We Know Some People Get Confused Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes And Were Often Asked About The Differences Between Them
Although type 1 and type 2 diabetes both have stuff in common, there are lots of differences. Like what causes them, who they affect, and how you should manage them. There are other types of diabetes like gestational and MODY. But this page is mainly about the differences between type 1 and type 2.
For a start, type 1 affects 8% of everyone with diabetes. While type 2 diabetes affects about 90%.
Lots of people get confused between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. This can mean you have to explain that what works for one type doesn’t work for the other, and that there are different causes.
The main thing to remember is that both are as serious as each other. Having high blood glucose levels can lead to serious health complications, no matter whether you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes. So if you have either condition, you need to take the right steps to manage it.
How Does Pcos Relate To Diabetes
Some theories suggest that insulin resistance can create an adverse reaction involving the endocrine system and, in this way, can help bring about type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the cells of the body become resistant to insulin, an abnormal amount of insulin is made, or both.
Over 30 million Americans have some form of diabetes, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
While type 2 diabetes is typically preventable or manageable through physical exercise and a proper diet, research shows that PCOS is a strong independent risk factor for developing diabetes.
In fact, women who experience PCOS in young adulthood are at an elevated risk for diabetes and, potentially, fatal heart problems, later in life.
Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors:
Your risk of developing type 2 diabetes is higher if your diet is high in carbs and fat but low in fiber, if youre not very physically active and/or if you have high blood pressure. High alcohol consumption and age are also risk factors. Though genes do play a role in the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes, it can be prevented with the right lifestyle choices, unlike type 1.
Don’t Miss: Glipizide Metformin Side Effects
When To See A Doctor
Visit your GP as soon as possible if you experience the main symptoms of diabetes, which include:
- weight loss and loss of muscle bulk
- itching around the penis or vagina, or frequent episodes of thrush
- cuts or wounds that heal slowly
- blurred vision
Type 1 diabetes can develop quickly over weeks or even days.
Many people have type 2 diabetes for years without realising because the early symptoms tend to be general.
What Are Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
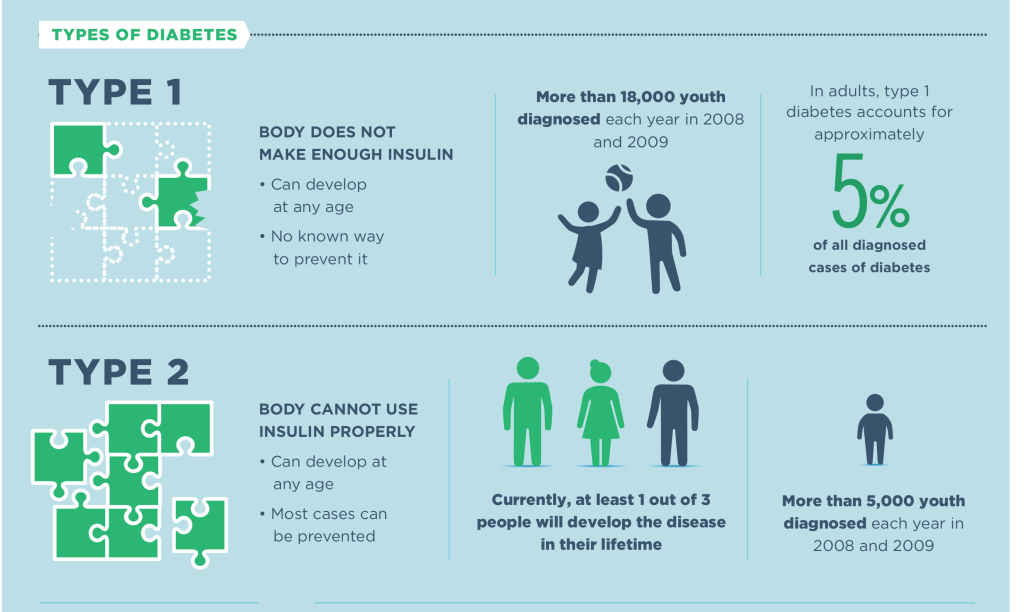
Type 1 diabetes was previously also known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetesas it mostly occurred before a person reached the age of 30. However, it can be diagnosed at any age. In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas produces little or no insulin.
Type 2 diabetes or adult onset diabetes or non-insulin-dependent diabetes is the more prevalent form of diabetes in which the body either resists the action of insulin or does not produce sufficient insulin.
Recommended Reading: Does Metformin Make You Tired
What Is A Diabetes Meal Plan
There’s no “magic” diabetes diet. However, there are dietary recommendations for people with diabetes. Diet methods for managing both type 1 and type 2 diabetes include:
- Carbohydrate counting
Signs and symptoms of diabetes, whether type 1 or type 2, do not differ.
- Early diabetes may not produce any symptoms at all.
- When symptoms do occur, the age of onset is typically different, with type 1 diabetes being diagnosed most often in younger people , while type 2 diabetes is diagnosed more commonly in adults. However, this is not always the case.
- The increasing incidence of obesity among children and adolescents has caused a rise in the development of type 2 diabetes in young people.
- Further, some adults with diabetes may be diagnosed with a form of late-onset type 1 diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes Complications
- Heart disease or heart attack
- Chronic kidney disease and kidney failure
- Damage to macrovascular and microvascular blood vessels
- Type 3 diabetes
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart disease or heart attack
- Chronic kidney disease and kidney failure
- Damage to macrovascular and microvascular blood vessels
- Type 3 diabetes
- Coronary artery disease
You May Like: Which Of These Is Not Produced By Pancreatic Islet Cells
Causes Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetes is extremely common in the U.S. According to the CDCs National Diabetes Statistics Report, 1 in 10 Americans have diabetes, and 1 in 3 Americans have prediabetes, or high blood sugar.
Anyone can get type 1 diabetes, but the condition is generally diagnosed around ages 13 to 14, the CDC says. In fact, type 1 diabetes used to be referred to as Juvenile Onset Diabetes because it is often diagnosed in young children. But adults over the age of 40 can develop type 1 diabetes, too, its just typically more rare.
Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is often seen in individuals who are middle-aged or older. You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you are age 45 or older, have a family history of the disease, or are overweight or obese. Although its generally seen in individuals aged 45 or older, more and more children and teens are developing type 2 diabetes, the CDC says.
Typically, type 1 diabetes is confirmed with antibody screening, Dr. Block says. This is a blood test that looks for islet antibodies or GAD antibodies. Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can also be diagnosed with the A1C test, or a blood test that examines your average blood sugar levels over the course of several months. An A1C level of 6.5 or higher indicates diabetesbut more tests are typically required to determine the type of diabetes you have.
Causes of type 1 diabetes
Causes of type 2 diabetes
Symptoms Of Type 1 And Type 2
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes share common symptoms. They are:
- going to the toilet a lot, especially at night
- being really thirsty
- feeling more tired than usual
- losing weight without trying to
- genital itching or thrush
- cuts and wounds take longer to heal
- blurred vision.
But where type 1 and type 2 diabetes are different in symptom is how they appear. Type 1 can often appear quite quickly. That makes them harder to ignore. This is important because symptoms that are ignored can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis .
But type 2 diabetes can be easier to miss. This is because it develops more slowly, especially in the early stages. That makes it harder to spot the symptoms. That is why it is important to know your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Some people have diabetes and dont know it. They can have it for up to 10 years without knowing.
Recommended Reading: Diabetes A1c Cutoff
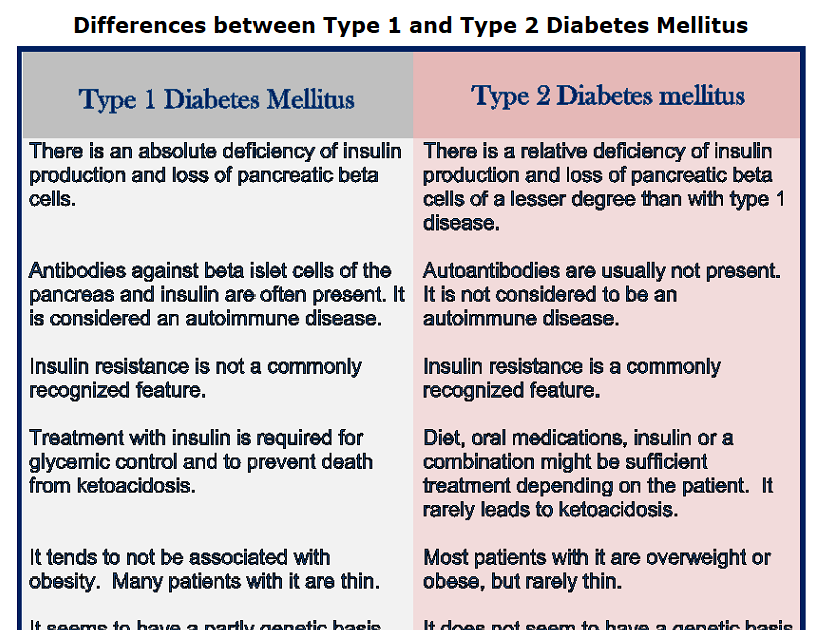
How Are These Diseases Different
|
Type 1 diabetes |
Type 2 diabetes |
|---|---|
|
Symptoms usually start in childhood or young adulthood. People often seek medical help, because they are seriously ill from sudden symptoms of high blood sugar. |
The person may not have symptoms before diagnosis. Usually the disease is discovered in adulthood, but an increasing number of children are being diagnosed with the disease. |
|
Episodes of low blood sugar level are common. |
There are no episodes of low blood sugar level, unless the person is taking insulin or certain diabetes medicines. |
|
It cannot be prevented. |
It can be prevented or delayed with a healthy lifestyle, including maintaining a healthy weight, eating sensibly, and exercising regularly. |
What Happens When You Have Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
If you have either type 1 or type 2 diabetes, it means you have too much glucose in your blood. This is the same for both types. But the difference between them is how this happens.
If you have type 1 diabetes, it means you have an autoimmune condition. This means your body has attacked and destroyed the cells that make a hormone called insulin. So you cant make insulin anymore.
We all need insulin as it helps take the glucose from our blood into our bodys cells. We then use this glucose for energy. Without insulin, the glucose level in your blood gets too high.
Type 2 diabetes is different. If youve got type 2, either your body doesnt make enough insulin, or your insulin doesnt work properly. This is known as insulin resistance. Like type 1, this means the level of glucose in your blood is too high.
Recommended Reading: Diabetic Feeling Dizzy
Insulin Insulin Pumps Insulin Pods
Every single person diagnosed with type 1 diabetes needs insulin via injection or pump in order to stay alive. People with type 1 diabetes may still produce a little bit of their own insulin, but it will not be enough to keep their body functioning.
Some people with type 2 diabetes need insulin while others do not. While weve been taught by magazines and news shows that diabetes can be cured with diet and exercise, thats far from the truth.
For multiple daily injections: If youre taking your insulin with a syringe or insulin pen, you will need a long-acting insulin thats taken once or twice a day to replicate the way your pancreas would normally release a constant drip, drip, drip of insulin all day and all night long.
Then, you will need a fast-acting insulin for meals, and for corrections when your blood sugar is high. Fast-acting insulin replicates the way your pancreas would normally release a large bolus of insulin to manage the food you eat.
For insulin pumps or pods: People using pumps or pods to deliver their insulin will only use fast or rapid-acting insulin that you program with your healthcare team to deliver insulin that drip, drip, drip all day long as well as larger boluses of insulin for meals and corrections.
Which Diets Are Recommended For Diabetes
Nutritional management is an important part of life for people with diabetes.
If you have type 1 diabetes, work with your doctor to identify how much insulin you may need to inject after eating certain types of food.
For example, carbohydrates can cause blood sugar levels to quickly increase in people with type 1 diabetes. Youll need to counteract this by taking insulin, but youll need to know how much insulin to take. Learn more about type 1 diabetes and diet.
People with type 2 diabetes need to focus on healthy eating. Weight loss is often a part of type 2 diabetes treatment plans, so your doctor may recommend a low-calorie meal plan. This could mean reducing your consumption of animal fats and junk food.
You May Like: Metformin Overdose Symptoms
Causes Of Type 2 Diabetes
People with type 2 diabetes have insulin resistance. The body still produces insulin, but its unable to use it effectively.
Researchers arent sure why some people become insulin resistant and others dont, but several lifestyle factors may contribute, including being inactive and carrying excess weight.
Other genetic and environmental factors may also play a role. When you develop type 2 diabetes, your pancreas will try to compensate by producing more insulin. Because your body is unable to effectively use insulin, glucose will accumulate in your bloodstream.
Type 2 diabetes is much more common than type 1.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Preventions , 34.2 million people in the United States were living with diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes in 2018. Thats a little over 1 in 10 people. Ninety to 95 percent of people with diabetes have type 2.
The percentage of people with diabetes increases with age.
About 10.5 percent of the general population has diabetes. Among those 65 years old and older, the rate reaches 26.8 percent. Only 25 out of every 10,000 Americans under 20 years old had been diagnosed with diabetes in 2018.
Men and women get diabetes at roughly the same rate. However, prevalence rates are higher among certain races and ethnicities.
Prevalence rates are higher for Hispanic Americans of Mexican or Puerto Rican descent than they are for those of Central and South American or Cuban descent.
How To Understand The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
According to the American Diabetes Association, there are approximately 1.4 million cases of diabetes diagnosed each year. Nearly eighty-six million people in the United States with prediabetes are on their way to becoming diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Although there are several forms of diabetes, there is much confusion about the difference between type 1 and type 2. Here is a look at the differences between the two most common forms of a disease that is becoming a global problem.
Read Also: Does Glimepiride Lower Blood Sugar
A1c Goals For Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
People living with type 1 or type 2 diabetes are all encouraged to achieve an HbA1c level at or below 7.0 percent for the best prevention of diabetes-related complications.
A crucial part of diabetes management for both type 1 and type 2 is testing your blood sugar. Using a glucometer or continuous glucose monitor each day is the only way to know if your choices around food, insulin, exercise, and other medications are keeping your blood sugar within a safe range.
For some people with diabetes especially those who have hypoglycemia unawareness or the elderly aiming for an A1c of 7.0 may present too much risk and stress.
Determining the right A1c goal for you based on your current diabetes management, your goals , and other stressors in your life can mean that tighter blood sugar management isnt realistic.
Instead, focus on doing the best you can with an A1c goal that is realistically achievable and safe for your life at this time.
- Read more on how to lower your A1c in Diabetes Strongs A1c Guide.
Type 1 & 2 What Is The Difference Between The Two
Diabetes Can It Be Prevented? How Is Treated?
Our bodies cells and organs need energy in order to perform various functions. Although many tissues use fat or proteins as a source of energy, some organs such as the brain and red blood cells rely on glucose for energy needs. A hormone called insulin, produced by the beta cells of the pancreas helps to convert blood sugar into usable energy, it also helps to control blood sugar levels and keep them in the normal range. Sometimes the pancreas is unable to produce enough or any insulin or fails to use insulin well, this results in an increase in the blood glucose levels.
Recommended Reading: What Happens In Type 1 Diabetes
Is Diagnosing Diabetes Types 1 And 2 Similar
Blood tests used to diagnose type 1 and type 2 diabetes include fasting blood sugar, a hemoglobin A1C test, and a glucose tolerance test. The A1C test measures the average blood sugar level over the past few months. The glucose tolerance test measures blood sugar after a sugary drink is given.
“The blood sugar testing we do to diagnose and manage type 1 diabetes is very similar to the testing we do for type 2 diabetes,” says Drincic. “We can do a blood test that looks for antibodies. That tells us if it is type 1 or 2.” In type 1 diabetes, the immune system makes antibodies that act against the cells in the pancreas that make insulin, and these antibodies can be detected in a blood test. Your doctor may suspect type 2 diabetes based on your symptoms and risk factors, such as obesity and family history.
When Should I Call My Doctor
Its important to monitor diabetes very closely if youre sick. Even a common cold can be dangerous if it interferes with your insulin and blood sugar levels. Make a sick day plan with your healthcare provider so you know how often to check your blood sugar and what medications to take.
Contact your provider right away if you experience:
- Confusion or memory loss.
- Nausea and vomiting for more than four hours.
- Problems with balance or coordination.
- Severe pain anywhere in your body.
- Trouble moving your arms or legs.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Type 2 diabetes is a disease where your body doesnt make enough insulin and cant use sugar the way it should. Sugar, or glucose, builds up in your blood. High blood sugar can lead to serious health complications. But Type 2 diabetes is manageable. Regular exercise and a healthy diet can help you manage your blood sugar. You may also need medication or insulin. If you have Type 2 diabetes, you should monitor your blood sugar at home regularly and stay in close communication with your healthcare provider.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 03/25/2021.
References
You May Like: Metformin Er Dosage
How To Treat Type 2 Diabetes:
Unlike type 1, people with type 2 diabetes often do not need to take insulin, because their bodies still produce a small amount of it. Though there are medications like Metformin available to assist in lowering blood sugar, the primary ways to treat type 2 diabetes are:
- A balanced diet. Eating fruits and vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins while avoiding more than the occasional high-fat, high-sugar food is the first and most essential step to treating type 2 diabetes.
- Exercise. Staying active is also very important. There are so many ways to get exercise. Try different activities to find a type of exercise you enjoy and work it into your weekly routine.
- Weight loss. Of course, if you work toward eating healthier and exercising, this may be a byproduct. Losing weight is less about the number on the scale and more about taking care of your body and reducing the strain on your pancreas.
- Blood glucose monitoring. Checking your blood sugar regularly will become a part of your daily routine. Its important to stay up-to-date on how your levels are doing throughout the day and adjust your food and activities accordingly. After a while youll figure out the regimen and balance that works best for you.

