Other Forms Of Diabetes
In 1% to 5% of people who have diabetes, other conditions might be the cause. These include diseases of the pancreas, certain surgeries and medications, and infections. In these cases, your doctor might want to keep an eye on your blood sugar levels.
Show Sources
American Diabetes Association: “Frequently Asked Questions about Pre-Diabetes,” “Type 2 Diabetes,” “The Dangerous Toll of Diabetes,” tion: “Gestational Diabetes,” “About Insulin and Other Drugs.”
National Library of Medicine: “Diabetes.”
National Diabetes Education Project: “About Diabetes and Pre-Diabetes.”
National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse : “National Diabetes Statistics, 2011.”
Merck Manual Consumer Version: âDiabetes Mellitus .â
CDC: âAbout Diabetes,â âPrediabetes: Your Chance to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes.â
World Journal of Diabetes: âType 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents.â
What Should I Expect If I Have Been Diagnosed With Diabetes
If you have diabetes, the most important thing you can do is keep your blood glucose level within the target range recommended by your healthcare provider. In general, these targets are:
- Before a meal: between 80 and 130 mg/dL.
- About two hours after the start of a meal: less than 180 mg/dL.
You will need to closely follow a treatment plan, which will likely include following a customized diet plan, exercising 30 minutes five times a week, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol and getting seven to nine hours of sleep a night. Always take your medications and insulin as instructed by your provider.
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- How did I get diabetes?
- If I have diabetes, will my children develop it, too?
- Will I need to take insulin?
- If I dont have a family history of diabetes, can I still get it?
- Can your diabetes get worse even if you do everything right?
- Can I prevent gestational diabetes?
- If I had gestational diabetes while pregnant, will I get type 2 diabetes later?
- Will the babies of a mom with gestational diabetes develop diabetes?
- How can I tell the difference between Charcot foot and gout in my foot?
Recommended Reading: Is Bananas Good For Diabetics
Informacin Sobre La Diabetes
La diabetes es una enfermedad crónica que afecta la forma en que el cuerpo convierte los alimentos en energía.
La mayoría de los alimentos que come se convierten en azúcar que se libera en el torrente sanguíneo. El páncreas produce una hormona llamada insulina, que actúa como una llave que permite que el azúcar en la sangre entre a las células del cuerpo para que estas la usen como energía.
Si una persona tiene diabetes, su cuerpo no produce una cantidad suficiente de insulina o no puede usar adecuadamente la insulina que produce. Cuando no hay suficiente insulina o las células dejan de responder a la insulina, queda demasiada azúcar en el torrente sanguíneo y, con el tiempo, esto puede causar problemas de salud graves, como enfermedad del corazón, pérdida de la visión y enfermedad de los riñones.
Todavía no existe una cura para la diabetes, pero se puede reducir mucho el efecto que tiene sobre la vida si se practican hábitos de estilo de vida saludables, se toman los medicamentos según sea necesario, se obtiene información sobre el automanejo de la diabetes y no se falta a las citas con el equipo de atención médica.
Who Gets Type 2 Diabetes
No one knows for sure what causes type 2 diabetes. But many kids who develop it have at least one parent with diabetes and a family history of the disease, so there seems to be a genetic risk.
Most people with type 2 diabetes are overweight. Excess fat makes it harder for the cells to respond to insulin, and not being physically active makes this even worse. Type 2 diabetes used to mostly affect adults, but now more and more U.S. kids and teens, especially those who are overweight, are developing the disease.
Also, kids in puberty are more likely to have it than younger kids, probably because of normal rises in hormone levels that can cause insulin resistance during this stage of fast growth and physical development.
p
Don’t Miss: Type 2 Diabetes Hereditary
What Is Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Advancements in technology have given us another way to monitor glucose levels. Continuous glucose monitoring uses a tiny sensor inserted under your skin. You don’t need to prick your finger. Instead, the sensor measures your glucose and can display results anytime during the day or night. Ask your healthcare provider about continuous glucose monitors to see if this is an option for you.
People With Difficulty Maintaining Blood Glucose Levels
The term brittle diabetes has been used to refer to people who have dramatic recurrent swings in blood glucose levels, often for no apparent reason. However, this term is no longer used. People with type 1 diabetes may have more frequent swings in blood glucose levels because insulin production is completely absent. Infection, delayed movement of food through the stomach, and other hormonal disorders may also contribute to blood glucose swings. In all people who have difficulty controlling blood glucose, doctors look for other disorders that might be causing the problem and also give people additional education on how to monitor diabetes and take their drugs.
Recommended Reading: Normal Dose Of Metformin
What’s New In The Treatment Of Type 2 Diabetes
Doctors and researchers are developing new equipment and treatments to help kids deal with the special problems of growing up with diabetes.
Some kids and teens already use new devices that make blood glucose testing and insulin injections easier and more effective. One of these is the insulin pump, a mechanical device that can be programmed to deliver insulin more like the pancreas does.
Researchers are also testing ways to stop diabetes before it starts. For example, scientists are studying whether diabetes can be prevented in those who may have inherited an increased risk for the disease.
What Is Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome
Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome develops more slowly than diabetic ketoacidosis. It occurs in patients with Type 2 diabetes, especially the elderly and usually occurs when patients are ill or stressed.If you have HHNS, you blood glucose level is typically greater than 600 mg/dL. Symptoms include frequent urination, drowsiness, lack of energy and dehydration. HHNS is not associated with ketones in the blood. It can cause coma or death. Youll need to be treated in the hospital.
Don’t Miss: Normal Metformin Dose
When To Contact A Medical Professional
- Chest pain or pressure
- Shortness of breath
- Red, painful skin that is spreading quickly
These symptoms can quickly get worse and become emergency conditions .
Also call your provider if you have:
- Numbness, tingling, or pain in your feet or legs
- Problems with your eyesight
- Sores or infections on your feet
- Symptoms of high blood sugar
- Symptoms of low blood sugar
- Frequent feelings of depression or anxiety
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed
Doctors can determine if a person has type 2 diabetes by testing blood samples for glucose. Even if a child or teen doesn’t have any symptoms of type 2 diabetes, doctors might test blood sugar in kids who are more likely to get it like those who are overweight.
Sometimes doctors may do another blood test, called the glycosylated hemoglobin test, to check for diabetes in children at higher risk for getting type 2 diabetes. This test shows how blood sugar levels have been running over the past few months.
If diabetes is suspected or confirmed, the doctor may refer you to a pediatric endocrinologist, a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the endocrine system in kids.
Don’t Miss: Alpha Cells Secrete Glucagon
Possible Driving Factors Behind Health Disparities
Annals of EpidemiologyPopulation Research and Policy ReviewJournal of General Internal Medicine PLoS MedicineJournal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities
Taking the ADAs 60-Second Type 2 Diabetes Risk Test can help you determine whether youre at a higher risk for diabetes based on a number of factors, including your race or ethnicity.
Liver Disease In Type 1 Diabetes
T1DM is an autoimmune disorder in which obesity is not believed to have a significant causal pathogenic role. However, with the high prevalence of obesity in the general population, patients with T1DM not uncommonly are overweight or obese. These individuals may develop NAFLD, with the prevalence of NAFLD correlating with the degree of obesity as reflected in their body mass index . Although altered glucose and lipid metabolism in inadequately controlled T1DM could theoretically contribute to the development of NAFLD, it is unclear if the prevalence of NAFLD is higher in T1DM than in non-diabetics with similar degrees of obesity.
Also Check: Insulin Works As An Antagonist To
Can Diabetes Kill You
Yes, its possible that if diabetes remains undiagnosed and uncontrolled it can cause devastating harm to your body. Diabetes can cause heart attack, heart failure, stroke, kidney failure and coma. These complications can lead to your death. Cardiovascular disease in particular is the leading cause of death in adults with diabetes.
Can Diabetes Cause Headaches Or Dizziness
Yes, its possible to develop headaches or dizziness if your blood glucose level is too low usually below 70 mg/dL. This condition is called hypoglycemia. You can read about the other symptoms hypoglycemia causes in this article.Hypoglycemia is common in people with Type 1 diabetes and can happen in some people with Type 2 diabetes who take insulin or medications such as sulfonylureas.
Don’t Miss: Metformin 1500 Mg
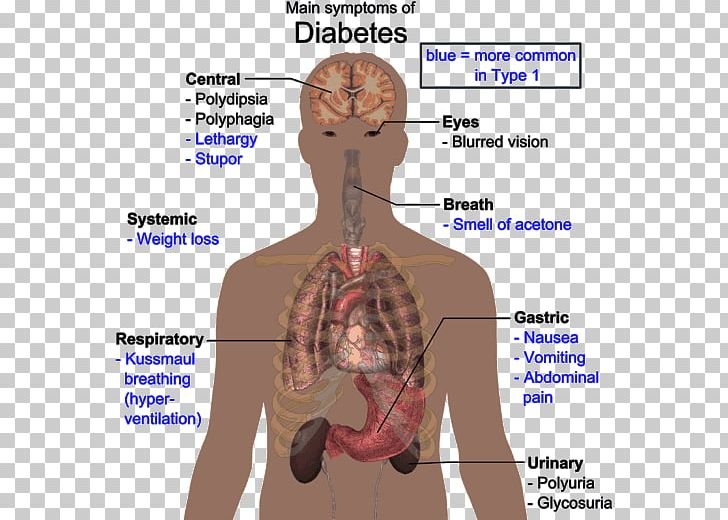
What Problems Can Happen With Type 2 Diabetes
Sometimes, kids and teens with type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, or obesity might develop thick, dark, velvet-like skin around the neck, armpits, groin, between fingers and toes, or on elbows and knees a cosmetic skin condition called acanthosis nigricans. This skin darkening can lighten over time with improvement in insulin resistance.
Polycystic ovary syndrome in girls is also often associated with insulin resistance. This hormone problem can make the ovaries become enlarged and develop cysts . Girls with PCOS might have irregular periods, might stop having periods, and may have excess facial and body hair growth. It also can cause fertility problems.
People with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes are also more likely to develop hypertension or abnormal levels of blood fats . When these problems cluster together, it’s called metabolic syndrome. People with metabolic syndrome are at risk for heart disease, stroke, and other health problems.
Diabetes also can cause heart disease and stroke, as well as other long-term complications, including eye problems, kidney disease, nerve damage, and gum disease. While these problems don’t usually show up in kids or teens who’ve had type 2 diabetes for only a few years, they can affect them in adulthood, particularly if their diabetes isn’t well controlled.
p
Diabetes: Definition Causes And Symptoms
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a disease that affects your bodys ability to produce or use insulin. Insulin is a hormone. When your body turns the food you eat into energy , insulin is released to help transport this energy to the cells. Insulin acts as a key. Its chemical message tells the cell to open and receive glucose. If you produce little or no insulin, or are insulin resistant, too much sugar remains in your blood. Blood glucose levels are higher than normal for individuals with diabetes. There are two main types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2.
What is Type 1 diabetes?
When you are affected with Type 1 diabetes, your pancreas does not produce insulin. Type 1 diabetes, once called juvenile diabetes, is often diagnosed in children or teens. However, it can also occur in adults. This type accounts for 5-10 percent of people with diabetes.
What is Type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body does not produce enough insulin, or when the cells are unable to use insulin properly, which is called insulin resistance. Type 2 diabetes is commonly called adult-onset diabetes since it is diagnosed later in life, generally after the age of 45. It accounts for 90-95 percent of people with diabetes. In recent years, Type 2 diabetes has been diagnosed in younger people, including children, more frequently than in the past.
Are there other forms of diabetes?
What causes diabetes?
How does diabetes affect my body?
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
Read Also: Rye Bread Good For Diabetes
How Is Type 3 Diabetes Diagnosed
There is currently no single agreed-upon method to diagnose type 3 diabetes.
In most cases, noticing one or multiple symptoms will result in a doctor running several cognitive tests. These tests, which test various aspects of cognition, are administered to determine your degree of cognitive impairment, and also eliminate other causes of impairment.
These cognitive tests tend to be frequently administered starting in early middle age, which can also help establish a baseline to show any decline in brain health.
On a physical level, there are two biomarkers that can help indicate the presence of type 3 diabetes: amyloid plaques, and neurofibrillary tangles.
Cognitive impairment combined with the presence of these biomarkers, along with other diabetes markers like high glucose levels, is a very strong indication of the presence of type 3 diabetes.
Who Is More Likely To Develop Type 2 Diabetes
You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you are age 45 or older, have a family history of diabetes, or are overweight. Physical inactivity, race, and certain health problems such as high blood pressure also affect your chance of developing type 2 diabetes. You are also more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you have prediabetes or had gestational diabetes when you were pregnant. Learn more about risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Read Also: Glucose Definition Medical
What Types Of Healthcare Professionals Might Be Part Of My Diabetes Treatment Team
Most people with diabetes see their primary healthcare provider first. Your provider might refer you to an endocrinologist/pediatric endocrinologist, a physician who specializes in diabetes care. Other members of your healthcare team may include an ophthalmologist , nephrologist , cardiologist , podiatrist , neurologist , gastroenterologist , registered dietician, nurse practitioners/physician assistants, diabetes educator, pharmacist, personal trainer, social worker, mental health professional, transplant team and others.
Favorite Resource For Diet Advice
Giving up some of the foods you once loved is arguably the biggest bummer about receiving a diabetes diagnosis. But with this Harvard-affiliated organizations expert diet guidance, you dont have to.
For more on “bad” foods you can eat in a diabetes diet, check out our article “5 ‘Bad’ Diabetes Foods You Can Enjoy in Moderation.”
Want to get involved? The IDF, which reaches 168 countries, makes it easy with their advocacy network page. Youll find different organizations that you can work with to help propel diabetes research, legislation, and awareness.
Don’t Miss: What Is A High Blood Sugar Reading
How Is Diabetes Diagnosed
Diabetes is diagnosed and managed by checking your glucose level in a blood test. There are three tests that can measure your blood glucose level: fasting glucose test, random glucose test and A1c test.
- Fasting plasma glucose test: This test is best done in the morning after an eight hour fast .
- Random plasma glucose test: This test can be done any time without the need to fast.
- A1c test: This test, also called HbA1C or glycated hemoglobin test, provides your average blood glucose level over the past two to three months. This test measures the amount of glucose attached to hemoglobin, the protein in your red blood cells that carries oxygen. You dont need to fast before this test.
- Oral glucose tolerance test: In this test, blood glucose level is first measured after an overnight fast. Then you drink a sugary drink. Your blood glucose level is then checked at hours one, two and three.
| Type of test |
|---|
Risk Factors For Type 2 Diabetes
There is no single cause of type 2 diabetes but some factors can put you at greater risk. They include:
- being age 40 or over
- being overweight
- having a family member who has diabetes
- having had gestational diabetes
- having given birth to a baby that weighed more than 4 kg at birth
- high blood pressure
- high cholesterol or other fats in the blood or
- member of a high-risk ethnic group.
Recommended Reading: Glucagon Signaling
Diabetes And Celiac Disease
The link between type 1 diabetes and celiac disease was first established in the 1960s. The estimated prevalence of celiac disease in patients with type 1 diabetes is approximately 6%, and about 1% in the general population. Due to the significantly higher prevalence of celiac disease in diabetes patients, many doctors recommend getting screened for celiac disease after a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes, and vice versa.
There is no established link between type 2 diabetes and celiac disease.
A 2013 study found that there were no standard uniform practices for screening type 1 diabetes patients for celiac disease. Of the facilities in the study that did screen for celiac disease, 60% only did so if there were symptoms present. The authors of the study suggested a uniform screening protocol be in place. Additionally, dietitians should acquire further education on the gluten-free diet for patients with type 1 diabetes and celiac disease.
Why Is Alzheimers Disease Considered Type 3 Diabetes
The negative effects of diabetes come from insulin resistance, a buildup of fatty acids in cells that are not meant to store fats. This prevents cells from effectively processing glucose, leading to hyperglycemia and many other side effects.
For an in-depth understanding of insulin resistance and the metabolic dysfunction it causes, check out our definitive guide to insulin resistance.
In the case of type 1 diabetes, insulin deficiency is primarily caused by the autoimmune attack of insulin producing beta cells in your pancreas, dramatically reducing your ability to manufacture and secrete insulin.
In the case of type 2 diabetes, oftentimes beta cells are capable of manufacturing and secreting sufficient insulin, but insulin resistance in your muscle and liver results in reduced insulin action in both tissues.
However, rather than manifesting early in life or in young to middle adulthood , type 3 diabetes typically affects adults 65 and older.
The other difference with type 3 diabetes is that it primarily manifests in damage to the brain, and can cause a dramatic decline in cognitive function.
You May Like: Does Insulin Raise Blood Pressure

