose, but their rigidity and restrictiveness may make them hard to follow and can result in other health issues if not followed properly.
Also Check: Is Oatmeal Good For Type 2 Diabetes
Ketosis May Help Insulin Work Better
There is a theory that when the body is in a state of ketosis on the ketogenic diet, insulin works better. If this were true, the ketogenic may be uniquely fitting for diabetics.;
Studies have shown improved insulin function and weight loss after people with diabetes consume a ketogenic diet this effect was greater on a ketogenic diet when compared to traditional calorie controlled diets .
One small study suggested a greater improvement in insulin function and weight loss following a ketogenic diet compared to a non-ketogenic low carbohydrate diet; .
While this theory seems promising, more studies are needed to determine if the state of ketosis improves insulin function in diabetics more than other low-carbohydrate diets that dont involve ketosis.;
Reductions In Diabetes Medications
Diabetes medications all have the same goalâto reduce elevated blood sugar. The common classes include:
- Insulin
- Sulfonylureas
- GLP-1 receptor agonists
- Metformin
When your blood sugar is no longer chronically elevated, these blood-sugar-lowering medications are no longer necessary. An ongoing study has shown that sustained nutritional ketosis can lead to the permanent removal of these medications.¹ⰠMedications that rapidly reduce blood sugar need to be removed first, such as insulin and sulfonylureas, sometimes in as little as 2 days to 2 weeks. Other medications like SGLT-2 inhibitors, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and metformin can be removed as long as you maintain normal blood sugar.
If you are on diabetes or blood pressure medications, Virta highly recommends that you get medical supervision before making any dietary changes.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Type 2 Diabetes
Different Types Of Keto Diets
What all of these types of the keto diet have in common is their goal to get your body into the natural metabolic state of ketosis so you can burn fat, instead of carbs, for energy.
Standard ketogenic diet
Consuming a high-fat, moderate-protein and low-carb diet. The percentages of your daily diet should be about 75% fat, 20% protein and 5% carbs.
High-protein ketogenic diet
Similar to the SKD, but with added protein. The ratio is about 60% fat, 35% protein and 5% carbs.
Cyclical ketogenic diet
Involves 5-6 days of the SKD followed by 1-2 days of refeeding days where the majority of calories come from carbohydrates.
Targeted ketogenic diet
Eating carbohydrates around the times that you exercise. Meant for people who are regularly working out at a very high-intensity or for an extended period of time.
What Does Keto Do To Your Blood Sugar
“When you remove carbs from the diet, blood sugar levels drop,” says Palinski-Wade. This is why keto can help improve blood sugar management and insulin sensitivity. “However, people shouldn’t choose foods solely based on their effect on blood sugar,” says Cleary. “Other factors such as fiber, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants and satisfaction must be taken into account. The keto diet would likely lead to better blood glucose control short-term; however, this would only lead to improvements in health status if the diet is followed long-term.”
Learn more: 12 Healthy Ways to Lower Your Blood Sugar
You May Like: How To Instantly Lower Blood Sugar
Relationship Between Type 2 Diabetes And Carbs
Type 2 diabetes means that the body doesn’t respond to insulin like it should. The hormone insulin helps your body utilize blood sugar, or glucose, for energy. For patients with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes, insulin is still produced but it may be in insufficient amounts or the body doesn’t use insulin properly. This causes blood sugar levels to increase. If not treated, chronically high blood sugar levels can lead to heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, eye damage, sleep apnea, and more.
To keep diabetes under control, you want to keep your blood sugar levels as close to normal as possible, says Osama Hamdy, MD, an associate professor at Harvard Medical School and senior staff physician at the Joslin Diabetes Center in Boston.;
“Glucose in blood comes predominantly from carbohydrates, so eating more carbohydrates increases blood glucose and reducing carbohydrates reduces blood glucose.”
That’s why the carb-cutting keto diet might be helpful for people with type 2 diabetes.
What Happened In Type 2 Diabetes Study: Saslow

“If you follow the ketogenic diet, it’s a very efficient way of losing weight and managing your blood glucose and getting off your glucose-lowering medicine,” says Dr. Saslow, PhD, the study leader.
The study was a follow-up to earlier research in which she and her team also found that those on the ketogenic diet lowered their HbA1c while those on the conventional low-fat diet did not.4 Just as in the current study, those on the low-carb keto diet also lost more weight.
The more recent study was conducted online to ascertain if this online approach proved effective in eliciting weight loss.1 Dr. Saslow’s team randomly assigned the 12 participants to the Keto diet and lifestyle improvement group and another 13 individuals to the traditional low-fat diet known as the Plate Method,1 supported by the American Diabetes Association.;
For the ketogenic eating plan, participants were instructed to reduce non-fiber-containing carbohydrates to between 20 and 50 grams a day, with no calorie restriction. The group following the plate method were told to eat their meals on a nine-inch plate, filling half of it with non-starchy vegetables , ¼ of the plate with whole grains and adding lean protein to the last quarter of the plate.1
Don’t Miss: How To Lower Blood Sugar At Home
What Is The Keto Diet
Itâs a low-carb, high-fat eating plan. Most of what you eat is fat, whether thatâs unsaturated fats like nuts, seeds, and avocados, or saturated fats like butter and coconut oil. About 20%-30% of your diet is protein, either lean or fatty . Youâre supposed to strictly limit carbs, even those that are typically considered healthy, such as beans, whole grains, milk, and many types of fruits and vegetables. On the keto diet, you eat less than 50 grams of carbs a day. To put that in perspective, one medium apple has 25 grams of carbs.
How does it work? Normally, your body fuels itself from sugar, or glucose, that it gets from carbs. After a few days of the keto diet, your body runs out of glucose. So it starts burning body fat instead. This is called nutritional ketosis. It creates fatty acid substances called ketones, which your body can use for energy.
How To Stay On Track
Success doesnt happen overnight, and I know that working hard will eventually get me to my goals, says Lele. And when it comes to finding motivation, being a mother certainly helps: My son helps me stay on track. I need to get healthier for my son to make sure Im always here for him, she says.
If youre interested in trying out the keto diet, or are already following the regimen, Lele suggests keeping the following in mind:
You May Like: How To Mix Nph And Regular Insulin
How A Ketogenic Diet Works
On a ketogenic diet, blood glucose levels are kept at a low but healthy level which encourages the body to break down fat into a fuel source known as ketones
The process of breaking down or burning body fat is known as ketosis
People on insulin will typically require smaller doses of insulin which leads to less risk of large dosing errors.
The diet helps burn body fat and therefore has particular advantages for those looking to lose weight, including people with prediabetes or those otherwise at risk of type 2 diabetes.
Less Muscle Mass Decreased Metabolism
Another consequence of keto-related weight changes can be a loss of muscle mass, says Kizerespecially if youre eating much more fat than protein. Youll lose weight, but it might actually be a lot of muscle, she says, and because muscle burns more calories than fat, that will affect your metabolism.
When a person goes off the ketogenic diet and regains much of their original weight, its often not in the same proportions, says Kizer: Instead of regaining lean muscle, youre likely to regain fat. Now youre back to your starting weight, but you no longer have the muscle mass to burn the calories that you did before, she says. That can have lasting effects on your resting metabolic rate, and on your weight long-term.
RELATED:;5 Long-Term Health Risks of Going Keto
Don’t Miss: What Happens If Insulin Is Taken After Food
The Keto Diet And Medication
Certain medications just dont mix with a keto diet.
Your doc will be able to tell you if any of the medications youre taking will react negatively to ketosis or a low carb intake.
If youre on any of the following meds, a keto diet probably isnt a viable option:
- Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors. These are common medications given to people with type 2 diabetes. Even on their own, SGLT2 inhibitors increase the risk of ketoacidosis, so combining them with the keto diet is extremely dangerous.
- Certain antipsychotic meds. Medications like risperidone , aripiprazole , and quetiapine fumarate may increase insulin resistance, which makes it harder for your body to break down ketones. Again, combining a keto diet with these drugs massively increases ketoacidosis risk.
- Some epilepsy drugs. In particular, divalproex sodium , zonisamide , and topiramate may interact with the effects of the keto diet.
You Have Access To More Energy For Cardio
Your body stores a lot more energy as fat than it does as glycogen . A keto diet allows you to tap into that reservoir of stored fat energy more easily.
This is why you sometimes hear about endurance athletes who have successfully switched to keto and continued to perform at a high level because they no longer hit the metaphorical wall.; They have access to a gigantic reservoir of fuel that was previously more difficult and took longer to access
Read Also: What Happens In Type 1 Diabetes
You Might Experience Mood Disturbances
Food and mood go hand in handfor better or for worse. As you deprive your body of carbohydrates, mood swings may result.
“When the brain gets less sugar from the blood for energy, this can impact mood and result in feeling irritated, fatigued, and difficulty concentrating,” says Palinski-Wade.
Feelings of restriction or the inability to socialize through food on a keto diet might make you feel extra blue. Before diving in, give some thought to how much you’re willing to sacrifice to attain keto success.
Keto For Type 1 Diabetes

In people with type 1 diabetes, an autoimmune reaction destroys the cells that produce insulin meaning they will always have to rely on insulin injections to control their blood sugar levels. While a low-carb diet has anecdotally been found to help some type 1 diabetics keep their blood glucose levels stable, there have been very few studies looking into its long-term safety and effectiveness, and there are a number of potential risk factors. For example, people with type 1 diabetes may experience sudden drops in blood glucose levels and be at a higher risk of hypoglycaemia when following a low-carb eating plan like keto.
Furthermore, when fat is broken down to make energy, as is the case with the keto diet, chemicals called ketones are made as a by-product. If the levels of ketones get too high in the body it can lead to life-threatening diabetic ketoacidosis. Furthermore, many patients with type 1 diabetes also have some degree of renal impairment, and the build-up of ketones and acids in the body may cause too much stress on the kidneys.
Keto is generally not recommended for type 1 diabetics for these reasons.
So, is the keto diet bad for diabetics? If you have any type of diabetes and wish to give the keto diet a try, it is always safest to do so in consultation with your healthcare team.
Also Check: What Is Type 1 Diabetes Caused By

