Which Diets Are Recommended For Diabetes
Nutritional management is an important part of life for people with diabetes.
If you have type 1 diabetes, work with your doctor to identify how much insulin you may need to inject after eating certain types of food.
For example, carbohydrates can cause blood sugar levels to quickly increase in people with type 1 diabetes. Youll need to counteract this by taking insulin, but youll need to know how much insulin to take. Learn more about type 1 diabetes and diet.
People with type 2 diabetes need to focus on healthy eating. Weight loss is often a part of type 2 diabetes treatment plans, so your doctor may recommend a low-calorie meal plan. This could mean reducing your consumption of animal fats and junk food.
What Are The Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes are serious and usually happen quickly, over a few days to weeks. Symptoms can include
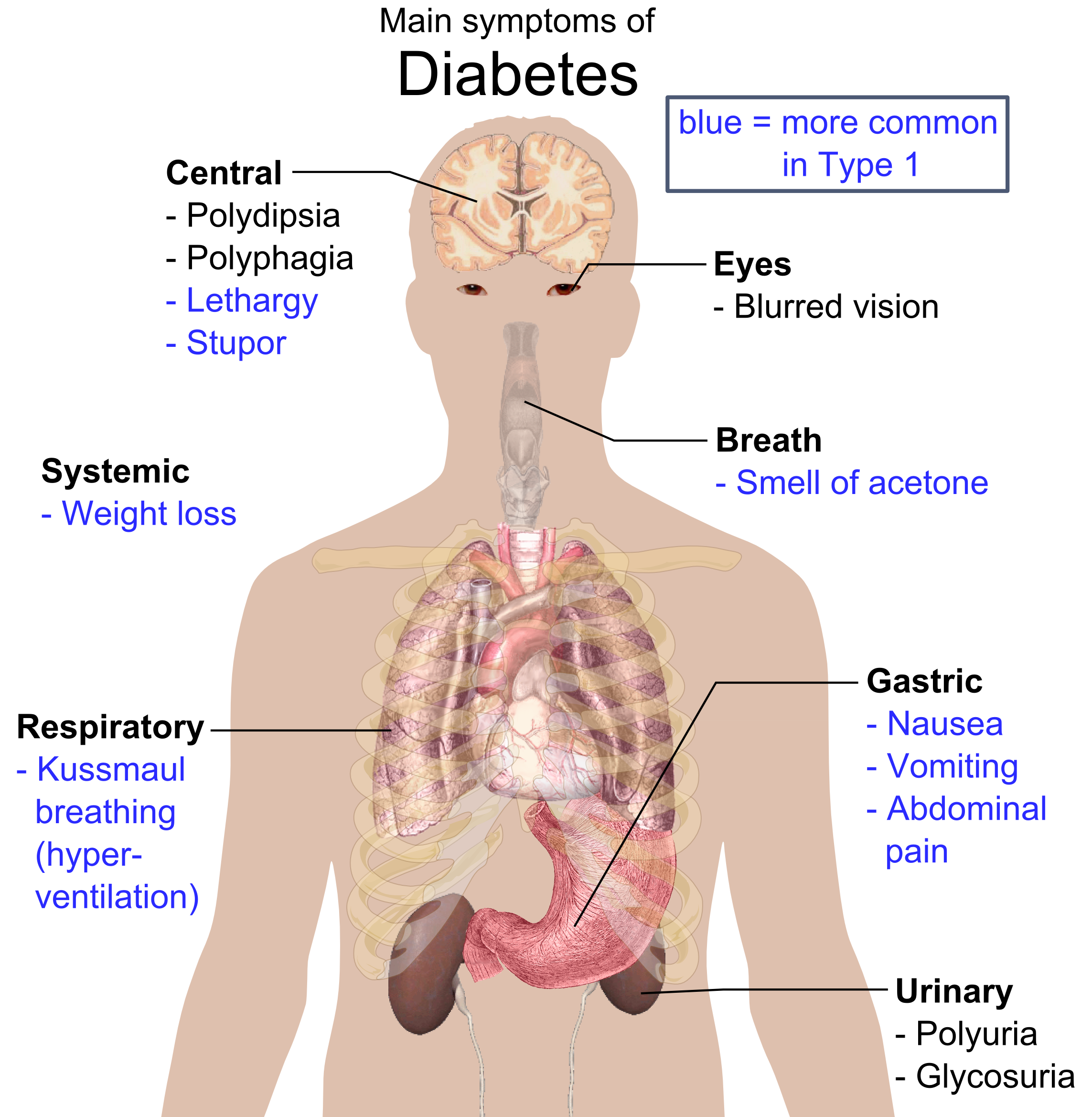
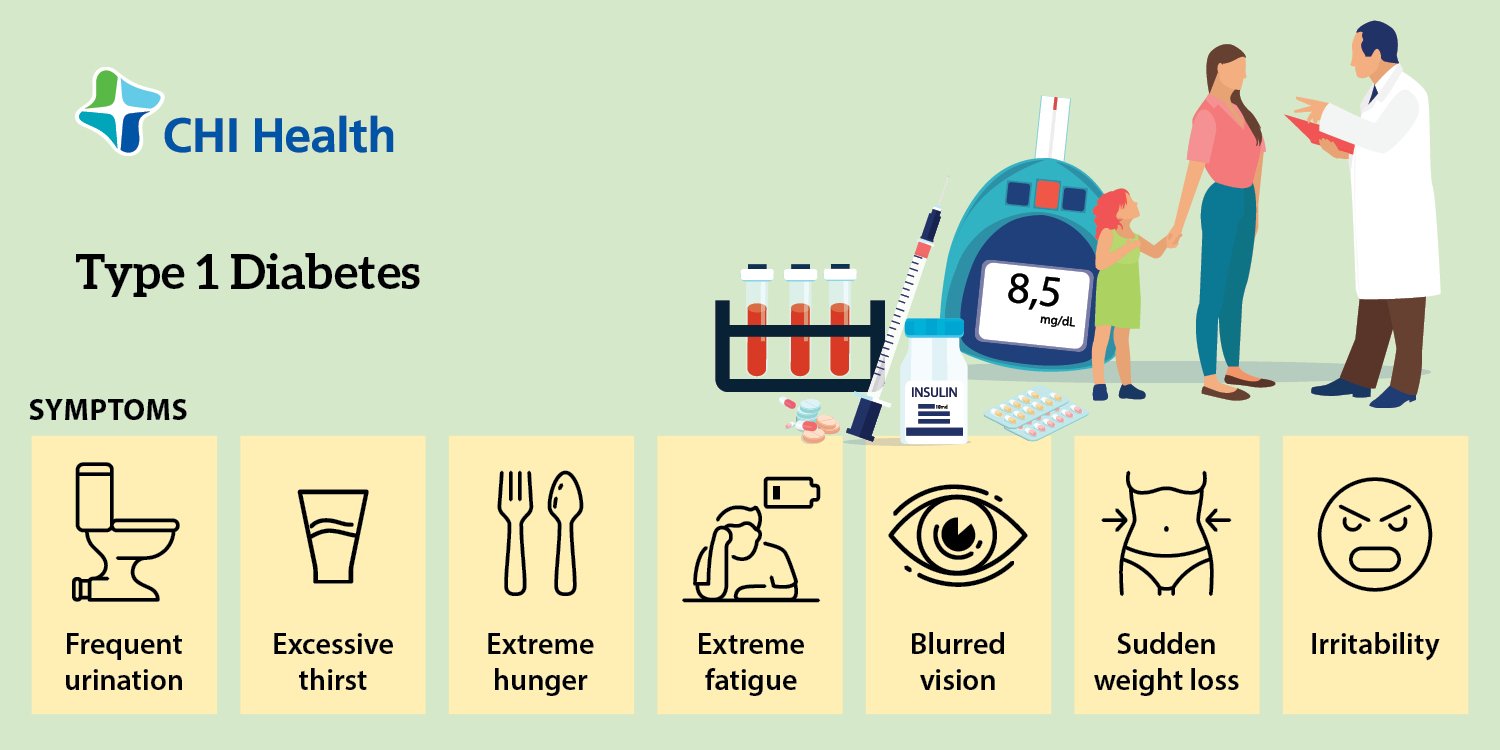
- increased thirst and urination
- trouble breathing
- trouble paying attention or feeling confused
DKA is serious and dangerous. If you or your child have symptoms of DKA, contact your health care professional right away, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes Onset In An Infant Or Child
The young child who is urinating frequently, drinking large quantities, losing weight, and becoming more and more tired and ill is the classic picture of a child with new-onset type 1 diabetes. If a child who is potty-trained and dry at night starts having accidents and wetting the bed again, diabetes might be the culprit.
Although it is easy to make the diagnosis diabetes in a child by checking blood sugar at the doctors office or emergency room, the tricky part is recognizing the symptoms and knowing to take the child to get checked. Raising the awareness that young children, including infants, can get type 1 diabetes can help parents know when to check for type 1 diabetes.
Sometimes children can be in diabetic ketoacidosis when they are diagnosed with diabetes. When there is a lack of insulin in the body, the body can build up high levels of an acid called ketones. DKA is a medical emergency that usually requires hospitalization and immediate care with insulin and IV fluids. After diagnosis and early in treatment, some children may go through a phase where they seem to be making enough insulin again. This is commonly called the honeymoon phase. It may seem like diabetes has been cured, but over time they will require appropriate doses of insulin to keep their blood sugar levels in the normal range.
You May Like: Bad Side Effects Of Metformin
Less Common T1d Tests
Because each case can be as unique as the individual, some doctors may employ the following tests to find markers of T1D to ensure the optimal treatment plan:
- C-PeptideWhile most tests check for antibodies, this test measures how much C-peptide is in a persons blood. Peptide levels typically mirror insulin levels in the body. Low levels of C-peptide and insulin can point to T1D.
- Insulin Autoantibodies This tests looks for the antibodies targeting insulin.
- Insulinoma-Associated-2 Autoantibodies This test looks for antibodies mounted against a specific enzyme in beta cells. Both the IA-2A and GADA tests are common T1D antibody tests.
- Zinc Transporter 8 This test looks at antibodies targeting an enzyme that is specific to beta cells.
- Islet Cell Cytoplasmic Autoantibodies Islet cells are clusters of cells in the pancreas that produce hormones, including insulin. This test identifies a type of islet cell antibodies present in up to 80 percent of people with T1D.
- Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Autoantibodies This test looks for antibodies built against a specific enzyme in the insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells.
Testing For Type 1 Diabetes
A simple blood test will let you know if you have diabetes. If youve gotten your blood sugar tested at a health fair or pharmacy, follow up at a clinic or doctors office to make sure the results are accurate.
If your doctor thinks you have type 1 diabetes, your blood may also be tested for autoantibodies that are often present with type 1 diabetes but not with type 2. You may have your urine tested for ketones , which also indicate type 1 diabetes instead of type 2.
Read Also: Metformin Dosage Prediabetes
Anyone Can Get Type 1 Diabetes
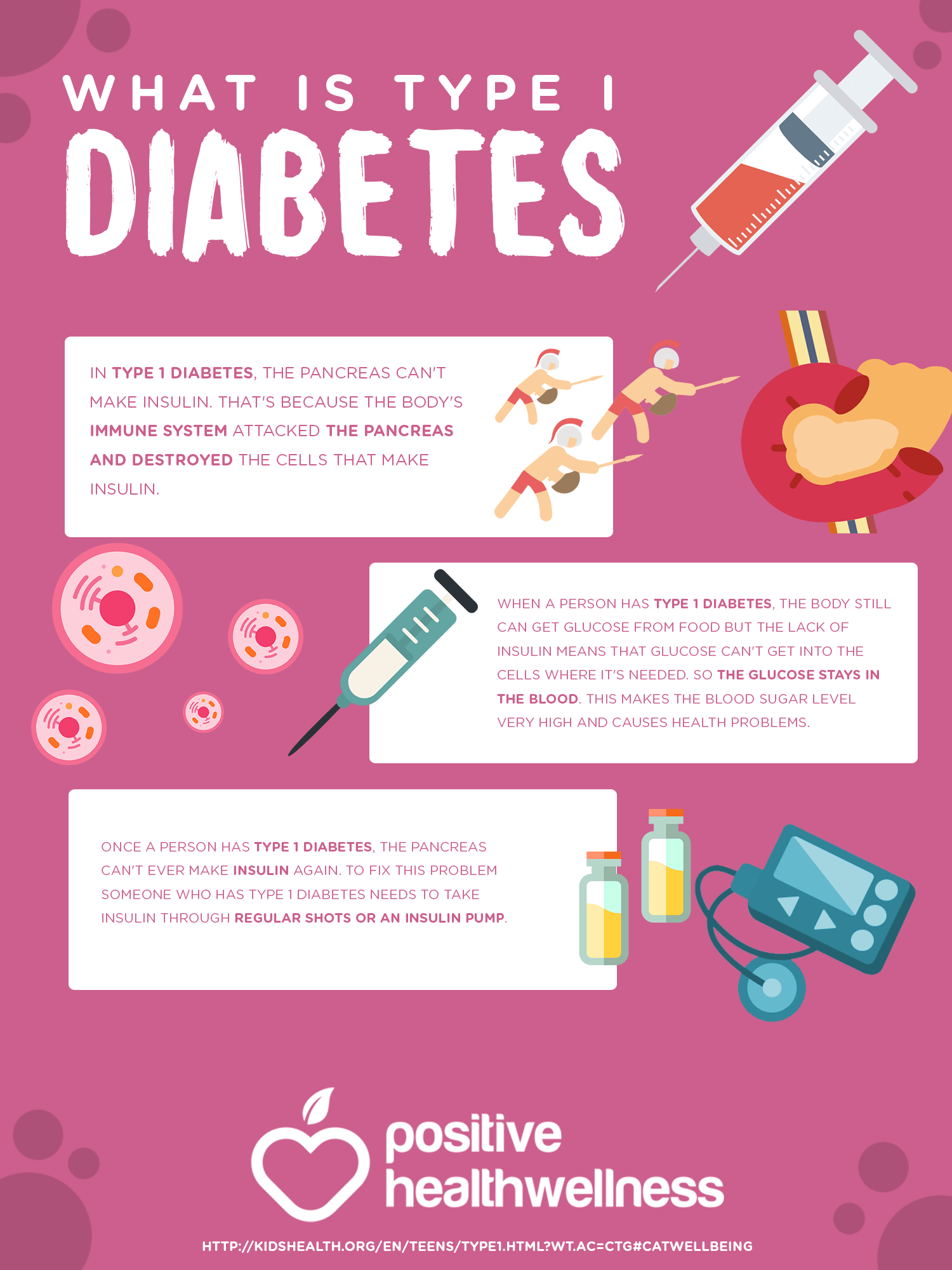
It isnt completely clear what causes type 1 diabetes, but we know that diet and lifestyle habits dont. Type 1 is thought to be the result of an autoimmune response, where your body attacks the cells in your pancreas that make insulin. Insulin is a hormone that acts like a key to let blood sugar into your bodys cells for use as energy. Sometimes infection with a virus seems to trigger the autoimmune response. Many people with type 1 diabetes have family members with type 1, but most dont.
The peak age for being diagnosed with type 1 diabetes is around 13 or 14 years, but people can be diagnosed when theyre much younger and older .
Identifying The Presence Of Diabetes
If you suspect that you may be developing any type of diabetes, ask your doctor for an A1c test or an oral glucose tolerance test .
Both of these blood tests are extremely helpful in identifying your ability to metabolize glucose, and can help indicate whether you may be living with insulin resistance or any type of diabetes.
You May Like: Advantages And Disadvantages Of Metformin
How Does Early Diagnosis Of Type 1 Diabetes Save Lives
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune condition that makes the body unable to produce insulin, the hormone that regulates blood sugar. Without insulin, our bodies cannot use the sugar in our bloodstream as energy, causing people to experience diabetic ketoacidosis or worse complications, including death.
If an individual goes undiagnosed or is misdiagnosed, these life-threatening complications become a reality. This is why recognizing the early symptoms of Type 1 diabetes is critical. Symptoms may develop rapidly and can be mistaken for the flu or other illnesses and a delayed diagnosis can have serious consequences.
Treatment Of Type 1 Diabetes
- taking insulin daily by injections or by insulin pump
- self-monitoring of blood sugar levels by regularly testing droplets of blood in a glucose meter
- self-testing of urine with a test strip for high levels of ketones not routinely, but when problems are suspected
- regulating diet so intake is matched to insulin and exercise
- increasing the amount of slow carbohydrates in the diet, such as beans and fruit, which take longer to be absorbed by the body
- regular exercise
- maintaining regular checks for diabetes complications.
You May Like: Hypertension Related To Diabetes
Other Type 1 Diabetes Treatments
Less-common type 1 diabetes treatments include:
- Artificial pancreas A cutting-edge device that combines an insulin pump, a CGM, and a dosing algorithm, says Dutta. The algorithm decides based on the CGM reading and the average over the last five minutes, to tell the pump, You dose X number of units of insulin, and it goes up and down depending on your glucose levels. Medtronics MiniMed 670G and 770G hybrid closed-loop systems, and Tandem Diabetes Cares closed-loop Control-IQ are FDA-approved artificial pancreases, he says.
- Jet injection Instead of a needle, an injector with an insulin cartridge delivers insulin beneath the skin via a jet of air, as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration describes.
- Inhaled insulin A rapid-acting inhaled insulin that you take at the beginning of each meal by breathing in powder through the mouth using an inhaler, according to the ADA. It is sold under the brand name Afrezza .
- Pramlintide This medication is taken with mealtime insulin and slows the movement of food through the stomach to keep blood sugar from spiking after a meal, according to MedlinePlus.
Types Of Diabetes Tests
- Fasting blood glucose test blood glucose levels are checked after fasting for between 12 and 14 hours. You can drink water during this time, but should strictly avoid any other beverage. People with diabetes may be asked to delay their diabetes medication or insulin dose until the test is completed.
- Random blood glucose test blood glucose levels are checked at various times during the day, and it doesnt matter when you last ate. Blood glucose levels tend to stay constant in a person who doesnt have diabetes
- Oral glucose tolerance test a high-glucose drink is given. Blood samples are checked at regular intervals for two hours.
You May Like: Why Does My Sugar Go Up At Night
The Role Of Food In Diabetes Management
It is important to understand how food impacts blood glucose for children with diabetes.
Food causes blood glucose to go up. Insulin causes blood glucose to go down. Too much food with not enough insulin can cause blood glucose to go too high. Not enough food with too much insulin can cause blood glucose to go too low. Further, the type and amount of food will affect how much and how quickly the blood glucose goes up. Balancing food and insulin together can help keep blood glucose in a normal range.
Carbohydrates, also known as carbs, are an important source of energy. They are also the main nutrient the body turns into blood glucose, also known as blood sugar. Everyone needs to eat some carbohydrates to stay healthy. Common carbohydrate foods include: bread, crackers, cereal, pasta, rice, fruit, and milk.
- Carbohydrates that are high in fiber such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables slow digestion and contribute to a feeling of fullness. High-fiber food can also reduce spikes in blood glucose after eating.
- Processed carbohydrates that are low in fiber can raise blood sugars too high. Eating fewer processed carbohydrates helps manage blood glucose levels.
A dietitian can help determine the right amount of carbohydrates and types for your child.
A healthy diet can mean different things to different people. A dietitian is very important to help with meal planning and understanding the right balance of foods for your child.
How Are Type1 And Type2 Diabetes Mellitus Similar
Both types are similar in that they can cause complications if not treated properly. Blindness, kidney failure, and amputations are just some of the possible complications of diabetes when it is left untreated. In addition, both types are monitored in a similar manner and both can be treated with insulin when necessary. Care must be taken with all diabetic patients to keep blood sugar levels consistent.
Don’t Miss: Blood Sugar 112
Diabetes Sick Day Rules
If you need to take insulin to control your diabetes, you should have received instructions about looking after yourself when you’re ill known as your “sick day rules”.
Contact your diabetes care team or GP for advice if you haven’t received these.
The advice you’re given will be specific to you, but some general measures that your sick day rules may include could be to:
- keep taking your insulin it’s very important not to stop treatment when you’re ill your treatment plan may state whether you need to temporarily increase your dose
- test your blood glucose level more often than usual most people are advised to check the level at least four times a day
- keep yourself well hydrated make sure you drink plenty of sugar-free drinks
- keep eating eat solid food if you feel well enough to, or liquid carbohydrates such as milk, soup and yoghurt if this is easier
- check your ketone levels if your blood glucose level is high
Seek advice from your diabetes care team or GP if your blood glucose or ketone level remains high after taking insulin, if:
- you’re not sure whether to make any changes to your treatment
- you develop symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis
- you have any other concerns
Read more about sick day rules
What Are The Risk Factors For Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Risk factors for type 1 diabetes include:
- Family history: People with a parent or sibling with type 1 diabetes have a higher risk of developing it themselves.
- Age: Type 1 diabetes can appear at any age, but its most common among children and adolescents.
- Geography: The prevalence of type 1 diabetes increases the farther away you are from the equator.
- Genetics: The presence of certain genes points to an increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
Youre at risk of developing type 2 diabetes if you:
- have prediabetes, or slightly elevated blood sugar levels
- are carrying excess weight or have obesity
- are Black, Hispanic, American Indian, or Alaska Native
- have an immediate family member with type 2 diabetes
Also Check: Is Metformin Bad
Who Gets Type 1
Anyone, at any age, can be diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes it is neither preventable nor curable. While the cause is unknown, studies prove that genes together with an environmental trigger result in the immune system turning on itself and destroying the bodys beta cells.
Many people are familiar with Type 2 diabetes, but there is not enough awareness of Type 1. Learn more about other forms of diabetes.
Sample And Eligibility Criteria
The study population consisted of T1D patients who used the specific outpatient clinic for T1D, called tertiary care service, at the UFMA High-complexity University Hospital, other non-specific endocrinology outpatient clinics for T1D, and considered secondary care services . With support from a diabetes specialist assigned in São Luís, State of Maranhão, the patients were referred for interview and spontaneous data collection during their routine consultations.
Inclusion criteria were patients with T1D of both sexes, aged older than 10 years old. The diagnosis of T1D was defined according to classic clinical criteria, such as polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, and weight loss associated with insulin therapy since diagnosis. We excluded patients who presented in the three months prior to the history of acute infectious disease or diabetic ketoacidosis, pregnancy and lactation.
You May Like: Drug Class Metformin
Duration Of Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is a lifelong illness that requires careful, daily management of blood sugar levels. The constant need to be thinking about diabetes can grow tiresome and frustrating for many young people, says Thomas. While their journey will be different from the experience of those who dont have type 1 diabetes, they can still live a fulfilling, successful life, and they may find that their unique experience gives them the ability to tap into an inner power they didnt realize they had.”
Dutta strikes a similarly optimistic tone. Do we have a cure? No. We have advances in the clinic, but not yet an approved therapy that cures type 1 diabetes. But, he adds, continuing advances in glucose monitoring and insulin delivery are making it easier for people to manage life with the disease.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
The oral glucose test takes the fasting test one step further. After fasting and having an initial blood test, people drink a sugary drink and then have their blood sugar tested over the course of approximately two hours. This shows the benchmark sugar without outside influences and later measures how the body responds to carbohydrate intake.
Also Check: How Long Does Blurred Vision Last With Metformin
How Do Health Care Professionals Diagnose Type 1 Diabetes
Health care professionals usually test people for type 1 diabetes if they have clear-cut diabetes symptoms. Health care professionals most often use the random plasma glucose test to diagnose type 1 diabetes. This blood test measures your blood glucose level at a single point in time. Sometimes health professionals also use the A1C blood test to find out how long someone has had high blood glucose.
Even though these tests can confirm that you have diabetes, they cant identify what type you have. Treatment depends on the type of diabetes, so knowing whether you have type 1 or type 2 is important.
To find out if your diabetes is type 1, your health care professional may test your blood for certain autoantibodies. Autoantibodies are antibodies that attack your healthy tissues and cells by mistake. The presence of certain types of autoantibodies is common in type 1 but not in type 2 diabetes.
Chronic Poor Metabolic Control
A careful multidisciplinary assessment should be undertaken for every child with chronically poor metabolic control to identify potential causative and associated factors, such as depression , eating disorders , lower socioeconomic status, lower family support and higher family conflict , and to identify and address barriers to improved glycemic control. Use of a standardized measure of risk factors has been shown to identify those at high risk for poor control, emergency room visits and DKA . Glycemic control may be particularly challenging during adolescence due to physiologic insulin resistance, depression and other psychological issues, and reduced adherence during a time of growing independence. Multipronged interventions that target emotional, family and coping issues have shown a modest reduction in A1C with reduced rates of hospital admission .
Also Check: Best Instant Oatmeal For Diabetics
Proven Coaching For All Types Of Diabetes
A diabetes diagnosis at any age can be a heavy weight on your shoulders, but the most important thing to know is that all forms of diabetes can be effectively managed with evidence-based lifestyle changes.
Still, we know that these can be easier said than done, which is why we offer an comprehensive coaching program and a supportive community to help you master diabetes and stay healthy for the decades to come.
Still, we know that these can be easier said than done, which is why we offer a comprehensive coaching program and a supportive community to help you master diabetes and stay healthy for the decades to come.
Working together, weve already seen hundreds of members of our community take control of their type 1 diabetes, like:
- Charlotte, who couldnt seem to figure out her diet no matter how hard she tried
- Jason, who suffered from diabetic nerve pain
- Sanna, who reversed stage 3 kidney disease
- Chris, who reversed 57 years of diabetes complications
- Affaf, who got control of her life after years feeling out of control
- Lindsay, who transformed her life with a plant-based diet
- Meghan, who mastered the low-fat, plant-based, whole-food diet
- Jessica, who switched from a high-fat diet and saw immediate results
We founded Mastering Diabetes to help share our own experience living with diabetes, and help guide others with evidence-based research to master diabetes themselves. We hope we can help you too!
Stop Guessing What to Eat

