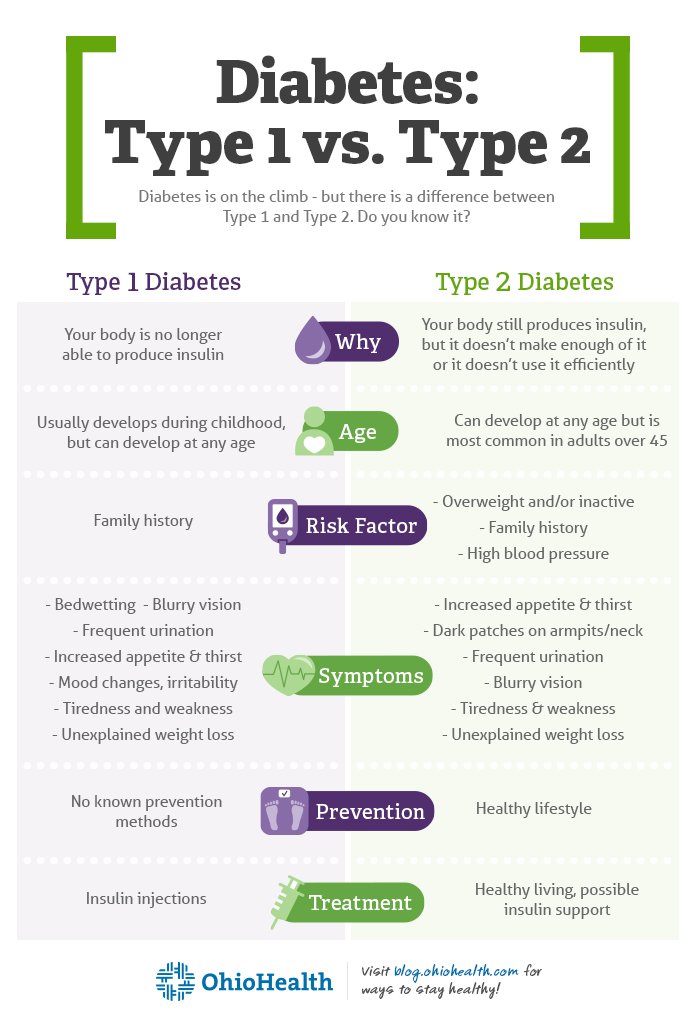
Diagnosing Type 1 Diabetes
To diagnose type 1 diabetes you’ll need to get blood tests done, one of which is called an A1C screening. A1C screenings measure your blood sugar levels from the past two to three months and can be used to diagnose type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and prediabetes. Life Line Screening also offers an A1C screening from the privacy of you own home through our home tests. You can learn more here.
How Is Type 1 Diabetes Diagnosed
Because the symptoms can develop rapidly, a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes is usually made by a pediatrician or a physician in the emergency room. Pediatricians might check a childs glucose levels if there is unexplained weight loss or sudden bedwetting. Glucose tests are also commonly run when a person with type 1 diabetes symptoms arrives at the hospital.
Doctors can also diagnose type 1 diabetes by running several tests to check blood-sugar levels. The primary screening test for type 1 diabetes is the random blood-sugar test, which tells physicians the amount of glucose circulating in a persons blood at a specific moment in time. A blood-sugar level of 200 milligrams per deciliter suggests diabetes.
The secondary test is a glycated hemoglobin test, or A1C test. This test measures the average amount of glucose in a persons bloodstream over the past 90 days as a percentage.
A normal A1C level is between 5 and 5.5%, while anything higher than 5.7% indicates diabetes. When diabetes is controlled, a persons A1C levels will be low.
Its a useful test because you dont want to overreact, says Dr. Christofides. If someone has hyperglycemia for a week or a couple days, their A1C isnt going to rise. This gives us a good reflection of what the glucose level was for the past three months.
Diagnostic Tests For Diabetes
Diabetes may be diagnosed based on A1C criteria or plasma glucose criteria, either the fasting plasma glucose or the 2-h plasma glucose value after a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test .
Criteria for the diagnosis of diabetes
The same tests are used to both screen for and diagnose diabetes. Diabetes may be identified anywhere along the spectrum of clinical scenarios: in seemingly low-risk individuals who happen to have glucose testing, in symptomatic patients, and in higher-risk individuals whom the provider tests because of a suspicion of diabetes. The same tests will also detect individuals with prediabetes.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
What Are The Treatments For Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes must be treated with insulin. To do this, a person with type 1 diabetes must inject insulin under their skin where it can be absorbed into their bloodstream to help glucose access the cells that require it. Insulin cant be taken in pill form because the digestive juices in the stomach would destroy the insulin before it could work.
Treating T1D is all about the amount and timing of insulin, as well as the best way to get the right dose of this essential hormone to assure that the glucose circulating in your blood is able to be properly absorbed by your body. Having too much glucose in your body can cause serious complications as can having too little glucose in your blood .
Insulin can be delivered by:
Lexie, known as the divabetic, is a Black diabetes advocate who posts everything from giveaways to advice on dating with type 1 diabetes. She frequently shares posts about diabetes-friendly food and humor.
Type 1 Diabetes Diagnosis
- A c-peptide value lower than 0.2ng/mL
- The presence of one or more diabetes autoantibodies
- A fasting blood glucose greater than 125 mg/dL
- A random finger stick blood glucose greater than 200 mg/dL
- An A1c greater than or equal to 6.5%
- An Oral Glucose Tolerance Test with a blood glucose value exceeding 200 mg/dL at any time
Recommended Reading: Gluconeogenesis And Diabetes
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes Treatment
Type 1 diabetes is treated with insulin and blood sugar self monitoring. Insulin can be administered either via a syringe, pen, or insulin pump. Many people with type 1 may also wear a continuous glucose monitor as well.
Type 2 diabetes can be treated a number of different ways depending on what stage of the disease it is diagnosed at:
Type 2 Diabetes And Insulin Injections
People with type 2 diabetes may need to take insulin injections, usually for one of two main reasons:
- Low sensitivity to insulin: The more excess body weight we carry, the less sensitive we are to insulin Being insensitive to insulin means insulin doesnt reduce blood glucose levels as much as it should. People with low insulin sensitivity often need to be injected with insulin to avoid hyperglycemia
- Beta cell failure: If you develop insulin resistance, you need more of it to keep your blood glucose levels stable. More insulin production means more work for the pancreas. Over time, the beta cells can become burnt out by the constant strain, and stop producing insulin altogether. Eventually, you can get to a similar situation as someone with type 1 diabetes, in which your body is incapable of producing the amount of insulin you need to keep blood glucose levels under control. Insulin injections are necessary in these situations
You May Like: How To Reduce Side Effects Of Metformin
Testing For Type 2 Diabetes And Prediabetes In Children And Adolescents
In the last decade, the incidence and prevalence of type 2 diabetes in adolescents has increased dramatically, especially in ethnic populations . Recent studies question the validity of A1C in the pediatric population, especially among certain ethnicities, and suggest OGTT or FPG as more suitable diagnostic tests . However, many of these studies do not recognize that diabetes diagnostic criteria are based on long-term health outcomes, and validations are not currently available in the pediatric population . The ADA acknowledges the limited data supporting A1C for diagnosing diabetes in children and adolescents. However, aside from rare instances, such as cystic fibrosis and hemoglobinopathies, the ADA continues to recommend A1C in this cohort . The modified recommendations of the ADA consensus report Type 2 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents are summarized in .
How To Treat Type 2 Diabetes:
Unlike type 1, people with type 2 diabetes often do not need to take insulin, because their bodies still produce a small amount of it. Though there are medications like Metformin available to assist in lowering blood sugar, the primary ways to treat type 2 diabetes are:
- A balanced diet. Eating fruits and vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins while avoiding more than the occasional high-fat, high-sugar food is the first and most essential step to treating type 2 diabetes.
- Exercise. Staying active is also very important. There are so many ways to get exercise. Try different activities to find a type of exercise you enjoy and work it into your weekly routine.
- Weight loss. Of course, if you work toward eating healthier and exercising, this may be a byproduct. Losing weight is less about the number on the scale and more about taking care of your body and reducing the strain on your pancreas.
- Blood glucose monitoring. Checking your blood sugar regularly will become a part of your daily routine. It’s important to stay up-to-date on how your levels are doing throughout the day and adjust your food and activities accordingly. After a while you’ll figure out the regimen and balance that works best for you.
Recommended Reading: Squeezing Finger For Blood Sugar Test
Type 1 And Type 2 Differences
Below is a guide to some of the main differences between type 1 and type 2.
|
Your body attacks the cells in your pancreas which means it cannot make any insulin. |
Your body is unable to make enough insulin or the insulin you do make doesnt work properly. |
|
|
We dont currently know what causes type 1 diabetes. |
We know some things can put you at risk of having type 2 like weight and ethnicity. |
|
|
The symptoms for type 1 appear more quickly. |
Type 2 symptoms can be easier to miss because they appear more slowly. |
|
|
Type 1 is managed by taking insulin to control your blood sugar. |
You can manage type 2 diabetes in more ways than type 1. These include through medication, exercise and diet. People with type 2 can also be prescribed insulin. |
|
|
Currently there is no cure for type 1 but research continues. |
Type 2 cannot be cured but there is evidence to say in many cases it can be prevented and put into remission. |
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms
When looking at the symptoms of type 1 vs type 2 diabetes, you may not notice a whole lot of differences. The symptoms are quite similar but will develop over a different timeline. Type 1 develops quite rapidly over a matter of weeks or a couple months and type 2 can develop over many years.
Common symptoms of diabetes include unexplained:
- Excessive thirst
- Muscle loss
You May Like: Best Testosterone Booster For Diabetics
What Happens When You Have Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
If you have either type 1 or type 2 diabetes, it means you have too much glucose in your blood. This is the same for both types. But the difference between them is how this happens.
If you have type 1 diabetes, it means you have an autoimmune condition. This means your body has attacked and destroyed the cells that make a hormone called insulin. So you cant make insulin anymore.
We all need insulin as it helps take the glucose from our blood into our bodys cells. We then use this glucose for energy. Without insulin, the glucose level in your blood gets too high.
Type 2 diabetes is different. If youve got type 2, either your body doesnt make enough insulin, or your insulin doesnt work properly. This is known as insulin resistance. Like type 1, this means the level of glucose in your blood is too high.
Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatments And Support
With Ilana Halperin MD and Elena Christofides MD
Learning you or your child has type 1 diabetes means taking an active role in health 24/7. Luckily, there are more low-key ways to track blood sugar and administer insulin than ever. From glucose monitoring to meal planning, were here to empower you with clear answers to all your pressing questions.
| Frequently Asked Questions | Support
Also Check: Which Of The Following Insulins Are Used For Basal Dosage
Causes Of Type 1 Diabetes
The bodys immune system is responsible for fighting off foreign invaders, such as harmful viruses and bacteria.
In people with type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakes the bodys own healthy cells for foreign invaders. The immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. After these beta cells are destroyed, the body is unable to produce insulin.
Researchers dont know why the immune system sometimes attacks the bodys own cells. It may have something to do with genetic and environmental factors, such as exposure to viruses. Research into autoimmune diseases is ongoing.
Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors
- Family history of type 1 diabetes
- Childhood consumption of cows milk, often before 1 year of age
- Mycobacterium avium paratuberculosis in dairy and meat products
- Enterovirus infections
- Family history of type 2 diabetes
- Diet high in fats, processed foods, and artificial sweeteners
- Weight above ideal
- Previous diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus
- Sedentary lifestyle
Just like the causes, the risk factors of type 1 diabetes are primarily uncontrollable, while the risk factors of type 2 diabetes are primarily related to your lifestyle.
Don’t Miss: How Many Carbs Should A Diabetic Have In One Day
Is Diagnosing Diabetes Types 1 And 2 Similar
Blood tests used to diagnose type 1 and type 2 diabetes include fasting blood sugar, a hemoglobin A1C test, and a glucose tolerance test. The A1C test measures the average blood sugar level over the past few months. The glucose tolerance test measures blood sugar after a sugary drink is given.
“The blood sugar testing we do to diagnose and manage type 1 diabetes is very similar to the testing we do for type 2 diabetes,” says Drincic. “We can do a blood test that looks for antibodies. That tells us if it is type 1 or 2.” In type 1 diabetes, the immune system makes antibodies that act against the cells in the pancreas that make insulin, and these antibodies can be detected in a blood test. Your doctor may suspect type 2 diabetes based on your symptoms and risk factors, such as obesity and family history.
Tests To Diagnose Both Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
- Fasting blood sugar test After an overnight fast your blood glucose level will be measured
- Glucose tolerance test After an overnight fast your blood glucose level will be measured, followed by a drink containing glucose. Your blood sugar will then be retested every half hour for two hours to see how your body is responding
- Random blood sugar test This test does not require an overnight fast but is taken any time of the day
- Hemoglobin A1c test As a diabetic, you definitely need to know about this. Hemoglobin A1c measures the average blood sugar control over the last two to three months. When glucose attaches to hemoglobin in the bloodstream it is called Hemoglobin A1c. The more glucose in the blood, the more hemoglobin A1c forms. This form of hemoglobin remains in the blood for 2-3 months therefore it gives a good reflection on what is going on in the body rather than a single snapshot result. A1C test results are reported as a percentage. The American Diabetic Association diagnose diabetes as an A1C of greater than or equal to 6.5%
Read Also: How Many Carbs Should A Diabetic Have In One Day
Can You Be Misdiagnosed With Type 2 Diabetes
Its possible for someone with type 2 diabetes to be misdiagnosed. They may have many of the symptoms of type 2 diabetes, but actually have another condition that may be more closely related to type 1 diabetes. This condition is called latent autoimmune diabetes in adults .
Researchers estimate that between 4 and 14 percent of people diagnosed with type 2 diabetes might actually have LADA. Many physicians are still unfamiliar with the condition and will assume a person has type 2 diabetes because of their age and symptoms.
In general, a misdiagnosis is possible because:
- both LADA and type 2 diabetes typically develop in adults
- the initial symptoms of LADA such as excessive thirst, blurred vision, and high blood sugar mimic those of type 2 diabetes
- doctors dont typically run tests for LADA when diagnosing diabetes
- initially, the pancreas in people with LADA still produces some insulin
- diet, exercise, and oral drugs usually used to treat type 2 diabetes work well in people with LADA at first
As of now, theres still a lot of uncertainty over how exactly to define LADA and what causes it to develop. The exact cause of LADA is unknown, but researchers have identified certain genes that may play a role.
LADA may only be suspected after your doctor realizes that youre not responding well to oral type 2 diabetes medications, diet, and exercise.
Is Type 1 Diabetes An Autoimmune Disease
When type 1 diabetes is triggered by a virus, someone predisposed to autoimmune conditions may develop an autoimmune response. This means that their bodys immune system will start attacking its own cells. In type 1 diabetes, the body attacks the beta cells in the pancreas that are responsible for producing insulin.
Read Also: Type 1 Diabetes Mayo Clinic
What Is Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which your bodys immune system attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in your pancreas.
This drastically reduces the ability of your body to produce insulin, the hormone responsible for signaling tissues that glucose is available in your blood, and people with type 1 diabetes require exogenous insulin .
Sometimes called juvenile-onset diabetes, type 1 diabetes typically occurs in children and young adults under the age of 30, though this is not always the case.
Currently, researchers have been unable to isolate one specific cause of type 1 diabetes, and there is no known cure. However, through diet and lifestyle, this form of insulin-dependent diabetes can be controlled and managed.
For more in-depth information on type 1 diabetes, you can visit our comprehensive article on the topic.
Which Diets Are Recommended For Diabetes

Nutritional management is an important part of life for people with diabetes.
If you have type 1 diabetes, work with your doctor to identify how much insulin you may need to inject after eating certain types of food.
For example, carbohydrates can cause blood sugar levels to quickly increase in people with type 1 diabetes. Youll need to counteract this by taking insulin, but youll need to know how much insulin to take. Learn more about type 1 diabetes and diet.
People with type 2 diabetes need to focus on healthy eating. Weight loss is often a part of type 2 diabetes treatment plans, so your doctor may recommend a low-calorie meal plan. This could mean reducing your consumption of animal fats and junk food.
You May Like: Is Type 2 Diabetes Hypo Or Hyper

