Alcohol Or Caffeine Intake
Both alcohol and caffeine have known diuretic effects. Drinking either one to excess is capable of triggering polyuria to the point of developing dehydration. Alcohol is always a diuretic, even to people who drink alcohol on a regular basis. The diuretic effects of caffeine can decrease over time in people who regularly drink it.
Diagnostic Criteria For Diabetes Mellitus
The criteria for the diagnosis of diabetes are shown in . Three ways to diagnose diabetes are possible, and each, in the absence of unequivocal hyperglycemia, must be confirmed, on a subsequent day, by any one of the three methods given in . The use of the hemoglobin A1c for the diagnosis of diabetes is not recommended at this time.
What Causes Increased Urine Output In Diabetes Mellitus
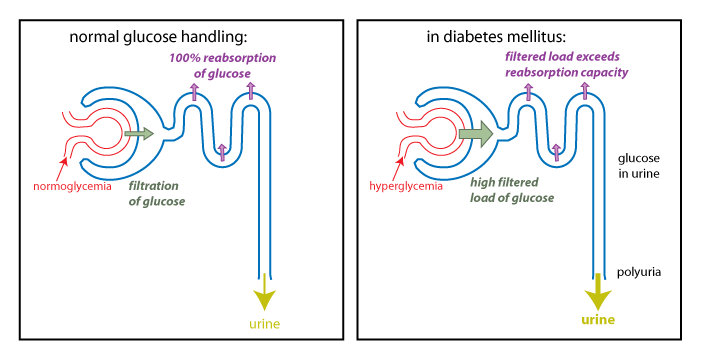
Causes. The most common cause of polyuria in both adults and children is uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, which causes osmotic diuresis, when glucose levels are so high that glucose is excreted in the urine. Water follows the glucose concentration passively, leading to abnormally high urine output.
Correspondingly, why is there an increase in urine output in diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common causes of polyuria. In this condition, high amounts of glucose collect in your kidney tubules and cause your urine volume to increase. Your urine volume can increase if there is not enough ADH produced.
Subsequently, question is, why do diabetics pee a lot at night? Diabetes and nocturia. Having high blood glucose levels can cause the body to excrete excess glucose via the urine. If you regularly have high blood glucose levels, you may increase the risk of picking up a urinary tract infection which can also increase the need to urinate through the night.
Likewise, what causes polyuria and polydipsia in diabetes mellitus?
Polyuria is usually the result of drinking excessive amounts of fluids , particularly water and fluids that contain caffeine or alcohol. It is also one of the major signs of diabetes mellitus. When the kidneys filter blood to make urine, they reabsorb all of the sugar, returning it to the bloodstream.
What causes too much urine?
You May Like Also
Also Check: What Diabetic Supplies Are Covered By Medicaid
What Are The Types Of Diabetes Insipidus
There are four types of diabetes insipidus:
- Central diabetes insipidus, the most common form, happens when the brain doesnt release enough ADH. This can be caused by damage to the pituitary gland or the hypothalamus, a section of the brain near the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus produces ADH and other hormones and controls their release. There are many possible causes of this damage, including an inherited defect in a gene, surgery or injury involving the head, tumors, and infections.
- Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus happens when there is enough ADH, but the kidneys dont respond to it properly and cant retain the water. This can be caused by a reaction to a medication, often lithium. It can also be caused by a defect in the genes, a high level of calcium in the blood , or kidney disease.
- Dipsogenic diabetes insipidus is not related to ADH, and is caused by drinking too much fluid. It occurs when the mechanism that makes a person feel thirsty is damaged, so the person feels thirsty even when fluid isnt needed. It can be caused by damage to the hypothalamus or by mental illness.
- Gestational diabetes insipidus affects pregnant women. It is caused by enzymes made by the placenta, a temporary organ that provides nourishment to the fetus. Sometimes these enzymes interfere with the kidneys ability to process ADH. Gestational diabetes insipidus usually goes away shortly after the pregnancy is over.
Classification Of Diabetes Mellitus And Other Categories Of Glucose Regulation

Assigning a type of diabetes to an individual often depends on the circumstances present at the time of diagnosis, and many diabetic individuals do not easily fit into a single class. For example, a person with gestational diabetes mellitus may continue to be hyperglycemic after delivery and may be determined to have, in fact, type 2 diabetes. Alternatively, a person who acquires diabetes because of large doses of exogenous steroids may become normoglycemic once the glucocorticoids are discontinued, but then may develop diabetes many years later after recurrent episodes of pancreatitis. Another example would be a person treated with thiazides who develops diabetes years later. Because thiazides in themselves seldom cause severe hyperglycemia, such individuals probably have type 2 diabetes that is exacerbated by the drug. Thus, for the clinician and patient, it is less important to label the particular type of diabetes than it is to understand the pathogenesis of the hyperglycemia and to treat it effectively.
You May Like: Insulin Transferrin Selenium
Prolonged Diarrhea Results In A Loss Of Fluid And
39.Which two ions are most important for acid-base balance in the body?40.The bicarbonate-carbonic acid buffer system helps maintain serum pH. The balance of the carbonic acid and bicarbonate ion levels are controlled by the:41.Alkalosis increases irritability and spontaneous stimulation of nerves by:a.Blocking normal nerve conduction.b.Increasing the permeability of nerve membranes.c.Blocking movement of calcium ions.d.Decreasing phosphate ion levels.42.Hypocalcemia causes weak cardiac contractions because:43.Serum potassium levels are affected by: 44.Which of the following is the primary control of serum Na+levels?45.The control center for thirst is located in the:a.Kidneysb.Thalamusc.Medullad.Hypothalamus46.Which statements apply to atrial natriuretic peptide? 47.What are the three mechanisms that control or compensate for serum pH? This is the end of the preview. Sign up to access the rest of the document.Continue reading > >
Definition And Description Of Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. The chronic hyperglycemia of diabetes is associated with long-term damage, dysfunction, and failure of various organs, especially the eyes, kidneys, nerves, heart, and blood vessels.
Several pathogenic processes are involved in the development of diabetes. These range from autoimmune destruction of the -cells of the pancreas with consequent insulin deficiency to abnormalities that result in resistance to insulin action. The basis of the abnormalities in carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism in diabetes is deficient action of insulin on target tissues. Deficient insulin action results from inadequate insulin secretion and/or diminished tissue responses to insulin at one or more points in the complex pathways of hormone action. Impairment of insulin secretion and defects in insulin action frequently coexist in the same patient, and it is often unclear which abnormality, if either alone, is the primary cause of the hyperglycemia.
Symptoms of marked hyperglycemia include polyuria, polydipsia, weight loss, sometimes with polyphagia, and blurred vision. Impairment of growth and susceptibility to certain infections may also accompany chronic hyperglycemia. Acute, life-threatening consequences of uncontrolled diabetes are hyperglycemia with ketoacidosis or the nonketotic hyperosmolar syndrome.
Recommended Reading: Are Pork Rinds Ok For Diabetics
Ps Of Diabetes Explanation
Diabetes is a medical condition affecting people all across the globe. If you have diabetes, you will have it for your entire life. There is no cure for diabetes. Fortunately, it can be managed. All you need to do is to make sure that the blood sugar level is within the normal range.
A significant part of diabetes management is being aware of the signs and symptoms. There are various symptoms associated with diabetes, but there are three cardinal signs you should watch out for. They are called the 3 Ps of diabetes.
They are polyuria, polydipsia, and polyphagia.
These symptoms can develop quickly, especially in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
We are going to discuss in detail the 3Ps of diabetes in this article.
What Is The Cause Of Polydipsia
An increase in thirst is caused by the excessive loss of water in the body secondary to frequent urination. To quench thirst, a diabetic patient drinks a lot of water.
However, the result is only temporary as the water being drunk will then be excreted in the urine. If you feel thirsty most of the time and at the same time urinate too often, then you need to start suspecting diabetes, especially if diabetes runs in your family.
Recommended Reading: High Blood Sugars Symptoms
What Is The Home Remedy For Frequent Urination
Perform the following steps to train your bladder:
- Keep a journal to determine how frequently you go to the bathroom.
- Delay urination with small intervals. Once you feel the need to pee, see if you can hold off for five minutes and work your way up.
- Schedule trips to the bathroom.
- Perform Kegel exercises regularly.
Polyuria And Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that causes your pancreas to stop producing insulin, a hormone that is essential to getting energy from food. It strikes people of all ages and is unrelated to diet or lifestyle. People living with this disease must regularly monitor their blood sugar levels, inject or infuse insulin, and carefully regulate doses with eating and activity throughout the day.
Read Also: Can Diabetes Cause Low Blood Pressure
Who Is It For
If you are prediabetic or struggle with Type 2 Diabetes, as well as you see that you do not obtain adequate quality sleep in the evening, Deep Sleep Diabetes Remedy program is more than likely the program for you. Kill 2 birds with one rock: enhance your sleep and energy levels and also reverse your diabetic issues with this program. why does polyuria develop with diabetes mellitus?
One More Thing I Found An Awesome Free Bonus For You!
Ive obtained terrific news! I located a site supplying a rather significant bonus offer on the Deep Sleep Diabetes Remedy. You can save a minimum of $47 on these bonuses however you have to act immediately. To get the rewards for free, please click the link below. Rush, due to the fact that the benefit is just offered for a limited time. why does polyuria develop with diabetes mellitus?
What To Keep In Mind

If you experience the 3Ps mentioned above, you need to seek medical attention, especially if you have a family history of diabetes.
Diabetes is something that should not be taken lightly as failure to manage the condition can be life-threatening. It could lead to diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state which could eventually lead to coma or death.
Read Also: Metformin Uses And Side Effects
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
Blood glucose levels can be measured easily at home or anywhere.
A fingerstick glucose test is most often used to monitor blood glucose. Most blood glucose monitoring devices use a drop of blood obtained by pricking the tip of the finger with a small lancet. The lancet holds a tiny needle that can be jabbed into the finger or placed in a spring-loaded device that easily and quickly pierces the skin. Most people find that the pricking causes only minimal discomfort. Then, a drop of blood is placed on a reagent strip. The strip contains chemicals that undergo changes depending on the glucose level. The glucose meter reads the changes in the test strip and reports the result on a digital display. Some devices allow the blood sample to be obtained from other sites, such as the palm, forearm, upper arm, thigh, or calf. Home glucose meters are smaller than a deck of cards.
Continuous glucose monitoring systems use a small glucose sensor placed under the skin. The sensor measures blood glucose levels every few minutes. There are two types of CGMs, with different purposes:
-
Professional
-
Personal
Professional CGMs collect continuous blood glucose information over a period of time . Health care providers use this information to make treatment recommendations. Professional CGMs do not provide data to the person with diabetes.
Special Populations And Settings
The term brittle diabetes has been used to refer to patients who have dramatic, recurrent swings in glucose levels, often for no apparent reason. However, this concept has no biologic basis and should not be used. Labile plasma glucose levels are more likely to occur in patients with type 1 diabetes because endogenous insulin production is completely absent, and in some patients, counter-regulatory response to hypoglycemia is impaired. Other causes include occult infection, gastroparesis , and endocrine disorders .
Patients with chronic difficulty maintaining acceptable glucose levels should be evaluated for situational factors that affect glucose control. Such factors include inadequate patient education or understanding that leads to errors in insulin administration, inappropriate food choices, and psychosocial stress that expresses itself in erratic patterns of drug use and food intake.
You May Like: How Many Points Does Metformin Lower Blood Sugar
Why Does Polyuria Occur In Patients With Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus causes polydipsia, or excessive thirst, because of high blood sugar. According to the Mayo Clinic, the kidneys remove excess sugar from the blood, which results in higher urine production. As the body loses water through increased urination, or polyuria, this triggers thirst, and the diabetic drinks more water.
Why Do People with Diabetes Have Polydipsia? Diabetics suffer with a number of problematic symptoms related to their disease. Aside from having to constantly monitor and regulate blood sugar, diabetics may run into other short-term health problems, many of.
His pediatrician suspects new onset diabetes mellitus.
if the patient presents in coma, because cerebral cells are subjected to greater degrees of cellular dehydration and a higher risk of.
Type 1 diabetes accounts for most of the rest. Diabetes Mellitus The more formal.
Insulin Resistance A condition that occurs when the body does not use insulin effectively.
Treatment Options in Bipolar Disorder: Mood Stabilizers Subsyndromal affective symptoms are more likely to occur with low levels (0.4 to.
dementia and other CNS disorders, diabetes mellitus, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis, and osteoporosis.
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a prototypic organ-specific.
therapy have evolved as data accumulated. Central tolerance occurs during lymphocyte development, in the thymus for T cells.
8 Oct 2012.
Diabetes mellitus causes diabetic bladder dysfunction .
increased urinary frequency , thirst , hunger.
Catheter Implantation And Conscious Cystometrography
In 8 studies, either an in vivo and/or in vitro CMG were done. A suprapubic bladder catheter was implanted. A small incision was made in the bladder wall and the catheter was implanted and fixed. The distal end of the tubing was sealed and the incisions were closed. CMG was performed a few days later according to study design. The bladder was filled via a catheter with 0.9% saline, while bladder pressure was recorded. Number of micturition cycles differed, but the means were calculated to analyze CMG parameters, including intercontraction interval, peak pressure and voided volume. In addition, functional capacity and bladder compliance were calculated.
You May Like: What Happens When Diabetes Goes Untreated
There Are Various Forms Of Diabetes Insipidus
- Neurogenic – the brain doesn’t produce enough of the hormone vasopressin. Some of the events that could cause this form of diabetes insipidus include head injury, infection , brain tumour, ruptured aneurysm or brain surgery. In about half of cases, the cause remains unknown .
- Nephrogenic – the kidneys aren’t sensitive to vasopressin and fail to respond. This comparatively rare form of diabetes insipidus is caused by an inherited disorder that affects the tubules, the tiny structures inside the kidneys that absorb water. Men are more prone to this condition than women. In adults nephrogenic diabetes insipidus can be caused by treatment with lithium and by hypercalcemia.
Pathogenesis Of Dka The Effect Of Severe Insulindeficiency
In the absence of insulin, glucose in blood cannot enter tissuecells where it is needed to provide energy, and the liverinappropriately continues to release glucose produced fromnon-carbohydrate sources and breakdown of glycogen to theblood.
The inevitable consequence is a rising blood glucoseconcentration. DKA is often described as starvation in themidst of plenty because tissue cells deficient of their muchneeded energy source, glucose, are bathed by extracellularfluid increasingly rich in glucose.
Most of the clinical signs and symptoms which characterizeDKA can be attributed to either raised blood glucose or lack of glucose within cells.
Theabnormalities in results of blood gas analysis stem mainly fromlack of glucose within cells but first, for completeness, theconsequences of hyperglycemia will be addressed.
Read Also: What Is Metformin 500 Mg Used For
What Is Diabetes Insipidus
Diabetes insipidus is a rare condition in which there is a problem with the secretion of antidiuretic hormone . ADH, also called vasopressin, controls the amount of water the kidneys release in the urine. ADH is stored in the pituitary gland, which is located behind the bridge of the nose.
Patients with diabetes insipidus have high amounts of urine that is diluted because of this inability to control the amount of water in the urine. Most cases of diabetes insipidus occur because there isnt enough ADH, or because the kidneys are not responding properly to ADH.
The body produces more ADH when it is dehydrated or losing blood pressure. The increase in ADH tells the kidneys to hold onto more water instead of releasing it in urine.
For example, if a person without diabetes insipidus were in the desert with no access to water, he or she would produce more ADH hormone and hold water from the urine a person with diabetes insipidus would continue to urinate the water and would become dehydrated.
It is important to note the difference between diabetes insipidus and other conditions that are associated with an increase in urination, such as diabetes mellitus and urinary tract infections.
Diagnosis Of Polyuria And Diabetes Insipidus
DEFINITION Polyuria has generally been defined as a urine output exceeding 3 L/day in adults and 2 L/m2 in children. It must be differentiated from the more common complaints of frequency or nocturia, which are not associated with an increase in the total urine output. The following is an overview of the diagnosis of polyuria and diabetes insipidus . The causes and treatment of polyuria due to central or nephrogenic DI are presented separately. CAUSES In the absence of a glucose-induced osmotic diuresis in uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, there are three major causes of polyuria in the outpatient setting, each of which is due to a defect in water balance leading to the excretion of large volumes of dilute urine : primary polydipsia, which is primarily seen in adults and adolescents central DI and nephrogenic DI . Primary polydipsia Primary polydipsia is characterized by a primary increase in water intake. This disorder is most often seen in middle-aged women and in patients with psychiatric illnesses, including those taking a phenothiazine, which can lead to the sensation of a dry mouth. Primary polydipsia can also be induced by hypothalamic lesions that directly affect the thirst center, as may occur with an infiltrative disease such as sarcoidosis . Central DI Central DI is associated with deficient secretion of antidiuretic hormone (Continue reading > >
You May Like: Average Dose Of Metformin

